DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37725
废旧电路板的低温熔融混碱处理和有价金属提取
马浩博1, 2,朱明伟1,何 杰2,陈 斌2,张丽丽2,江鸿翔2,孙小钧2,赵九洲2
(1. 沈阳航空航天大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110136;
2. 中国科学院金属研究所,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:废旧电路板是一种物理结构和化学组成复杂的固体废物,蕴藏丰富的有价金属资源。本文以废旧电路板中处理难度较大的内存条为对象,开展废旧内存条(WMM)低温熔融混碱(MH)处理回收研究,考察温度、时间、物料比等工艺参数对内存条非金属与金属解离的影响,探讨了熔融碱处理过程中内存条非金属(溴化环氧树脂、玻璃纤维等)的降解机理。研究发现,当温度为400 ℃、碱与内存条物料比mMH/mWMM为5时,在反应釜中持续反应60 min后,内存条中非金属物料的降解率可达95.45%,最终获得由Cu、Fe、Ni及贵金属Au、Ag等组成的混合多金属产物。
关键词:金属回收、废旧电路板、废旧内存条、熔碱处理
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-02-0443-10 中图分类号:TF111 文献标志码:A
引文格式:马浩博, 朱明伟, 何 杰, 等. 废旧电路板的低温熔融混碱处理和有价金属提取[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(2): 443-452. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37725
MA Hao-bo, ZHU Ming-wei, HE Jie, et al. Pyrolysis processing and metal recycling of waste circuit boards by using low-temperature alkaline melts[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(2): 443-452. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37725
随着电子制造业的快速发展,电子电器设备不断更新换代,导致大量电子废弃物(Waste electrical and electronic equipment,WEEE)的产生。电路板约占电子电器产品的3%~5%,2025年我国每年废旧电路板总量将达到45万t[1-4]。通常,电路板以玻璃纤维为骨架,以溴化环氧树脂作为黏结剂,将金属铜箔和玻璃纤维连接,形成结构复杂且外力作用下难以破坏的复合材料。研究表明,电路板含有丰富的有价金属,如Cu、Fe、Ni、Pb、Sn、Zn等常见金属,以及Au、Ag、Pt、Pd、Sb等稀贵金属。这其中一些金属的含量相当于天然矿物中金属品位的几十倍至上百倍[5-7]。据估计每吨废旧电路板可提取Au约0.2~0.3 kg、Ag 1~2 kg、Sn 25~30 kg、Cu 130~150 kg、Ni 25~30 kg,回收价值十分可观[8]。然而,在废旧电路板中同时含有大量有毒害的重金属如Pb、Cd、Cr等,而且在其回收处理过程中,溴化环氧树脂中的大量卤素可生成卤代类二恶英(多溴代二苯二恶英(PBDDs)及多溴代二苯呋喃(PBDFs))等有毒物质[9]。由此可见,废旧电路板的合理回收对缓解我国有色金属资源紧缺具有重要意义。由于废旧电路板的物理结构复杂且化学组分具有危害性,回收处理过程存在诸多挑战。近年来,国内外科研工作者发展了多种废旧电路板回收处理方法,如机械处理、火法冶金、湿法冶金、生物冶金等[10-16]。
