DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.09.25
铜闪速吹炼过程杂质元素分配行为的热力学分析
李明周1, 3,周孑民1, 2,张文海1,李贺松2,童长仁3
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
3. 江西理工大学 冶金与化学工程学院,赣州 341000)
摘 要:利用已开发的铜闪速吹炼过程多相平衡热力学数学模型,计算某典型铜闪速吹炼生产工况,验证模型热力学分析的可行性,进而考察粗铜含硫(CSCu)、渣中钙铁比(RCaFe)、富氧浓度(CO,体积分数)、吹炼温度(T)对杂质元素在吹炼产物中分配行为的影响。结果表明:提高CSCu、T或降低RCaFe、CO将导致杂质在粗铜中分配率升高、而入渣率降低、有害杂质挥发率升高。在铜锍量和成分一定条件下,吹炼过程宜在“低粗铜含硫与吹炼温度”和“高渣中钙铁比与富氧浓度”条件下进行。综合考虑粗铜质量和渣含铜,CSCu、RCaFe和T建议分别控制在0.20%、0.4和1526 K左右,而CO应根据制氧成本和炉内反应状况适当控制。
关键词:铜闪速吹炼;杂质元素;分配行为;多相平衡;热力学
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-09-1951-09 中图分类号:TF81 文献标志码:A
1949年投入工业生产的奥托昆普闪速炼铜工艺对铜锍熔炼技术的发展带来了巨大的影响[1],被普遍认为是成熟的清洁冶炼工艺[2-4],目前由闪速熔炼生产的金属铜已占世界矿产铜产量的50 %以上。然而,铜锍吹炼技术仍然由P-S转炉吹炼占主导,至今已有100多年的历史[5],虽然具有简单、可靠和物料适应性强等优点,但也存在作业不连续、烟气SO2浓度低、SO2烟气低空污染等问题。为了解决P-S转炉吹炼存在的这些问题,20世纪70年代以后出现了连续吹炼工艺,如三菱熔池吹炼和肯尼科特闪速吹炼等[6],其中,闪速吹炼工艺以其环保好、产能大、硫捕集率高、易实现自动化等优势,近10年来在中国发展迅速,成为重要的铜锍吹炼工艺技术。
当前,随着金属铜产量和消费量的提高,世界铜精矿的含铜品位呈下降的趋势,而含Pb、Zn、As、Sb、Bi、Ni等杂质元素较高的复杂铜精矿的量逐年提高,给铜冶炼的产品质量和环保控制带来较大的压力;铜冶炼技术的发展使“四高”强化熔炼[7]技术成为主流,“四高”强化熔炼的作业条件对冶炼过程中杂质元素的分配行为产生了较大的影响,优化工艺控制,有效地控制杂质元素在各物相中的分布,低成本地生产出优质的阴极铜产品,同时实现杂质元素经济的综合回收和安全处置,需要对冶炼过程中杂质元素的分布行为进行深入研究,为生产控制提供理论基础。
铜闪速吹炼过程是一个高温、多相、多组分的复杂反应过程,各变量间的交互耦合效应难以确定,传统实验检测手段难以研究其物理化学过程。借助计算机模拟技术[8-11],采用多相平衡计算模型[12-15]对高温冶炼过程进行的热力学分析,是一种有效的研究手段,受到研究者的广泛关注。JALKANEN等[16]、MAKINEN等[17]、ITAGAKI等[18]、谭鹏夫等[19]对铜闪速熔炼过程中杂质元素的分配行为进行了计算机模拟研究,获得的预测结果与实测值吻合较好。NAGAMORI等[20]、CHAUBAL等[21]、RICHARDS等[22]和ASTELJOKI等[23]对诺兰达和P-S转炉吹炼工艺过程的杂质行为进行了研究;SUOMINEN等[24]、CHAUBAL等[6]、SWINBOURNE等[1]对闪速吹炼工艺的微量元素(Pb、As、Sb、Bi)的分布行为进行了热力学分析,为生产实践提供了理论指导。然而,这些研究仅考虑了铜锍品位、富氧量等因素对部分杂质分布行为的影响,而粗铜含硫、富氧浓度、渣中钙铁比和吹炼温度等因素对粗铜质量、渣含铜和多种杂质在产物中的分配行为等指标的影响,相关研究少有报道。
