


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1556-1562
Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy during compression at elevated temperatures
ZHANG Zhi-ye1, PAN Qing-lin1,2, ZHOU Jian1, LIU Xiao-yan1, CHEN Qin1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering of Ministry of Education,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 18 July 2011; accepted 28 October 2011
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy and its microstructural evolution were investigated by isothermal axisymmetric hot compression tests at temperatures from 340 to 500 ℃ and strain rates ranging from 0.001 to 10 s-1. The steady flow stress increased with increasing the strain rate or decreasing the deformation temperature, which can be described by a hyperbolic-sine constitutive equation with the deformation activation energy of 150.25 kJ/mol. The tendency of dynamic recrystallization enhanced at high deforming temperatures and low strain rates, which corresponded to low Z values. With decreasing Z value, the main softening mechanism of the alloy transformed from dynamic recovery to dynamic recrystallization, correspondingly, the subgrain size increased and the dislocation density decreased.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy; hot deformation; flow behavior; microstructural evolution
1 Introduction
Novel Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy has been developed by adding a small amount of scandium and zirconium on the base of medium-strength weldable Al-Zn-Mg alloy. The alloy has high strength, good corrosion resistance and welding performance, belonging to a new era of high-strength weldable structure material. Al-Zn-Mg- Sc-Zr alloy can be applied to aerospace, nuclear energy and ship industries [1-3]. Many investigations on Al-Zn-Mg alloy containing Sc have been reported [4-8]. KIM et al [4] investigated the effect of the addition of Sc on the hot-worked Al-Zn-Mg alloy. The results indicated that 0.3% Sc can refine the grain, and the strength and elongation of the alloy increased with the increase of Sc content. DEV et al [5] investigated the effect of Sc addition on microstructure and properties of welding seam. The results indicated that the addition of Sc can refine the grain in welding seam, so as to decrease the density of solidification crack and to increase the strength of the welding seam. YIN et al [7] and HE et al [8] investigated the preparation, microstructure and properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy. Both of their results indicated that the high strength of the alloy was mainly associated with the fine grain strengthening caused by the addition of Sc and Zr, the subgrain strengthening and precipitation strengthening of Al3(Sc,Zr) particles and η′ precipitates. However, systematic studies on the deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy during hot compression have not been reported yet. There is lack of relevant theoretical basis for the actual hot-working processing parameters. In this work, the effects of deformation conditions on the flow behavior and microstructural evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy during compression deformation at elevated temperatures are investigated, which hopefully can provide indispensable information for optimizing the existing rolling processing parameters.
2 Experimental
The experimental Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy was prepared with pure Al, Zn, Mg and Al-Cu, Al-Mn, Al-Sc, Al-Zr master alloys by ingot metallurgy in a resistance furnace. The ingot whose nominal composition is given in Table 1 was homogenized at 460 ℃ for 24 h, and then machined to cylindrical specimens with size of d10 mm×15 mm. Convex depressions of 0.2 mm depth were additionally machined on both ends of the specimen in order to entrap the lubricant of graphite mixed with machine oil during compression tests, so that the friction between the specimen and the die surface could be minimized.
Table 1 Nominal composition of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zn alloy (mass fraction, %)

The isothermal axisymmetric hot compression tests of Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy were carried out on a Gleeble-1500 thermal mechanical simulator, at temperatures of 340, 380, 420, 460 and 500 ℃ with strain rates of 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0 and 10 s-1, respectively. Each specimen was first heated up to the deformation temperature and held isothermally for 180 s prior to initiation of compressing. After being compressed to a nominal strain of 0.6, the specimen was immediately quenched in water and then sectioned parallel to the compression axis. The cutting samples were prepared by conventional methods for microstructural observations on a POLYVER-MET metallographic microscope and a TECNAI G2 20 transmission electron microscope (TEM).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flow stress behavior
The typical true stress—true strain curves obtained during hot compression of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy are shown in Fig.1. It can be seen that in the initial stage of deformation, the flow stress increased sharply as the strain increased, until a peak stress exhibited at a certain strain. Then the flow stress mainly kept constant or gradually decreased with increasing the strain. The deformation at elevated temperatures is a competing process of the dynamic softening and the work hardening [9]. At the beginning of the deformation, the dislocation density increases dramatically. Consequently, the work hardening exceeds the dynamic softening, leading to the rapid increase in stress. As the deformation progresses, the dynamic softening, i.e. dynamic recovery or dynamic recrystallization occurs, which can offset or partially offset the effect of the work hardening. Figure 1(a) shows the typical curves featured in dynamic recrystallization, while Fig. 1(e) demonstrates the characteristics of dynamic recovery, which is a periodic variation between stress concentration and stress relaxation.
