水中二溴海因在紫外辐照下的分解和副产物的形成机理
黄鑫1,蒲韵竹1,高乃云2,丁国际1
(1. 上海大学 环境与化学工程学院,上海,200444;
2. 同济大学 污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室,上海,200092)
摘要:研究1,3-二溴-5,5-二甲基海因(DBDMH)水溶液中的有效溴、溴离子和溴酸根离子在紫外(UV)辐照下的转化过程,并探讨pH、光照波长和氨氮等因素对次溴酸溶液的光促歧化反应的影响。研究结果表明:普通消毒剂量的DBDMH水溶液(质量浓度为3.2 mg/L)紫外辐照5 min后可产生质量浓度较大的溴酸根离子(>25.9 μg/L);溴酸根离子是次溴酸光促歧化反应的中间产物;在实验条件下,紫外光波长越短,越有利于有效溴的光解和溴酸根的生成,而pH的影响较小;氨氮通过与有效溴反应形成溴氨抑制溴酸根离子的生成。
关键词:二溴海因;溴酸根;有效溴;UV;水处理
中图分类号:TU991 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)03-0835-06
Decomposition and byproducts formation of DBDMH in water in UV irradiation
HUANG Xin1, PU Yun-zhu1, GAO Nai-yun2, DING Guo-ji1
(1. School of Environment and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
Abstract: 1,3 dibromo-5,5 dimethylhydantoin(DBDMH) decomposition with ultraviolet (UV) irradiation was studied by following the transformation of available bromine, bromide and bromate. Detailed experiments were conducted to fully explore the effect of pH, wavelength and ammonia on photo-induced disproportionation of hypobromous acid. The results show that more than 25.9 μg/L of bromate forms with initial 3.2 mg/L DBDMH close to the normal dosage of swimming pool disinfection. Generally, a shorter wavelength leads to a higher production rate of bromate and a higher decomposing rate of free bromine. The effect of pH is ignorable. Ammonia is able to completely suppress the formation of bromate by reacting with free bromine to form bromamines.
Key words: DBDMH; bromate; available bromine; UV; water treatment
1,3-二溴-5,5-二甲基海因(C5H6Br2N2O2)简称二溴海因(DBDMH),是一种新型杀菌消毒剂,因其在水中稳定性好、含溴量大及反应活性高,被广泛用于工业水、游泳池及养殖水环境的消毒处理[1-2]。二溴海因在水中以次溴酸的形式释放出有效溴[3]。当水中存在NH3-N时,次溴酸与氨反应形成溴氨[4]。具有氧化性的次溴酸和溴氨统称为有效溴。商品二溴海因消毒剂中的所谓“活性成分”是指有效溴(Br+),包括次溴酸和溴氨。有效溴活性高,易分解,而二溴海因以缓释形式释放出有效溴,克服了这一缺点[5]。光照是影响消毒剂分解速率及其生成产物的重要因素。江敏等[6]采用自然光照加速了溴氯海因的降解。Cooper等[7-8]发现紫外光照引发自由基反应,加速有效氯和有效溴的降解,并生成氯酸根和溴酸根离子。溴酸根具有较大的致癌风险[9]。我国的饮用水水质标准(质量浓度)为10 μg/L。目前,尚未见从溴平衡角度对光照引起水中二溴海因的分解研究。本文作者首先对紫外(UV)辐照二溴海因水溶液的主要产物进行分析,并进一步考察紫外辐照次溴酸溶液体系,探讨pH、氨氮和光照等因素对次溴酸溶液光促歧化反应的影响。通过对比,对二溴海因水溶液中溴元素在紫外辐照下的转化机理进行分析。
