文章编号:1004-0609(2008)S1-0416-06
锌冶炼含汞污酸生物制剂处理新技术
王庆伟,柴立元,王云燕,李青竹
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙410083)
摘 要:针对锌冶炼行业含高浓度多种重金属的污酸特性,采用生物制剂配合-水解新工艺进行处理,工业试验运行过程中对污酸及处理后出水中各重金属及氟、氯的浓度进行监测,并对产生的渣样进行分析。结果表明:重金属浓度分别由汞14.78~56.70 mg/L、砷13.71~40.15 mg/L、锌20.50~58.90 mg/L、铅12.8~64.2 mg/L、镉2.1~13.6 mg/L、铜0.54~1.44 mg/L、氟339~512 mg/L、氯472~3400 mg/L脱除至汞0.029~0.049 mg/L、砷0.029~0.065 mg/L、锌0.11~0.37 mg/L、铅0.1~0.43 mg/L、镉低于0.01 mg/L、铜低于0.1 mg/L、氟0.054~4.99 mg/L、氯29.5~43.7 mg/L,处理后出水中各重金属含量及氟、氯含量均远低于《污水综合排放标准》(GB8978—1996)。配合渣中的汞含量高达29.95%,可作为汞原料进行回收,水解渣中重金属含量低,便于妥善处理和处置。
关键词:污酸;生物制剂;配合;水解
中图分类号:X 703.1 文献标识码:A
Novel technology for treatment of acidic wastewater containing Hg by biologics in zinc smelter
WANG Qing-wei, CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Yun-yan, LI Qing-zhu
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Acidic wastewater with high concentration of heavy metals discharged from zinc smelter industry was treated by the novel technology of biologics complex-hydrolyzation, and the removal effect of heavy metals(Hg, As, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu) and F-, Cl- was examined. During stable industrial experiments heavy metals and F-, Cl- of acidic wastewater are removed from 14.78-56.70 mg/L Hg2+, 13.71-40.15 mg/L As, 20.50-58.90 mg/L Zn2+, 12.8-64.2 mg/L Pb2+, 2.1-13.6 mg/L Cd2+, 0.54-1.44 mg/L Cu2+, 339-512 mg/L F- and 472-3400 mg/L Cl- to 0.029-0.049 mg/L Hg2+, 0.029-0.065 mg/L As, 0.11-0.37 mg/L Zn2+, 0.1-0.43 mg/L Pb2+, 0-0.01 mg/L Cd2+, 0-0.1 mg/L Cu2+, 0.054-4.99 mg/L F- and 29.5-43.7 mg/L Cl- respectively, which are all lower than those required in “Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard” (GB8978─1996). Sediment from stable industrial experiments was analyzed. The result shows that mercury in complexing sediment reaches 29.95% and low concentration of heavy metals in hydrolytic sediment makes it easier to dispose and treat.
Key words: acidic wastewater; biologics; complexing; hydrolyzation
锌冶炼收尘系统排出的高温烟气送入硫酸车间前,在净化工序的空塔中被绝热蒸发冷却、洗涤除杂。空塔稀酸循环系统中为避免喷淋水中氟、氯离子浓度过高而排放出的一部分废酸,即为污酸。由于高温烟气中含有大量的细颗粒烟尘、金属蒸汽、SO2和SO3等,在洗涤过程中这些物质进入污酸,导致污酸的性质非常复杂,体现在如下几点:1) 成分复杂。污酸中含有铜、铅、锌、镉、砷、汞等重金属离子。2) 酸度高。污酸中硫酸的质量分数在1%~4%之间,还含有大量的SO2气体。3) 重金属浓度高且波动大。污酸中重金属的浓度在数小时内由几个毫克波动到几百甚至几千毫克。4) 金属赋存状态复杂。以汞为例,研究发现污酸中的汞包括悬浮颗粒态汞、胶体态汞和离子态汞[1-2]。
