文章编号:1004-0609(2007)07-1160-06
LaNi4.5Al0.5储氢合金固溶相的密度泛函研究
陈 东1,周理海1,余本海1,王春雷1,高 涛2,张东玲1
(1. 信阳师范学院 物理电子工程学院,信阳 464000;
2. 四川大学 原子与分子物理研究所,成都 610065)
摘 要:基于密度泛函理论,采用全势线性缀加平面波方法(FLAPW),研究LaNi4.5Al0.5储氢合金固溶相α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5和α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0中H原子的占位、态密度和电子密度,分析了H原子的加入对固溶体电子结构和稳定性的影响。结果表明:从能量角度计算得到α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5中H原子最可能占据靠近Al的6m位,α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0中的两个H原子最可能占据6m和4h*位;随着H原子的增加,晶胞主要沿着c轴方向膨胀;Al和Ni, H 之间的相互作用是合金含氢固溶体保持稳定的主要因素;态密度图中低能量区域的态密度越大固溶体越稳定;如果EF处于带隙的底部,则体系较稳定。计算结果与已有的实验结果非常一致。
关键词:LaNi4.5Al0.5合金;密度泛函理论;线性缀加平面波方法(FLAPW);固溶相
中图分类号:TG 139.7 文献标识码:A
Density functional theory study on solid solution phase
of LaNi4.5Al0.5 hydrogen storage alloys
CHEN Dong1, ZHOU Li-hai1, YU Ben-hai1, WANG Chun-lei1, GAO Tao2, ZHANG Dong-ling1
(1. School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Xinyang Normal University, Xinyang 464000, China;
2. Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
Abstract: Based on the density functional theory (DFT) and full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FLAPW) method, the hydrogen occupied sites, electron densities and densities of states were analyzed for the solid solution phase α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 and α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0. The hydrogen atom in α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 is found to prefer the 6m position near aluminum atom, the two hydrogen atoms in α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5H1.0 are most likely to take the 6m and 4h* sites by total energy minimization calculation. The lattice expansion is mainly along the c axis. The interaction between aluminum and nickel, hydrogen plays a dominant role in the stability of LaNi4.5Al0.5Hx solid solution phase. The smaller the shift of EF towards higher energy region, the more stable the compounds will be. The calculated results are compared with the existent experimental data and discussed in light of previous works.
Key words: LaNi4.5Al0.5 alloys; density functional theory; full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FLAPW) method; solid solution phase
LaNi5合金是稀土系储氢合金的典型代表,它具有储氢量大、易活化、平衡压力适中、吸放氢速度快等优点[1-2]。为了满足实际工作的需要,人们用金属M取代部分Ni形成合金LaNi5-yMy(M=Fe,Co,Mn,Al等),其中Al无论从价格、稳定性和易熔炼等角度都具有优越性。当Al含量适中时,合金的储氢量减少不多,但其稳定性和热力学性质都能得到明显改善。
近年来,人们对La-Ni-Al合金固溶体进行了深入研究,认为在固溶体中,H原子只占据部分格位,其合金结构仍然保持不变。然而,目前对于合金固溶体中H原子的占位及其电子结构的实验研究仍然很少;而了解氢在合金中的占位以及由此引起的合金电子结构的变化,可以更好地研究晶体结构的各向异性膨胀和对合金热力学性质的影响,对合金的优化设计起指导作用。
本文作者基于密度泛函理论,采用全势线性缀加平面波(Full-potential linearized augmented plane wave, FLAPW)方法,从原子水平上计算分析LaNi4.5Al0.5Hx的晶体结构,首次发现H原子最有可能占据的格位,并分析Al和H对晶体几何结构和电子结构的影响。
1 计算模型及理论方法
1.1 晶体结构
LaNi5具有CaCu5型晶体结构,其中La占1a(0,0,0),Ni占据2c(0.3333,0.6667,0)和3g(0.5,0, 0.5)Wyckoff格位,属于六方晶系,空间群为P6/mmm。为了解决LaNi4.5Al0.5中Al含量是分数的问题,本模拟中构建了双晶胞模型:沿z方向构建两个LaNi5晶胞,然后使用Al原子取代一个Ni原子。Jensen等[3]通过X射线粉末衍射法分析认为,对于LaNi5-xAlx而言,当x≤1.3时,合金仍保持CaCu5结构;Szajek[4]对LaNi4Al的研究认为,Al原子优先占据3g格位; Percheron[5-6]认为Al原子只能占据3g格位;Zhang 等[7]认为三元合金LaNi4.5Al0.5中Al原子之间不能相邻。因此本文作者构建了Al原子替代3g格位(0.5a, 0.5a, 0.75c)处的Ni原子的双晶胞模型,其中含有2个La原子、9个Ni原子、1个Al原子;用公式表示 为2La+9Ni+ Al=2( LaNi4.5Al0.5),其结构示意图如图1所示。
1.2 理论方法
本计算采用全势线性缀加平面波方法,该方法是计算晶体电子结构最精确的方法之一。在计算中首先从密度泛函理论出发,将晶体的多电子Schr?dinger方程化为单电子Schr?dinger方程(Kohn-Sham方程),然后通过引入线性缀加平面波基函数对单电子Kohn-Sham方程进行计算,同时引入广义梯度近似理论(GGA)将单电子的交换能表示为电子密度及其梯度的函数,对于该项有不同的简化方法,本计算使用PBE96[8]。对LaNi5的计算表明,该方法与实验结果最为接近[9]。线性缀加平面波方法中基函数的选取和对Kohn-Sham方程自洽场求解时势能模型的建立都采用“Muffin-Tin”模型。

