Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 285-291
Effects of direct current electric field on corrosion behaviour of copper, Cl- ion migration behaviour and dendrites growth under thin electrolyte layer
Hua-liang HUANG1,2, Zhi-quan PAN1, Xing-peng GUO2, Yu-bing QIU2
1. School of Chemical Engineering and Pharmacy, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430073, China;
2. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Received 13 November 2012; accepted 14 October 2013
Abstract: Effect of direct current electric field (DCEF) on corrosion behaviour of copper printed circuit board (PCB-Cu), Cl- ion migration behaviour, dendrites growth under thin electrolyte layer was investigated using potentiodynamic polarization and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Results indicate that DCEF decreases the corrosion of PCB-Cu; Cl- ions directionally migrate from the negative pole to the positive pole, and enrich on the surface of the positive pole, which causes serious localized corrosion; dendrites grow on the surface of the negative pole, and the rate and scale of dendrite growth become faster and greater with the increase of external voltage and exposure time, respectively.
Key words: copper; dendrites; migration; direct current electric field; thin electrolyte layer; copper printed circuit board
1 Introduction
Atmospheric corrosion is an electrochemical corrosion process under thin electrolyte layer (TEL). The corrosion of electronic components is similar to atmospheric corrosion, but it is more sensitive and complex than usual atmospheric corrosion. With the rapid expansion of electronic industry and wide application of electronic products in various environments, the corrosion of electronic system (or device) significantly increases [1,2]. With the increasing integration of electronic systems and the decreasing space distance of circuit and device, the electric field between these metal electronic components becomes greater and greater, which will result in more sensitivity to the corrosion of electronic system. For example, a corrosion mass loss of 10-12 g is sufficient to cause the whole circuit failure. However, the study of corrosion behaviour and mechanism of electronic systems is very limited, the domestic research work is rare so far [3-6]. Internationally, the corrosion of electronic systems was been paid more and more attentions in recent years [1,7-16], but the correlative results can not accurately reveal the intrinsic mechanism of the corrosion of electronic systems. So, it is very important to deeply understand the corrosion mechanism of electric systems, and eventually establish reliable atmospheric corrosion protection technology of electric systems.
In communication and electronic industries, electronic components are connected to various electronic chips in integrated circuit (IC). Upon running the IC, a strong electric field will form among these electronic components. Then, the different corrosion behaviour of electronic components is expected under electric field since the electric field would affect the transfer process of ions in TEL. Furthermore, the electric field modal should affect corrosion behaviour of electronic components. For example, the direction and strength of direct current electric field (DCEF) is always the same. When metal connects with the positive pole of DCEF, anodic dissolution of metal will occur. When metal connects with the negative pole of DCEF, metal will be protected. It is imaginable that when the external DCEF is imposed on the corrosion cell, DCEF will certainly affect the migration of ions, and then affect corrosion behaviour and mechanism of metals.
Electrochemical migration (ECM) caused by corrosion is a main reason of electronic product failure, especially for printed circuit board (PCB) and microelectronic devices. ECM includes 3 processes, such as the anodic dissolution, ion migration under the electric field and the cathodic reduction deposition. Although the operating voltage is only a few volts, the strength of electric field between the adjacent lines on PCB may reach 102-103 V/cm due to the high integration. The greater the electric field gradient is, the faster ECM is, which can lead to circuit failure even in a few minutes. Some studies have shown that ECM, behaviour of the different metals is significantly different, such as aluminum, silver, copper, tin, lead and gold, which have a high sensitivity to ECM [1]. ECM has two forms [10]. One is the metal ions migrating to cathode to form dendrites. Another is conducting anodic filaments (CAFs) which grows from the anode to the cathode. ECM caused by corrosion will eventually cause a short circuit leakage current of the circuit, which results in the electronic system failure.
Copper is an important electronic material, and is widely used in electronic components and tends to corrosion in the atmosphere. Chloride, especially from polymeric packaging materials, is an important natural aggressive contaminant to enhance the corrosion of metals [2]. The effect of DCEF on ECM behaviour of electronic materials was studied [8-10,17-22], but the effect of DCEF on Cl- ion migration behaviour and dendrites growth under TEL is not reported.
