Li+, Mg2+, Na+和 K+在LiFePO4/ FePO4结构中的电化学行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第4期
论文作者:赵中伟 司秀芬 梁新星 刘旭恒 何利华
文章页码:1157 - 1164
关键词:LiFePO4/ FePO4电极;NaFePO4;锂;钾;卤水
Key words:LiFePO4/FePO4 electrodes; NaFePO4; lithium; potassium; brine
摘 要:因Na+、K+总与Li+、Mg2+伴生在卤水中,故在Li+、Mg2+研究的基础上,我们继续开展Na+、K+的系列研究。循环伏安测试结果表明:在LiFePO4/ FePO4结构中,Na+表现出一定的循环性能,其还原峰为-0.511 V,比Li+的(-0.197 V) 更负。因此,为了抑制Na+的嵌入,需控制低电位。而K+的还原峰不能明显观察到,表明K+难于嵌入到FePO4结构中。以取自中国西部的实际Mg/Li比为493的卤水作电解液,在槽电压0.7 V时进行电解实验。结果表明:Li+、Mg2+和Na+的最终脱出量每1 g LiFePO4分别可达24.1 mg、7.32 mg 和 4.61 mg,所得溶液中的Mg/Li比从493降至0.30,Na/Li比从16.7降至0.19。因此,可以看出即使在超高Mg/Li比的卤水液中,如果控制得当,也能使得Li+和其它杂质有效分离。
Abstract: Besides Li+ and Mg2+, the electrochemical behavior of Na+ and K+ in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures was studied since they naturally coexist with Li+ and Mg2+ in brine. The cyclic voltammogram (CV) results indicated that Na+ exhibits some reversibility in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures. Its reduction peak appears at -0.511 V, more negative than that of Li+ (-0.197 V), meaning that a relatively positive potential is beneficial for decreasing Na+ insertion. The reduction peak of K+ could not be found clearly, indicating that K+ is difficult to insert into the FePO4 structure. Furthermore, technical experiments using real brine with a super high Mg/Li ratio (493) at a cell voltage of 0.7V showed that the final extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+ and Na+ that can be attained in 1 g LiFePO4 is 24.1 mg, 7.32 mg and 4.61 mg, respectively. The Mg/Li ratio can be reduced to 0.30 from 493, and the Na/Li ratio to 0.19 from 16.7, which proves that, even in super high Mg/Li ratio brine, if a cell voltage is appropriately controlled, it is possible to separate Li+ and other impurities effectively.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1157-1164
Zhong-wei ZHAO1,2, Xiu-fen SI1, Xin-xing LIANG1, Xu-heng LIU1, Li-hua HE1
1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Metallurgy and Material Processing of Rare Metals, Changsha 410083, China
Received 4 September 2012; accepted 28 March 2013
Abstract: Besides Li+ and Mg2+, the electrochemical behavior of Na+ and K+ in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures was studied since they naturally coexist with Li+ and Mg2+ in brine. The cyclic voltammogram (CV) results indicated that Na+ exhibits some reversibility in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures. Its reduction peak appears at -0.511 V, more negative than that of Li+ (-0.197 V), meaning that a relatively positive potential is beneficial for decreasing Na+ insertion. The reduction peak of K+ could not be found clearly, indicating that K+ is difficult to insert into the FePO4 structure. Furthermore, technical experiments using real brine with a super high Mg/Li ratio (493) at a cell voltage of 0.7V showed that the final extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+ and Na+ that can be attained in 1 g LiFePO4 is 24.1 mg, 7.32 mg and 4.61 mg, respectively. The Mg/Li ratio can be reduced to 0.30 from 493, and the Na/Li ratio to 0.19 from 16.7, which proves that, even in super high Mg/Li ratio brine, if a cell voltage is appropriately controlled, it is possible to separate Li+ and other impurities effectively.
Key words: LiFePO4/FePO4 electrodes; NaFePO4; lithium; potassium; brine
1 Introduction
Lithium resources have attracted considerable attention since the Li-ion rechargeable battery is being used to store energy generated from solar radiation, wind, and ocean waves in order to alleviate concerns about a global warming and a dependence on foreign oil or gas that could endanger social stability [1]. Lithium extraction from minerals is costly and the lithium mineral reserves are limited, making it difficult to meet the demands of modern energy industry [2-4]. Consequently, there has a greatly increased interest in extracting lithium from seawater and salt lake brine, even though the lithium concentration in sea water is quite low (0.17 mg/L) [5-8].