图1 LaNi4.5Al0.5的双晶胞结构
Fig.1 Structure of double unit cell of LaNi4.5Al0.5
本计算采用WIEN2k软件,上述方法已包含在该程序中[10]。
2 计算结果及分析
本模拟中所有计算都是在密度泛函理论框架下进行的。计算中La、Ni、Al、H的Muffin-tin半径分别取为1.32、1.23、1.15和0.37 nm。进行初始化时,采用PBE96方法处理电子的交换相关能,选取能量 -81.6 eV分开内层电子和价电子,各原子的电子组态分别为:La 5s25p65d16s2,Ni 3p63d84s2,Al 3s23p1,H 1s1。采用Monkhorst-Pack方法,在不可约布里渊区内取300个k点,平面波截断能量取300 eV,球内球谐波函数展开指数取为12.0。进行结构优化时,采用如下两步交替法:1) 保持c/a不变,变化体积V;2) 保持体积V不变,变化c/a比值。两种运算分别反复进行,直到前后两次计算结果之差小于1%。在能量求解自洽场迭代过程中收敛精度控制为ΔΕ≤0.001 36 eV。本计算采用牛顿力学方法对每个原子的平衡位置进行初步优化,在计算中考虑相对论效应。
2.1 优化计算结果
由于化学键和能带填充情况的变化,因此H原子的加入将直接影响到合金的晶胞体积和电荷相互作用。根据Westlake[11]最优模型的构造原理,在母体金属晶格中,H原子主要占据四面体和八面体空隙,且最先填充半径大于0.04nm的空隙。LaNi5单胞中共含有3f、4h、6m、12n和12o这5个格位,空隙半径由大至小的顺序为:6m>12n>12o>4h>3f[12]。对10种不同格位中各含有一个H原子的双胞进行计算,求出H原子占据何格位后晶胞的总能量最低,依照能量判据,认为该位置就是H原子最可能占据的位置。为了得到最优结果,对晶胞进行结构优化和内坐标弛豫。结果如表1和表2所列。
表1和表2中不带‘*’号的空隙位置代表靠近Al原子一侧的格位。由表可以看到,H原子取代6m格位后固溶体能量最低,H原子最可能占据6m位。计算结果与Du等[13]采用中子衍射法对LaNi5-xAlx的研究结果一致。根据Ono等[14]关于H原子进入顺序的假设可知:6m格位的能量仅次于基平面的空隙位,且空隙半径较大。考虑到Ono等的上述假设和格位的大小关系,对第二个H原子只建立6种最可能的模型,计算发现4h*格位是H原子最可能占据的位置。由此可见,H原子并不是按照空隙大小顺序进入合金的,这很可能是由于先加入的H原子使格位发生畸变,影响了第二个H原子进入的格位。
LaNi4.5Al0.5的晶格常数为:a=0.504 3 nm,c= 0.403 0 nm[5];LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的晶格常数为:a=0.504 3 nm,c=0.404 2 nm;LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的晶格常数为:a=0.505 5 nm,c=0.410 8 nm。可以看到,随着H原子的加入,晶胞主要沿c轴方向膨胀。
2.2 态密度分析
2.2.1 LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的态密度分析
图2所示是La的分波态密度。图3所示是LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5和La、Ni、Al的总波态密度图,图中以EF=-9.956 6 eV为零点,比LaNi4.5Al0.5的EF升高-0.165 9 eV[15],比LaNi5的升高0.069 7 eV[9],这主要是H原子和Al原子的贡献,且都是s轨道的贡献大于p轨道的。费米能级处的n(EF)为8.89,通过 [16]计算可得,LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的电子比热系数为20.97 mJ/mol,其中kB为玻尔兹曼常数。
[16]计算可得,LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的电子比热系数为20.97 mJ/mol,其中kB为玻尔兹曼常数。
因为在计算中采用双晶胞结构,所以总波态密度和各原子的分波态密度都是单胞的2倍。对比图3和图4可知,Ni原子的电子占据了导带的绝大部分权重,
表1 LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5晶胞中H原子的位置及晶胞总能量
Table 1 Total energy and interstitial sites in unit cell of LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5