鉴于此,本文作者采用已构建的铜闪速吹炼过程多相平衡数学模型,在前期对产物主要组分进行热力学分析的基础上,系统考察粗铜含硫(CSCu)、渣中钙铁比(RCaFe)、富氧浓度(CO,体积分数)、吹炼温度(T)对Pb、Zn、As、Sb、Bi、Ni等杂质元素在吹炼产物中分配行为的影响,为铜闪速吹炼过程工艺参数优化与杂质控制提供理论指导。
1 铜闪速吹炼过程多相平衡数学模型
1.1 铜闪速吹炼多相平衡数学模型
假定铜闪速吹炼多相平衡产物有3相:粗铜相、炉渣相和烟气相。平衡各相组成如下:
1) 粗铜相有Cu、Cu2S、Cu2O、Fe、FeS、Pb、Zn、As、Sb、Bi、Ni;
2) 炉渣相有FeO、Fe3O4、FeS、Cu2O、Cu2S、PbO、ZnO、As2O3、Sb2O3、Bi2O3、SiO2、CaO、MgO、NiO;
3) 烟气相有SO2、O2、N2、S2、PbS、PbO、Zn、ZnS、AsO、AsS、As2、SbO、SbS、Sb、BiO、BiS、Bi。
基于以上产物假设,利用前期研发的铜闪速吹炼过程的多相平衡数学模型,预测各生产控制条件对产物量及其组成的影响。
1.2 各相产物杂质分配率定义
定义e杂质元素在p相中的质量分配率(%)为
 (1)
(1)
式中:e表示Pb、Zn、As、Sb、Bi、Ni等杂质元素,p表示B(粗铜相)、S(炉渣相)、G(烟气相)等产物相,mp,e表示e杂质元素在p相中的质量。
在吹炼过程中,进入烟气和炉渣的杂质分别经过收尘和水淬后,以烟尘和吹炼渣形式返回熔炼系统,在系统内形成循环。因此,为有效脱除杂质,通常期望杂质尽可能少入粗铜相外(即DB,x要小)、多入炉渣相(即DS,x要大),从系统直接开路、降低杂质循环量,最终使粗铜相杂质含量降低。
1.3 热力学数据
铜闪速吹炼多相平衡产物各相各组分的吉布斯自由能根据式(2)计算,组分标准吉布斯自由能等相关热力学参数由MetCal desk软件[25]查询获得,具体见表1。炉渣和粗铜相各组分的相关活度系数列于表2,烟气相中各组分活度系数均为1。表2中xFeO、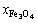 、
、 、
、 为炉渣中FeO、Fe3O4、SiO2、Cu2S组分的摩尔分数,
为炉渣中FeO、Fe3O4、SiO2、Cu2S组分的摩尔分数,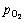 为烟气中氧分压。
为烟气中氧分压。
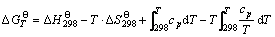 (2)
(2)
2 铜闪速吹炼过程的多相平衡模拟
采用所构建闪速吹炼多相平衡数学模型,以国内某“双闪”铜冶炼企业2015年6~8月份的平均操作参数作为条件,计算铜闪速吹炼过程平衡产物物相组成。
工艺条件:铜锍加入量72 t/h,石灰2.35 t/h,石灰含CaO 91%,SiO2 6%,富氧浓度80%,富氧量14415 Nm3/h,吹炼温度1523 K,铜锍平均组分含量见表3。