In this work, the effect of DCEF on corrosion behaviour of copper printed circuit board (PCB-Cu), Cl- ion migration behaviour, dendrites growth under TEL is studied by potentiodynamic polarization and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) using a home-made thin layer electrochemical cell.
2 Experimental
To study the effect of DCEF on corrosion behaviour of PCB-Cu, Cl- ion migration behaviour and dendrites growth under TEL by potentiodynamic polarization, a thin layer electrolytic cell was developed. The details of experimental setup were reported elsewhere [23]. Four identical PCB-Cu electrodes with the size of 20 mm× 1.5 mm × 0.035 mm were used, as shown in Fig. 1. The distance between any two adjacent PCB-Cu electrodes was 0.5 mm. The two outermost PCB-Cu electrodes, as two poles for applying electric field, were connected with two poles of electric field devices. The schematic diagram of electric field is also shown in Fig. 1. The two PCB-Cu electrodes in the middle were used as working electrode (WE) and counter electrode (CE), respectively. These electrodes were welded to copper wires respectively to assure the electric connection for potentiodynamic measurements, and the weld points were sealed with silicone. The PCB-Cu specimens were embedded in the upper end surface of a plexiglass cylinder. A hole with a diameter of 2 mm through the PCB-Cu sample and the plexiglass cylinder was drilled at the position 0.5 mm apart from the WE and CE. Saturated NaCl agar was embedded in the hole as salt bridge. The bottom of plexiglass cylinder was connected to a U-shape tube which was filled with saturated NaCl solution. A saturation calomel electrode (SCE) was set at the U-shape tube as a reference electrode. Prior to test, the PCB-Cu electrodes were ground to 1000 grit silicon carbide paper, and then polished with 14-20 μm diamond paste, degreased with acetone and rinsed with distilled water.
The test temperature and relative humidity (RH) were 65 °C and 95%, respectively. 1.5 mL of 0.1 mol/L NaCl solution was naturally dripped on the surface of PCB-Cu electrodes, and then spread on the surface of plexiglass cylinder, the surface area of the electrolyte spreading was about 12.5 cm2. The TEL with the initial thickness of about 1.2 mm was formed. However, the thickness of TEL reduced quickly due to the vaporazation of solution. A constant temperature and humidity of the chamber can ensure the constant thickness of TEL. According to Ref. [24], when the relative humidity is in the range of 60%-100%, the thickness of the formed TEL is in the range of 10 nm-1 μm on a clear surface. Therefore, it can imagine the thickness of TEL in this study (RH=95%) is very thin. The actual thickness of TEL in this experiment was not measured since it was quite difficult to measure such thin TEL.
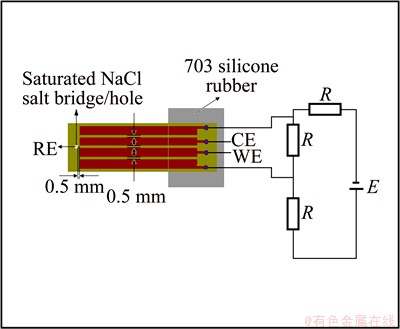
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of PCB-Cu and electric field for polarization test
The polarization curves of PCB-Cu under different conditions were measured using CS350 electrochemical workstation. The electrochemical cell was typical three-electrode mode with SCE as reference electrode. After being stabilized 75 min, the TEL was formed, and then different electric field was applied for 45 min before polarization measurement. The polarization curve measurement was conducted from -0.3 to 0.01 V (vs SCE) versus open circuit potential (OCP) under electric field with a scan rate of 0.5 mV/s.
The electrodes were rinsed with deionized water after exposure to TEL under electric field. After being stabilized for 75 min, different electric fields were applied. The surface morphologies of PCB-Cu were observed by SEM. The chemical composition of dendrites was confirmed by EDS, and the line-scan analysis of the four copper electrodes in the same horizontal position was also carried out by EDS.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of DCEF on corrosion behaviour of PCB- Cu
Figure 2 shows the cathodic polarization curves of PCB-Cu under TEL with and without DCEF. It is seen that the cathodic polarization current densities of PCB-Cu decrease with the increase of the strength of DECF, suggesting that DCEF decreases the corrosion of PCB-Cu. This situation should be attributed to the decrease of Cl- ion concentration in TEL and the reduction of TEL thickness under DCEF.