表2 LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0晶胞中H原子的位置及晶胞总能量
Table 2 Total energy and interstitial sites in unit cell of LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0

费米能级EF处的态密度主要由Ni原子的3d带提供;而La的态密度主要出现在价带3.7和-16.0 eV附近,La的f分量构成了价带的主要部分。总波态密度主要是由Ni的3d和La的4f带构成的,在-7.1~-6.5 eV附近有且仅有一个带隙。
总波态密度图中-9~-5 eV处的态密度主要是H-s、Al-s和Ni-s,p,d轨道的贡献。在低能量区内,Ni

图2 La的分波态密度
Fig.2 Partial DOS of La
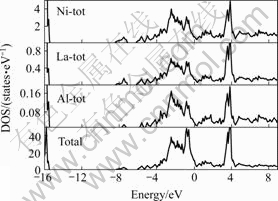
图3 La、Ni、Al以及LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的总波态密度
Fig.3 Total DOS of La, Ni, Al and LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5

图4 Ni的分波态密度
Fig.4 Partial DOS of Ni
原子对总波态密度的贡献最大,Al原子次之,H原子的贡献虽小但也不可忽略。由图3~5可知,Ni—H之间的相互作用是最强的,Al—H间的相互作用次之,H—La之间的相互作用最小。很显然,H和Ni、Al之间的相互作用是LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5合金保持稳定的主要因素。

图5 LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5合金中Al和H的分波态密度
Fig.5 Partial DOS of Al and H in LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 alloy
2.2.2 LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的态密度分析
由图6可见,LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0中H原子的s、p分量都是LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5中H原子s、p分量的近2倍,这是由于H原子增加到两个的缘故。费米能级处的n(EF)=8.91,LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的电子比热系数为21.02 mJ/mol。随着H原子的加入,晶胞费米面能量从-10.122 5、-9.956 6升高到-9.875 0 eV,而EF处的态密度从8.86、8.89增加到8.91 states/eV,这是H和Al的贡献。
在LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0中La-4f轨道和Ni-3d轨道仍是总波态密度的主要贡献者。图7中LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的总波态密度与LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5的相比变化也不明显,

图6 LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0合金中Al和H的分波态密度
Fig.6 Partial DOS of Al and H in LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0 alloy