机械处理,是指先用破(粉)碎设备将电路板变成颗粒,再根据金属与非金属之间的物性差异采用分选技术将金属颗粒与非金属颗粒分离的方法[13]。火法冶金是由简单的露天焚烧技术发展起来的一种方法。将废旧电路板在高温冶炼炉中加热,非金属物料焚烧后形成浮渣而金属物料则呈合金熔体流出,再经电解处理提取金属铜和贵金属[14]。湿法冶金,是将废旧电路板置于浓硝酸、硫酸或王水等强酸或强氧化剂溶液中,金属物质与之发生化学反应溶解后剥离沉淀物,然后利用络合、分离、还原、结晶或萃取等反应,选择性提取溶液中贵金属如Au、Ag、Pd等的过程[15]。生物冶金,是利用某种微生物或其代谢产物与废旧电路板中金属的相互作用,通过吸附、氧化、还原、浸取等反应实现电路板中有价金属回收[16]。每种方法均具有自身的优势和不足,如表1所示。
基于熔融盐氧化技术[17-18],本文以共晶成分的NaOH-KOH混合碱为反应介质,以废旧电路板中处理难度最大的内存条为对象,开展内存条低温熔融混碱处理及有价金属回收研究。相对于常规电路板热解,共晶成分的NaOH-KOH混合碱具有较低的熔化温度(170 ℃),废旧电路板在该熔碱介质中热解不但可以降低能耗,而且溴化环氧树脂热解过程中产生的绝大部分卤素和二氧化碳被熔盐吸收,进而有效抑制卤代类二恶英等有毒性物质的生成。
1 实验
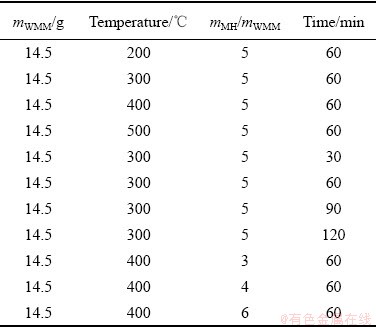
本研究所用废旧内存条由某废旧电脑市场提供,实验前将内存条剪成10 mm×10 mm的小块,并在烘箱中恒温100 ℃烘干1 h。按照质量分数41%NaOH-59%KOH配置混碱,其中NaOH和KOH均为分析纯。
将混碱(Mixture of hydroxides,MH)与内存条(Waste memory module,WMM)按一定质量比混合,研究反应温度和时间等参数对废旧内存条非金属降解率的影响。实验流程如图1所示,相关实验参数设置如表2所示。降解实验在自制的反应釜内进行。首先将混碱置于反应釜坩埚中,通过电阻加热,使其完全熔化,并将釜内温度稳定在设定温度。然后将块状内存条加入混碱熔体中发生反应,反应过程中通入空气;釜内反应产生的气体则经过碱性水溶液洗气吸附后排向空气。反应所得固液混合物通过规格为150目的筛网(孔径:106 μm)进行过滤,筛网上的固相残留物经清洗和烘干后进行后续分析和处理。采用下式计算非金属降解率(R):
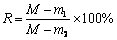 (1)
(1)
式中:M为内存条总质量;m1为反应结束后内存条剩余质量;m2为混合金属质量。
将非金属去除后的内存条通过真空电弧熔炼获得合金锭(冶炼电流为180 A,温度1800 ℃,时间3 min,氩气氛)。采用Magix Pro PW2440型X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)对内存条进行成分分析;采用配有能谱附件的Inspect F50扫描电子显微镜(SEM-EDS)表征合金的形貌及成分。
表1 废旧电路板多种回收方法比较
Table 1 Comparison of various recycling methods for WPCBs

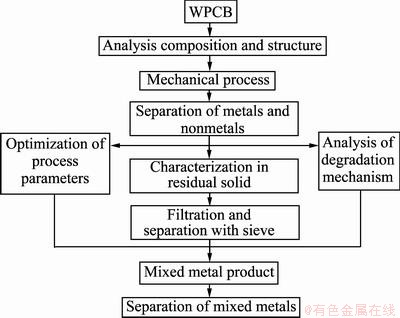
图1 废旧电路板金属回收技术路线图
Fig. 1 Flowchart for recovery and process control of metal resources in WPCBs
2 结果与分析
2.1 电路板的表征
表2 废旧内存条低温熔融碱处理实验参数
Table 2 Experimental parameters for low-temperature molten-alkaline treatment of WMMs