含汞废水的传统处理方法主要有化学沉淀法、金属还原法、吸附法、离子交换法、电解法、微生物法等[3-9]。传统方法共同的缺点是:用于处理含汞质量浓度1~100 mg/L的废水时往往操作费用和原材料成本相对过高,制约了其广泛的工业应用,含汞废水仍然是环境的重要污染源之一[10-11],污酸的治理仍是一个世界性的难题[12-14]。因此,迫切需要开发一种高效的技术处理含汞废水,尤其是处理复杂多金属含汞污酸,以革新传统的污酸处理技术,阻断重金属汞对水体的污染,保证饮水安全。
针对污酸的特性,本课题组首创了生物制剂法处理含汞污酸的新技术,已完成试验室和中试(30 m3/h)研究,并取得了很好的处理效果。该新技术通过了专家组的鉴定,认定达到了国际领先水平,解决了污酸治理这一世界性难题,为确保饮用水安全提供了技术支撑。本研究中作者重点探讨工业试验连续运行过程中污酸中各重金属及氟、氯的脱除效果及产生的渣中各种重金属的分布情况。
1 实验方法
1.1 实验流程
由沸腾焙烧收尘净化工段送20 m3/h污酸进入一级配合反应槽,与生物制剂、脱汞剂进行配合反应,并溢流进入二级配合反应槽继续反应。在此过程中,原子态汞与脱汞剂反应长大形成“胶团”,离子态汞及铜、铅、锌、镉、砷等与生物制剂配合形成配合体。配合反应后溢流进入一级水解槽,加入电石泥浆调pH至10~11进行一级水解反应,待三级水解反应完成后,加入适量PAM后进入浓缩机实现液固分离,上清液溢流外排。工艺流程如图1所示。

图1 生物制剂处理污酸工业实验流程
Fig.1 Flowchart of industrial experiment of acidic wastewater treated by biologics
1.2 实验控制条件
实验期间污酸流量为20 m3/h,脱汞剂加入量为20 g/m3,生物制剂按照污酸中汞浓度的40倍进行投加,利用电石泥调节pH值,一级水解pH值控制在10~11之间,PAM的加入量为5 g/m3 。
1.3 分析方法
实验期间委托湖南省监测站进行48 h的连续监测,其中汞每2 h取样监测一次,铜、铅、锌、镉、砷、氟、氯每4 h取样监测一次。
铜、铅、锌、镉采用原子吸收分光光度法测定,仪器型号VARIAN220;砷采用原子荧光分光光度法测定,仪器型号AFS2201;汞采用USEPA7473进行分析,监测下限为0.05 ?g/L;氟化物和氯化物采用离子色谱法测定,仪器型号HJ/T84-2001。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 污酸中汞、砷的去除效果
图2和3所示分别为污酸及处理后出水中汞和砷的浓度。由图2和图3可知,实验过程中污酸中汞浓度在14.78 mg/L至56.70 mg/L之间波动,砷浓度在13.71 mg/L至40.15 mg/L之间波动,经过生物制剂处理后,出水中汞浓度在0.029 mg/L至0.049 mg/L之间,出水中砷浓度在0.029 mg/L至0.065 mg/L之间,均低于国家《污水综合排放标准》。这表明生物制剂对污酸中的汞和砷都有很好的去除效果。
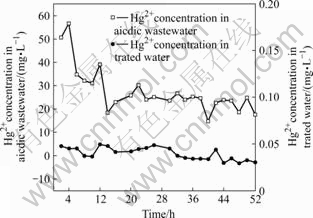
图2 生物制剂法对污酸中汞的去除效果
Fig.2 Removal effect of Hg2+ from acidic wastewater by biologics

图3 生物制剂法对污酸中砷的去除效果
Fig.3 Removal effect of As from acidic wastewater by biologics
2.2 污酸中锌、铅、镉、铜的去除效果
图4~7分别为生物制剂对污酸中锌、铅、镉、铜的去除情况的影响。可见,污酸中各重金属的浓度波动很大,实验过程中污酸中锌浓度在20.50 mg/L至58.90 mg/L之间波动,铅浓度12.8~64.2 mg/L,镉浓度2.1~13.6 mg/L,铜浓度0.54~1.44 mg/L,经过生物制剂处理后的出水中锌浓度0.11~0.37 mg/L,铅浓度为0.1~0.43 mg/L,镉浓度一直低于检测限0.01 mg/L,铜浓度一直低于检测限0.1 mg/L,均低于国家《污水综合排放标准》。这表明生物制剂按照污酸中汞的40倍投加对污酸中各重金属均有很好的去除效果。
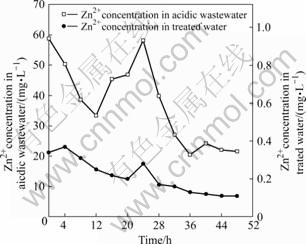
图4 生物制剂法对污酸中锌的去除效果
Fig.4 Removal effect of Zn2+ from acidic wastewater by biologics
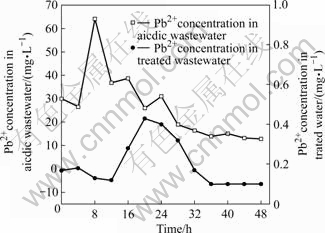
图5 生物制剂对污酸中铅的去除效果
Fig.5 Removal effect of Pb2+ from acidic wastewater by biologics

图6 生物制剂法对污酸中镉的去除效果