Figure 1 also reveals that the peak flow stress fluctuated under different deformation conditions. At a given deforming temperature, the peak stress increased with increasing the strain rate. And at a given strain rate, the peak stress decreased with increasing the deformation temperature. Dynamic softening is a common characteristic for many aluminum alloys deformed at elevated temperatures. The actual soften mechanism will be discussed in detail in the following sections by comparison with the deformation activation energy calculations and microstructural observations.
3.2 Constitutive equations
The hot deformation of metallic materials is a thermal activation process. Similar to the creep phenomenon, the strain rate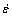 is related to the temperature T, the deformation activation energy Q and the stress σ by the Arrhenius equation expressed as:
is related to the temperature T, the deformation activation energy Q and the stress σ by the Arrhenius equation expressed as:
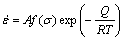 (1)
(1)
where Q is the deformation activation energy, R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, A is a material constant and f(σ) is the stress function which can be expressed by any of the following equations [10-13]:
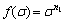 (2)
(2)
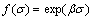 (3)
(3)
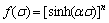 (4)
(4)
where the term α is the stress multiplier; n1, n and β are material constants; σ is generally taken as the peak flow stress σp [14,15]. By substituting Eqs. (2) and (3) separately into Eq. (1), the power law equation and the exponential equation can be got respectively. The former breaks down at high stress values, while the latter breaks down at low stress values [5,14,15]. Over a wide range of stresses, the hyperbolic-sine law is considered to be the most suitable expression for explaining the hot deformation behavior. Combining Eq. (1) with Eq. (4), the constitutive equation can obtained as:
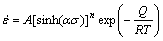 (5)
(5)
In order to correlate the strain rate, the deformation temperature and the deformation activation energy, the Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z) has been proposed [12], which can be expressed as:
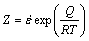 (6)
(6)
Combining Eqs. (5) and (6), the Z parameter as a hyperbolic-sine function can be obtained:
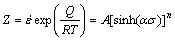 (7)
(7)
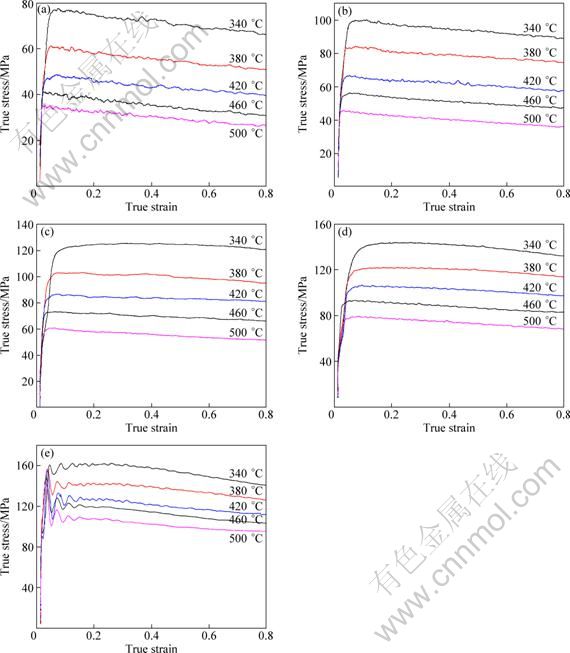
Fig. 1 True stress—true strain curves of alloy at different strain rates and temperatures: (a) 0.001 s-1; (b) 0.01 s-1; (c) 0.1 s-1; (d) 1 s-1; (e) 10 s-1
In the present study, the peak flow stress (σp) is taken for the σ term in the above expressions. Determination of the value of the stress multiplier α to obtain the best fit is of great significance in the analysis of the results. Though no single solution for α exists and its value for Al alloys in the literature varies from 0.01 to 0.08 [14,16], the value of α can also be defined as α≈β/n1 [17], where β and n1 can be determined through the linear regression of ln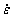 vs σ data and ln
vs σ data and ln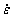 vs ln σ data, respectively, under the deformation temperatures from 340 ℃ to 500 ℃. The values of β and n1 are taken as the average values of the slopes of ln
vs ln σ data, respectively, under the deformation temperatures from 340 ℃ to 500 ℃. The values of β and n1 are taken as the average values of the slopes of ln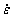 vs σ plots and ln
vs σ plots and ln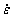 vs ln σ plots in Fig. 2. And the value of α is therefore determined as 0.0114 for the Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy.
vs ln σ plots in Fig. 2. And the value of α is therefore determined as 0.0114 for the Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy.
