
Effects of electric field treatment on microstructures of
GH4199 superalloy after long-term aging
LIU Yang(刘 杨)1, WANG Lei(王 磊)1, WANG Shuai(王 帅)1,
QIAO Xue-ying(乔雪璎)2, WANG Yan-qing(王延庆)2
1. Key Laboratory for Anisotropy and Texture of Materials,
Ministry of Education, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China;
2. Central Iron & Steel Research Institute, Beijing 100081, China
Received 28 July 2006; accepted 15 September 2006
Abstract: The effects of electric field intensity and treatment temperature on the microstructures of GH4199 superalloy after long-term aging were investigated. The results show that the number and size of carbides and TCP(σ phase and μ phase) phase in the alloy increase with increasing electric field intensity at the same heat treatment temperature and holding time. While the number and size of carbides and TCP phase are weekly influenced by treatment temperature with lower electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm. When the treat temperature is up to 1 093 K, annealing twins appear in the alloy, and the number of twins increases with increasing holding time. Since the electric field can provide the enough energy for the movement of vacancies and atom, it is considered that the nucleus of the twins formed with formation stack faults due to the mismatch of local atom in crystal caused by the vacancies, and the twins will grow with the increase of holding time. Meanwhile, such promoting effects on atom movement of the electric field increase with the increase of the electric field intensity, meantime the carbides and TCP phase grow fast with the increase of electric field intensity.
Keywords: GH4199 superalloy; electric field treatment; long-term aging
1 Introduction
Following the developing aeronautical industry, the alloying degree of superalloy is increased. However, it has been found that the ductility and toughness of superalloy decrease evidently due to the presence of the relatively complex-structured intermetallic TCP(σ phase and μ phase) phase during exposured to the conditions of high load and high temperature [1-2]. And it cannot be controlled with the traditional heat treatment methods to improve the ductility of the alloy, so it is important to find a new method for renewing or improving the ductility of superalloy.
The electric field treatment as one new treatment method, has received a lot of attention in the past few years [3-7]. And many researches have been made on the development of the application of electric field on solidification of the superalloy[8-9]. However, up to now, no reports are available on the application of electric field treatment on heat treatment of the superalloy. In the present research, the electric field treatment was employed on GH4199 superalloy to investigate the effects of electric field intensity, treatment temperature and holding time on the microstructures of GH4199 superalloy after long-term aging. The purpose of present study is to investigate the potential application for electric field treatment on the progress of research on superalloy.
2 Experimental
The material used for the present research is a Ni-based superalloy, named GH4199. It was fabricated with double-vacuum melting method into d 250 mm ingot, then forged into plate with dimension of 70 mm×180 mm, followed by rolled into plate with thickness of 1 mm. The chemical compositions of GH4199 alloy are listed in Table 1.
The solution treatment of the alloy was carried out at 1 423 K for 20 min and then aged at 1 073 K for 20 h. In order to investigate the effects of electric field treatment on the alloy, the specimens were prepared with electric field treatment and without it.
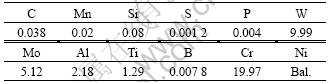
Table 1 Chemical compositions of GH4199 alloy (mass fraction, %)
The microstructures of specimens before and after electric field treatment were examined by both optical microscope (OLYMPUS GX71) and transmission electron microscope (TECNAI G2) with the acceleration voltages of 200 kV. Tensile test was carried out on SANS-CMT5105 type tensile testing machine at room temperature and elevated temperature of 1 073 K, with a cross head speed of 0.5 mm/min.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of electric field intensity on micro- structures of GH4199 alloy
The microstructures of GH4199 alloy after electric field treated at 673 K for 600 min with different parameters are shown in Fig.1.
During the long-term aging of GH4199 alloy at 1 073 K, the presence of carbides (mainly M23C6 and M7C3) at grain interiors and grain boundaries and the presence of acicular TCP phase (s phase and m phase) inside grain are shown in Fig.1(a)[10-11]. There is no obvious change of carbides and TCP phase of the alloy after electric field treated at 673 K and electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm for 600 min. However, when the electric field intensity increases to 4 kV/cm, the carbides at grain boundary obviously grow up, the block carbides disperse inside grain coarsen and TCP phase also coarsens with the change from acicular to rod-like, and the ratio of length to width decreases. The carbides and TCP phase grow to be much coarser when the electric field intensity is up to 8 kV/cm.