1 材料与方法
1.1 UV辐照实验
UV辐照装置如图1所示。
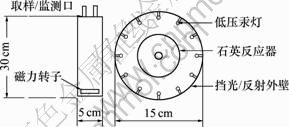
图1 UV反应装置
Fig.1 Schematic of UV reactor
装置为自制圆筒形铁质反应器,外壁内侧固定12根紫外灯管,通过开关对称控制灯管。使用C波段紫外灯(UVC)或A波段紫外灯(UVA),UVC灯主波长为253.7 nm,少部分发射波长为185 nm。UVA灯主波长为360 nm。反应器中间放置体积为0.6 L的有效容积石英杯。使用不同材质的石英杯,一种是普通石英,可透过大部分UVC波长的光,另一种是掺Ti无臭氧石英,可将波长λ<220 nm的光滤除。装置底部悬空通过气泵换气散热。每次实验前,灯管预热2~3 min。
辐照溶液为配制的次溴酸溶液或二溴海因溶液,按2.5 mmol/L加入磷酸盐缓冲溶液以避免pH较大波动。实验期间每隔一定时间取水样10 mL,其中:5 mL用作有效溴测定,另外5 mL用于测定其中各阴离子浓度。
1.2 试剂
主要试剂有:ABTS(2,2-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazo- line)-6-sulfonic acid-diammonium salt),购自上海生工生物工程有限公司(Sangon Biotech Co.,Ltd);商用二溴海因消毒片(上海钟磊环保科技有限公司生产),将其研磨成粉末,密封待测。试剂均为分析纯,均用超纯水(Milli-Q)配制。实验所用UVC和UVA灯为市售普通8 W杀菌灯管,掺钛无臭氧石英(优级品)购自宝盛石英制品有限公司。
次溴酸存储液配制具体方法参考文献[10]。冰浴中使用AgNO3溶液滴定红棕色溴水,直至无色为止,过滤,冷藏待用。其反应方程式为:
Br2+AgNO3+H2O → AgBr(沉淀)+BrO-+NO3-+2H+ (1)
在波长300,400和500 nm下测定HOBr存储液吸光度,依据摩尔吸光系数ε(其中ε(Br2)300=9.0 mol-1?cm-1,ε(Br2)400=172 mol-1?cm-1,ε(Br2)500=37.3 mol-1?cm-1,ε(HOBr)300=43.4 mol-1?cm-1, ε(HOBr)400=4.0 mol-1?cm-1,ε(HOBr)500=0.27 mol-1?cm-1)标定纯次溴酸溶液。标定显示新配制的HOBr存储液中Br2含量(质量分数)未超过3%。
通过离子色谱对溴酸根和溴离子含量进行分析,结果表明新配制的次溴酸溶液中含有少量的溴酸根和溴离子(总量未超过10%),每日实验的次溴酸均新鲜配制。
1.3 分析方法
使用万通研究级离子色谱仪测定溴酸根离子和溴离子含量;采用METROSEP A SUPP 5-250色谱柱,进样量为100 μL,抑制电导检测;使用3.2 mmol/L Na2CO3/1.0 mmol/L NaHCO3 淋洗液,流速为0.7 mL/min。溴酸根离子和溴离子的检测限(质量浓度)分别约为5 ?g/L和2 ?g/L。
采用ABTS显色分光光度(HACH双波长紫外-可见分光光度计(DR2800))测定溶液中的有效溴。理论上,1 mol Br+(次溴酸或溴氨)在酸性条件下与2 mol ABTS反应形成2 mol氧化自由基,自由基溶液显绿色,在405 nm处摩尔吸光度为31 600 mol-1?cm-1。取10 mL水样于25 mL比色管中,加入1 mL硫酸(0.05 mol/L)和1 mL质量浓度为1 g/L的ABTS,用去离子水稀释至25 mL,放置1 min,测405 nm处吸光度[11]。前期实验结果表明:采用ABTS分光光度法可准确测定低质量浓度(0.08~1.61 mg/L)二溴海因水溶液中有效溴的质量浓度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 DBDMH溶液辐照中溴元素和氨氮元素的转变