本研究所采用内存条为FR-4型电路板,外部构造和内部结构如图2所示。图2(a)所示为内存条平面图,内存条主体为PCB板,表面覆盖一层绿色阻焊剂(Solder mask),主要成分为丙烯酸低聚物和丙烯酸单体。PCB板上焊接着多种复杂电子器件:金黄色触点为金手指;下方细小长方体为贴片式电阻;较大黑色块体为内存芯片,两端通过白色针脚与PCB板连接;内存芯片和金手指周围装有大量微
小电容;PCB板右上角八脚小芯片为SPD。内存条断面如图2(b)中所示,内存条为层状结构,大部分金属被包裹在非金属中。上下表面黑色部分为内存芯片,主要成分为SiO2,其内部中心Si片和两侧金属针脚(平均成分为Fe60Ni40)包裹其中。电容等电子器件通过铅锡合金焊接在无阻焊剂覆盖位置,电子器件之间则通过细小铜导线连接,电容中含有贵金属Ag以及稀有金属Ti。最右侧金黄色细条为金手指,由Au、Cu、Ni组成,Au含量高达84%。PCB板内部主要由铜箔、玻璃纤维、溴化环氧树脂组成。玻璃纤维填充于铜箔中间与两侧形成类编织板结构(横截面为圆),主要成分为Al2O3、CaO、SiO2;溴化环氧树脂作为黏结剂将三者黏结在一起。由此可见,内存条物理结构复杂,这种相互包裹的结构使金属回收较为困难。

图2 废旧内存条的结构
Fig. 2 External(a) and internal(b) structure of WMM
2.2 熔融混碱中内存条非金属的降解
2.2.1 反应温度对内存条非金属降解率的影响
图3所示为物料比mMH/mWMM=5且反应时间60 min条件下,反应温度对内存条非金属降解率的影响。由图3(a)可见,非金属降解率随温度呈升高趋势。反应温度为200 ℃时非金属降解率很低,仅为36.47%;当温度达到300 ℃时,非金属降解率显著升高,达到91.9%。在此温度以上降解率随反应温度缓慢上升;当温度达到400 ℃时降解率可达95.45%,继续提高反应温度对非金属降解率影响很小。图3(b)~(d)所示分别为不同反应温度时内存条经熔碱处理后的结果。温度对内存条反应进程具有显著影响,不同反应温度下内存条的形貌变化很 大[19]。由图3(b)可见,200 ℃时内存条中玻璃纤维未发生反应,玻璃纤维与铜箔仍然通过溴化环氧树脂紧密粘连在一起。电容、电阻从内存条上脱落表明反应温度达到焊料(铅锡合金)熔化温度即可实现内存条表面焊接元件分离。与此同时,内存芯片中的Si被反应去除,但包覆在表面的SiO2则未发生反应。由此可见,200 ℃时去除的非金属主要为表面阻焊剂以及芯片中心的Si,非金属降解率很低。由图3(c)可见,300 ℃时内存条中溴化环氧树脂被降解,除中心区域外铜箔之间的玻璃纤维基本反应完全,这与文献结果一致[20]。内存芯片依然以大块形式存在,但残渣中可以看到少量小颗粒内存芯片及部分从中掉落的针脚,表明内存芯片反应很不充分。由图3(d)可见,400 ℃时内存条玻璃纤维的去除效果与300 ℃时相似,但内存芯片被完全去除,针脚从其上脱落。此时,固体非金属残渣主要为未除净的玻璃纤维、碳渣、盐和电阻。500 ℃时反应结果与400 ℃时反应结果基本相同(相关图片未在此显示)。
2.2.2 反应时间对非金属降解率的影响
图4所示为反应温度300 ℃且mMH/mWMM=5条件下,非金属降解率随反应时间的变化。由图4(a) 可见,随着反应时间增加,非金属降解率从88.84%缓慢增加至90.62%。与普通废旧电路板的处理结果不同[18],在当前处理温度下延长反应时间对非金属降解率影响不大,内存条的复杂结构导致熔碱反应的动力学条件变差。不同反应时间的结果如图4(b)~(d)所示,由图可见大部分玻璃纤维均被反应去除仅少量玻璃纤维仍存在于铜箔中心,但内存芯片只有少量发生反应。反应结果随时间无明显变化,尽管反应时间延长1倍仍不能达到400 ℃时的去除效果,表明采用降低温度延长时间的方式无法提高非金属的降解率,温度对反应进程(尤其是内存芯片的反应)至关重要。综合考虑能源消耗及非金属去除效果,选择400 ℃作为反应温度。