During the electric field treatment, the electric field can provide more energy for diffusion and vacancy, which leads to the increase of the atom diffusion speed and the driving force of growth and coarsening of second phase. Under electric field treatment, not only the speed of atom diffusion into the second phase increases but also the speed of atom diffusion between the neighboring second phases increases, these cause the coarsening of carbides and TCP phase. On the other hand, the enlargement of phase interface area is attributed to the growth of carbides and TCP phase. Since the carbides and TCP phase have a low deformability, it results in an increase in the formation and bonding of the cracks and makes a disadvantage for the strength and ductility of the alloy.

Fig.1 Optical microstructures of GH4199 alloy treated at 673 K for 600 min with different electric field intensities: (a) Without electric field; (b) 2 kV/cm; (c) 4 kV/cm; (d) 6 kV/cm; (e) 8 kV/cm
3.2 Effects of treated temperature and holding time on microstructure
The higher electric field intensity causes the coarsening of the carbides and TCP phase because of the effects of accelerating the atom diffusion by electric field treatment. Experiments were carried out at different temperatures to investigate the effects of treated temperature on the microstructures of the alloy. Fig.2 shows the microstructures of the GH4199 alloy at different electric field treatment temperatures for 300 min with an electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm.
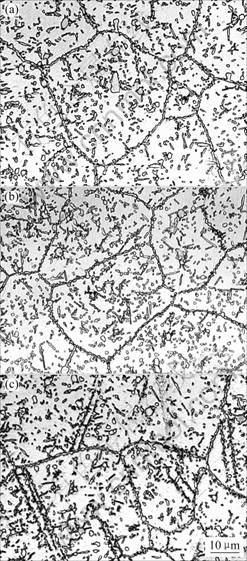
Fig.2 Optical microstructures of GH4199 alloy at different electric field treatment temperatures for 300 min with electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm: (a) Room temperature; (b) 673 K; (c) 1 093 K
No obvious change of the number, size and distribution of carbides and TCP phases can be seen in specimens after electric field treated at different temperatures for 300 min with a electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm. The results show that the effects of increasing treated temperature on the diffusion speed of element are very week when treated with 2 kV/cm within a short holding time. It should be mentioned that when the temperature is increased to 1 093 K, some lath microstructures appear, as shown in Fig.2(c).The lath microstructures are confirmed as twin by TEM micrograph and SAD patterns shown in Fig.3.

Fig.3 TEM morphology, selected area electronic diffraction pattern (a) and analysis of annealing twin (b) for GH4199 alloy
Fig.4 shows the microstructures of GH4199 alloy after electric field treated at 1 093 K for different time with a electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm. It is clear that during electric field treatment at 1 093 K, annealing twins appear and the number of twins increases with the increase of the holding time.
Under lower electric field intensity, with the increase of the treated temperature, the effects of electric field on vacancies in alloy increase. It is easy for vacancies to move to the grain boundary or surface of the crystalline. The formation of fault can be attributed to the formation of stack faults due to the mismatch of local atom in crystal caused by the movement of vacancies and atoms because of the low fault energy of FCC metal. Because the fault energy of coherent twin boundaries is lower than that of the high angle boundaries [12], annealing twins can be easily nuclear and become stable. Under the same treated temperature and electric field intensity, the number of twins increases with increasing holding time and the twins grow with increasing holding time, due to the increasing energy on vacancies and atom.

Fig.4 Optical microstructures of GH4199 alloy with different holding time treated at 1 093 K with electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm: (a) 0; (b) 300 min; (c) 600 min
3.3 Effects of formation of annealing twin on tensile properties
Fig.5 shows the variation of tensile properties of GH4199 alloy at room and elevated temperatures with the holding time of electric field at 1 093 K and 2 kV/cm. It can be seen that compared with no-electric field treated (aged at 1 093 K for 600 min) specimens, the tensile strength of the treated specimens at both room and elevated temperatures appear no-evident change, while the elongation increases notably. It is because the ductility of GH4199 alloy can be improved by the electric field treatment. The elongation of alloy at room temperature becomes a peak value treated for 120-300 min and has a little decrease as the time over 300 min. And the peak increasing value of elongation is about 26.6% higher than that of without treated. The strength of GH4199 alloy fluctuates with the increasing holding time within a range less than 1.1%. In other words, after the electric field treated at 1 093 K for 300 min with electric field intensity of 2 kV/cm, there is no change for the tensile strength of GH4199 alloy, but the ductility is improved.

