文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)06-0999-07
磷元素对铜基金属粉末选区激光烧结作用机理
顾冬冬, 沈以赴
(南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院, 南京 210016)
摘 要: 对不同CuP含量的多组分铜基金属粉末(Cu-CuSn-CuP)进行了选区激光烧结实验。 利用X射线衍射和扫描电镜研究了添加元素P对烧结致密度及显微组织的影响。 研究表明: P元素能在烧结过程中充当脱氧剂而与Cu反应生成CuPO3; 但当P过量时, 则会因熔体过热倾向明显而加剧氧化; 适量增加P元素能改善烧结件层间结合性; 而P元素过量则会因生成过多磷渣而降低润湿性及致密度; P元素亦能充当稀释剂而降低熔体粘度及表面张力, 从而改善烧结致密度及组织均匀性; 但若P元素过量时, 则会因熔体粘度过低而导致球化现象。 实验结果证实, 该组铜基金属粉末体系中CuP的最佳含量为15%。
关键词: 铜基金属粉末; 添加剂; 选区激光烧结; 液相烧结 中图分类号: TG146; TG665
文献标识码: A
Mechanism of P element in selective laser sintering of copper-based metal powder
GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu
(College of Materials Science and Technology,
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China)
Abstract: The selective laser sintering experiment of the multi-component copper-based metal powder systems (Cu-CuSn-CuP) with different CuP contents was carried out. The effects of the P addition on the densification and the resultant microstructural features of the laser sintered powder were investigated by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results show that P can act as deoxidizer to react with Cu and form CuPO3. However, excessive P addition results in a larger degree of superheat of the melt, hence aggravating the oxidation. The bonding coherence between the sintered layers increases with the increase of the content of phosphorus. However, at a large amount of P, the solid-liquid wettability and the resultant densification decrease due to the excessive formation of P slag. Element P can also act as a fluxing agent to decrease the surface tension and viscosity of the melt, thereby improve the sintered densification and the microstructural homogeneity. Whereas, with excessive P addition, an extremely low melt viscosity causes balling phenomena. The results show that the optimal mass fraction of the CuP in the powder system is 15%.