Figure 3 shows the SEM morphologies of PCB-Cu after corrosion under TEL with and without DCEF for 24 h. It is obvious that the corrosion of PCB-Cu decreases with the increase of the strength of DCEF, which further confirms the results of polarization measurements under DCEF.
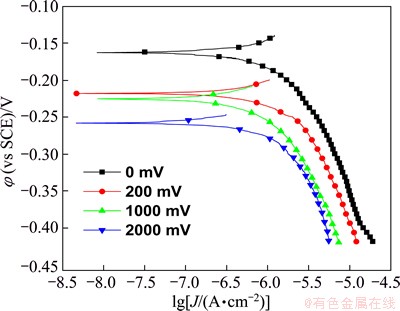
Fig. 2 Cathodic polarization curves of PCB-Cu under TEL containing 0.1 mol/L NaCl with and without DCEF at 95% RH and 65 °C
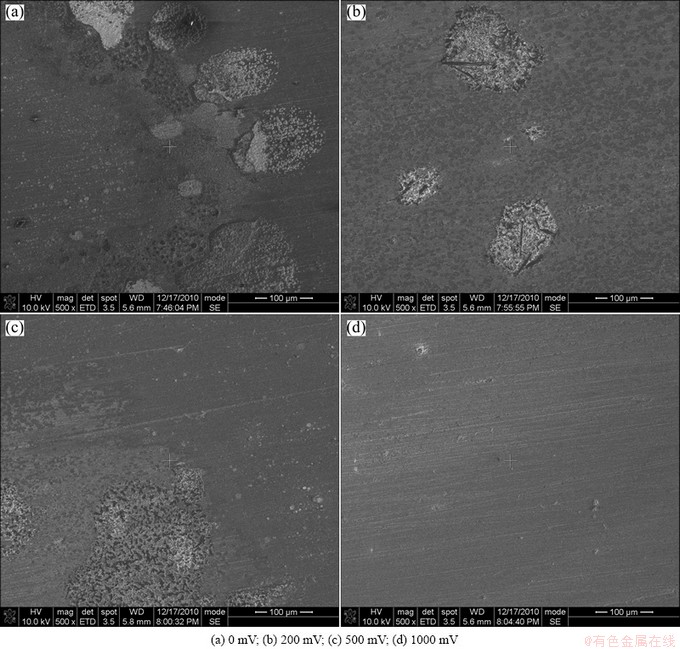
Fig. 3 SEM surface morphologies of PCB-Cu under TEL containing 0.1 mol/L NaCl with and without DCEF at 95% RH and 65 °C for 24 h
3.2 Effect of DCEF on Cl- ion migration behaviour
Figure 4 shows the EDS line-scan results of four copper electrodes in the same horizontal line under DCEF. It is seen that the Cl- ion content on the surface of copper electrodes gradually increases from the negative pole to the positive pole, which is consistent with our previous experimental results [25]. Based on the polarization test results and the surface morphologies, the directional migration of Cl- ions can be confirmed under DCEF.
Figure 5 shows the SEM morphologies of blank specimen without DCEF and the positive poles under various DCEF for 8 d, respectively. It is seen that more loose corrosion products are observed with the increase of the strength of DCEF, which suggests the more serious corrosion with the higher DCEF. This phenomenon can be attributed to two reasons: 1) Cl- ions enrich on the positive pole of DCEF due to directional migration resulting in serious corrosion; 2) the anodic polarization of electrode under the external positive voltage.
3.3 Effect of DCEF on dendrites growth
Figure 6 shows the SEM morphologies of dendrites on the negative pole surface with different DCEF for 8 d. It is seen that there are clear black dendrites on the negative pole surface. Moreover, the growth of dendrites becomes faster with the increase of the external voltage. Figure 6(a) shows a typical copper-flower.