Fig.6 Removal effect of Cd2+ from acidic wastewater by biologics
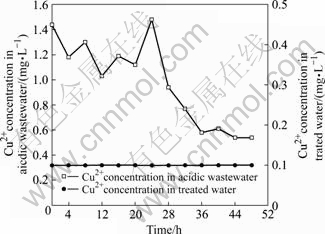
图7 生物制剂法对污酸中铜的去除效果
Fig.7 Removal effect of Cu2+ from acidic wastewater by biologics
2.3 污酸中氟、氯的去除效果
图8和9分别为生物制剂对污酸中氟、氯的去除情况的影响。实验过程中污酸中的氟浓度均超过339 mg/L,最高达到了512 mg/L,通过生物制剂深度处理后,出水中氟浓度在0.054 mg/L至4.99 mg/L之间,低于国家《污水综合排放标准》。实验期间污酸中氯离子的浓度波动极大,最低浓度为472 mg/L,最高浓度达到了3.4 g/L,经过生物制剂处理后的出水氯离子浓度29.5~43.7 mg/L,去除率稳定在98%以上。这表明生物制剂对污酸中的氟和氯有很好的去除效果。
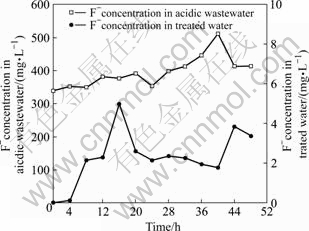
图8 生物制剂法对污酸中氟的去除效果
Fig.8 Removal effect of F- from acidic wastewater by biologics
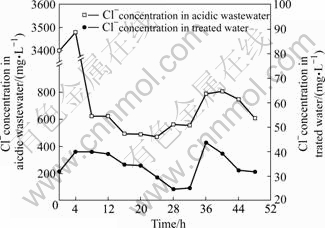
图9 生物制剂法对污酸中氯的去除效果
Fig.9 Removal effect of Cl- from acidic wastewater by biologics
2.4 配合渣与水解渣性质
生物制剂处理污酸过程中会产生两种渣,即配合渣和水解渣。配合渣主要来自污酸中的烟尘颗粒、金属沉淀物和被破坏了结构的胶体颗粒;水解渣是污酸通过电石泥调节pH过程中生物制剂与重金属形成配合物的水解对重金属的深度脱除产生的渣。对实验过程中配合渣进行能谱和物相分析,结果如图10和图11所示。
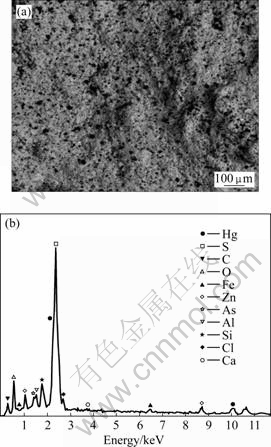
图10 配合渣的SEM及EDX图
Fig.10 SEM image(a)and EDX pattern(b) of bio-complexing sediment

图11 配合渣的XRD谱
Fig.11 XRD pattern of bio-complexing sediment
由图10可以看出,配合渣中含有Pb、Hg、S、C、O、Fe、Zn、As、Al、Si、Cl、Ca等元素;由各元素的含量分析可知,配合渣中汞含量高达29.95%,铅27.72%,其次为氧11.64%, 碳9.61%,硫9.53%,锌4.22%,再次为砷0.45%,铝1.49%,铁1.21%,硅2.38%,氯1.46%,钙0.36%(质量分数)。配合渣中的汞主要来自污酸中的悬浮颗粒态和胶体态汞。图11表明配合渣中的汞以非晶态形式存在,配合渣中的铅主要以硫酸铅和氧化铅的形式存在。
对水解渣进行能谱和物相的分析,结果如图12和13表示。由图12可以看出,水解渣中钙含量高达37.68%,氧37.37%,碳12.79%,硫3.28%,氟2.52%,其次为钠1.30%, 砷0.80%,铝0.63%,硅0.72%,镉0.47%,钾0.11%,铁1.74%,锌0.58%。由图12可以看出,水解渣的主要成分为CaCO3、CaSO4和CaF2,各重金属在水解渣中的含量都较低,且均以离子状态存在,毒性小,便于处理与处置。
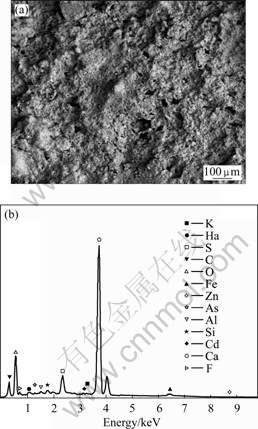
图12 水解渣的SEM及EDX图
Fig.12 SEM image (a) and EDX pattern (b) of hydrolytic sediment
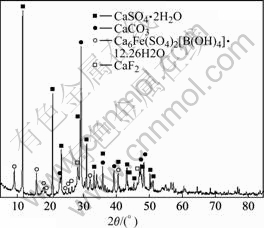
图13 水解渣的X射线衍射谱
Fig.13 XRD pattern of hydrolytic sediment
3 结论
1) 中试试验期间污酸流量20 m3/h,脱汞剂按照20 g/m3,生物制剂按污酸中汞浓度的40倍投加,水解过程pH值控制在10以上时,污酸经过处理后的上清液中汞0.029~0.049 mg/L、砷0.029~0.065 mg/L、锌0.11~0.37 mg/L、铅0.1~0.43 mg/L、镉低于0.01 mg/L、铜低于0.1 mg/L、氟0.054~4.99 mg/L、氯29.5~43.7 mg/L,处理后出水中各重金属含量均能达到《污水综合排放标准》(GB8978─1996)。
2) 实验过程中收集的配合渣中汞的质量分数达到了29.95%,可以作为汞冶炼企业的原料回收其中的重金属。水解渣中重金属含量低、毒性小,便于安全处理和处置。
3) 生物制剂与脱汞剂无二次污染、环境友好、工艺清洁,而且水解过程采用电石泥为中和剂,为电石泥的使用开辟了一条新途径,极大降低了污酸处理成本,亦达到了“以废治废”的目的。
REFERENCES
[1] 袁倬斌, 朱 敏, 韩树波. 汞的形态分析研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 1999, 18(2): 150-156.
