真空压铸过程中不同工艺条件对界面换热行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第12期
论文作者:杨红梅 于文波 曹永友 李晓波 郭志鹏 熊守美
文章页码:2599 - 2606
关键词:真空压铸;界面换热行为;金属-模具界面;压室预结晶晶粒
Key words:vacuum die casting; interfacial heat transfer behavior; metal-die interface; externally solidified crystals
摘 要:真空压铸可减小铸造过程中的“气隙”现象。基于不同压铸条件,如低速速度(VL)、高速速度(VH)、浇注温度(Tp)和模具初始温度(Tm),通过实验测量金属与模具界面的温度,采用反算法获得真空条件下界面换热系数。结果表明,真空系统的应用使铸件与模具更加紧密接触,明显提高界面换热系数值并减小铸件的晶粒尺寸;当浇注温度由680 °C提高到720 °C或低速速度由0.1 m/s提高到0.4 m/s时,界面换热系数峰值随之提高,而高速速度和模具初始温度对界面换热系数的影响可以忽略。
Abstract: Vacuum die casting can reduce the “air entrapment” phenomenon during casting process. Based on the temperature measurements at metal-die interface with different processing parameters, such as slow shot speed (VL), high shot speed (VH), pouring temperature (Tp) and initial die temperature (Tm), inverse method was developed to determine the interfacial heat transfer coefficient (IHTC). The results indicate that a closer contact between the casting and die could be achieved when the vacuum system is used. It is found that the vacuum could strongly increase the values of IHTC and decrease the grain size in castings. The IHTC could have a higher peak value with increasing the Tp from 680 to 720 °C or the VL from 0.1 to 0.4 m/s. In addition, the influence of the VH and Tm on IHTC could be negligible.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 2599-2606
Hong-mei YANG1,2, Wen-bo YU1,2, Yong-you CAO1,2, Xiao-bo LI1,2, Zhi-peng GUO1,2, Shou-mei XIONG1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Received 29 November 2017; accepted 16 July 2018
Abstract: Vacuum die casting can reduce the “air entrapment” phenomenon during casting process. Based on the temperature measurements at metal-die interface with different processing parameters, such as slow shot speed (VL), high shot speed (VH), pouring temperature (Tp) and initial die temperature (Tm), inverse method was developed to determine the interfacial heat transfer coefficient (IHTC). The results indicate that a closer contact between the casting and die could be achieved when the vacuum system is used. It is found that the vacuum could strongly increase the values of IHTC and decrease the grain size in castings. The IHTC could have a higher peak value with increasing the Tp from 680 to 720 °C or the VL from 0.1 to 0.4 m/s. In addition, the influence of the VH and Tm on IHTC could be negligible.
Key words: vacuum die casting; interfacial heat transfer behavior; metal-die interface; externally solidified crystals
1 Introduction
Many works have proven that the heat transfer behavior at the metal-mold interface plays an important role on the microstructure and the consequent mechanical properties of the final product in all the casting processes [1,2], such as, high pressure die casting (HPDC), gravity die casting, low pressure die casting, squeeze casting, sand casting and semisolid casting. The statistics in 2012 reveals that the pressure die-castings of Mg and Al account for about 83.6% Mg and 59.7% Al in industry structure [3]. Herein, it is necessary to obtain the reliable experimental values of the interfacial heat- transfer for HPDC. It has been proven that this can be characterized by an interfacial heat flux (q) and an interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h, also IHTC) [4,5].
In the HPDC process, liquid metal is transferred into the shot sleeve from the crucible and injected into the water-cooled die under high pressure. This typical process makes the heat transfer in HPDC process different from the most of the conventional casting processes [6,7]. As a result of this question, study about the interfacial heat transfer behavior at the metal-die interface has been carried out, especially, after the emergence of new numerical approaches associated with inverse heat conduction problems. For example, EL-MAHALLAWY et al [8] reported that a further increase in the applied casting pressure could hardly change the thermal field and the heat flux. DOUR et al [9] reported that high shot speed and high die temperature, rather than the casting pressure, had a prominent role in the heat transfer coefficient and heat flux. PAPAI and MOBLEY [10] found that the peak value of heat flux or heat transfer coefficient decreases as the initial die temperature increases. By using a special temperature sensor unit (developed by Tsinghua University, China) [11,12], the influence of runner system type, as well as the influence of casting geometry and processing parameters on the interfacial heat transfer coefficient during HPDC was investigated. It was found that the process parameters such as casting pressure and shot speed only have secondary influence on the IHTC peak value in comparison to the initial die temperature.