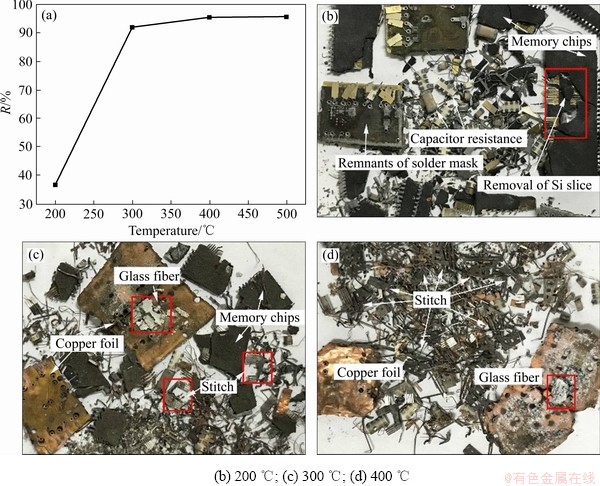
图3 废旧内存条非金属降解率随温度的变化及不同温度处理后对应内存条的宏观形貌
Fig. 3 Non-metal degradation rate of WMMs as function of reaction temperature(a) and macroscopic morphologies((b), (c), (d)) of corresponding WMMs after reacting with alkaline melts at different temperatures

图4 废旧内存条中非金属降解率随时间的变化及不同时间处理后对应内存条的宏观形貌
Fig. 4 Non-metal degradation rate of WMMs as function of reaction time(a) and macroscopic morphologies((b), (c), (d)) of corresponding WMMs after reacting with alkaline melts for different times
2.2.3 物料比对非金属降解率的影响
图5所示为反应温度400 ℃,反应时间为60 min的条件下,物料比(mMH/mWMM )对内存条中非金属降解率的影响。由图5(a)中可见,随着物料比增加,内存条中非金属降解率逐渐增大。当物料比增至5时,进一步提高物料比对非金属降解率影响很小。不同物料比时内存条反应情况如图5(b)~(d)所示。由图5(b)可见,mMH/mWMM=3时,Si被完全去除且残渣中有少量内存芯片颗粒及大量针脚,表明大部分内存芯片被去除。铜箔表面阻焊剂以及内部环氧树脂均被去除,但撕开铜箔后仍可见玻璃纤维。由图5(c)可见,mMH/mWMM=4时,内存芯片基本去除,铜箔之间的玻璃纤维残留量变少。由图5(d)可见, mMH/mWMM=5时,铜箔之间大部分玻璃纤维已被去除。进一步增加物料比至mMH/mWMM=6时,反应情况与mMH/mWMM==5时结果相似,说明当mMH/mWMM==5时,混碱量足以保证内存条中非金属被基本去除。
综上所述,在通入空气的条件下,选取反应温度400 ℃、mMH/mWMM=5、反应时间60 min的工艺参数较为合适,内存条非金属降解率可达95.45%。
2.2.4 非金属降解机理
聚合物的分解一般属于自由基反应。当提供的能量大于键能时,键发生断裂从而产生自由基。键能较低的键会优先断裂,产生的自由基引发其他键的断裂从而导致新自由基出现。内存条中最主要有机物为双酚A型溴化环氧树脂,溴化环氧树脂在这一过程中会逐渐降解。由文献[21-22]可知,C6H5O—CH2(263 kJ/mol)<C—C(332 kJ/mol)<C6H5—Br (336.8 kJ/mol)<C6H5—O(358 kJ/mol)<C=C (605.6 kJ/mol)<C=O(736.4 kJ/mol)。因此,当能量较低时,键断裂首先从键能较弱的C6H5O—CH2处开始,降解为双酚A、四溴双酚A、异丙醇。异丙醇会发生脱水反应和脱氢反应[23],产物分别为丙烯+水、甲烷+乙醛+氢气。随着能量的提高,C—C(332 kJ/mol)、C6H5—Br(336.8 kJ/mol)、C6H5—O(358 kJ/mol)键断裂,双酚A、四溴双酚A发生均裂反应,生成溴自由基、苯酚自由基、苯自由基、异丙苯自由基和甲基。当能量进一步提高时,C=C(605.6 kJ/mol)和C=O(736.4 kJ/mol)键断裂,丙烯均裂为乙基自由基和甲基自由基,乙醛进一步分解为CO2(CO)和CH4。最后,这些自由基通过一系列的重组和结合反应生成热解产物[20]:对溴苯酚、邻溴苯酚、苯酚、邻甲基苯酚、对甲基苯酚、对苯基苯酚、对异丙基苯酚、溴化氢和甲烷等,上述反应在300 ℃基本完成。结合BOROJOVICH等[24]提出的部分降解机理,溴化环氧树脂在当前实验条件下的可能降解过程如图6所示。