将生产中该时期粗铜和炉渣样各元素分析测试值与模拟计算值进行对比,结果见表4,杂质在产物相中的分配率与文献值对比结果见表5。
由表4结果可知,各产物相组分计算值接近生产检测值,其中粗铜中Cu、S、Fe、Pb、Zn、Sb、Bi和Ni元素计算值与生产检测值误差绝对值分别0.505%、0.004%、0.062%、0.359%、0.004%、0.068%、0.003%和0.013%,炉渣中除Ni元素未测试外,其他各元素误差分别为2.130%、0.144%、2.390%、1.858%、0.059%、0.398%、0.013%和0.019%;表5结果表明,杂质在产物中的分配行为与文献结果[1, 27]基本吻合。可见,采用多相平衡数学模型能反映铜闪速吹炼的实际情况,用于该过程产物组成预测和杂质分配行为等热力学分析是可行的。
3 铜闪速吹炼杂质分配行为分析
铜锍加入量固定在72 t/h,成分见表3,通过改变粗铜含硫(CSCu)、渣中钙铁比(RCaFe)、富氧浓度(CO)、吹炼温度(T),考察杂质(Pb、Zn、As、Sb、Bi、Ni)在铜闪速吹炼产物相(粗铜、炉渣和烟气)中的分配行为。
表1 组分的热力学参数
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters of components
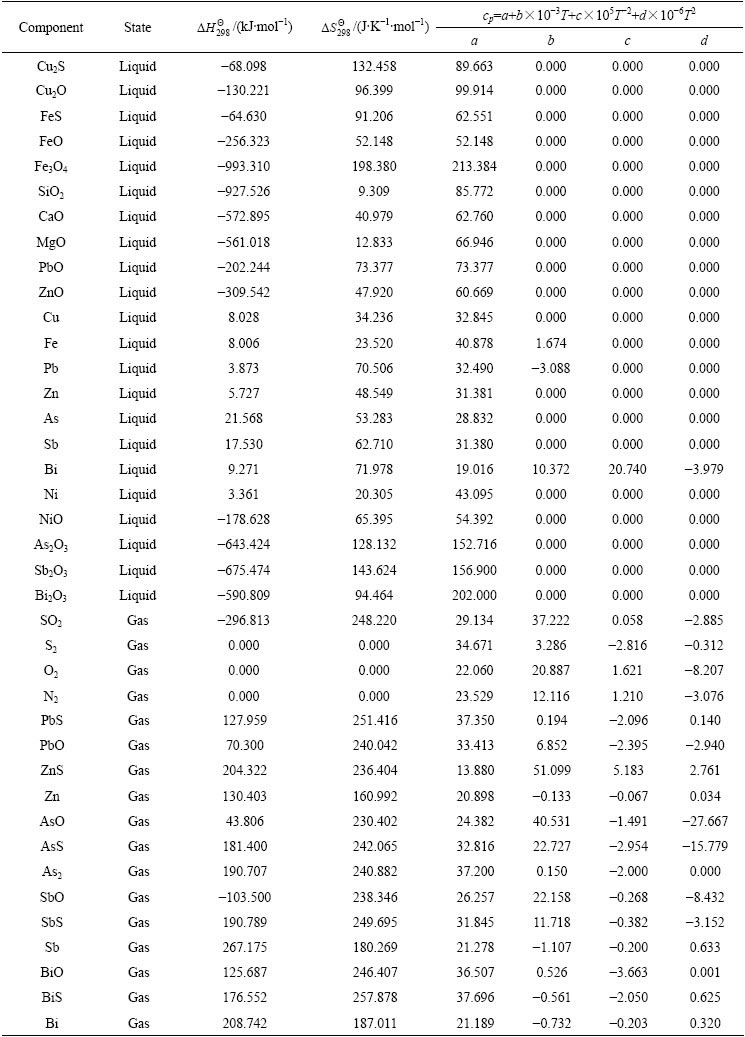
表2 组分的活度系数
Table 2 Activity coefficient of components

表3 入炉铜锍组分含量
Table 3 Component content of initial matte (mass fraction, %)

表4 模拟结果与生产数据
Table 4 Simulation results and industrial data

表5 杂质分配率模拟结果
Table 5 Simulation results and industrial data
3.1 粗铜含硫的影响
在渣中钙铁比0.30、富氧浓度80%、温度1523 K条件下,模拟计算了粗铜含硫CSCu在0.05%~0.95%范围内变化时杂质在产物中的分配行为,结果见图1。
图1结果表明,随CSCu增加,粗铜中除Zn分配率小幅增加外,其他杂质分配率增加,炉渣中杂质分配率均呈下降趋势,且在CSCu高于0.2%后,两相中杂质分配率变化幅度减小,而烟气中除Zn分配率快速增加外,其他杂质分配率变化不明显。
提高粗铜含硫(CSCu),可通过降低炉内氧势来实现,此时铜锍粉中包括杂质在内的各金属硫化物氧化程度降低,因此,杂质氧化入渣率降低,粗铜中杂质分配率相对升高。综合考虑前期研究中“过低CSCu会导致渣含铜较高”的分析结果,建议CSCu控制在0.20%左右。
3.2 渣中钙铁比的影响
在粗铜含硫0.25%、富氧浓度80%、温度1523 K条件下,渣中钙铁比RCaFe在0.15~0.85范围内变化时,计算结果见图2。
图2结果表明,随RCaFe增加,各杂质元素在粗铜中分配率减小,在炉渣中分配率增大,而在烟气中除Zn的分配率降低外,其他杂质分配率变化不明显。
通过增加熔剂,可提高渣中RCaFe,降低渣中Fe3O4相对含量,渣流动性变好,但杂质氧化物造渣趋势同样增加,杂质在渣相中分配率增大,粗铜中杂质相对降低,质量变好。但综合考虑前期研究中“过高RCaFe渣含铜升高”的分析结果,建议RCaFe控制在0.4左右。
3.3 富氧浓度的影响