Key words: copper-based metal powder; additive; selective laser sintering; liquid phase sintering
选区激光烧结(selective laser sintering, SLS)作为典型的快速成形技术, 能直接烧结疏松状态下的金属粉末形成任意形状的高致密度三维实体零件, 而一般不需要或很少需要预处理或后处理等辅助工艺手段[1]。 近年来, SLS工艺正逐步用于制造功能性金属零件原型及小批量复杂形状金属模具[2]。
目前, 金属粉末SLS的研究主要集中在预合金粉末(如Ti6Al4V[3], 青铜[4], 不锈钢[5], 高速钢[2], 低碳钢[6], 工具钢[7])和多组分金属粉末(如Cu-SCuP[8], Fe-Cu-W[9], Fe-C[1], Fe-C-Cu-Mo-Ni[10])。 已有的研究主要包括两方面: 开发适用于SLS的金属粉末; 研究激光烧结过程的基本规律(如成形机制、 组织演变、 激光工艺参数的影响)。 然而, 目前已商业化的SLS专用金属粉末材料仍屈指可数, 已有的研究较多选用市售粉末冶金材料作为实验原材料, 因其并非专门为SLS而设计, 故其化学成分和物理性能一般难以满足SLS的特殊使用要求, 致使激光成形件普遍存在球化严重、 致密度低、 翘曲变形和表面粗糙度高等工艺缺陷[11]。 事实上, 金属粉末SLS涉及复杂的物理冶金和化学冶金过程, 包括多重传热、 传质及化学反应等[12]。 但已有的报道对于SLS过程中诸多特殊的冶金问题仍缺乏深入的研究。
本文作者在设计制备SLS专用多组分铜基金属粉末(Cu-CuSn-CuP)的基础上, 成功进行了一系列激光烧结实验, 并对金属粉末SLS致密化机理[13]及工艺参数对烧结组织及致密度的影响[14]等作了较为深入的探讨。 研究还发现, 在粉末体系中添加P元素, 对激光烧结性能有重要影响; 类似的发现在Agarwala等[4]和Zhu等[15]的研究报道中也有提及。 然而, 尽管P元素是铸造、 冶炼、 焊接及粉末冶金领域常用的除气剂和脱氧剂, 但对于其在SLS中的作用机理却未曾有过深入的研究报道。 本文作者对具有不同P元素配比的Cu基金属粉末进行SLS实验, 通过对烧结试样物相、 表面形貌及显微组织的表征, 探讨了P元素对金属粉末SLS组织特征及致密度的影响规律, 以期最终获取组织和性能良好且可控的烧结试样。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
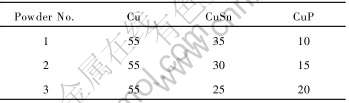
实验材料为多组分铜基金属粉末, 包括下列3种组分: 纯度99%的电解铜粉, 不规则外形, 平均粒度的54μm; 水雾化CuSn预合金粉末(Sn质量分数为10%), 椭球状外形, 平均粒度28μm; 气雾化CuP预合金粉末(P质量分数为8.4%), 球状外形, 平均粒径16μm, P元素以与基体元素Cu形成Cu3P的形式加入粉末体系。 3种组分(Cu, CuSn, CuP)分别按表1所列的质量分数加以混合。
1.2 实验方法
表1 不同组分比例下的粉末体系
Table 1 Powder systems with various component(mass fraction, %)