图5 废旧内存条中非金属降解率随物料比的变化及不同物料比处理后对应内存条的宏观形貌
Fig. 5 Non-metal degradation rate of WMMs as function of mMH/mWMM (a) and macroscopic morphologies((b), (c), (d)) of corresponding WMMs treated by alkaline melts with different mMH/mWMM values
在碱性条件下,环氧树脂的降解产物可继续反应生成钠盐,从而促进降解反应。对溴苯酚、邻溴苯酚等含溴的芳香族化合物在强碱环境中会发生脱卤反应[25],Br被熔碱捕捉而形成NaBr;而苯酚、对甲基苯酚等酚类化合物则与强碱作用形成酚类钠盐(见图7)。由此,降解产生的大部分有机蒸气和CO2、HBr等酸性气体均被熔碱和洗气瓶中NaOH溶液吸收生成Na2CO3、NaBr等无害物质,最终排出气体中氢含量很高,可被用作燃料和化工原料[18]。
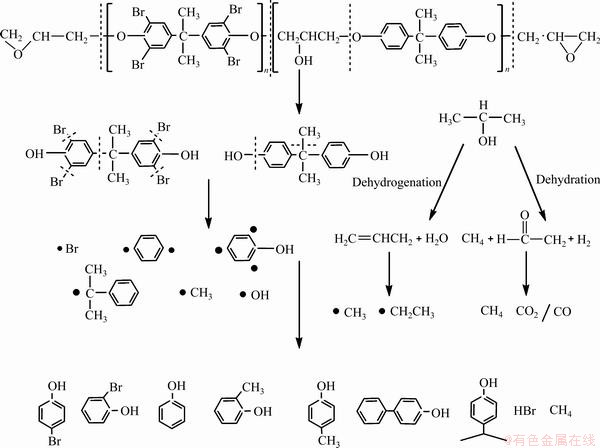
图6 内存条中溴化环氧树脂的降解路径
Fig. 6 Possible degradation path of brominated epoxy resin in WMMs
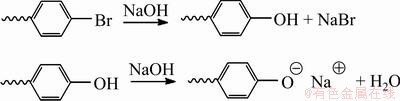
图7 芳香族化合物与强碱反应式
Fig. 7 Reaction of aromatic compounds with strong base
温度对无机非金属反应过程具有显著影响。内存芯片和玻璃纤维与熔碱主要发生如下反应(以熔融NaOH来代表熔碱):
Si+2NaOH(l)+H2O(g)=Na2SiO3+2H2(g) (2)
SiO2+2NaOH(l)=Na2SiO3+H2O (3)
Al2O3+2NaOH(l)=2NaAlO2+H2O (4)
根据Kirchhoff定律和Gibbs-Helmholtz方程可求得标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能随温度变化的函数:

 (5)
(5)
式中: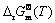 为标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能;T为反应温度;I为积分常数,a、b、c和d为各物质的热容参数;
为标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能;T为反应温度;I为积分常数,a、b、c和d为各物质的热容参数;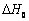 积分常数。
积分常数。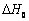 和I数值可通过将
和I数值可通过将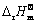 (298 K)和
(298 K)和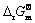 (298 K)分别带入式(5)求得。
(298 K)分别带入式(5)求得。