在粗铜含硫0.25%、渣中钙铁比0.35、温度1523K
条件下,富氧浓度CO在65%~95%范围内变化时,计算结果见图3。

图1 CSCu对各相杂质分配率的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of CSCu on distribution rates of impurities

图2 RCaFe对各相杂质分配率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of RCaFe on distribution rates of impurities
图3结果表明,随CO增加,粗铜中除Zn分配率变化不明显外,其他杂质分配率均小幅降低,渣中各杂质元素分配率呈增加趋势,而烟气中各杂质分配率呈降低趋势,其中Zn分配率降幅更大。可见,提高CO主要起降低富氧量和强化反应的作用,而对提高产品质量及杂质脱除仅有一定程度的影响,与CSCu相比更显微弱。因此,在低制氧成本前提下,为强化炉内反应过程,可采用高CO铜闪速吹炼工艺。
3.4 吹炼温度的影响
在粗铜含硫0.25%、富氧浓度80%、渣中钙铁比0.35条件下,吹炼温度T在1493~1573K范围内变化时,计算结果见图4。

图3 CO对各相杂质分配率的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of CO on distribution rates of impurities
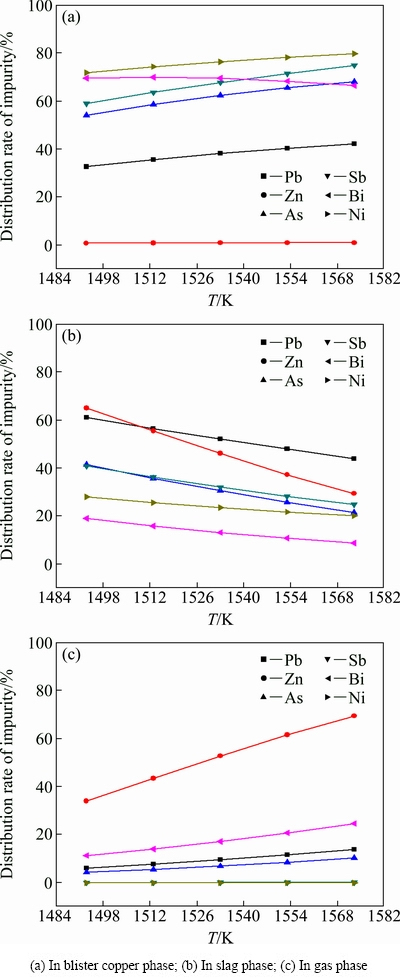
图4 温度对各相杂质分配率的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of temperature on distribution rates of impurities
图4(a)结果表明,随吹炼温度升高,粗铜中除Bi分配率小幅减小和Zn分配率微幅增加外,其他杂质分配率呈增加趋势,炉渣中各杂质分配率降低,而杂质在烟气中分配率呈增加趋势。可见,降低吹炼温度,可增加除杂效果、减少有害杂质挥发率,结合前期研究“温度过低易导致渣含铜升高”的分析结果,建议吹炼温度控制在1526 K左右。
4 结论
1) 基于所建立的铜闪速吹炼过程多相平衡热力学模型,计算了某典型铜闪速吹炼生产工况,计算结果与生产实践基本吻合,表明该模型可用于铜闪速吹炼过程热力学分析和杂质分配行为研究。
2) 各杂质分配行为的热力学分析结果表明,提高CSCu、T或降低RCaFe、CO将导致杂质在粗铜中分配率升高、而入渣率降低、有害杂质挥发率升高。在铜锍量和成分一定条件下,吹炼过程宜在“低粗铜含硫与吹炼温度”和“高渣中钙铁比与富氧浓度”条件下进行。
3) 结合前期各相产物主要组分的热力学分析结果,为同时保证产品质量和杂质脱除效果,CSCu、RCaFe和T建议分别控制在0.20%、0.4和1526 K,而CO应根据制氧成本和炉内反应状况适当控制。
REFERENCES
[1] SWINBOURNE D R, KHO T S. Computational thermodynamics modeling of minor element distributions during copper flash converting[J]. Metall Materi Trans B, 2012, 43(4): 823-829.