LiFePO4 with ordered olivine structure was first reported by PADHI et al [9], who proposed LiFePO4 as a potential cathode material in non-aqueous batteries. In our previous study [10], through cyclic voltammogram (CV) tests and electrolytic technical experiments, it was proved that LiFePO4/FePO4 electrode materials can separate Li+ and Mg2+ effectively due to their subtle electrochemical differences. The results indicated that the insertion of Mg2+ and Li+ occurs at different potentials and the existence of Mg2+ obviously influences the behavior of Li+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures. A high Mg/Li ratio causes large redox peak separation of Li+. The insertion capacity of Li+ peaks at a cell voltage of 0.8 V while the Mg/Li ratio is the lowest. A relatively positive potential is unfavorable for inserting Mg2+ because it needs more serious polarization to favor substitution at the Li+ ion sites. Thus, a low potential helps to separate Mg2+ and Li+ ions, although a long electrolytic time is needed.
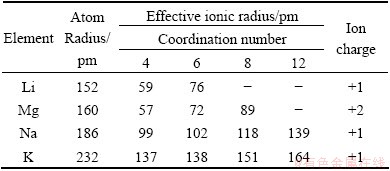
However, we know that brine contains other cations besides Li+ and Mg2+, such as Na+, K+ and Ca2+ (We will not consider Ca2+ here due to its very low concentration in brine). For successfully extracting Li+ from brine, the electrochemical behavior of these ions in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures cannot be ignored. Their chemical properties are listed in Table 1 [11]. In this study, we further focus on investigating the electrochemical behavior of Na+ and K+ as well as their comparison with Li+ and Mg2+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures.
Table 1 Chemical properties of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation of LiFePO4/FePO4 electrodes
A mixture of 90% (mass fraction) LiFePO4/C [12], 5% carbon black and 5% polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) was combined in N-methyl-2 pyrolidone. This was applied onto a flat base and heated for 12 h at 120 °C under a vacuum, after which its non-working surfaces were insulated with epoxy. The density of the prepared LiFePO4 was around 20 mg/cm2. The prepared LiFePO4 electrode was trimmed to 6 cm×7 cm (to fit in the electrolytic cell) to serve as the cathode. Porous foam nickel (Changsha LYRUN, China) with the same size was chosen as the anode. An electrolytic cell filled with 600 mL of 0.5 mol/L NaCl or KCl aqueous solution (supporting electrolyte) was provided with a constant electrolysis potential of 1.0 V. The distance between the porous foam nickel and the LiFePO4 electrode is typically 10 mm. The electrolysis ran for 10 h to ensure the lithium ions could be completely extracted from LiFePO4.
2.2 Preparation of electrolyte
A typical synthetic solution containing 220 mg/L Li+, 3675 mg/L Na+ and 3792 mg/L K+ (similar to their compositions in brine) was prepared by dissolving LiCl, NaCl and KCl in distilled water, respectively. Brine was sampled from salt lake brine of west China, which has a super high Mg/Li ratio (493). Its chemical composition is listed in Table 2. The concentrations of Li+, Na+ and K+ were determined by AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Persee of Beijing, China), while that of Mg2+ by ICP-AES (IRIS intrepid XSP, Thermo Electron Corporation). All reagents used were of analytical grade.
2.3 Electrochemical measurements
Cyclic voltammograms were obtained using a three-electrode cell with or without N2 flow. The working electrode was square (1 cm2 with 1 mm thickness) LiFePO4. This square was electrically connected with Pt wire. The graphite and saturated calomel electrodes (SCE) served as counter and reference electrodes, respectively. The working electrode was cycled between -1.3 and 1.3 V or -1.0 and 1.0 V at a scan rate of 0.2 mV/s. On each occasion, the potential scan started at -1.3V or -1.0 V, moving initially in the cathodic direction. All the cyclic voltammetry experiments were recorded via CHI660A electrochemical workstation (Chenhua, Shanghai, China) at ambient temperature (25±1) °C.
2.4 Preparation of electrolytic cell for technical experiments
A sketch of the rectangular PTEE electrolytic cell with the dimensions of 10 cm×8 cm×9.5 cm is shown in Ref. [10]. The integrated electrolytic cell was divided in the middle by a permselective membrane (American IONAC) which allows anions to pass through, but blocks cations.
2.5 Electrolytic technical experiments
Each technical experiment included two steps as follows.
Step1
Cathode: LiFePO4; Electrolyte: 600 mL of 0.5 mol/L NaCl or KCl solution;
Anode: FePO4; Electrolyte: 600 mL of Li+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ chloride solution or brine;
Reaction time: 600 min
The LiFePO4 and FePO4 electrodes (both have the same dimensions) were placed into the electrolytic cell as shown in Ref. [10]. Each half-cell was filled with different electrolyte as indicated and was equipped with a magnetic stirrer.