Figure 7 shows the EDS results of chemical composition of dendrites. It is seen that the chemical composition of black dendrites includes Cu and O, and the mass ratio of Cu to O is 4:1, which indicates that the chemical composition of dendrites should be CuO. This can be explained that copper directly dissolves in the form of Cu2+ ion at high anodic overpotential, and Cu2+ ions migrate to cathode under DCEF and then reduce and deposit on the cathode surface. However, copper will oxide to CuO under hot-wet environment. Therefore, the main composition of the dendrites is CuO.
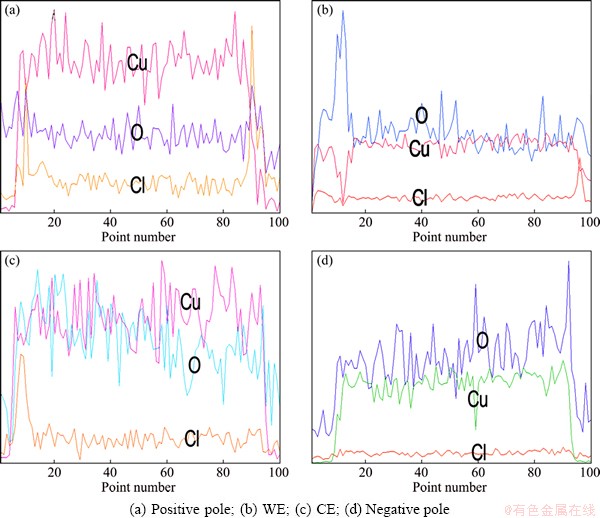
Fig. 4 Line-scan results of four electrodes on surface of PCB-Cu after being exposed for 24 h
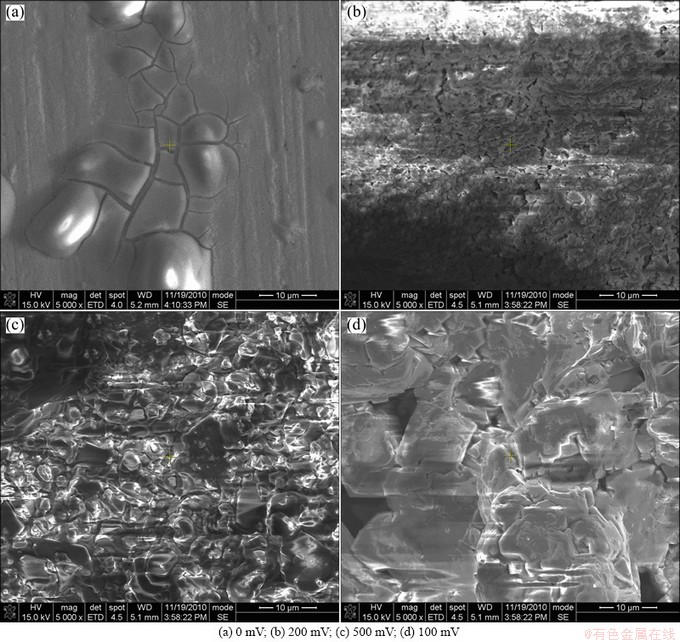
Fig. 5 SEM morphologies of blank specimen and positive poles with DCEF under TEL containing 0.1 mol/L NaCl at 95% RH and 65 °C after being exposed for 8 d
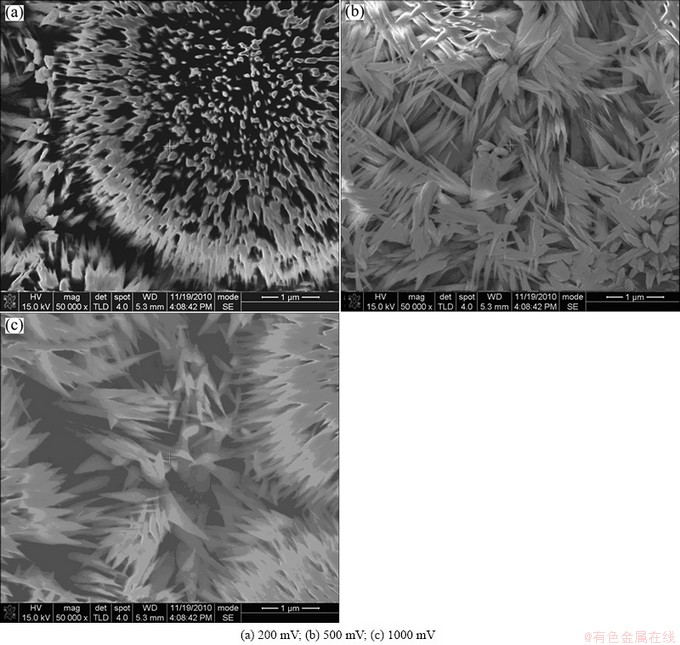
Fig. 6 SEM morphologies of dendrites grown on surface of negative copper electrodes under TEL containing 0.1 mol/L NaCl with different DCEF at 95% RH and 65 °C after being exposed for 8 d
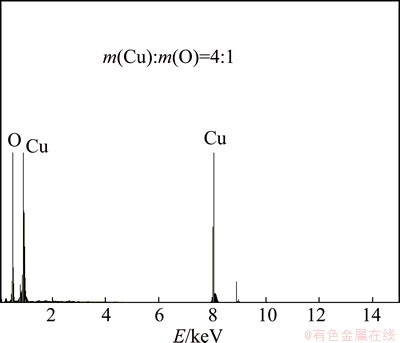
Fig. 7 EDS results of chemical composition of dendrites
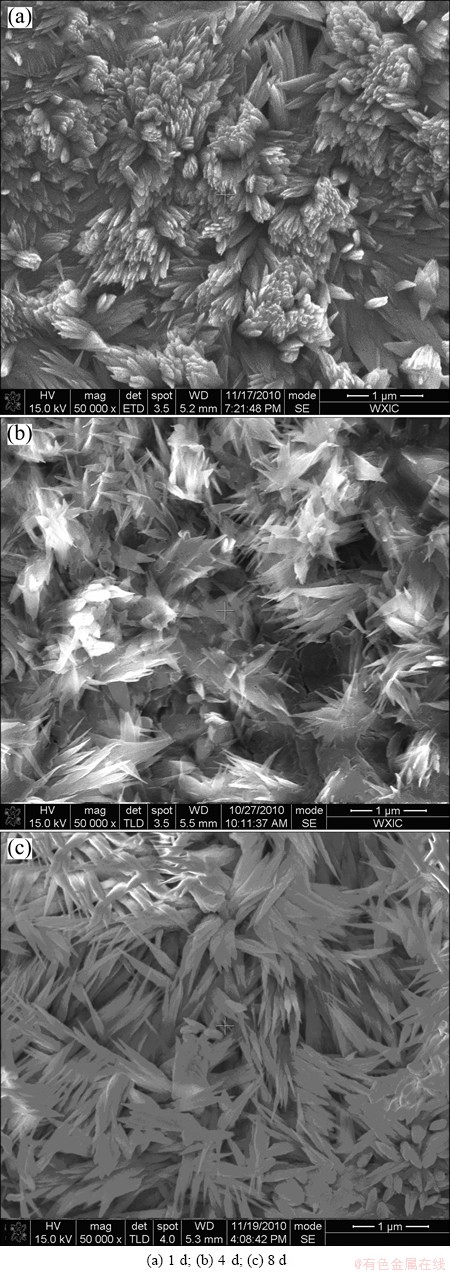
Fig. 8 SEM morphologies of dendrites grown on surface of negative PCB-Cu under TEL containing 0.1 mol/L NaCl at 95% RH and 65 °C with different exposure time