[2] FISCOR S. Outokumpu technology: Makes process improvements possible[J]. Engineering and Mining Journal, 2004, 205(9): 43-45.
[3] KOJO I V, JOKILAAKSO A, HANNIALA P. Flash smelting and converting furnaces: A 50 year retrospect[J]. JOM, 2000, 52(2): 57-61.
[4] KOJO I, LAHTINEN M, MIETTINEN E. Flash converting-sustainable technology now and in the future[C]// KAPUSTA J, WARNER T. International Peirce-Smith Converting Centennial. California: TMS, 2009: 383-395.
[5] 吴继烈. 冰铜闪速吹炼工艺评述[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2014(6): 34-39.
WU Ji-lie. Review of flash converting of copper matte[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2014(6): 34-39.
[6] CHAUBAL P C, SOHN H Y, GEORGE D B, BAILEY L K. Mathematical modeling of minor-element behavior in flash smelting of copper concentrates and flash converting of copper mattes[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1989, 20(1): 39-51.
[7] 宋修明, 陈 卓. 闪速炼铜过程研究[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社,2012: 280-286.
SONG Xiu-ming, CHEN Zhuo. Research of copper flash smelting process[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 280-286.
[8] 谭鹏夫, 张传福. 铜熔炼过程中伴生元素分配行为的计算机模型[J]. 金属学报, 1997, 33(10): 1094-1100.
TANG Peng-fu, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Computer model of distribution behavior of accessory elements in copper smelting[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1997, 33(10): 1094-1100.
[9] 李明周, 黄金堤, 童长仁, 张文海, 周孑民, 李贺松, 张 鹏. 铜电解槽内电解液流场的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(8): 2259-2267.
LI Ming-zhou, HUANG Jin-di, TONG Chang-ren, ZHANG Wen-hai, ZHOU Jie-min, LI He-song, ZHANG Peng. Numerical simulation of electrolyte flow in copper electrolytic cell[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(8): 2259-2267.
[10] LIU J H, GUI W H, XIE Y F, YANG C H. Dynamic modeling of copper flash smelting process at a smelter in China[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2014, 38(7): 2206-2213.
[11] TAN P. Modeling and control of copper loss in smelting slag[J]. JOM, 2011, 63(12): 51-57.
[12] 童长仁, 刘道斌, 杨凤丽, 吴金财. 基于元素势的多相平衡计算及在铜冶炼中的应用[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008, 8(S1): 45-48.
TONG Chang-ren, LIU Dao-bin, YANG Feng-li, WU Jin-cai. Multiphase equilibrium calculation based on element potential and its application in copper flash smelting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008, 8(S1): 45-48.
[13] 汪金良, 张传福, 张文海. Fe3O4 在铜闪速炉反应塔中的形成热力学[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(12): 4787-4792.
WANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Chuan-fu, ZHANG Wen-hai. Formation thermodynamic of Fe3O4 in reaction shaft of flash smelting furnace[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(12): 4787-4792.
[14] 汪金良, 张文海, 张传福. 硫化铅矿闪速熔炼过程的热力学分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 2952-2957.
WANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Wen-hai, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Thermodynamic analysis of lead sulfide flash smelting process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(11): 2952-2957.
[15] 汪金良, 张传福, 张文海. 铅闪速熔炼过程的多相平衡模型[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(2): 429-434.
WANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Chuan-fu, ZHANG Wen-hai. Multi-phase equilibrium model of lead flash smelting process[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(2): 429-434.
[16] JALKANEN H K, HOLAPPA L E K, MAKINEN J K. Some novel aspects of matte-slag equilibria in copper smelting[C]// SOHU H Y, GEOGE D B, ZUNKEL A D. Advances in Sulfide Smelting. New York: The Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1983: 277-292.
[17] MAKINEN J K, JAFS G A. Production of matte, white metal, and blister copper by flash furnace[J]. JOM, 1982, 34(6): 54-59.
[18] ITAGAKI K, YAZAWA A. Thermodynamic evaluation of distribution behavior of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in copper smelting[C]//SOHU H Y, GEOGE D B, ZUNKEL A D. Advances in Sulfide Smelting. New York: The Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1983: 119-142.