It can also be noted that α is important only for the convenience of the mathematical fitting for obtaining linear parallel lines of the ln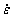 vs ln[sinh(ασ)] plots [9,14-16], which in this case is shown in Fig. 3(a), using the above α value of 0.0114.
vs ln[sinh(ασ)] plots [9,14-16], which in this case is shown in Fig. 3(a), using the above α value of 0.0114.
The deformation activation energy Q is determined from the following relationship [16,18]:
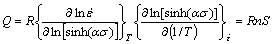 (8)
(8)
where n is the average slope of ln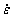 vs ln[sinh(ασ)] plots at various deformation temperatures and S is the mean slope of the ln[sinh(ασ)] vs (1000/T) plots at different strain rates. These plots for Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy are shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b).
vs ln[sinh(ασ)] plots at various deformation temperatures and S is the mean slope of the ln[sinh(ασ)] vs (1000/T) plots at different strain rates. These plots for Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy are shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b).
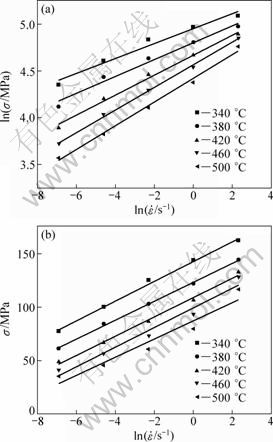
Fig. 2 Relationships between σ and : (a) lnσ vs ln
: (a) lnσ vs ln ; (b) σ vs ln
; (b) σ vs ln
The variation of the flow stress under different deformation conditions can be well illustrated by the Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z) as Eq. (7). Taking natural logarithm of both sides of Eq. (7), we have another expression for the Z parameter:
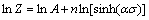 (9)
(9)
where A and n are determined through the linear regression of ln Z-ln[sinh(ασ)] data. As shown in Table 2, the values of ln Z at various strain rates and deformation temperatures can be calculated using Eq. (6). It is evident that Z value increases with increasing the strain rate and decreasing the deformation temperature, which is similar to the variation of the peak flow stress (σp) shown in Fig. 1. The reported literatures indicated that dynamic recrystallization is generally more pronounced at low Z values [9,11,16,17,18]. Figure 3(c) shows the ln Z vs ln[sinh(ασ)] plot, indicating an ideal linear fitting for the alloy studied. Table 3 presents some constants and Q value of the alloy.
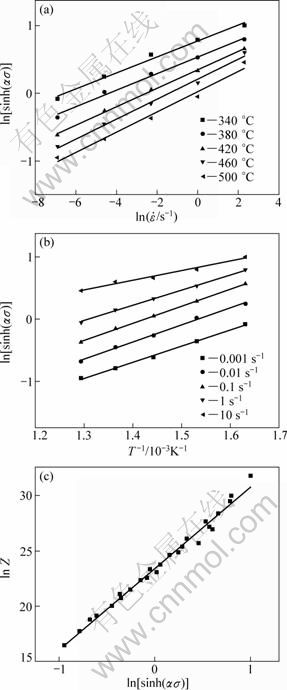
Fig. 3 Relationships between 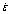 , T-1, ln Z and σ: (a) ln[sinh(ασ)] vs ln
, T-1, ln Z and σ: (a) ln[sinh(ασ)] vs ln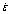 ; (b) ln[sinh(ασ)] vs 1000/T; (c) ln Z vs ln[sinh(ασ)]
; (b) ln[sinh(ασ)] vs 1000/T; (c) ln Z vs ln[sinh(ασ)]
Table 2 ln Z values of specimens under different deforming conditions
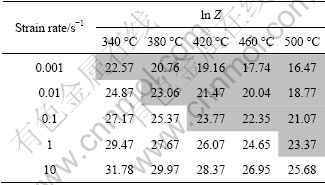
Table 3 Constants and Q value of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy

By substituting all of the above values into Eq.(5), we can get the constitutive equation of Al-Zn-Mg- 0.25Sc-Zr alloy under hot compression deformation, with a deformation activation energy of 150.25 kJ/mol.
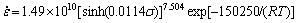 (10)
(10)
3.3 Microstructural evolution
Figure 4 shows the optical microstructures of Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr alloy deformed under different deformation conditions. Only elongated grains are observed in Fig. 4(a) at the temperature of 420 ℃ with the strain rate of 10 s-1. While at lower strain rates (Figs. 4(b) and (c)), the microstructures are composed of elongated grains along with some newly refined grains, indicating that partial dynamic recrystallization occurred in evidence during hot compression deformation. And the recrystallized grain size increased with decreasing the strain rate. With increasing the deformation temperature and decreasing the strain rate, both the grain size and the volume fraction of the recrystallized grains increased (Fig. 4(d)). So, the tendency of dynamic recrystallization is dependent sensitively on the deformation temperature and the strain rate, which can be described by one single Z parameter.