Figure 8 shows the SEM morphologies of dendrites grown on the negative pole surface with DCEF after different exposure time. It is seen that the growth process of dendrites is from nanoparticles to dendrites. According to Figs. 6 and 8, there is an important effect of DCEF and exposure time on dendrites growth behaviour. The rate of dendrites growth increases with increasing the strength of DCEF (Fig. 6), which may be explained as follows. With the same exposure time, the greater the DCEF is, the more Cu2+ ions are produced due to rapid anodic dissolution in the positive pole. Then, the deposition of copper (the growth rate of dendrites) is faster, and more dendrites are deposited in the negative pole. It can be seen from Fig. 8 that, the formation process of dendrites is from the nanoparticle to the body structure, which suggests that Cu2+ ions continuously generate in the positive pole under DCEF, and then are reduced and deposed on the negative pole. Based on the above analysis, the process of dendrites growth is divided into three stages: the first is the incubation period of dendrites, namely, Cu2+ ions produced due to anodic polarization migrate to the negative pole of DCEF; the second is the nucleation period of dendrites, Cu2+ ions are reduced and deposited on the negative pole of DCEF; and the third is the stable growth period of dendrites, Cu2+ ions continuously generate in the positive pole, and then are continuously reduced and deposited on the negative pole of DCEF, the length of dendrites growth increases with the increase of exposure time.