It was found that lowering atmospheric pressure in the shot sleeve and die cavity in HPDC could minimize the porosity of the castings for the subsequent heat treatment processing without the blistering risk. However, until now, less work has been performed to investigate the evolution of interface heat transfer behavior from HPDC to vacuum die casting [13,14]. Herein, in this work, we investigated this evolution by cover-plate die designed by Siemens Company. Furthermore, the effects of process parameters, such as slow shot speed, high shot speed, pouring melt temperature and die temperature, on q and h values were also studied.
2 Experimental
2.1 Casting design
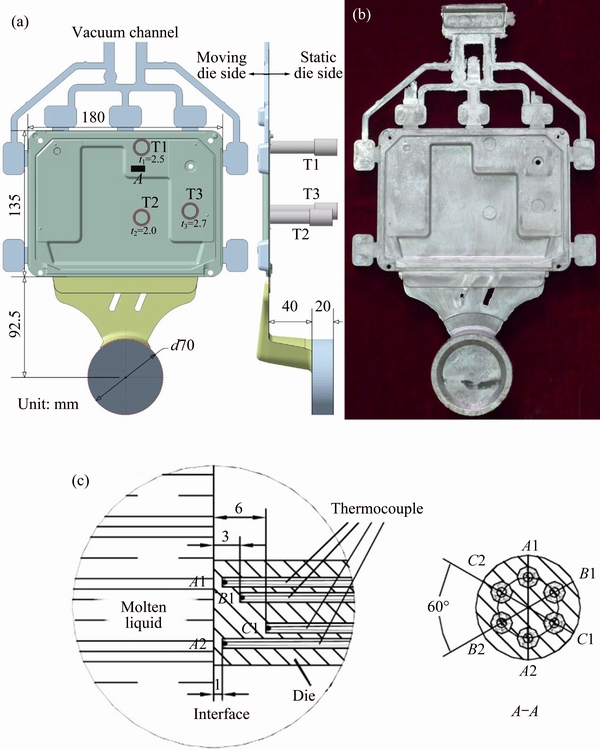
Fig. 1 Configuration and dimension of cover-plate casting (a, b) and schematic diagram of temperature measurement details about metal-die interface (c)
A practical automobile die casting namely the “cover-plate” casting was used in the present study, and the configuration of it is shown in Figs. 1(a) and (b). The biscuit of the casting was designed with a diameter of 70 mm and a thickness of 20 mm. The dimension of cover-plate is 180 mm (length) × 135 mm (width) × (2.0-2.7) mm (thickness). The temperature measurements were performed at three positions marked as T1, T2 and T3 with their corresponding thicknesses of 2.5, 2.0 and 2.7 mm, respectively. A fast sensor response and proper location of the sensor should be satisfied for the inverse method application [11]. In order to gain a sufficiently rapid response time and obtain accurate temperature readings, a special temperature sensor unit (TSU) was designed and installed in the fixed die. Figure 1(c) shows the configuration of the temperature sensor unit. In convenience, six thermocouples were inserted and welded inside a H13 steel block (its chemical composition is same as that of the die, as given in Table 1). Each of these thermocouple probes was sheathed with a stainless steel circle of 0.5 mm in diameter and 0.045 mm in wire diameter. Six thermocouple probes were placed with three different distances to the metal-die interface: 1, 3 and 6 mm, and at each distance, two thermocouples were used to adjust (i.e., A1 and A2, B1 and B2, and C1 and C2). Real-time temperature data were then recorded using Spartan data logging system (96 isolated analog input channels) manufactured by the Integrated Measurement Corporation with a sampling rate of 500 Hz. In series of tests, the response time was in a range of 7-10 ms. The interfacial heat transfer coefficient was calculated using an inverse method based on the principle proposed by BECK [15] and our previous work [11,12]. A common approach is based on the minimization of the sum of the squared errors between the calculated and the measured data, i.e.,

where Ti and Yi are calculated and measured temperatures at various thermocouple locations. The chemical compositions of the AM60B and the die material H13 steel are given in Table 1. Table 2 gives the thermal properties of the related materials in this study.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of AM60B alloy and H13 steel (mass fraction, %)
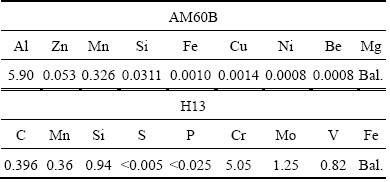
Table 2 Thermal properties of related materials