Step 2
Cathode: MeFePO4 (from the anode of step 1) (Me: Li+, Mg2+, Na+ or K+); Electrolyte: 600 mL of 0.5 mol/L NaCl or KCl solution;
Anode: FePO4; Electrolyte: 600 mL of Li+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ chloride solution or brine;
Reaction time: 600 min
After running step 1 for 10 h, the electrodes were thoroughly flushed with 50-55 °C distilled water. The cathode used in Step 2 (lithium-eliminated) became the anode in step 2; and the anode from step 1 (lithium-saturated) became the cathode in step 2. A voltage was applied for 10 h. Using this approach, lithium in brine or enriched lithium solution can be extracted and concentrated in the supporting electrolyte solution. In each experiment, 1 mL sample was accurately withdrawn for analysis at different reaction times.
Table 2 Chemical composition of salt lake brine sampled from west China (unit: mg/L)

2.6 Data process
The inserted capacity or extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ was calculated as follows.
Inserted capacity:
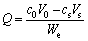 (1)
(1)
Extracted capacity:
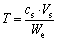 (2)
(2)
where Q is the inserted capacity, mg/g; T is the extracted capacity, mg/g; c0 the initial concentration of metal in solution, mg/L; cs the final concentration of metal in solution, mg/L; V0 the initial volume of the solution, L; Vs the final volume of the solution, L; We the molar mass of LiFePO4.
The Me/Li ratio was calculated as follows:
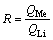 or
or 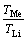 (3)
(3)
where R is the Me/Li ratio; Me=Mg or Na; QMe the inserted capacity of Me; TMe the extracted capacity of Me.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Li/Na separation
Before this study, more attention was paid to the Mg2+ impurity, since the Mg/Li separation has traditionally been a big challenge for Li+ extraction from brine. While examining the electrochemical behavior of the cations in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures, it was unexpectedly found that Na+ had some embedded concentration. For an explanation, it is needed to first discuss the NaFePO4 structure in detail based on the previous studies.
NaFePO4 has two kinds of structures [13]. One is the maricite phase, which is synthesized at a high temperature or under hydrothermal conditions. On contrary to the olivine LiFePO4, the maricite phase presents one-dimensional, edge-sharing FeO6 octahedrons and no cationic channels. The other structure is an olivine-based NaFePO4 phase, which is obtained by the cation exchange from LiFePO4. The complete sodiation of the olivine FePO4 is formed and reversible. MOREAU et al [14] proved that an olivine-based NaFePO4 phase is stable enough not to be transformed into the maricite phase while cycling. Unlike the Li/FePO4 system, however, it occurs in two steps, with the formation of the intermediate Na0.7FePO4 composition. They also proved that the insertion site of Na+ is the same as that of Li+ in the FePO4 matrix. When the cell is charged up to 4 V, the following cycles show very poor reversibility. The cycling does not exceed 4-5cycles.
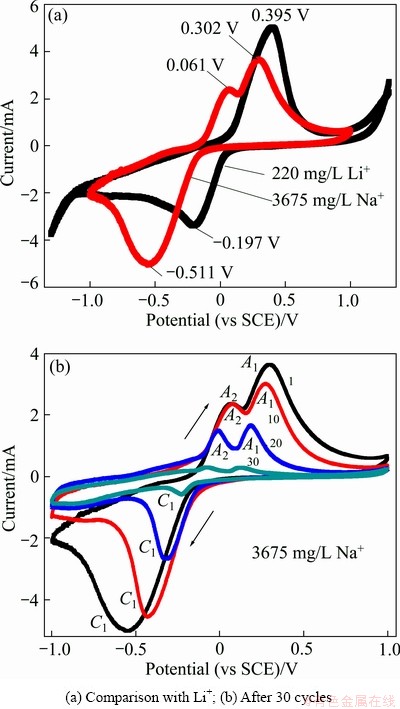
Fig. 1 CV curves of Na+ in FePO4/LiFePO4 structures at scan rate of 0.2 mV/s
3.1.1 CV test of Na+ in chloride solution
Figure 1(a) shows the CV curve of Na+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures with a scan rate of 0.2 mV/s in 3675 mg/L Na+ chloride solution, with the curve of 220 mg/L Li+ for comparison. It can be seen that a couple of redox peaks of Na+ are located at 0.302 and -0.511 V, respectively. The corresponding peak separation is of 0.813 V, indicating that Na+ shows some reversibility in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures. Its reduction peak appears at -0.511 V, more negative than that of Li+ (-0.197 V), meaning that a low potential helps to decrease Na+ insertion. In addition, Na+ has two oxidation peaks, which should originate from the transfer of the intermediate Na0.7FePO4 between NaFePO4 and FePO4 structures as discussed above. Figure 1(b) shows the cycling performance of Na+ in the same solution. Its concentration decreases fast. After 30 cycles, the intensity of the redox peaks basically disappears. From the point of view of lattice dynamics, ZAGHIB et al [15] explained that the spectroscopic features of olivine NaFePO4 are structurally related to that of LiFePO4, but the splitting of the intramolecular 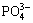 vibrations in NaFePO4 suggests stronger interactions between ions in the elementary cell. They also calculated that the NaFePO4 crystal cell parameters are slightly larger than those of the lithium equivalent: a=10.4063(6)