利用软件HSC chemistry可计算出200~500 ℃范围内式(2)~(4)的标准反应吉布斯自由能分别为-491~-486 J/mol、-107~-126 J/mol和-55~-74 J/mol。由此数据可知,在200~500 ℃之间,Si、SiO2和Al2O3均可自发与熔融NaOH反应。Si与熔融NaOH反应的驱动力更大,故200 ℃时Si即可被完全去除。反应(3)的吉布斯自由能始终比反应(4) 的吉布斯自由能低,说明在当前温度范围内SiO2比Al2O3更容易与熔碱反应。因此,在400 ℃下,主要成分为Si和SiO2的内存芯片优先与熔碱反应。玻璃纤维中Al2O3含量较高且被铜箔紧密包裹,导致SiO2不能与熔碱充分接触,故开始阶段熔碱主要与内存芯片反应,仅少量玻璃纤维被去除。随着反应进行和碱量增加,内存芯片反应完全,玻璃纤维开始充分反应,最终大部分非金属与熔碱反应而被去除。反应后熔体中除了未发生反应的KOH、NaOH,还有新生成的碳酸盐、硅酸盐、铝酸盐和溴盐。往冷却后的熔体中加入蒸馏水,将其中的不溶物过滤分离并去除溶液中的卤盐,剩余的溶液通过烘干获得混碱得以重复利用[18]。
2.3 混合金属的回收
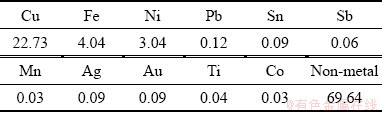
图8所示为废旧内存条熔碱处理后所得固态产物以及将其熔炼成锭后的微观组织。EDX分析表明,基体为富Cu相,平均成分为Cu90.4Ni5.21Fe4.29Sn0.1;Fe、Ni以枝晶形式分布Cu基体相中,枝晶相的平均化学成分为Fe57.32Ni23.5Cu18.73Sb0.1Mn0.11Ti0.14Co0.1。内存条中各金属成分含量如表3所示,内存条涉及的元素种类多、有价金属含量高,尤其是丰富的贵金属Au和Ag使其具有很高的循环经济价值。为了将有价金属Cu、Au、Ag与Fe、Ni分离,可根据熔碱处理后金属产物的磁性差异设计磁选分离方法直接进行初级物理分离,亦可利用原子间相互排斥作用设计Fe-Cu基金属液-液相分离系统,将其分离成富Fe和富Cu两种物料[3-4]。这为降低后续精细分离与提取过程中的能耗和二次污染提供了条件。
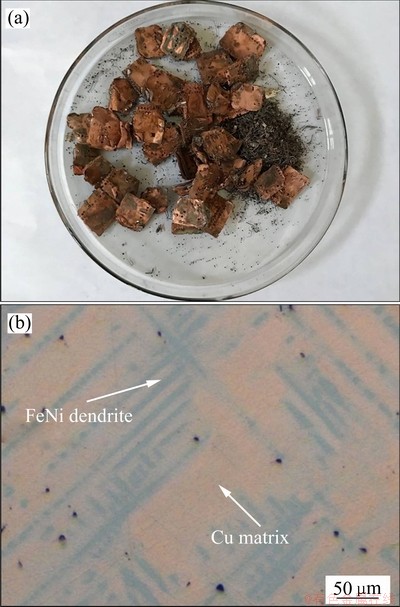
图8 温度400 ℃、时间60 min、mMH/mWMM=5时获得的混合多金属及其熔炼后的组织图像
Fig. 8 Mixed metals obtained from WMMs after reaction with mMH/mWMM=5 for 60 min at 400 ℃ (a) and microstructure of alloy after arc smelting of mixed metals (b)
表3 废旧内存条的化学成分
Table 3 Composition of WMMs employed in this work by XRF (mass fraction, %)
3 结论
1) 反应温度和物料比是影响废旧内存条非金属降解率的主要因素。随着温度从200 ℃升高至400 ℃,内存条中非金属的反应顺序为:阻焊剂→溴化环氧树脂和玻璃纤维→内存芯片,最终获得Cu、Fe、Ni、Ag、Au等混合金属产物。熔融碱处理废旧内存条的最佳工艺参数如下:反应温度为400 ℃,物料比为5,反应时间为60 min。内存条中非金属去除率可达95.45%。
2) 内存条中非金属反应主要为有机物的降解和无机物的熔碱反应。双酚A型溴化环氧树脂经过逐级断键降解为含溴的芳香族化合物、酚类化合物、CO2、HBr、H2O、H2等。CO2和溴等有害物质被熔融混碱所吸收,回收处理过程环保。无机非金属Si、SiO2及Al2O3则与熔碱反应生成相应的硅酸盐和铝酸盐经溶解洗涤去除。
REFERENCES
[1] REUTER M A. Metal recycling: Opportunities, limits, infrastructure[R]. A Report on the Global Metal Flows to the International Resource Panel, UNEP, 2013.