2.2 Casting processing parameters
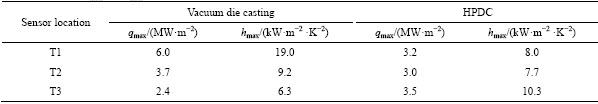
The experiments were performed using AM60B alloy on a TOYO 650 t cold-chamber die casting machine (Toyo Machinery & Metal Co., Ltd., Akashi, Japan). The configuration of shot sleeve and the distribution of shot speed are shown in Fig. 2. During the HPDC process, the molten AM60B liquid was transferred into the shot sleeve from a crucible through feeding pipe. Then, the plunger tip moved with different speeds at different steps. Concerning about basic process, the plunger tip moved with a slow shot speed of 0.15 m/s from 70 mm to 270 mm under a filling ratio of 20.1%. Subsequently, for pushing the melt into the die cavity, the plunger moved at 4.0 m/s in the high shot speed for the rest length of the shot sleeve. At 295 mm, the casting pressure was increased to 87 MPa. In each set of experiment, only one of the processing parameters, including slow shot speed (VL), high shot speed (VH), pouring temperature (Tp), initial die temperature (Tm) was varied and the rest parameters were kept the same as the basic condition as given in Table 3. There were 200 shots performed and the first 20 shots were used to preheat the dies to reach the thermal equilibrium state.
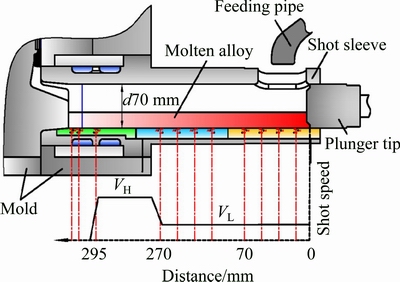
Fig. 2 Configuration description of shot sleeve and distribution of shot speed
Table 3 Parameters of slow shot speed (VL), high shot speed (VH), pouring temperature (Tp) and initial die temperature (Tm)
2.3 Microstructural observation
The specimens were cut from the position marked as A near the position T1 in Fig. 1 by electro-discharge machining and then mounted in epoxy. The cross sections of assemblies were ground with silicon carbide and then successively polished with 6, 3, 1 and 0.25 μm diamond suspensions. To avoid the work-hardening caused by conventional grinding, a chemo-mechanical polishing was performed using Al2O3 suspension (particle size: 0.04 μm). Subsequently, the specimens were etched with a diluted acetic acid solution (50 mL distilled water, 150 mL anhydrous ethyl alcohol and 1 mL glacial acetic acid) to reveal the microstructure. Software Micro-image Analysis and Process System (MIAPS) was employed to perform the quantitative analysis of the ESCs area fraction.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Differences of interfacial heat transfer between HPDC and vacuum die casting
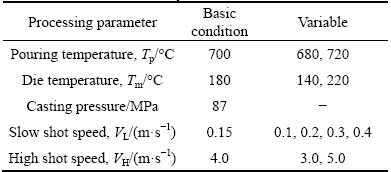
Figure 3 presents the die temperature evolutions with time at position T1 in HPDC and vacuum die casting performed under the basic condition. The die temperature curve was obtained by the average values measured at the same distance. The maximum variation between two temperature profiles measured at the same distance never exceeded 4 °C. The similarly repeated curves strongly suggested that these temperature measurements are credible. As for vacuum die casting, the die temperature peaks at 1 and 3 mm could reach 265 and 215 °C, respectively. These values are much higher than those obtained from HPDC (225 and 200 °C). This difference indicated that the vacuum system in vacuum die casting process could ameliorate the heat transfer ability in die cavity.