在水溶液中,二溴海因中溴主要以有效溴Br+、溴离子Br-和溴酸根BrO3- 3种形式存在。UV照射二溴海因时溴类与氮类浓度的变化趋势见图2。由图2(a)可知:UV辐射二溴海因水溶液时,有效溴Br+的浓度随着辐射时间的增加而逐渐连续降低;同时,BrO3-和Br-浓度相应增加。说明在UV辐照下有效溴Br+一部分转变为溴离子Br-,另一部分转变为溴酸根BrO3-。根据文献[12],BrO3-在紫外灯照射下也可转化为Br-,若BrO3-为初始物,则中间产物为HOBr/OBr-。由于HOBr/OBr-在UV辐射下转化为Br-的速度很快,溴离子的最终浓度远远大于溴酸根的浓度[13]。这与实验结果一致。
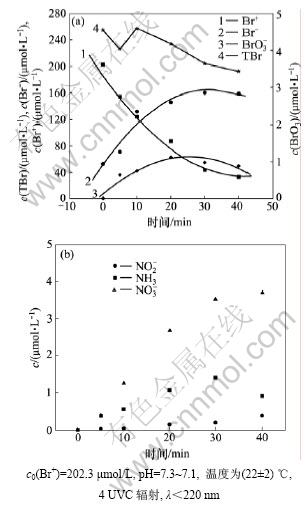
图2 UV辐照二溴海因时氮类浓度的变化趋势
Fig.2 Concentration of DBDMH solution for different bromine species during UV irradiating
BrO3-+ hv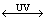 HOBr/OBr-+ hv
HOBr/OBr-+ hv Br- (3)
Br- (3)
将图2中有效溴、溴离子、溴酸根的总和视为总溴:TBr=Br-+BrO3-+Br+。从图2可见:总溴在实验后期的变化不超过初始值的16.4%,基本保持平衡,说明能够测定大部分溴元素。后期总溴浓度逐步降低的原因可能是出现了无法测定的少量二溴胺和三溴胺。二溴海因光降解时产生氨氮,氨氮和次溴酸可迅速反应,生成溴胺化合物,包括大部分一溴胺和少量二溴胺、三溴胺。由于二溴胺、三溴胺和ABTS反应时计量系数比一溴胺的大,造成测定时低估了这部分溴浓度。文献[14-15]报道:阴离子在强紫外辐照下能形成微量的活泼自由基,在适宜的环境中最终生成挥发性有机物气态副产物。这也可能是总溴浓度降低的原因之一。
NH3+HOBr→NH2Br+H2O
k=8×107 mol-1·s-1 (4)
式中:k为计算系数。
由图2(b)可见:辐照二溴海因时NO3-,NH3和NO2-浓度均上升;其中,NO3-浓度提高最快,NH3浓度提高速度次之,NO2-浓度提高速度最小。NH3在辐射后期浓度有所下降,其原因主要是海因化合物(C5H5N2O2)的分解。而硝酸根和亚硝酸根离子主要来自UV辐照下NH3的氧化,NH3在UV辐照下可以迅速地被氧化成NO2-和NO3-[16]。此外,UV辐照下水中溴胺化合物也可能快速分解生成含氮副产物和Br-。
二溴海因不同初始浓度对溴酸根生成浓度的影响见图3。从图3可见:二溴海因溶液初始浓度越大,溴酸根生成速度越快;当UV辐射20 min时,3种不同浓度二溴海因溶液生成溴酸根浓度达到最大,其后随辐射时间的延长,溴酸根浓度略有下降。注意到图3中初始40.5 μmol Br/L(3.2 mg Br/L) DBDMH溶液辐照5 min后,生成了0.2 μmol/L(25.9 μg/L)以上的溴酸
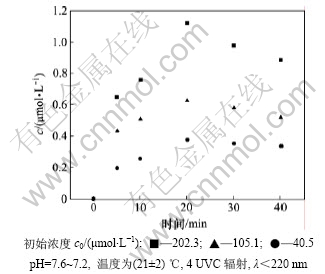
图3 二溴海因不同初始浓度对溴酸根生成浓度的影响
Fig.3 Effect of initial concentration of DBDMH on bromate formation
根离子,远超过质量浓度为10 μg/L的饮用水标准。目前尚没有泳池用水的溴酸根离子标准,但仍说明泳池中使用高剂量消毒液有可能导致溴酸根离子浓度显著增加。
显然,有效溴浓度越大,生成溴酸根的速度越快,浓度越大。在辐照后期,大部分有效溴已经转化为溴离子,相应的溴酸根生成速度减少,而溴酸根离子在紫外照射下分解。本实验中生成和分解这2种作用在20 min时达到平衡。因此,溴酸根离子可视为二溴海因水溶液中次溴酸降解过程形成的一种中间产物,而持续紫外照射可减少溴酸根离子的超标风险。
2.2 次溴酸溶液辐照过程中溴元素的转变
2.2.1 波长的影响
波长对次溴酸降解和溴酸根生成的影响见图4。从图4可见: 3种主波长辐照下(l=254 nm,(254+185) nm,360 nm),波长越短,有效溴消耗速度越快,溴
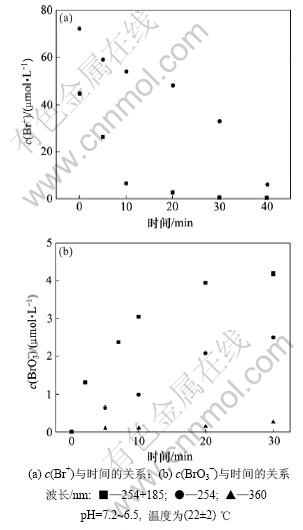
图4 波长对次溴酸降解和溴酸根生成的影响