图7 La、Ni、,Al以及LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的总波态密度
Fig.7 Total DOS of La, Ni, Al and LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0
这可能是由于H原子含量较少和H对总波态密度的贡献较小的缘故。La的态密度主要集中在3.5 eV处。带隙的宽度比α-LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5要宽,这是胞膨胀造成的。
与LaNi5的总波态密度相比[15],LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5和LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0(图3和7)的总波态密度在低能量区出现子带,其中-6 eV附近的态密度是与Al—H和Ni—H之间的相互作用相联系的;-5 eV附近的态密度则是由Ni—Al间的相互作用引起的。由于晶胞膨胀,La—Ni间的相互作用有所减弱;随着H原子的加入,费米能级处的态密度逐渐增大,体系的稳定性降低。实验得到影响体系稳定性的两个因素分别为:1) 低能量区的态密度越大,体系越稳定;2) 如果EF处于伪带隙的底部,则体系较稳定。
2.3 电子密度分析
了解电子密度的空间分布,对分析材料中的原子成键状况和研究材料特性都是非常重要的。通过电荷空间密度分布就可以得出材料中原子的成键状况。
图8和9所示分别为LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5( )面和LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0(
)面和LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0( )面的电子密度图。图中没有出现局域的键电荷,说明金属原子与H原子之间存在的是金属键。由图8可见,H原子的电子密度主要是沿Ni—H方向弥散,Al—H之间的相互作用比Ni—H之间的相互作用弱,但比La—H之间的相互作用强。Al原子虽然只是接近该面,但是与Ni原子之间仍存在一定的相互作用,这很可能是合金抗粉化能力增强的原因。La原子与H原子的电子云几乎没有发生交叠,这说明H与La这种氢化物的形成元素[16]之间的化学键很弱,这与单质元素La和H之间能形成很强的化学键是完全不同的。
)面的电子密度图。图中没有出现局域的键电荷,说明金属原子与H原子之间存在的是金属键。由图8可见,H原子的电子密度主要是沿Ni—H方向弥散,Al—H之间的相互作用比Ni—H之间的相互作用弱,但比La—H之间的相互作用强。Al原子虽然只是接近该面,但是与Ni原子之间仍存在一定的相互作用,这很可能是合金抗粉化能力增强的原因。La原子与H原子的电子云几乎没有发生交叠,这说明H与La这种氢化物的形成元素[16]之间的化学键很弱,这与单质元素La和H之间能形成很强的化学键是完全不同的。
在固溶体中可以认为H—Ni间的相互作用是合金