Figure 4 presents the variations of interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h) and interfacial heat transfer flux (q) obtained from inverse method of AM60B alloy at positions T1, T2 and T3 during the 30th cycle under the basic condition. The peak values of q and h vary at different positions and casting thicknesses. The peak values of interfacial heat transfer coefficient (hmax) and interfacial heat transfer flux (qmax) are listed in Table 4. As for vacuum die casting, the interfacial heat transfer coefficient (hmax) of position T1 near the overflows reaches 19.0 kW·m-2·K-1, the second peak value is 9.2 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T2 near the gate of the thinnest position, and the lowest peak is 6.3 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T3 near the gate of the thickest position. Similar patterns exist in the heat flux (qmax). In this work, the thicknesses of die cavity at T1, T2 and T3 are 2.5, 2.0 and 2.7 mm, respectively. The hmax and qmax values at position T1 in vacuum die casting are much higher than those in HPDC, corresponding to 8.0 kW·m-2·K-1 and 3.2 MW·m-2, respectively, these values at position T2 in vacuum die casting are higher than those in HPDC, but these values of position T3 in vacuum die casting are lower than those in HPDC. This indicates a trend that the IHTC peaks near the overflow is higher than that near the gate, and the IHTC at the thinnest position is higher than that at the thickest position. It is opposite the general trend that the IHTC peaks near the gate is higher than that near the overflow, and the IHTC at the thickest position is higher than that at the thinnest position in HPDC. According to the previous reports [11-13], the interface becomes increasingly important on the heat transfer when the interface is changed. Furthermore, these differences strongly suggest that vacuum system in HPDC can reduce the gas in die cavity to ameliorate the interfacial contact conditions between die and melt. The position T1 near the vacuum pumping has higher vacuum degree than the position T2 and T3 far from the vacuum pumping, so high vacuum degree can significantly reduce the pressure of the filling metal, so as to decrease the amount of trapped gas between the die and metal and achieve a closer contact of metal-mold interface, and lager contact area is more conductive to heat transfer. In addition, it can be found that the curves of q and h at three positions rapidly rise to the peak and overlap together in HPDC. However, in vacuum die casting, the rising part of the q and h curves at position T3 is later up to peak, indicating that the melt firstly reaches T1, T2 and then T3, that is to say, the high vacuum degree could influence the melt flow and improves interfacial heat transfer flux (q) and interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h) by increasing the contact area between the die and metal during the filling stage.
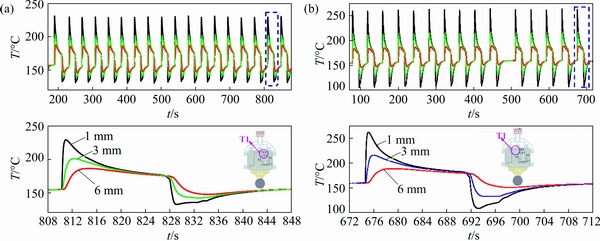
Fig. 3 Die temperature measured at position T1 at 1, 3 and 6 mm apart from melt-die interface in HPDC (a) and vacuum die casting (b)
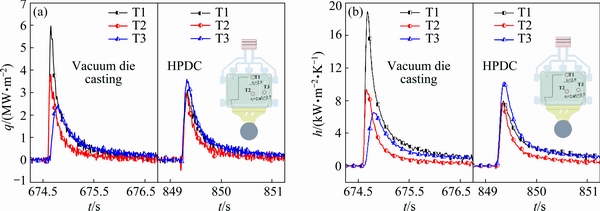
Fig. 4 Variations of interfacial heat flux (q) and interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h) of AM60B alloy with time at positions T1, T2 and T3 in 30th cycle
Table 4 Values of qmax and hmax in Fig. 4
For checking the vacuum effect on microstructural morphology of AM60B alloy, the specimens for microstructural observations were extracted from the position A near T1 because the strongest variation of the IHTC was found at position T1. The relevant microstructures are shown in Fig. 5. For both HPDC processes, the externally solidified crystals (ESCs) tend to aggregate in the center along the thickness direction of the castings. Compared with the HPDC, the vacuum-assisted system in the HPDC significantly reduces the size and amount of ESCs, and the ESCs tend to become smaller and more globular. To achieve a better understanding on the effect of vacuum, quantitative analysis of the ESCs average diameter and area fraction were performed with an area of 300 μm × 200 μm. The percentages and average size of ESCs are 11.44% and 8 μm in vacuum die casting, and these in HPDC are 22.09% and 17 μm, respectively. It is found that the HPDC under the vacuum could significantly change the morphology and distribution of the microstructure. According to the previous report, higher q and h values mean a better contact between the melt and die and could arouse a faster heat release. Then, the faster heat release results into a faster solidification rate [10,16-18]. Herein, AM60B produced by vacuum die casting has much more fine structure and less ESCs than that produced by HPDC, as shown in Figs. 5(c) and (d).