4 Conclusions
1) The effect of DCEF on corrosion behaviour of PCB-Cu, Cl- ion migration behaviour, dendrites growth under TEL is studied using potentiodynamic polarization and SEM with EDS. The cathodic polarization results indicate that the cathodic polarization current densities of PCB-Cu decrease with the increase of DCEF, which suggests that DCEF decreases the corrosion of PCB-Cu.
2) The EDS results indicate that Cl- ion content gradually increases from the negative pole to the positive pole under DCEF, which confirms the directional migration of Cl- ions.
3) Dendrites are observed on the negative pole surface under DCEF, and the growth of dendrites is faster and greater with the increase of the external voltage and exposure time.
References
[1] JELLESEN M S, MINZARI D, RATHINAVELU U,  P, AMBAT R. Investigation of electronic corrosion at device level [J]. The Electrochemical Society, 2010, 25(30): 1-14.
P, AMBAT R. Investigation of electronic corrosion at device level [J]. The Electrochemical Society, 2010, 25(30): 1-14.
[2] COMIZZOLI R B, FRANKENTHAL R P, MILNER P C, SINCLAIR J D. Corrosion of electronic materials and devices [J]. 1986, 234(4774): 340-345.
[3] ZHONG Xian-kang, ZHANG Guo-an, QIU Yu-bin, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Xing-peng, FU Chao-yang. The corrosion of tin under thin electrolyte layers containing chloride [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 66: 14-25.
[4] ZHONG Xian-kang, ZHANG Guo-an, QIU Yu-bin, CHEN Zhen-yu, ZOU Wen-xin, GUO Xing-peng. In situ study the dependence of electrochemical migration of tin on chloride [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2013, 27: 63-68.
[5] ZHANG Wei, CHENG Dan-hong, YU Zu-zan, WERNER J. In situ observation and research on electrochemical migration of SnAgCu solder joints [J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2007, 26(6): 64-68. (in Chinese)
[6] ZHANG Liang-jing, LIU Xiao-yang. Electrochemical migration and Anti-CAF laminates [J]. Printed Circuit Information, 2007, 11: 20-21. (in Chinese)
[7] OZKI, TOSHINORI I, YUICHI. A review on corrosion prevention and control of various electronic components [J]. Corrosion Engineering, 2003, 52(4): 185-194.
[8] NOH B I, LEE J B, JUNG S B. Effect of surface finish material on printed circuit board for electrochemical migration [J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2008, 48: 652-656.
[9] AMBAT R, MΦLLER P. Corrosion investigation of material combinations in a mobile phone dome-key pad system [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 2866-2879.
[10] LEE S B, YOO Y R, JUNG J Y. Electrochemical migration characteristics of eutectic SnPb solder alloy in printed circuit board [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 504: 294-297.
[11] LOPEZ B G, VALDEZ S B, ZLATEW K R, FLORES P J, CARRILLO B M, SCHORR W M, Corrosion of metals at indoor conditions in the electronics manufacturing industry [J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2007, 54(6): 354-359.
[12] VELEVA L,  Initial stages of indoor atmospheric corrosion of electronics contact metals in humid tropical climate: tin and nickel [J]. Revista de Metalurgia, 2007, 43(2): 101-110.