Table 2 shows the ln Z values of the specimens deformed under different conditions. The shadow area demonstrates the probable occurrence of partial or full dynamic recrystallization. It is thus obvious that dynamic recrystallization only takes place at low Z values, which must be below or equal to e23.77s-1. With lower Z values, the tendency of dynamic recrystallization enhances.
Figure 4 also reveals that at lower deforming temperatures and higher strain rates, there are a large quantity of second-phase particles inside the grains and pinning on the grain boundaries, which hinder the grain boundary slipping. Thus, the deformation resistance is enhanced. With increasing the deformation temperature or decreasing the strain rate, the second-phase particles reduce, making the grain boundaries easy to slip, and the deformation resistance decreases.
TEM images of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy deformed under different conditions are shown in Fig. 5. At high Z values, the dislocations reorganize through sliding and climbing, which leads to a slight decrease in dislocation density and the formation of the dislocation walls. As the deformation proceeds, some dislocation walls segment the grains and sub-structures form as shown in Fig. 5(a). The main softening mechanism at high Z values remains to be dynamic recovery rather than dynamic recrystallization. With decreasing Z value, the sufficient migration of metallic atoms and dislocations lead to the merging of some subgrains, as shown in Fig. 5(b), and the low-angle grain boundaries transform into high-angle grain boundaries through absorbing dislocations. Then the recrystallized nucleus form (Fig. 5(d)), and the grain boundaries become straight and clear (Figs. 5(c) and (d)). Subsequently, the recrystallized grains grow through the migration of dislocations and high-angle grain boundaries. Consequently, with decreasing Z value, that is increasing the deformation temperature and/or decreasing the strain rate, the subgrain size increases while the dislocation density decreases, as seen in Fig. 5. The main softening mechanism of Al-Zn-Mg- 0.25Sc-Zr alloy transforms from dynamic recovery to dynamic recrystallization, as shown in Fig. 4. Correspondingly, the flow stress decreases dramatically at certain points in Fig. 1.
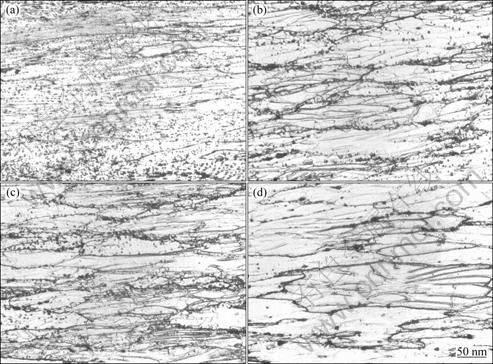
Fig. 4 Optical microstructures of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy deformed under different conditions: (a) 420 ℃, 10 s-1; (b) 420 ℃, 0.1 s-1; (c) 420 ℃, 0.001 s-1; (d) 500 ℃, 0.1 s-1
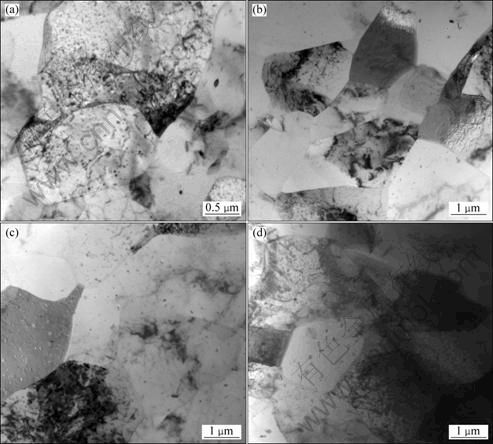
Fig. 5 TEM images of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy deformed under different conditions: (a) 420 ℃, 10 s-1; (b) 420 ℃, 0.1 s-1; (c) 420 ℃, 0.01 s-1; (d) 460 ℃, 0.1 s-1
4 Conclusions
1) The steady flow stress increases with increasing the strain rate or decreasing the deformation temperature, which can be described by a hyperbolic-sine constitutive equation with the deformation activation energy of 150.25 kJ/mol.
2) Dynamic recrystallization only occurs at low Z values, which must be below or equal to e23.77s-1. The tendency of dynamic recrystallization enhances at lower Z values which correspond to high deformation temperatures and low strain rates.