vibrations in NaFePO4 suggests stronger interactions between ions in the elementary cell. They also calculated that the NaFePO4 crystal cell parameters are slightly larger than those of the lithium equivalent: a=10.4063(6)  , b= 6.2187(3)
, b= 6.2187(3) 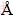 , c=4.9469(3)
, c=4.9469(3) 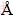 and V=320.14(3)
and V=320.14(3) 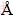 3 for NaFePO4; and a=10.332(4)
3 for NaFePO4; and a=10.332(4) 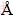 , b=6.010(5)
, b=6.010(5) 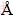 , c=4.692(2)
, c=4.692(2) 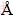 , and V=291.35(10)
, and V=291.35(10) 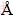 3 for LiFePO4. The about 0.2
3 for LiFePO4. The about 0.2 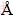 increase for the parameters b and c is consistent with that of ionic radii from lithium (76 pm) to sodium (102 pm). But parameter a, on the contrary, increases only by 0.07
increase for the parameters b and c is consistent with that of ionic radii from lithium (76 pm) to sodium (102 pm). But parameter a, on the contrary, increases only by 0.07 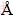 . In this direction, the FeO6 octahedrons distortion in NaFePO4 is much higher, which is linked by PO4 tetrahedrons, while PO4 tetrahedrons are known for being particularly rigid entities.
. In this direction, the FeO6 octahedrons distortion in NaFePO4 is much higher, which is linked by PO4 tetrahedrons, while PO4 tetrahedrons are known for being particularly rigid entities.
3.1.2 Electrolytic technical experiments
1) Sodium extraction from aqueous solution at cell voltage of 1.0 V
In this experiment, 3675 mg/L Na+ chloride solution was used to study Na+ insertion into the FePO4 structure at a cell voltage of 1.0 V. Since the concentration of Na+ is high, and its insertion ability into FePO4 is limited, it is difficult to accurately determine its concentration change during the process of insertion. For this reason, Figure 2 just gives the deintercalated contents of Na+. There is considerable Na+ extracted in 0.5 mol/L KCl solution, meanwhile, the deintercalated concentration of Li+ under the same condition except that electrolyte is replaced with 220 mg/L Li+ is provided for comparison. The result shows that the extracted Li+ content is nearly 3.5 times as much as that of Na+ since the relative atomic mass of Na+ (22.99) is 3.3 times larger than that of Li+ (6.941), which indicates that the selectivity of FePO4/LiFePO4 to Li+ is prior to that of Na+.
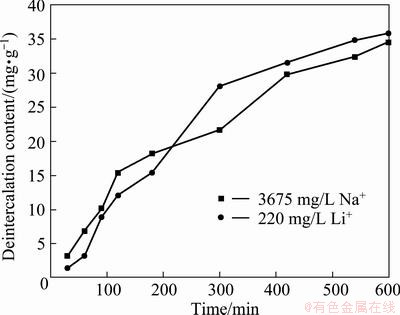
Fig. 2 Comparison of Na+ extraction from NaFePO4 with Li+ extraction from LiFePO4 at 1.0 V
2) Li/Na separation from low concentration solution at cell voltage of 0.7 V
From the CV test of Na+, it can be seen that its reduction peak appears at -0.511 V, more negative than that of Li+ (-0.197 V). Additionally, from the above study at a cell voltage of 1.0 V, the inserted capacity of Na+ is considerable. Hence, it seems that a lower electrolytic voltage should be maintained in order to decrease the insertion of Na+. A low concentration electrolyte with a mixed 60 mg/L Li+ and 60 mg/L Na+ solution was prepared to further explore the separation of Li+ and Na+. The voltage was set as 0.7 V. Figure 3(a) displays that the concentration of Na+ nearly remained unchanged during the whole insertion process, but the variation of Li+ was very obvious. Figure 3(b) shows the corresponding extraction process in 0.5 mol/L KCl solution, from which the same conclusion is drawn.
3) Li/Na separation from high sodium concentration solution at cell voltage of 0.7 V
Based on the above results, the mixed solution of
Na+ and Li+ was prepared according to their composition in brine (Table 2), which contained 220 mg/L Li+ and 3675 mg/L Na+. The experiment was done at a cell voltage of 0.7 V. The results are shown in Fig. 4. It shows that the separation of Na+ and Li+ is good. The inserted capacity of Li+ reached 29.05 mg/g, its extracted capacity was 25.92 mg/g; but the extracted capacity of Na+ was only 7.32 mg/g. The Na/Li ratio was reduced to 0.28 from 16.7.