[2] ZHOU Y, QIU K. A new technology for recycling materials from waste printed circuit boards[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1/3): 823-828.
[3] CHEN B, HE J, XI Y Y, et al. Liquid-liquid hierarchical separation and metal recycling of waste printed circuit boards[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 364: 388-395.
[4] 陈 斌, 何 杰, 孙小钧, 等. Fe-Cu-Pb合金液-液相分离及废旧电路板混合金属分级分离与回收[J]. 金属学报, 2019, 55(6): 751-761.
CHEN Bin, HE Jie, SUN Xiao-jun, et al. Liquid-liquid phase separation of Fe-Cu-Pb alloy and its application in metal separation and recycling of waste printed circuit boards[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 55(6): 752-761.
[5] 郭学益, 江晓健, 刘静欣, 等. 梯级碱溶分步提取废弃电路板中有价金属[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(2): 406-413.
GUO Xue-yi, JIANG Xiao-jian, LIU Jing-xin, et al. Recovery of metal values from waste printed circuit boards using a cascading alkali leaching process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 406-413.
[6] LI J, SHRIVASTAVA P, GAO Z, et al. Printed circuit board recycling: A state-of-the-art survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electronics Packaging Manufacturing, 2004, 27(1): 33-42.
[7] D’ADAMO I, FERELLAA F, GASTALDIA M, et al. Towards sustainable recycling processes: Wasted printed circuit boards as a source of economic opportunities[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 2019, 149: 455-467.
[8] LI K, XU Z. Application of supercritical water to decompose brominated epoxy resin and environmental friendly recovery of metals from waste memory module[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(3): 1761-1767.
[9] DUAN H, LI J, LIU Y, et al. Characterization and inventory of PCDD/Fs and PBDD/Fs emissions from the incineration of waste printed circuit board[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(15): 6322-6328.
[10] 赵 斌, 武晓燕, 魏显珍, 等. 废线路板资源化回收技术研究与展望[J]. 再生资源与循环经济, 2016, 9(8): 31-34.
ZHAO Bin, WU Xiao-yan, WEI Xian-zhen, et al. Research and prospects of recycling technology of waste printed circuit boards[J]. Recyclable Resources and Circular Economy, 2016, 9(8): 31-34.
[11] 郭学益, 刘静欣, 田庆华. 废弃电路板多金属粉末低温碱性熔炼过程的元素行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1757-1763.
GUO Xue-yi, LIU Jing-xin, TIAN Qing-hua. Elemental behavior of multi component metal powders from waste printed circuit board during low temperature alkaline smelting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1757-1763.
[12] 郭学益, 刘子康, 黄国勇. (CH3)3COOH-NaOH体系处理废弃电路板中焊锡技术[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(1): 152-158.
GUO Xue-yi, LIU Zi-kang, HUANG Guo-yong. Recovery of solder from waste printed circuit boards in (CH3)3COOH-NaOH system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(1): 152-158.
[13] ZHANG L G, XU Z M. A review of current progress of recycling technologies for metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment[J]. J Clean Prod, 2016, 127: 19-36.
[14] HAGELüKEN C. Recycling of electronic scrap at umicore precious metals refining[J]. Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2006, (12): 111-120.
[15] KINOSHITA T, AKITA S, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Metal recovery from non-mounted printed wiring boards via hydrometallurgical processing[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 69(1/3): 73-79.
[16] 郭晓娟. 热解技术处理废弃印刷线路板的实验研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2008.