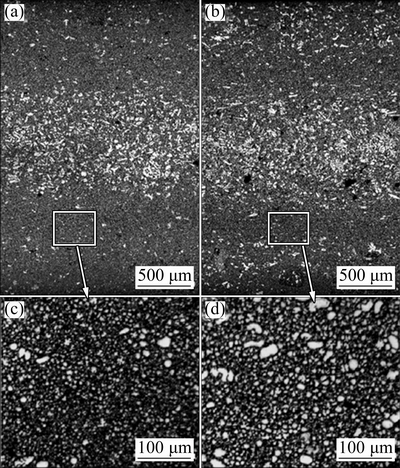
Fig. 5 Cross sectional morphologies of AM60B alloy at position A (T1) in vacuum die casting (a, c) and HPDC (b, d)
3.2 Influence of different casting parameters on q and h in vacuum die casting
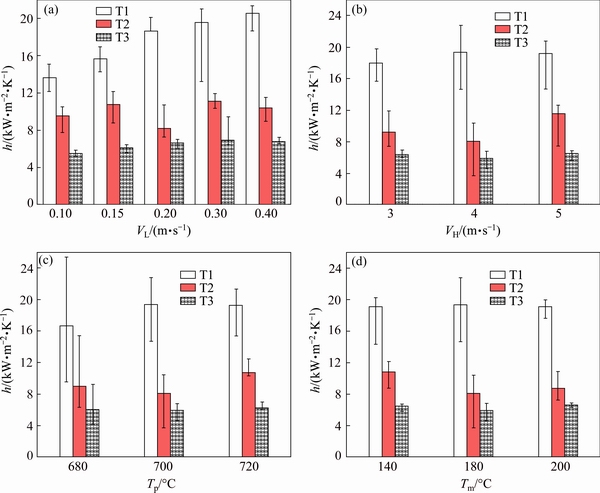
Fig. 6 Effect of slow shot speed (VL) (a), high shot speed (VH) (b), pouring temperature (Tp) (c) and initial die temperature (Tm) (d) on interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h) at positions T1, T2 and T3
Figure 6 summarizes the effect of slow shot speed (VL), high shot speed (VH), pouring temperature (Tp) and initial die temperature (Tm) on interfacial heat transfer coefficient (h) at three positions T1, T2 and T3. In details, with increasing the slow shot speed (from 0.1 to 0.4 m/s), hmax increases from 13 to 21 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T1, and increases from 5 to 7 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T3. As seen, the peak values of h increases with increasing the slow shot speed. The same trend is found with pouring temperature increasing from 680 to 720 °C: the hmax increases from 16 to 19.4 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T1 and increases from 8 to 11 kW·m-2·K-1 at position T2. According to the previous report about heat transfer behavior between melt and shot sleeve, lower slow shot speed could allow more heat release and increase the content of ESCs [14,17,18]. Finally, the melt with much lower temperature is filled into die cavity. Hence, the lower h is found under the lower slow shot speed. Similarly, the higher pouring temperature means that the melt with higher temperature could be filled into die cavity under the same casting parameters. However, when the high shot speed is increased from 3.0 to 5.0 m/s, and the die temperature is increased from 140 to 220 °C, no variation of IHTC is found, so, the influence of high shot speed and die temperature could be negligible. In addition, the fluctuation of IHTC is found at position T2 with increasing the slow shot speed, as shown in Fig. 6(a), and no variation of IHTC is found at position T3 with increasing pouring temperature, as shown in Fig. 6(c), which should be caused by the effect of thickness of die cavity on h in step-casting [19,20].
The relevant microstructures of the cross section at different slow shot speeds and pouring temperatures of vacuum die casting are shown in Figs. 7 and 8, respectively. With increasing of slow shot speed from 0.1 to 0.4 m/s and pouring temperature from 680 to 720 °C, the ESCs tend to aggregate in the center of the specimens, and the width of aggregation becomes smaller, which is consistent with the result of LAUKLI et al [18]. This suggests that much more heat could be released in the cavity with increasing the slow shot speed. Herein, less ESCs with smaller size are found at higher slow shot speed and higher pouring temperature because of the higher h. This is accordance with the variation of q and h shown in Fig. 6. This phenomenon is based on the idea of local slip occurring in the dendrite network as a result of fluid passing a stagnant solidifying wall layer [21-23]. In addition, the samples were solution treated at 413 °C for 16 h and then aged at 168 °C for 16 h. Figure 8 shows that more ESCs with larger size can be found in the center of castings at lower pouring temperature, especially at 680 °C.