[19] 谭鹏夫, 张传福. 砷, 锑, 铋, 铅和锌在铜闪速熔炼过程中的行为[J]. 矿冶工程, 1997, 17(2): 53-56.
TANG Peng-fu, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Behaviors of As, Sb, Bi, Pb and Zn in copper flash smelting process[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 1997, 17(2): 53-56.
[20] NAGAMORI M, CHAUBAL P C. Thermodynamics of copper matte converting: Part IV. A priori predictions of the behavior of Au, Ag, Pb, Zn, Ni, Se, Te, Bi, Sb, and As in the Noranda process reactor[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1982, 13(3): 331-338.
[21] CHAUBAL P C, NAGAMORI M. Volatilization of arsenic and antimony in copper matte converting[J]. Metall Materi Trans B, 1983, 14(2): 303-306.
[22] RICHARDS K J, GEORGE D B, BAILEY L K. A new continuous copper converting process[C]//SOHU H Y, GEOGE D B, ZUNKEL A D. Advances in Sulfide Smelting. New York: The Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1983: 489-498.
[23] ASTELJOKI J, BAILEY L, GEORGE D, RODOLFF D. Flash converting—Continuous converting of copper mattes[J]. JOM, 1985, 37(5): 20-23.
[24] SUOMINEN R, JOKILAAKSO A, TASKINEN P, LILIUS K. Behaviour of copper mattes in simulated flash converting conditions[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Metallurgy, 1991, 20(245): 245-250.
[25] 李明周, 童长仁, 黄金堤, 李俊标, 汪金良. 基于 Metcal 的铜闪速熔炼-转炉吹炼工艺全流程模拟计算[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2015(9): 20-25.
LI Ming-zhou, TONG Chang-ren, HUANG Jin-di, LI Jun-biao, WANG Jin-liang. Simulated calculation of overall process flow of copper flash smelting and converting based on Metcal[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2015(9): 20-25.
[26] 黄金堤, 李 静, 童长仁, 李明周, 徐志峰. 废杂铜精炼过程中动态多元多相平衡热力学模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(12): 3513-3522.
HUANG Jin-di, LI Jing, TONG Chang-ren, LI Ming-zhou, XU Zhi-feng. Dynamic multicomponent and multiphase equilibrium thermodynamics model during scrap copper refining process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(12): 3513-3522.
[27] 朱祖泽, 贺家齐. 现代铜冶金学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 414-415.
ZHU Zu-ze, HE Jia-qi. Modern metallurgy of copper[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 414-415.
Thermodynamics analysis of distribution behavior of impurity elements during copper flash converting
LI Ming-zhou1, 3, ZHOU Jie-min1, 2, ZHANG Wen-hai1, LI He-song2, TONG Chang-ren3
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. School of Metallurgy & Chemical Engineering Jangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China)
Abstract: With the developed multi-phase equilibrium mathematical model of the copper flash converting process, the typical production condition of the converting process was calculated, and the feasibility of the thermodynamic analysis by this model was verified. Then the effects of the content of sulfide in blister copper(CSCu), the ratio of Ca/Fe in slag(RCaFe), the oxygen-rich concentration(CO) and the converting temperature(T) on the distribution behavior of impurity elements in the converting product were studied using this model. The results show that, increasing CSCu, T or decreasing RCaFe, CO will lead to be the results in higher distribution rate of impurities in blister copper, lower removal rate of impurities into the slag and higher volatile rate of harmful impurities. For the matte with a certain amount and a certain composition, appropriate conditions of melting process are “low CSCu , T ”and “high RCaFe, CO”. However, considering the quality of blister copper and slag containing copper, the CSCu, RCaFe and T should be controlled at about 0.20%, 0.4 and 1526 K, respectively, and the CO should be controlled properly based on oxygen generation cost and the reaction conditions in the furnace.
Key words: copper flash converting; impurity element; distribution behavior; multi-phase equilibrium; thermodynamics
Foundation item: Project (2013BAB03B05) supported by the National Science-technology Support Plan Projects of China
Received date: 2016-07-26; Accepted date: 2017-01-16
Corresponding author: LI he-song; Tel: +86-18684696162; E-mail: lihesong611@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划资助项目(2013BAB03B05)
收稿日期:2016-07-26;修订日期:2017-01-16
通信作者:李贺松,教授,博士;电话:18684696162;E-mail:lihesong611@csu.edu.cn