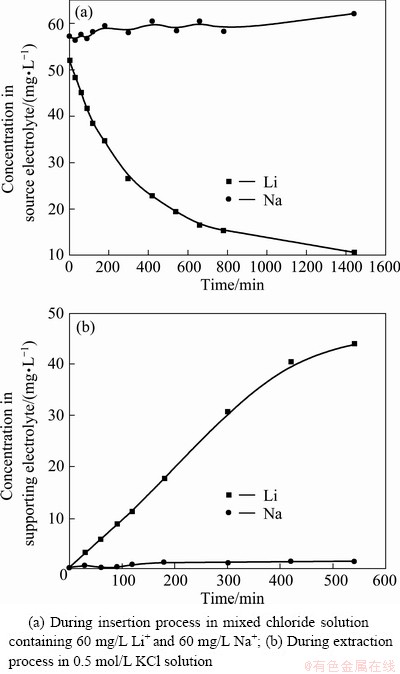
Fig. 3 Concentration changes of Li+ and Na+ at cell voltage of 0.7 V
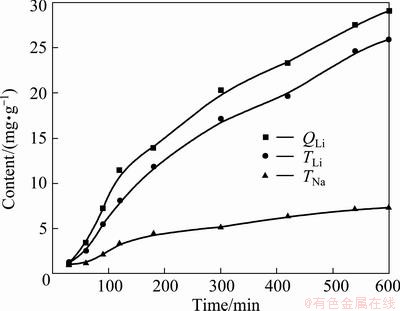
Fig. 4 Inserted capacity QLi from mixed chloride solution containing 220 mg/L Li+ and 3675 mg/L Na+ during insertion process as well as extracted capacity TLi and TNa in 0.5 mol/L KCl solution during extraction process at 0.7 V
3.2 K/Li separation
3.2.1 CV test of K+ in chloride solution
Figure 5 shows the CV curve of in 3792 mg/L K+ chloride solution, with the curve of Li+ for comparison. The redox peaks cannot be found clearly, which indicates that K+ is difficult to insert into the FePO4 structure. From Table 1, it can be seen that the ionic radius of K+ is 138 pm, nearly twice that of Li+ (76 pm). Therefore, the fact that K+ is difficult to move back and forth in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures is not unexpected.
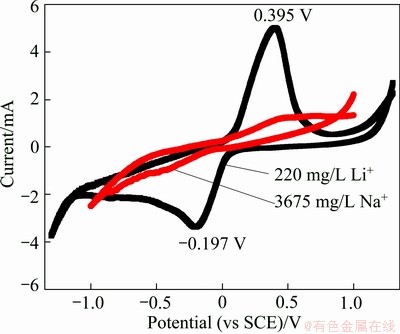
Fig. 5 CV curve of K+ compared with that of Li+ in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures at scan rate of 0.2 mV/s
3.2.2 Electrolytic technical experiments
A chloride solution containing 3792 mg/L K+ was used to study the insertion of K+ into the FePO4 structure at a cell voltage of 1.0 V. Figure 6 gives the concentration changes of K+ during the insertion process. It can be seen that the concentration of K+ remains nearly unchanged from start to finish.
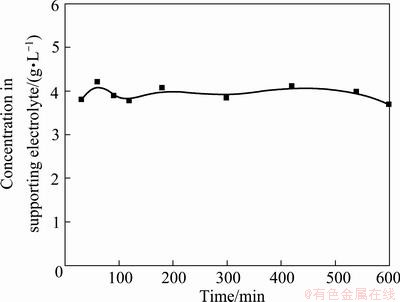
Fig. 6 Concentration changes of K+ during insertion process in 3792 mg/L K+ solution at cell voltage of 1.0 V
Figure 7 displays the concentration changes of Li+ and K+ when the mixture solution contained 3792 mg/L K+ and 220 mg/L Li+. The concentration of K+ hardly varies, but the Li+ extraction is obvious. So it can be concluded that the existence of K+ has little effect on lithium extraction, even at a high voltage.