Fig.5 Variation of tensile properties of GH4199 alloy with electric treated at (a) Room temperature; (b) 1 073 K for different holding time
The plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials results from the deformation of both grains and grain boundaries. The misorientation between the grains and the boundaries are considered as the key factor of obstruction effect for plastic deformation. The formation of the twin has been stated by some researchers to improve the strength and ductility of metals [13]. The twining during the electric treated GH4199 alloy changes the orientation of some crystals, and thus enables the crystal slip which is unfavorable for the slipping formerly to relieve stress concentration and increase the plastic deformation before crack. On the other hand, the formation of annealing twin can improve the ductility of the alloy through changing the direction of the crack growth and increasing the plastic deformation work and delaying the fracture time. Furthermore, the promotion effect of the electric field treatment on slipping of the grain boundary is also one of the mechanisms for the improvement of ductility of the alloy [14].
4 Conclusions
1) During the electric field treated GH4199 alloy with long-term aging, the increase of the electric field intensity is the key factor for promoting the elements diffusion. With the intensity increasing, the size and number of carbides and TCP phase in the alloy are increased and severely coarsened. If the treatment is carried out at a lower intensity, the temperature and holding time have no obvious effects on carbides and TCP phase.
2) With the electric field treatment, annealing twins are formed in long-term aged GH4199 alloy due to the promoting effect on the movement of vacancies by electric field treatment, and such twins grow with the increase of holding time. The elongation of GH4199 alloy can be improved by the annealing twin, but the strength of the alloy cannot be influenced notably with the electric field treatment.
References
[1] HUANG Qian-yao, LI Han-kang. Superalloy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002: 246.(in Chinese)
[2] KONG Y H, CHEN Q Z. Effect of minor additions on the formation of TCP phases in modified RR2086 SX superalloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, A366(2): 135-143.
[3] CONRAD H. Enhanced phenomena in metals with electric and magnetic fields(Ⅰ): electric fields[J]. Materials Transactions, 2005, 46(6): 1083-1087.
[4] JUNG K, CONRAD H. External electric field applied during solution heat treatment of the Al-Mg-Si alloy AA6022[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(21): 6483-6486.
[5] CONRAD H, KARAM N, MANNAN S. Effect of prior cold work on the influence of electric current pulses on the recrystallization of copper[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1984, 18(3): 275-280.
[6] LIU Wei, WU Gui-lin, GODFREY A, LIU Qing. Effects of electrical field treatment on recrystallization of copper single crystal[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(6): 495-499.
[7] CONRAD H, KARAM N, MANNAN S. Effect of electric current pulses on recrystallization kinetics of copper[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1988, 22(2): 235-238.
[8] LI Wan-feng, YANG Yuan-sheng, YU Li, ZHANG Jun, HU Zhuang-qi. Effect of direct current electric field on the microstructure of nickel-based superalloy K417G[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2001(9): 7-13. (in Chinese)
[9] YANG Yuan-sheng, FENG Xiao-hui, CHENG Gen-fa, HU Zhuang-qi. Solidification of nickel-based crystal superalloy by electric field[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2005, 18(6): 679-685.
[10] CUI Tong, ZHANG Yu-suo, GUO Shi-wen, WANG Lei, YANG Hong-cai. Study of TCP phase precipitating in GH4199 superalloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 17(5): 645-650.
[11] ZHANG Xiao-bin, LIU Chang-sheng, LU Jun-ying, YANG Hong-cai. Secondarily precipitated phases of a Ni-based superalloy during durable thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2005, 26(4): 253-256.(in Chinese)
[12] HU Geng-xiang, QIAN Miao-gen. Metallography[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1980. 105. (in Chinese)
[13] SUN Qiao-yan, ZHU Rui-hua, LIU Cui-ping, YU Zhen-tao. Twinning behavior and its effect on mechanical behavior of commercial titanium at cryogenic temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006,16(4): 592-598.(in Chinese)
[14] CAO W D, LU X P, SPERCHER A F, CONRAD H. Superplastic deformation behavior of 7475 aluminum alloy in an electric field[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1990, A129(2): 157-166.
(Edited by CHEN Wei-ping)
Corresponding author: WANG Lei; Tel: +86-24-83867725; E-mail: wanglei@mail.neu.edu.cn