图8 LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 ( )面的电子密度
)面的电子密度
Fig.8 Charge density in ( ) plane of LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 (103eV/nm3)
) plane of LaNi4.5Al0.5H0.5 (103eV/nm3)
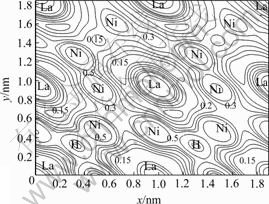
图9 LaNi4.5Al0.5H 1.0( )面的电子密度
)面的电子密度
Fig.9 Charge density in ( ) plane of LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0 (103eV/nm3)
) plane of LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0 (103eV/nm3)
吸氢和放氢的主要特征。Ni原子和La原子之间的相互作用与LaNi5相比有所减弱。吸氢后LaNi4.5Al0.5H1.0的c轴由0.403 0 nm[18]膨胀到0.410 9 nm,增大1.96%,而a轴增量小于LaNi5H3的c轴增量(5.12%)[19-20],可见Al原子的加入有效地提高了合金的抗粉化能力,增大循环寿命。
3 结论
1) 基于密度泛函理论和全势线性缀加平面波方法,研究α-LaNi4.5Al0.5Hx (x=0.5, 1.0)的电子结构和H原子占位。通过对两种固溶体中不等价格位含氢的总能最小化计算认为,第一个H原子最容易占据6m格位,第二个H原子最可能占据4h*格位;先加入的H原子引起晶格畸变,影响了后续H原子占据的位置。
2) 影响体系稳定性的两个因素为:一是低能量区的态密度越大,体系越稳定;二是如果EF处于伪带隙的底部,则体系较稳定。
3) 随着H原子的加入,晶胞主要沿着c轴方向膨胀,其各向异性增强;H—Ni之间的相互作用较强,H—Al之间的相互作用相对较弱,而H—La之间相互作用最弱;Al原子的加入有效提高了合金的抗粉化能力和循环寿命。
REFERENCES
[1] Nakamura H, Nguyen-Manh D, Pettifor D G. Electronic structure and energetics of LaNi5, α-La2Ni10H and β-La2Ni10H14[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1998, 281: 81-91.
[2] Kisi E H, Wu E, Kemali M. In-situ neutron powder diffraction study of annealing activated LaNi5[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2002, 330/332: 202-207.
[3] Jensen J O, Bjerrum N J. Systematic B-metal substitution in CaNi5[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1999, 293/295: 185-189.
[4] Szajek A, Jurezyk M, Rajewski W. The electronic and electrochemical properties of the LaNi5, LaNi4Al and LaNi3CoAl systems[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2000, 307: 290-296.
[5] Percheron-Guégan A, Lartigue C, Achard J C. Neutron and X-ray diffraction profile analyses and structure of LaNi5, LaNi5-xAlx and LaNi5-xMnx intermetallics and their hydrides(deuterides)[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1980, 74: 1-12.
[6] Lartigue C, Percheron-Guégan A, Achard J C. Hydrogen (deuterium) ordering in the β-LaNi5Dx (x>5) phases: a neutron diffraction study[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1980, 75: 23-29.
[7] Zhang R J, Wang Y M, Lu M Q, Xu D S, Yang K. First-principles study on the crystal, electronic structure and stability of LaNi5-xAlx (x=0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1)[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 3445-3452.
[8] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77: 3865-3868.
[9] 齐新华, 高 涛, 朱正和, 李跃勋, 陈 波, 范智剑. LaNi5电子与能量结构的全电子计算[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2004, 21: 366-372.
QI Xin-hua, GAO Tao, ZHU Zheng-he, LI Yue-xun, CHEN Bo, FAN Zhi-jian. Full-electronic calculations on the equilibrium structure and energy of LaNi5 crystal[J]. J At Mol Phys, 2004, 21: 366-372.
[10] Schwarz K, Blaha P. Solid-state calculation using WIEN2k[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2003, 28: 259-273.
[11] Westlake D G. A geometric model for the stoichiometry and interstitial site occupancy in hydrides(deuterides) of LaNi5, LaNi4Al and LaNi4Mn[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1983, 91: 275-292.
[12] Soubeyroux J L, Percheron-Guégan A, Achard J C. Localization of hydrogen (deuterium) in –LaNi5Hx (x=0.1 and 0.4)[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1987, 129: 181-186.
[13] Du H L, Zhang W Y, Wang C S, Wang J Z, Han J Z, Yang Y C, Chen B, Xie C M, Sun K, Zhang B S. Neutron powder diffraction study on the structures of LaNi5-xAlxDy compounds[J]. Solid State Communications, 2003, 128: 157-161.
[14] Ono S, Nomura K, Akiba K. Phase transformations of the LaNi5-H2 system[J]. J Less-Common Met, 1985, 113: 113-117.
[15] 高 涛, 齐新华, 陈 波. Al合金化对LaNi5-xAlx的结构影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15: 1092-1099.
GAO Tao, QI Xin-hua, CHEN Bo. Alloying effects on electronic structures of LaNi5-xAlx[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15: 1092-1099.
[16] Hector L G Jr, Herbst J F, Capehart T W. Electronic structure calculations for LaNi5 and LaNi5H7: energetics and elastic properties[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2003, 353: 74-85.
[17] Van Vucht J H N, Kuipers F A, Bruning H C M, et al. Reversible room-temperature absorptions large quamtities of hydrogen by intermetallic compounds[J]. Philips Res Repts, 1970, 25: 133-140.
[18] 康 龙, 罗永春. LaNi5-xAlx贮氢合金的研究[J]. 稀土, 1996, 22: 11-15.
KANG Long, LUO Yong-chun. Research on LaNi5-xAlx hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Rare Earth, 1996, 22: 11-15.
[19] 齐新华, 高 涛, 陈 波. α-LaNi5H0.5与β-LaNi5H3的全电子优化计算[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41(9): 910-916.
QI Xin-hua, GAO Tao, CHEN Bo. Full-electron calculation of α-LaNi5H0.5 and β-LaNi5H3[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2005, 41(9): 910-916.
[20] 王 宏, 刘祖岩. LaNi5最大储氢量的晶体结构分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004, 33: 239-241.
WANG Hong, LIU Zu-yan. Crystal structure analysis on maximum hydrogen capacity of LaNi5[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33: 239-241.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学-中国工程物理研究院联合基金(10276027)
收稿日期:2006-09-20;修订日期:2007-03-12
通讯作者:陈 东;电话:13253854009; E-mail: chchendong2010@163.com