实验使用的烧结系统主要包括连续CO2激光及相关光路系统, 最大输出功率为1kW, 且功率连续可调; 自动铺粉装置; 用于控制成形工艺的计算机系统。 激光烧结实验在室温下进行, 且不加保护气氛。 通过工艺实验优化下列参数: 光斑直径为0.3mm, 激光功率为350W, 扫描速率0.04m/s, 扫描间距0.15mm, 铺粉厚度0.30mm; 进而制备尺寸为45mm×20mm×10mm的烧结试样。
用于金相分析的试样依照规定程序制备, 腐蚀剂选用含FeCl3(5g), HCl(10mL)和蒸馏水(100mL)的溶液, 腐蚀时间为30s。 烧结试样的物相利用BRUKER D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪表征。 试样表面形貌和显微组织利用QUANTA 200型扫描电镜及光学显微镜分析, 元素分布利用EDAX型能谱表征。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 物相分析
图1所示为不同CuP比例下激光烧结试样的X射线衍射谱。 由图1可见, 在烧结组织中, 起始Cu相仍有保留, 而预合金CuSn则以α-CuSn固溶体这一新形态存在。 研究表明[13], 此组粉末体系SLS基本上沿用液相烧结机制。 纯Cu熔点相对较高(约1083℃), 充当结构金属, 即能在液相烧结过程中保留其固相核心, 未熔部分可作为液相在随后的结晶过程中的非自发形核核心; 预合金CuSn因具有较低的固相线温度(840℃)和液相线温度(1020℃), 故充当粘结金属, 即在SLS过程中发生熔化, 生成的液相通过毛细等力的作用产生流动并润湿、 包覆骨架金属Cu, 以实现烧结致密化。 考虑到激光作用下液相生成与凝固过程极快, 故液相的流动对金属粉体SLS致密化起主导作用。
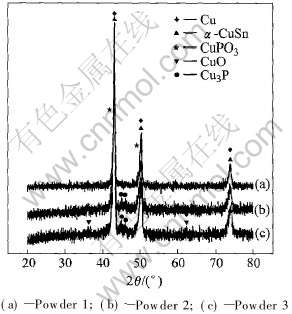
图1 激光烧结试样的X射线衍射谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of laser sintered samples
由图1可看出, 烧结试样中均出现新物相CuPO3。 在SLS过程中, 预合金CuP因其具有较低的共晶温度(714℃), 故将发生熔化。 游离态的P元素将充当脱氧剂, 而发生下列化学反应:
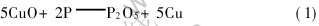
在298.15K温度下, CuO和P2O5的生成反应吉布斯能(ΔGf)分别为-128.29kJ/mol和-1355.68kJ/mol[16], 则反应(1)的吉布斯能变化(ΔG)为-714.23kJ/mol, ΔG〈0, 故反应可自发进行。 而还原产物P2O5将进一步与铜的氧化物反应生成铜的磷酸盐CuPO3[13]。 上述反应使得Cu颗粒表面能避免氧化, 进而能在烧结过程中形成金属/金属接触界面, 故能显著提高固液润湿性。 若缺乏P元素, 则易使Cu颗粒表面出现氧化薄层, 而此界面润湿性较差, 故会降低烧结性能。
图1还表明, 由于起始CuP含量不同, 烧结组织中P元素的存在形态也互有差异。 当CuP含量为15%和20%时, Cu3P(预合金CuP的初始存在形态)均保留于烧结试样中(图1(b)和(c))。 由于在SLS过程中, 激光束进行逐点、 逐行的移动扫描, 激光在任意辐照区域的作用时间极为短暂(小于4ms[1]), 激光作用的局部性与短暂性致使粉末体系中的Cu3P难以发生完全熔化。 而当CuP含量为20%时, 烧结组织中出现CuO(图1(c))。 尽管此时CuP含量较高, 但P的脱氧效果并不明显。 由于预合金CuSn和CuP在SLS过程中都将发生熔化所致, 虽然CuSn和CuP的比热容相当(分别为0.37J/(g·K)和0.39J/(g·K)[16]), 但粉末体系中CuP粒径较CuSn细得多, 故CuP比表面积较大, 其升温熔化更明显; 随着CuP含量增加, 其在SLS过程中的熔化量增加, 熔体过热倾向明显, 这直接导致高温下烧结体系氧化严重[12]。
2.2 表面形貌分析