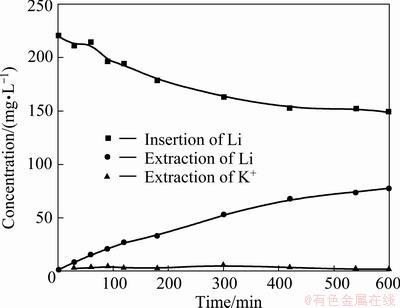
Fig. 7 Concentration changes of Li from a mixed chloride solution containing 220 mg/L Li+ and 3792 mg/L K+ during insertion process and those of Li and K in 0.5 mol/L NaCl solution during extraction process at 1.0 V
3.3 Li+ extraction from brine
3.3.1 CV test in brine
The electrochemical behavior of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures was investigated, respectively. The CV curves of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ are shown in Fig. 8(a). Their different behavior in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures can be clearly seen. Li+ is inserted first, Na+ second, followed by Mg2+, and the reduction peak of K+ cannot be found clearly. The redox peak separation of Li+ is 0.592 V, that of Mg2+ is 1.403 V, and that of Na+ is 0.813V. So we can make good use of this electrochemical difference to selectively extract Li+ from brine. To confirm that, a CV test was performed, between -1.0 V to 1.0V in real brine electrolyte from west China (Table 2) at a scan rate of 0.2 mV/s. Figure 8(b) shows that a couple of redox peaks are located at -0.621 V and 0.485 V, accompanied by lithium inserting/ extracting into/out of the FePO4/ LiFePO4 structures. In our previous study [10], it was proved that the existence of Mg2+ obviously influences the behavior of Li+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures. A high Mg/Li ratio causes a large redox peak separation of Li+. Here, the Mg/Li ratio was super high, up to 493, which caused the redox peaks interval of Li+ to be 1.106 V. But even so, after 16 scanning cycles, the intensity of the redox peaks remained at a similar magnitude, indicating good stability and cycling performance of the LiFePO4/FePO4 electrodes in such brine.
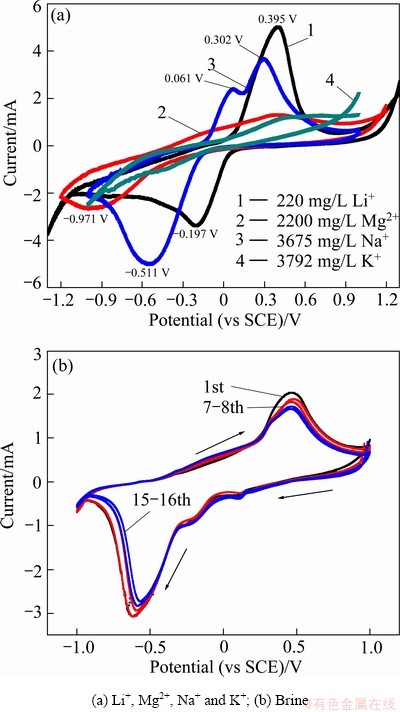
Fig. 8 CV curves in LiFePO4/ FePO4 structures at scan rate of 0.2 mV/s
3.3.2 Electrolytic technical experiments
From Table 2, it can be seen that, in the brine solution, the Mg2+ concentration is so high that the Mg/Li ratio reaches 493, but the Na/Li ratio is only 16.7. If the common methods such as evaporation, crystallization, precipitation process are used, brine needs to be evaporated and concentrated over 120 times, and needs additional steps to remove Ca2+ and Mg2+, which boosts the production cost to far greater than the commercial value of the products.
As mentioned above, the reduction peak of Na+ is -0.511 V and that of Mg2+ is -0.971 V. Both are more negative than that of Li+ (-0.197V), which means that a negatively polarized potential is favorable to the insertion of Na+ and Mg2+. Thus, a lower electrolytic cell voltage, corresponding to a lower polarization of electrode, should be maintained in order to obtain a better separation effect between Li+ and impurities. Here, the voltage was again set as 0.7 V. The results are shown in Fig. 9. It can be seen that the concentration changes of Na+ and Mg2+ in solution are slight, but the Li+ concentration increase is obvious. The final extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+ and Na+ that can be attained in 1 g LiFePO4 are 24.1 mg, 7.32 mg and 4.61 mg, respectively.
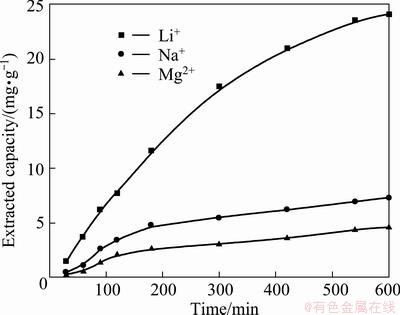
Fig. 9 Extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+ and Na+ during extraction process in 0.5 mol/L KCl solution at 0.7 V when real brine is provided as inserted electrolyte
The Mg/Li ratio is reduced to 0.30 from 493, and the Na/Li ratio is dropped to 0.19 from 16.7. It indicates that even in a super high Mg/Li ratio brine, if a cell voltage is appropriately controlled, it is possible to separate Li+ and other impurities.