The presence of ESCs could lead to shrinkage pore during solidification, and this type of porosities was the potential sources for the crack initiation [17,24]. The large and scattering ESCs significantly reduce the mechanical properties. Based on the relationship between the IHTC and the casting solid microstructure, the boundary condition model described above is applied to calculating the thermal field and thermal equilibrium of the “cover-plate” casting, and guiding the die design.

Fig. 7 Optical micrographs of cross section of AM60B alloy (at position A in Fig. 1(a)) cast with different slow shot speeds
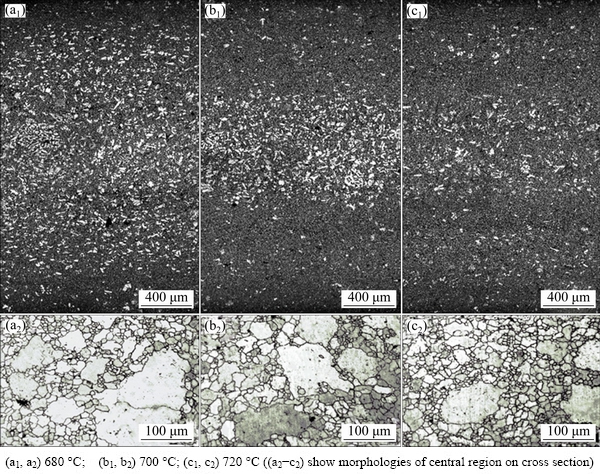
Fig. 8 Optical micrographs of cross section of AM60B alloy (at position A in Fig. 1(a)) cast with different pouring temperatures
4 Conclusions
1) The temperature peaks at 1 and 3 mm reach 265 and 215 °C near the flow in vacuum die casting which are much higher than those in HPDC (225 and 200 °C). The interfacial heat flux and transfer coefficient reach 6.0 MW·m-2 and 19.0 kW·m-2·K-1 near the flow in vacuum die casting which are much higher than those in HPDC (3.2 MW·m-2 and 8.0 kW·m-2·K-1).
2) Under vacuum die casting, the filling process is modified and the microstructural observation reveals that less ESCs and more fine grains form.
3) In vacuum die casting process, increasing the pouring temperature from 680 to 720 °C or slow shot speed from 0.1 to 0.4 m/s could lead to a higher IHTC peak value. The influence of high shot speed (VH, 3.0-5.0 m/s) and initial die temperature (Tm, 140-220 °C) on q and h could be negligible.
References
[1] KAI H, PEHLKE R D. Metal-mold interfacial heat transfer [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1985, 16: 585-594.
[2] ZHANG Ang, LIANG Song, GUO Zhi-peng, XIONG Shou-mei. Determination of the interfacial heat transfer coefficient at the metal-sand mold interface in low pressure sand casting [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 88: 472-482.
[3] SAMEER D K. Magnesium and its alloys in automotive applications—A review [J]. American Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2015, 4: 12-30.
[4] LONG A, THORNHILL D, ARMSTRONG C, WATSON D. Determination of the heat transfer coefficient at the metal/die interface for high pressure die cast AlSi9Cu3Fe [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31: 3996-4006.
[5] DARGUSCH M S, HAMASAIID A, DOUR G, LOULOU T, DAVIDSON C J, St JOHN D H. The accurate determination of heat transfer coefficient and its evolution with time during high pressure die casting of Al-9%Si-3%Cu and Mg-9%Al-1%Zn alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2007, 9: 995-999.
[6] JIA Liang-rong, XIONG Shou-mei, LIU Bai-cheng. Study on numerical simulation of mold filling and heat transfer in die casting process [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2000, 16: 269-272.
[7] CHIANG K T, LIU N M, TSAI T C. Modeling and analysis of the effects of processing parameters on the performance characteristics in the high pressure die casting process of Al-Si alloys [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 41: 1076-1084.
[8] EL-MAHALLAWY N A, TAHA M A, POKORA E, KLEIN F. On the influence of process variables on the thermal conditions and properties of high pressure die-cast magnesium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 73: 125-138.