图2所示为不同CuP含量下烧结试样的表面形貌。 SLS是基于激光束逐行扫描而烧结粉体成形, P元素含量对烧结线组织特征(如连续性、 致密性等)影响显著。 当CuP含量较低(10%)时, 骨架金属Cu颗粒间通过烧结颈形成较为微弱的连接(图2(a)); 随着CuP含量的增加(15%), 烧结线呈连续分布, 致使组织致密性提高(图2(b)); 当CuP含量增至20%时, 烧结线由粗大且断续的金属球体构成(球化现象), 其间分布有宽而深的连续孔隙(图2(c))。
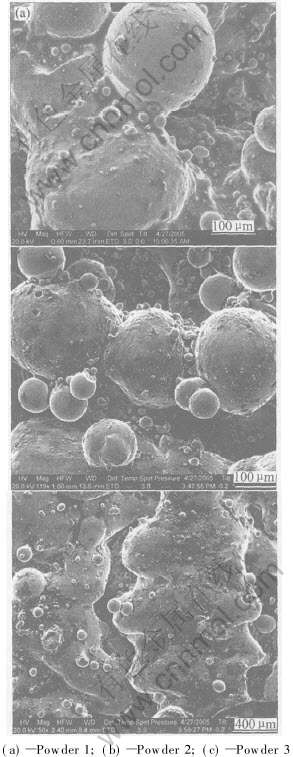
图2 激光烧结试样的表面形貌
Fig.2 Surface morphologies of laser sintered samples
在SLS过程中, 激光束以一定速度逐行扫描粉层, 将形成圆柱形的金属熔化轨迹。 因表面张力效应所引起的液柱不稳定性, 将使这一连续液柱发生形变, 以最终获取平衡态。 研究表明[17], 在激光波长λ>πD(D为液柱未断裂前的直径)的条件下, 易使液柱受到扰动而发生断裂。 因此, 当激光波长λ一定时, D越大, 液柱越不易断裂。 在粉末SLS过程中, P元素能充当稀释剂[13], 随着CuP含量的增加, 能有效降低液相粘度及其表面张力, 液相能充分流动和铺展, 也即D将增大, 故液柱不易断裂, 致使形成连续烧结线(图2(a)和(b))。 而当CuP含量过高时, 因CuP颗粒的比表面积和热吸收率均大于CuSn颗粒的, 故其液相表面张力的温度系数较高[18], 也即表面张力效应随烧结温度提高而增加的趋势更明显, 这将显著提高液相的热毛细管力, 并使熔体流动方向由向外铺展变为向内收缩[14, 18], 故将导致球化(图2(c))。
2.3 显微组织分析
图3所示为烧结试样横截面抛光后的显微组织。 由图3可见, 试样均具有较为明显的层状结构, 这与SLS逐层铺粉、 逐层烧结的成形方式有关。 然而, 烧结组织中的孔隙形状、 大小和分布以及由此导致的层间结合性却因CuP含量的变化而有显著差异。 当CuP含量为10%时, 烧结层间隔有细长的孔隙, 层间结合性较差(图3(a)); 当CuP含量增至15%时, 形成较为致密的烧结层, 层间无横向贯通的孔隙, 而是非连续地分布有少量不规则形状的孔隙(图3(b)); 而当CuP含量为20%时, 烧结性能明显恶化, 烧结层间几乎未有粘结, 其间充满大量连续分布的孔隙(图3(c))。
由于SLS是基于粉末逐层固化成形的, 若当前烧结层的熔融材料难以对已烧结层进行有效润湿, 则将影响层间结合性, 严重时将导致脱层现象[12]。 对于铜基金属粉末SLS, 随着P含量在合理范围内的增加, 能有效防止已烧结层发生氧化, 故在后续SLS过程中, 熔体在毛细管力作用下能在已烧结层表面顺利润湿并铺展, 进而使层间获得良好的冶金结合(图3(a)和(b))。 而当CuP过量时, 则将显著降低烧结致密度(图3(c))。 原因在于, 在SLS过程中, P元素与氧反应生成磷渣(主要是磷的氧化物及磷酸盐), 其质量比Cu和CuSn的要轻得多, 故将在液相烧结过程中上浮于烧结层表面。 适量的磷渣能充当保护膜, 防止表层氧化; 但若CuP含量过高, 表层生成的磷渣过多, 则会显著降低润湿性, 后续烧结层难以与之有效粘结, 故将降低烧结致密度。
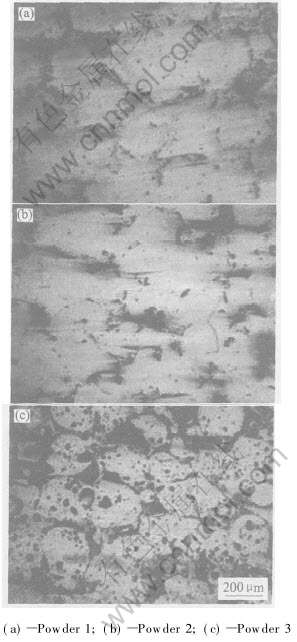
图3 激光烧结试样横截面抛光后的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of polished crosssections of laser sintered samples