3.4 Stoichiometric changes of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+
Till now, the electrochemical behavior of Li+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ in LiFePO4/FePO4 structures has been investigated in detail. However, in our previous discussion, it was mentioned that it is difficult to determine the concentration changes during the insertion process due to the low inserted capacities of Na+, Mg2+, K+ and their high concentration in brine. In our previous study [10], we analyzed the stoichiometric changes of Li+ and Mg2+ at a cell voltage of 1.0V in synthetic brine. Here, we further focused on Li+, Na+, K+ and Mg2+ in real brine at 0.7 V. Similarly, at different reaction time, the electrode materials were removed from the solution, and then washed three times with 50-55 °C distilled water. The electrodes were firstly dissolved in 1:1 HCl solution for 2-3 h at 60-80 °C, and then filtered with filter paper. The resulting liquor was prepared to determine the concentration of Li+, Na+ and K+ by AAS, while that of Mg2+ by ICP-AES. The lithium source was brine sampled from the salt lake brine of west China.
FePO4 was used to insert Li+, Na+, K+ and Mg2+ from real brine solution. The inserted Li+, Na+ and Mg2+ were extracted in a 0.5 mol/L KCl solution, but K+ in a 0.5 mol/L NaCl solution. Figure 10(a) shows the stoichiometric changes of Li+ and Na+ at different reaction time, and Fig. 10(b) shows the changes of Mg2+ and K+. As can be seen, about 0.211 Na+ per formula unit could be inserted, of which 0.191 could be extracted out in the following charge. 0.055 K+ ions could be inserted in the first reduction, while 0.040 could be removed in the subsequent charge. As for Li+ and Mg2+, here 0.550 Li+ was inserted, slightly higher than that of 0.535 in Ref. [10]. The capacity of Mg2+ insertion was smaller (0.140 Mg2+), and 0.124 extraction was observed.
POUL et al [16] used potentiometric ion sensors to test whether it was possible to insert Na+, Mg2+ and K+ into the lithium-free phosphate FePO4. The results showed that about 0.65 Na+ ion per formula unit could be inserted at a C/10 regime (one Na+ per 10 h), of which only 0.5 could be extracted out in the following charge. The polarization between charge and discharge voltages was as high as 1 V. The capacity obtained for Mg2+ insertion was smaller (0.2 Mg2+ or 0.4 equivalent electron), even when using a lower cut-off voltage, and no reversibility was observed under these cycling conditions. This was most likely due to the high charge density of Mg2+, which led to higher polarization. To better understand this Mg2+ insertion process, they used the GITT technique. The polarization continuously increased from 0.7 V at x=0.05 to about 2 V, as more Mg2+ ions were inserted until the end of discharge. A discharge capacity (0.38 Mg2+or 0.76 equivalent electron) was obtained; more than half of which could be extracted out on oxidation. Therefore, they concluded that the Mg2+ insertion process is partly reversible for Na+. Regarding K+ ions, they showed that 0.16 K+ could be inserted in the first reduction, while 0.12 K+ could be removed on the subsequent charge. It can be seen that their conclusion is very similar to the present results. From the above discussion, it can be concluded that once the appropriate cell voltage is controlled, lithium can be selectively separated from brine.
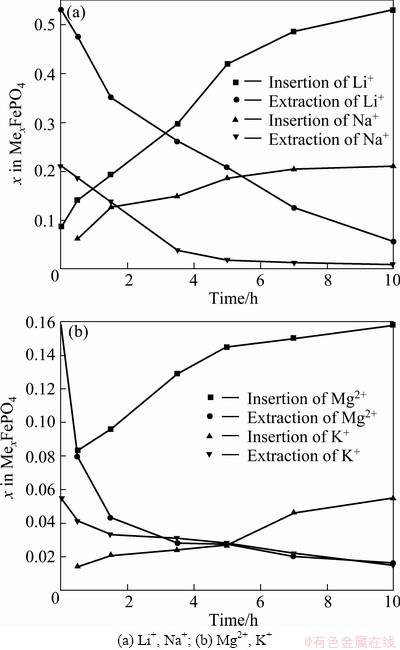
Fig. 10 Stoichiometric changes during insertion process from real brine as well as its corresponding extraction changes in 0.5 mol/L NaCl solution(Li+, Mg2+, K+) and 0.5 mol/L KCl solution (Na+) at 0.7 V
4 Conclusions
The CV tests indicated that the reduction peak of Li+ was -0.197 V, Na+ was -0.511 V, Mg2+ was -0.971 V, while that of K+ couldn’t be found clearly, which means that a negatively polarized potential helps the insertion of Na+ and Mg2+. Thus, a lower electrolytic cell voltage, corresponding to a lower polarization of electrode, should be controlled in order to obtain better separation effect between Li+ and impurities. Real brine with a super high Mg/Li ratio (493) was used to investigate Li+ extraction and its separation with Mg2+ and Na+ at 0.7 V. The results indicated that the final extracted capacity of Li+, Mg2+ and Na+ that can be attained in 1 g LiFePO4 are 24.1 mg, 7.32 mg and 4.61 mg, respectively. The Mg/Li ratio could be reduced to 0.30 from 493, and that of Na/Li to 0.19 from 16.7. Thus, it is indicated that even in a super high Mg/Li ratio brine, if a cell voltage is appropriately controlled, it is possible to separate Li+ and other impurities.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Professor Xi-chang Shi (Central South University) for kindly providing the brine solution.