Initial stages of indoor atmospheric corrosion of electronics contact metals in humid tropical climate: tin and nickel [J]. Revista de Metalurgia, 2007, 43(2): 101-110.
[13] MINAMITANI R, AMANUMA T, MATSUI K. Corrosion sensors to evaluate corrosiveness of installation environment for electronic equipment [J]. Corrosion Engineering, 2005, 54(10): 476-482.
[14] SASAKI T, KANAGAWA R, OHTSUKA T, MIURA K. Corrosion products of tin in humid air containing sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide at room temperature [J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 847-854.
[15] MEDGYES B,  In situ optical inspection of electrochemical migration during THB tests [J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2011, 22: 694-700.
In situ optical inspection of electrochemical migration during THB tests [J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2011, 22: 694-700.
[16] AMBAT R, JENSEN S G, MΦLLER P. Corrosion reliability of electronic systems [J]. ECS Transactions, 2008, 6(24): 17-28.
[17] YAN B D, WARREN G W, WYNBLATT P. An examination of the failure of electronic devices by cyclic voltammetry and potential step methods [J]. Corrosion, 1987, 43: 118-126.
[18] MEILINK S L, ZAMANZADEH M, WARREN G W. Modelling the failure of electronic devices by dendrite growth in bulk and thin layer electrolytes [J]. Corrosion, 1988, 44: 644-651.
[19] ZAMANZADEH M, LIU Y S, WYNBLATT P. Electrochemical migration of copper in adsorbed moisture layers [J]. Corrosion, 1989, 45: 643-648.
[20] ZAMANZADEH M, MEILINK S L, WARREN G W. Electrochemical examination of dendritic growth on electronic devices in HCl electrolytes [J]. Corrosion, 1990, 46: 665-671.
[21] WARREN G W, WYNBLATT P, ZAMANZADEH M. The role of electrochemical migration and moisture adsorption on the reliability of metallized ceramic substrates [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1989, 18: 339-353.
[22] MINZARI D, JENSEN M S, MΦLLER P, WAHLBERG P, AMBAT R. Electrochemical migration on electronic chip resistors in chloride environments [J]. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2009: 9.
[23] HUANG Hua-liang, DONG Ze-hua, GUO Xing-peng. The effects of Cl- ion concentration and relative humidity on atmospheric corrosion behaviour of PCB-Cu under adsorbed thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 1230-1236.
[24] TOMASHIOV N D. Development of the electrochemical theory of metallic [J]. Corrosion, 1964, 20: 7t-14t.
[25] HUANG Hua-liang, GUO Xing-peng, ZHANG Guo-an, DONG Ze-hua. Effect of direct current electric field on atmospheric corrosion behaviour of copper under thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 3446-3449.
薄层液膜下直流电场对铜的腐蚀行为、氯离子迁移行为和枝晶生长的影响
黄华良1,2,潘志权1,郭兴蓬2,邱于兵2
1. 武汉工程大学 化工与制药学院,武汉 430073;
2. 华中科技大学 化学与化工学院,武汉 430074
摘 要:采用动电位极化和表面分析技术(SEM/EDS),研究薄层液膜下直流电场对印刷电路板铜的腐蚀行为、氯离子迁移行为和枝晶生长的影响。结果表明:直流电场使铜的腐蚀减弱;氯离子在直流电场作用下由负极到正极发生定向迁移,并且富集于电场的正极,导致电场正极发生严重的局部腐蚀;枝晶生长于电场的负极,并且其速率和尺寸随着外加电压的增加和暴露时间的延长而分别加快和变大。
关键词:铜;枝晶;迁移;直流电场;薄层液膜;印刷电路板
(Edited by Chao WANG)
Foundation item: Project (50871044) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012M511207) supported by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China; Project (10122011) supported by the Science Research Foundation of Wuhan Institute Technology, China
Corresponding author: Hua-liang HUANG; Tel: +86-27-87194465; Fax: +86-27-87194980; E-mail: hhlo425@aliyun.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63059-4