[9] DOUR G, DARGUSCH M, DAVIDSON C, NEF A. Development of a non-intrusive heat transfer coefficient gauge and its application to high pressure die casting: Effect of the process parameters [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 169: 223-233.
[10] PAPAI J, MOBLEY C. Die thermal fields and heat fluxes during die casting of 380 aluminum alloy in H-13 steels [C]// Proceedings of the NADCA Congress and Exposition. Detroit, 1991.
[11] CAO Yong-you, GUO Zhi-peng, XIONG Shou-mei. Determination of the metal/die interfacial heat transfer coefficient of high pressure die cast B390 alloy [J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2012, 33: 1-10.
[12] GUO Zhi-peng, XIONG Shou-mei, CHO Sang-hyun, CHOI Jeong-kil. Study on heat transfer behavior at metal/die interface in aluminum alloy die casting process I: Experimental study and determination of the interracial heat transfer coefficient [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43: 1149-1154.
[13] KASPRZAK W, SOKOLOWSKI J H, YAMAGATA H, ANIOLEK M, KURITA H. Energy efficient heat treatment for linerless hypereutectic Al-Si engine blocks made using vacuum HPDC process [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2011, 20: 120-132.
[14] WANG Qing-liang, XIONG Shou-mei. Vacuum assisted high- pressure die casting of AZ91D magnesium alloy at different slow shot speeds [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 3051-3059.
[15] BECK J V. Nonlinear estimation applied to the nonlinear inverse heat conduction problem [J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 1970, 13: 703-716.
[16] XIONG Shou-mei, LIU Bai-cheng. Study on numerical simulation of mold-filling and solidification processes of shaped casting [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 1999, 12: 4-10.
[17] LI Xiao-bo, GUO Zhi-peng, XIONG Shou-mei. Correlation between porosity and fracture mechanism in high pressure die casting of AM60B alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2016, 32: 54-61.
[18] LAUKLI H I, GOURLAY C M, DAHLE A K. Migration of crystals during the filling of semi-solid castings [J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36: 805-818.
[19] WANG Qing-liang, XIONG Shou-mei. Effect of multi-step slow shot speed on microstructure of vacuum die cast AZ91D magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 375-380.
[20] ZHANG Jian-min, WANG G C, HE Yan-ming, HE X D. Effect of joining temperature and holding time on microstructure and shear strength of Ti2AlC/Cu joints brazed using Ag-Cu filler alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 567: 58-64.
[21] DAHLE A K, STJOHN D H. Rheological behaviour of the mushy zone and its effect on the formation of casting defects during solidification[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 47(1): 31-41.
[22] YU Wen-bo, CAO Yong-you, LI Xiao-bo, GUO Zhi-peng, XIONG Shou-mei. Determination of interfacial heat transfer behavior at the metal/shot sleeve of high pressure die casting process of AZ91D alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2017, 1: 52-58.
[23] WANG Bai-shu, XIONG Shou-mei. Effects of shot speed and biscuit thickness on externally solidified crystals of high-pressure diet cast AM60B magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 767-772.
[24] LI Xiao-bo, XIONG Shou-mei, GUO Zhi-peng. On the porosity induced by externally solidified crystals in high-pressure die-cast of AM60B alloy and its effect on crack initiation and propagation [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2015, 633: 35-41.
杨红梅1,2,于文波1,2,曹永友1,2,李晓波1,2,郭志鹏1,2,熊守美1,2
1. 清华大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100084;2. 清华大学 先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
摘 要:真空压铸可减小铸造过程中的“气隙”现象。基于不同压铸条件,如低速速度(VL)、高速速度(VH)、浇注温度(Tp)和模具初始温度(Tm),通过实验测量金属与模具界面的温度,采用反算法获得真空条件下界面换热系数。结果表明,真空系统的应用使铸件与模具更加紧密接触,明显提高界面换热系数值并减小铸件的晶粒尺寸;当浇注温度由680 °C提高到720 °C或低速速度由0.1 m/s提高到0.4 m/s时,界面换热系数峰值随之提高,而高速速度和模具初始温度对界面换热系数的影响可以忽略。
关键词:真空压铸;界面换热行为;金属-模具界面;压室预结晶晶粒
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (2016YFB0301001) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project (2015M580093) supported by the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Shou-mei XIONG; Tel: +86-10-62773793; E-mail: smxiong@tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64907-6