3) With decreasing Z value, the main softening mechanism of the alloy transforms from dynamic recovery to dynamic recrystallization, correspondingly, the subgrain size increases and the dislocation density decreases.
References
[1] YANG Zhi-qiang, YIN Zhi-min. Research and development of aluminium-scandium alloy in Russia [J]. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2003, 31(11): 34-40. (in Chinese)
[2] YIN Zhi-min, PAN Qing-lin, JIANG Feng, LI Han-guang. Scandium and its alloys [M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2007: 421-423. (in Chinese)
[3] LING Zhao-yi. Introduction of the development of new aluminum alloys—Aluminum and scandium alloys [J]. Materials Guide, 1992(3): 10-16. (in Chinese)
[4] KIM J H, KIM J H, YEOM J T, LEE D G, LIM S G, PARK N K. Effect of scandium content on the hot extrusion of Al-Zn-Mg-(Sc) alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 187-188: 635-639.
[5] DEV S, STUART A A, KUMAAR R C R D, MURTY B S, RAO K P. Effect of scandium additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg alloy welds [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 467(1-2): 132-138.
[6] DOMACK M S, DICUS D L. Evaluation of Sc-bearing aluminum alloy C557 for aerospace applications [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2002, 396-402: 839-847.
[7] YIN Zhi-min, JIANG Feng, PAN Qing-lin, GUO Fei-yue, ZHU Da-peng, SONG Lian-peng, ZENG Yu, WANG Tao. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Mg and Al-Zn-Mg based alloys containing minor scandium zirconium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13(3): 515-520.
[8] HE Zhen-bo, YIN Zhi-min, LIN Sen, DENG Ying, SHANG Bao-chuan, ZHOU Xiang. Preparation, microstructure and properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy tubes[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(4): 641-646.
[9] LIU Xiao-yan, PAN Qing-lin, HE Yun-bin, LI Wen-bin, LIANG Wen-jie, YIN Zhi-min. Flow behavior and microstructural evolution of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy during hot compression deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 500: 150-154.
[10] POIRIER J P. Crystal plastic deformation at high temperature [M]. GUAN De-lin, transl. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 1989. (in Chinese)
[11] SHEN Jian. Study on the plastic deformation behavior of 2091 Al alloy at elevated temperatures [D]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology, 1996. (in Chinese)
[12] JONAS J J, SELLARS C M, TEGART M W J. Strength and structure under hot working conditions [J]. International Metallurgical Reviews, 1969, 130(14): l-24.
[13] SHEPPARD T, PARSON N C, ZAIDI M A. Dynamic recrystallization in Al-7Mg alloy [J]. Metal Science, 1983, 17(10): 481-490.
[14] McQUEEN H J, RYAN N D. Constitutive analysis in hot working [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 322(1-2): 43-63.
[15] MEDINA S F, HERNANDEZ C A. General expression of the Zener-Hollomon parameter as a function of the chemical composition of low alloy and microalloyed steels [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(1): 137-148.
[16] BARDI F, CABIBBO M, EVANGELISTA E, SPIGARELLI S, VUKCEVIC M. An analysis of hot deformation of an Al–Cu–Mg alloy produced by powder metallurgy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 339(1-2): 43-52.
[17] CHEN Z Y, XU S Q, DONG X H. Deformation behavior of AA6063 aluminium alloy after removing friction effect under hot working conditions [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 21(6): 451-458.
[18] ZHANG Hui, JIN Neng-ping, CHEN Jiang-hua. Hot deformation behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr aluminum alloys during compression at elevated temperature [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 437-442.
Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr合金的热压缩变形行为和微观组织演化
张志野1,潘清林1,2,周 坚1,刘晓艳1,陈 琴1
1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用等温轴对称热压缩实验对Al-Zn-Mg-0.25Sc-Zr合金的热变形行为和微观组织演化进行研究。变形温度为340~500 ℃,应变速率为0.001~10 s-1。结果表明:稳态流变应力随着应变速率的增加和变形温度的降低而增大,该合金的流变应力行为可用双曲正弦形式的本构方程来描述,其变形激活能为150.25 kJ/mol。在变形温度较高和应变速率较低(即Z参数较低)的条件下,动态再结晶更容易发生。随着Z参数的变小,合金的主要软化机制由动态回复转变为动态再结晶,合金中的位错密度降低,亚晶尺寸增大。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金;热变形;流变行为;微观组织演化
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (2012CB619503) supported by the High-tech Research and Development Program of China
Corresponding author: PAN Qing-lin; Tel/Fax: +86-731-88830933; E-mail: pql@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61355-1