References
[1] GOODENOUGH J B, KIM Y. Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22: 587-603.
[2] HAMZAOUI A H, M’NIF A, HAMMI H, ROKBANI R. Contribution to the lithium recovery from brine [J]. Desalination, 2003, 158(1-3): 221-224.
[3] YU Jun-qing, GAO Chun-liang, CHENG Ai-ying, LIU Yong, ZHANG Li-sa, HE Xian-hu. Geomorphic, hydroclimatic and hydrothermal controls on the formation of lithium brine deposits in the Qaidam Basin, Northern Tibetan Plateau, China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 50: 171-183.
[4] STEPHEN E K, PAUL W G, PABLO A M, GREGORY A K, MARK P E, TIMOTHY J W. Global lithium resources: Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48: 55-69.
[5] GAO Feng, ZHENG Mian-ping, NIE Zhen, LIU Jian-hua, SONG Peng-sheng. Brine lithium resource in the salt lake and advances in its exploitation [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 483-492. (in Chinese)
[6] JEON W A, DONG J K, KHUYEN T T, MYONG J K, TUTI L, TAM T. Recovery of lithium from Uyuni salar brine [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 117-118: 64-70.
[7] YUAN Jun-sheng, JI Zhi-yong. The progress of extracting lithium from seawater [J]. Sea-lake Salt and Chemical Industry, 2003, 32(5): 29-33. (in Chinese)
[8] ABE M, CHITRAKAR R. Recovery of lithium from seawater and hydrothermal water by titanium (IV) [J]. Antimonate Cation Exchanger, Hydrometallurgy, 1987, 19(1): 117-128.
[9] PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, GOODENOUGH J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194.
[10] ZHAO Zhong-wei, SI Xiu-fen, LIU Xu-heng, HE Li-hua, LIANG Xin-xing. Li extraction from high Mg/Li ratio brine with LiFePO4/ FePO4 as electrode materials [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 133: 75-83.
[11] DEAN J A. Lange’s handbook of chemistry [M]. 15th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc, 1999.
[12] LIU Xu-heng, ZHAO Zhong-wei. Synthesis of LiFePO4/C by solid–liquid reaction milling method [J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 197(3): 309-313.
[13] BURBA C M, FRECH R. Vibrational spectroscopic investigation of structurally-related LiFePO4, NaFePO4, and FePO4 compounds [J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2006, 65(1): 44-50.
[14] MOREAU P, GUYOMARD D, GAUBICHER J, BOUCHER F. Structure and stability of sodium intercalated phases in olivine FePO4 [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(14): 4126-4128.
[15] ZAGHIB K, TROTTIER J, HOVINGTON P, BROCHU F, GUERFI A, MAUGER A, JULIEN C M. Characterization of Na-based phosphate as electrode materials for electrochemical cells [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(22): 9612-9617.
[16] POUL N L, BAUDRIN E, MORCRETTE M, GWIZDALA S, MASQUELIER C, TARASCON J M. Development of potentiometric ion sensors based on insertion materials as sensitive element [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2003, 159(1-2): 149-158.
赵中伟1,2,司秀芬 1,梁新星1,刘旭恒1,何利华 1
1. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 稀有金属冶金与材料制备湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:因Na+、K+总与Li+、Mg2+伴生在卤水中,故在Li+、Mg2+研究的基础上,我们继续开展Na+、K+的系列研究。循环伏安测试结果表明:在LiFePO4/ FePO4结构中,Na+表现出一定的循环性能,其还原峰为-0.511 V,比Li+的(-0.197 V) 更负。因此,为了抑制Na+的嵌入,需控制低电位。而K+的还原峰不能明显观察到,表明K+难于嵌入到FePO4结构中。以取自中国西部的实际Mg/Li比为493的卤水作电解液,在槽电压0.7 V时进行电解实验。结果表明:Li+、Mg2+和Na+的最终脱出量每1 g LiFePO4分别可达24.1 mg、7.32 mg 和 4.61 mg,所得溶液中的Mg/Li比从493降至0.30,Na/Li比从16.7降至0.19。因此,可以看出即使在超高Mg/Li比的卤水液中,如果控制得当,也能使得Li+和其它杂质有效分离。
关键词:LiFePO4/ FePO4电极;NaFePO4;锂;钾;卤水
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Foundation item: Project (K1205034-11) supported by Technology Program of Changsha, China
Corresponding author: Zhong-wei ZHAO; Tel: +86-731-88830476; Fax: +86-731-88830477; E-mail: zhaozw@mail.csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62578-9