GUO Xiao-juan. Experimental study on pyrolysis of waste printed circuit boards[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2008.
[17] LIN C, CHI Y, JIN Y. Experimental study on treating waste printed circuit boards by molten salt oxidation[J]. Waste & Biomass Valorization, 2017, 8(7): 2523-2533.
[18] FLANDINET L, TEDJAR F, GHETTA V, et al. Metals recovering from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs) using molten salts[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 213: 485-490.
[19] STUHLPFARRER P, LUIDOLD S, ANTREKOWITSCH H. Recycling of waste printed circuit boards with simultaneous enrichment of special metals by using alkaline melts: A green and strategically advantageous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 307: 17-25.
[20] GAO R, ZHAN L, GUO J, et al. Research of the thermal decomposition mechanism and pyrolysis pathways from macromonomer to small molecule of waste printed circuit board[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 121234.
[21] YIN J, LI G, HE W, et al. Hydrothermal decomposition of brominated epoxy resin in waste printed circuit boards[J]. Journal of Analytical & Applied Pyrolysis, 2011, 92(1): 131-136.
[22] 湛志华. 废弃电路板环氧树脂真空热裂解实验及机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
ZHAN Zhi-hua. Vacuum pyrolysis and the mechanism research on waste epoxy printed circuit boards[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[23] KANDOLA B K, HORROCKS A R, MYLER P, et al. Thermal characterization of thermoset matrix resins[J]. ACS Symposium Series, 2001, 797(27): 345-360.
[24] BOROJOVICH E J C, AIZENSHTAT Z. Thermal behavior of brominated and polybrominated compounds I: Closed vessel conditions[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2002, 63(1): 105-128.
[25] LUDA M P, GIOVANNI C, BALABANOVICH A I, et al. Scavenging of halogen in recycling of halogen-based polymer materials[J]. Macromolecular Symposia, 2002, 180(1): 141-152.
Pyrolysis processing and metal recycling of waste circuit boards by using low-temperature alkaline melts
MA Hao-bo1, 2, ZHU Ming-wei1, HE Jie2, CHEN Bin2, ZHANG Li-li2, JIANG Hong-xiang2, SUN Xiao-jun2, ZHAO Jiu-zhou2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang Aerospace University, Shenyang 110136, China;
2. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The printed waste circuit boards(WPCBs) are not only kind of solid waste with complicated physical structure and chemical composition, but also some resources rich in valuable metals. The recycling of waste memory modules (WMMs), which is the most difficult to deal with among WPCBs, was investigated in the present work. The effects of temperature, time and material ratio on the dissociation of the non-metals and metals in WMMs were analyzed. The degradation mechanism of the non-metallic parts in WMMs (brominated epoxy resin, fiber glass, etc.) during molten-alkali treatment was proposed from the thermodynamic viewpoint. The results show that the degradation rate of non-metallic materials in WMMs can reach 95.45% if the reaction is continuously kept at 400 ℃ for 60 min in the reaction kettle with the mass ratio of mixture of hydroxides to WMM (mMH/mWMM)of 5. The obtained metal mixture contains the elements Cu, Fe, Ni and precious metals Au and Ag.
Key words: metal recycling; waste printed circuit boards; waste memory modules; molten alkali
Foundation item: Projects(51974288, 51774264, 51574216) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(JYT19063) supported by the Basic Research Plan of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education, China; Project(2019-MS-332) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China
Received date: 2020-03-18; Accepted date: 2020-12-04
Corresponding author: HE Jie; Tel: +86-24-83973120; E-mail: jiehe@imr.ac.cn
ZHU Ming-wei; Tel: +86-24-89724198; E-mail: mwzhu@sau.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51974288,51774264,51574216);辽宁省教育厅基础研究项目(JYT19063);辽宁省自然科学基金资助项目(2019-MS-332)
收稿日期:2020-03-18;修订日期:2020-12-04
通信作者:何 杰,研究员,博士;电话:024-83973120;E-mail:jiehe@imr.ac.cn
朱明伟,副教授,博士;电话:024-89724198;E-mail:mwzhu@sau.edu.cn