图4所示为不同CuP含量下激光烧结试样的显微组织。 由图4可见, 烧结组织的连续性、 均匀性及致密性受P元素含量的影响较为显著。 当CuP含量为10%时, 形成连续的网状枝晶组织, 但其均匀性较差(图4(a)); 随着CuP含量增至15%时, 形成发达、 致密的枝晶, 其组织均匀性亦有所改善(图4(b)); 而当CuP含量为20%时, 无连续枝晶生成, 表现出较差的组织均匀性及致密性(图4(c))。 为进一步研究烧结组织中的元素分布, 分别进行EDX线扫描分析(如图4中直线所示)。 图5所示为Cu, Sn和P元素的分布情况。 由图5可见, 随着CuP含量的增加, 烧结组织中Cu和Sn元素分布无显著差异, 但P元素分布的波动性却逐渐明显, 表明当CuP含量较高时, P元素将在局部区域发生偏聚。 比较发现, 对应于CuP含量为15%的烧结组织中(图4(b)), 各元素分布最为均匀(图5(b))。
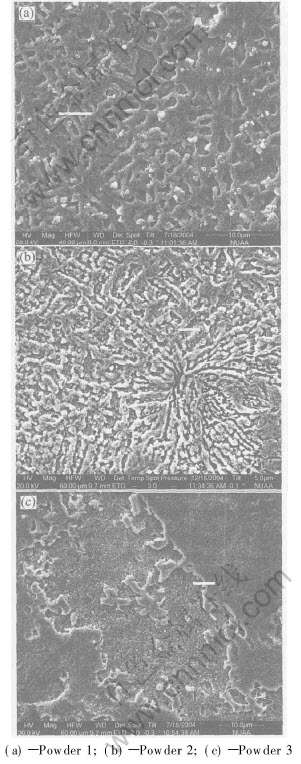
图4 激光烧结试样的显微组织
Fig.4 Microstructures of laser sintered samples
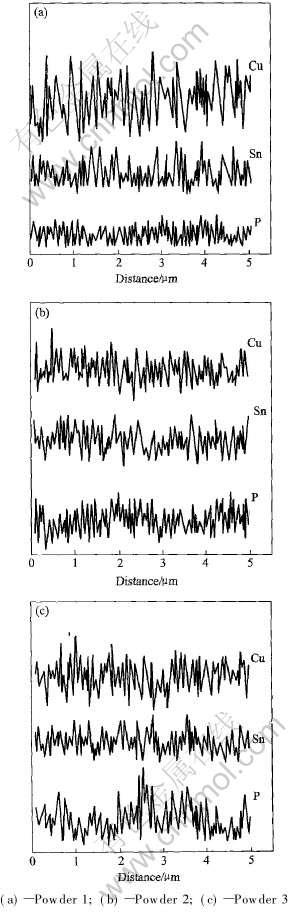
图5 激光烧结组织中Cu, Sn和P元素的分布
Fig.5 Distributions of Cu, Sn and P elements in laser sintered structures
研究表明[13-14], 多组分金属粉末SLS主要是基于液相毛细管力作用下骨架金属颗粒的快速重排而实现烧结致密化, 故烧结性能的优劣主要取决于液相对固相的润湿性。 通常, 润湿性受控于固液表面能, 降低表面能则有利于改善润湿性[4]; 而金属/金属体系的表面能较低, 故其润湿性较好。 然而, Cu颗粒表面难免含有诸多杂质, 尤其是其表面不均匀地分布着氧化薄层。 在此情况下, 固液体系的润湿性可由有效润湿角θe来表示:
cosθe=(1-s)cosθa+s cosθb(2)
式中 b, s分别表示颗粒表面难润湿部分及其面积; a为可润湿部分。 式(2)表明, 减少Cu颗粒表面难润湿的氧化物薄层能有效改善润湿性。 图4(a)和(b)表明, 在粉体中适量添加P元素, 能有效改善润湿性及烧结性。 由于一方面P元素能充当脱氧剂而去除Cu颗粒表层的氧化物, 并能防止其在烧结过程中的二次氧化; 另一方面, P元素能充当稀释剂而降低固液体系的表面张力, 这不仅能促进液相流动和铺展, 还有助于降低固液润湿角[4], 以此加速Cu颗粒在液相润湿作用下的重排率。
然而, 过度增加P元素却难以进一步改善烧结性能(图4(c)), 反会出现P元素在局部区域的偏聚(图5(c))。 在粉末SLS过程中, 固液混合体系的整体流变性将决定烧结性能的优劣, 而固液混合粘度μ可表示为[19]

式中 μ0为熔体粘度; φl为液相体积分数; φm为临界体积分数。 在此之上, 固相混合体系本质上具有无限大粘度。 固相颗粒粘结性受控于μ0, 此粘度须足够低, 以使液相能充分包覆并润湿固相颗粒。 然而, 固液混合粘度μ又须足够高, 以防止球化效应[4]。 若CuP过量时, 将加剧对液相的稀释作用; 再加之其熔点较低, SLS过程中熔体过热倾向明显, 故μ0会显著降低, 直接导致球化现象, 进而降低其烧结性能。 而P元素将在球化过程中偏聚于球化颗粒内部, 致使其在烧结组织内难以均匀分布。
3 结论
1) P元素能充当脱氧剂而防止SLS过程中Cu颗粒表面氧化; 但若P元素过量, 则会因熔体过热倾向明显而加剧氧化。
2) 适量增加P元素能改善烧结件的层间结合性; 而过量则会因生成过多磷渣而降低润湿性及致密度。
3) P元素能充当稀释剂而改善润湿性, 进而提高烧结组织均匀性; 但若P元素过量, 则会因熔体粘度过低而导致球化现象。
4) 多组分Cu-CuSn-CuP金属粉末体系中CuP的最佳质量分数为15%。
致谢
感谢中国工程物理研究院机械制造工艺研究所王洋研究员、 杨家林工程师、 沈显峰博士在激光烧结实验中所给予的大力帮助。
REFERENCES
[1]Simchi A, Pohl H. Direct laser sintering of iron-graphite powder mixture[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 383(2): 191-200.