Fig.4 Effect of wavelength on free bromine decay and bromate formation during UV irradiation
酸根越容易生成;在l=(254 +185) nm时,10 min后有效溴浓度降至6.7 μmol/L以下;在l=254 nm时,40 min内呈近似线性下降规律,单位时间下降量约为-1.6 μmol/(L·min);而l=360 nm时,40 min内降低量很少(数据偏少未列出)。各波长辐照下溴酸根离子的生成量也呈现出相对应的规律。生成量在l=(254+185) nm时最大,l=254 nm时次之;而在l=360 nm时,几乎没有生成溴酸根离子。图4所示结果说明:次溴酸的歧化反应(式(2))受紫外光波长影响很大。根据能量公式E=hν,波长越短,能量E越大。对于次溴酸和溴酸根离子,短波长均加速了两者的分解。但次溴酸的分解又增加了溶液中的溴酸根离子浓度,所以,实验中溴酸根离子的浓度仍然增加。
2.2.2 pH的影响
pH对次溴酸降解和溴酸根生成的影响见图5。图5表明:pH对次溴酸浓度的影响不大。由图5(a)可见:
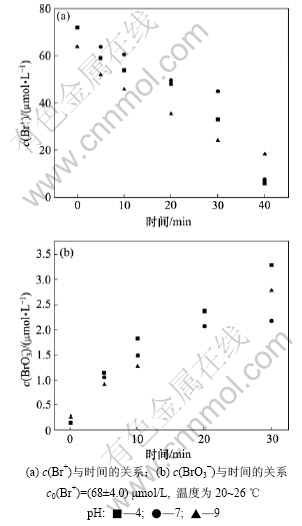
图5 pH对次溴酸降解和溴酸根生成的影响
Fig.5 Effect of pH on free bromine decay and bromate formation during UV irradiation
将浓度归一化后,在pH=4,7和9时曲线斜率分别为0.020,0.019和0.018;pH变化将改变次溴酸中HOBr/OBr-的浓度。Phillip等[10]认为OBr-和HOBr光降解速率之比大约为1.0:0.8。次溴酸的电离平衡常数pKa=8.69,因此,pH为4和7时HOBr含量均占绝大部分(>98%),相差不大;而pH为9时,分解速率略下降。同样地,3种pH下溴酸根的生成速率和浓度在前20 min内均几乎一致。在辐照后期,由于残余次溴酸的浓度差别增大,溴酸根的生成量也有细微差别。
泳池水pH呈中性,所以,对二溴海因光分解的速率和产物影响不大。
2.2.3 氨氮的影响
二溴海因辐照中持续产生NH3-N,NO2-和NO3- (图1),因此,在次溴酸溶液中加入氨氮以探讨其对次溴酸歧化反应的影响。图6所示为零时刻HOBr的初始浓度。从图6可见:氨氮显著加快了次溴酸的衰减;
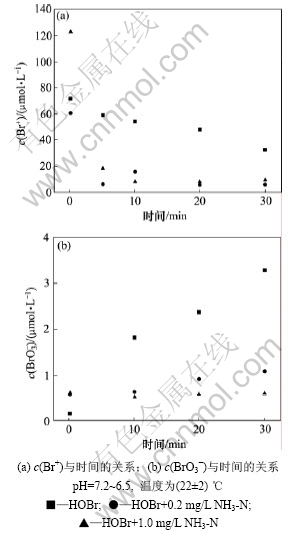
图6 氨氮对次溴酸降解和溴酸根生成的影响
Fig.6 Effect of ammonia on free bromine decay and bromate formation during UV irradiation
在60 ?mol/L(4.8 mg/L)次溴酸中加入0.2 mg/L氨氮后,5 min内便降至20 ?mol/L以下。有效溴快速下降的原因是:氨氮与溶液中有效溴快速反应生成溴胺类化合物(式(4));此外,氨氮光氧化形成NO2-和NO3-过程也能够加速次溴酸的分解。较为相似的离子是氨氮和NO2-,其光氧化加速了溴酸根离子的光分解[17]。
由于形成溴氨而减少了次溴酸的浓度,因此,溶液中加入氨氮后溴酸根离子的浓度也显著降低。尽管溴氨在UV辐照下的分解产物尚未明确,但从氯胺的光解产物推测,其最终产物不含溴酸根离子,可能是溴离子Br-和氮元素类产物如NO2-,NO3-和N2O[18]。这解释了相同辐照强度下,202.3 ?mol/L二溴海因(图4)和72.0 ?mol/L次溴酸(图4)生成溴酸根离子的速度相近的原因,说明二溴海因水解中产生的氨氮抑制了溴酸根离子的形成。
3 结论
(1) 在UV辐照下,水中二溴海因分解为有效溴Br+和海因。前者继续分解产生溴酸根和溴离子,后者分解产生氨氮,并在紫外光作用下将其氧化为NO2-和NO3-。
(2) 溴酸根离子是次溴酸光促歧化反应的中间产物。在实验条件下,紫外光波长降低可促进有效溴的光解和溴酸根的生成;pH对次溴酸浓度的影响较小;氨氮通过与有效溴反应形成溴氨,抑制溴酸根离子的生成。
参考文献:
[1] 马玉林, 王荷生, 陈继平. 二溴海因对医疗污水消毒后用比色法测定有效溴残留量[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2006, 16(6): 693-714.
MA Yu-lin, WANG He-sheng, CHEN Ji-ping. Detection of residual available bromine by spectrophotometric method in medical wastewater after DBDMH disinfection[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2006, 16(6): 693-714.
[2] Kalcrayanand N, Arthur T M, Bosilevac J M, et al. Effectiveness of 1,3-Dibromo-5,5 dimethylhydantoin on reduction of escherichia coli O157:H7-and salmonella-inoculated fresh meat[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 2009, 72(1): 151-156.
[3] Song S J, Lui P, Song Q J, Quantification of dibromo- dimethylhydantoin disinfectants in water by chemiluminescent method[J]. Anal Sci, 2007, 23(3): 327-330.
[4] Debordea M, Gunten U V. Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment: Kinetics and mechanisms, A critical review[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(1): 13-51.
[5] 徐丽君. 二溴海因水基制剂研制[D]. 无锡: 江南大学化学与材料工程学院, 2008: 15-45.
XU Li-jun. A study on the aqueous formulations of 1,3-dibromo- 5,5-dimethylhydantoin[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University. School of Chemical and Material Engineering, 2008: 15-45.
[6] 江敏, 吴昊, 罗春芳, 等. 溴氯海因在水环境中的降解及其对4种水生生物的急性毒性[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2008, 3(6): 570-576.
JIANG Min, WU Hao, LUO Chun-fang, et al. Study on the degradation rule of bromo-chloro-dimethyl hydantoin (BCDMH) and its acute toxicity to four aquatic organisms[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2008, 3(6): 570-576.
[7] Cooper W J, Jones A C, Whitehead R F, et al. Sunlight-induced photochemical decay of oxidants in natural waters: Implications in ballast water treatment[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2007, 41(10): 3728-3733.
[8] Huang X, Gao N Y, Deng Y. Bromate ions formation in dark chlorination and ultraviolet (UV)/chlorination processes for bromide-containing water[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(2): 246-251.
[9] 王伟, 蒋颂辉, 朱惠刚, 等. 溴酸盐的遗传毒性[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2003, 20(3): 137-138.
WANG Wei, JIANG Song-hui, ZHU Hui-gang, et al. Study on the genotoxicity of bromate[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2003, 20(3): 137-138.
[10] Lahoutifard N, Lagrange P, Lagrange J, et al. Kinetics and mechanism of nitrite oxidation by HOBr/BrO- in atmospheric water and comparison with oxidation by HOCl/ClO-[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2002, 106: 11891-11896.
[11] Pinkernell U, Nowack B, Gallard H, et al. Methods for the photometric determination of reactive bromine and chlorine species with ABTS[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(18): 4343-4350.
[12] Phillip N H, Gurten E, Diyamandoglu V. Transformation of bromine species during decomposition of bromate under UV light from low pressure mercury bapor lamps[J]. Science and Engineering, 2006, 28(4): 217-228.
[13] Zhao Q, Shang C, Zhang X. Effects of bromide on UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process[J]. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 2009, 9(6): 627-634.
[14] Gonzalez M G, Oliveros E, Worner M. et al. Vacuum-ultraviolet photolysis of aqueous reaction systems[J]. J Photoch Photobiol C, Photochem Rev, 2004, 5(3): 225-246.
[15] Espinoza L A T, Frimmel F H. Formation of brominated products in irradiated dioxide suspensions containing bromide and dissolved organic carbon[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(6/7): 1778-1784.
[16] Hofmann R, Andrew R C. Ammoniacal bromamines-a review of their influence on bromate formation during ozonation[J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(3): 599-604.
[17] Watts M J, Linden K G. Chlorine photolysis and subsequent OH radical production during UV treatment of chlorinated water[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(13): 2871-2878.
[18] Li J, Blatchley III E R. UV photodegradation of inorganic chloramines[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2009, 43(1): 60-65.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-08-25;修回日期:2010-10-29
基金项目:国家科技重大专项资助项目(2008ZX07421-002);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50908138, 50878163)
通信作者:高乃云(1950-),女,陕西府谷人,博士,教授,从事水处理理论与技术研究;电话:021-65982691;E-mail: gaonaiyun@sina.com