[2]Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A. Effect of sintering atmosphere and carbon content on the densification and microstructure of laser-sintered M2 high-speed steel powder[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 403(1-2): 290-298.
[3]Das S, Beaman J J, Wohlert M, et al. Direct laser freeform fabrication of high performance metal components[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 1998, 4(3): 112-117.
[4]Agarwala M, Bourell D, Beaman J, et al. Direct selective laser sintering of metals[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 1995, 1(1): 26-36.
[5]Morgan R, Sutcliffe C J, ONeill W. Density analysis of direct metal laser re-melted 316L stainless steel cubic primitives[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39 (4): 1195-1205.
[6]Chatterjee A N, Kumar S, Saha P, et al. An experimental design approach to selective laser sintering of low carbon steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 136(1-3): 151-157.
[7]Childs T H C, Hauser C, Badrossamay M. Selective laser sintering (melting) of stainless and tool steel powders: experiments and modeling[A]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture[C]. 2005, 219(4): 339-357.
[8]Zhu H H, Fuh J Y H, Lu L. Microstructural evolution in direct laser sintering of Cu-based metal powder[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2005, 11(2): 74-81.
[9]Zhu H H, Fuh J Y H, Lu L. Formation of Fe-Cu metal parts using direct laser sintering[A]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science[C]. 2003, 217(1): 139-147.
[10]Simchi A, Petzoldt F, Pohl H. On the development of direct metal laser sintering for rapid tooling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 141(3): 319-328.
[11]Tang Y, Loh H T, Wong Y S, et al. Direct laser sintering of a copper-based alloy for creating three-dimensional metal parts[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 140(1-3): 368-372.
[12]Das S. Physical aspects of process control in selective laser sintering of metals[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003, 5(10): 701-711.
[13]顾冬冬, 沈以赴, 杨家林, 等. 多组分铜基金属粉末选区激光烧结致密化机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(4): 596-602.
GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu, YANG Jia-lin, et al. Densification mechanism of multi-component Cu-based metal powder in selective laser sintering process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(4): 596-602.
[14]顾冬冬, 沈以赴, 吴鹏, 等. 铜基金属粉末选区激光烧结的工艺研究[J]. 中国激光, 2005, 32(11): 1561-1566.
GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu, WU Peng, et al. Processing conditions of Cu-based metal powder in selective laser sintering[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2005, 32(11): 1561-1566.
[15]Zhu H H, Lu L, Fuh J Y H. Influence of binders liquid volume fraction on direct laser sintering of metallic powder[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 371(1-2): 170-177.
[16]Barin I, Platzki G. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances[M]. Weinheim: VCH, 1995.
[17]Simchi A, Pohl H. Effects of laser sintering processing parameters on the microstructure and densification of iron powder[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 359(1-2): 119-128.
[18]Niu H J, Chang I T H. Instability of scan tracks of selective laser sintering of high speed steel powder[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(11): 1229-1234.
[19]Tolochko N, Mozzharov S, Laoui T, et al. Selective laser sintering of single- and two-component metal powders[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2003, 9(2): 68-78.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(10276017); 航空科学基金资助项目(04H52061); 南京航空航天大学科研创新基金资助项目(S0403-061)
收稿日期: 2005-11-28; 修订日期: 2006-01-15
通讯作者: 沈以赴, 教授; 电话: 025-85687494; E-mail: yifushen@nuaa.edu.cn
(编辑李艳红)