YUAN Zhuo-bin, ZHU Min, HAN Shu-bo. Progress in speciation anslysis of mercury[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1999, 18(2): 150-156.
[2] 栗 旸, 段志敏, 沈其萍, 王建华. 水中汞分析研究进展[J]. 环境与健康, 2005, 12(5): 399-400
LI Yang, DUAN Zhi-min, SHEN Qi-ping, WANG Jian-hua. Research advances in analysis of trace mercury in water[J]. Environment and Health, 2005, 12(5): 399-400
[3] 唐 宁, 柴立元, 闵小波. 含汞废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2004, 24(8): 5-8
TANG Ning, CHAI Li-yuan, MIN Xiao-bo. Research development in the treatment of mercury-wastewater[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2004, 24(8): 5-8.
[4] 张松梅, 李立清. 谷壳灰吸附水中汞的试验探讨[J].江苏环境科技, 1999, 12(4): 4-6.
ZHANG Song-mei, LI Li-qing. Discussion of experiment on the adsorption of mercury in water by rice husk ash[J]. Jiangshu Environmental Technology, 1999, 12(4): 4-6.
[5] 朱又春, 林建民, 林美强, 曾 胜. 电池厂含汞废水的微电解处理[J]. 工程与技术, 1999, 3: 12-14.
ZHU You-chun, LIN Jian-ming, LIN Mei-qiang, ZENG Sheng. Micro-electrolysis treatment of mercury-contained wasterwater discharged from battery factory[J]. Engineering and Technology, 1999, 3: 12-14.
[6] ANSARI M H, DESHKAR A M, KELKAR P S, DHARMADHIKARI D M, HASAN M Z. Mercury removal from wastewater by steamed hoof powder[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1999, 40(7): 109-116.
[7] LARSON, KAREN A, WIENCEK J M. Liquid ion exchange for mercury removal from water over a wide pH range[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1992, 31(12): 2714-2722.
[8] NAVARRO R R, SUMI K, FUJII N, MATSUMURA M. Mercury removal from wastewater using porous cellulose carrier modified with polyethyleneimine[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(10): 2488-2494.
[9] KAPOOR A, VIRARAGHAVAN T. Adsorption of mercury from wastewater by fly ash[J]. Adsorption Science and Technology, 1992, 9(3): 130-147.
[10] ZHANG Fu-shen, NRIAGU J O, ITOH H. Mercury removal from water using activated carbons derived from organic sewage sludge[J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(3): 389-395.
[11] DI N F, LANCIA A, DI N M, KARATZA D, MUSMARRA D. Capture of mercury ions by natural and industrial materials[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 132(3): 220-225.
[12] BARRON Z J, LABORIE S, VIERS P, RAKIB M, DURAND G. Mercury removal and recovery from aqueous solutions by coupled complexation-ultrafiltration and electrolysis[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004, 229(2): 179-186.
[13] LEONHAUSER J, ROHRICHT M, WAGNER D I, DECKWER W D. Reaction engineering aspects of microbial mercury removal[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2006, 6(2): 139-148.
[14] MEENA A K, MISHRA G K, KUMAR S, RAJAGOPAL C, NAGAR P N. Low-cost adsorbents for the removal of mercury (Ⅱ) from aqueous solution—A comparative study[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2004, 54(4): 537-548.
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划重点资助项目(2007BAC25B01);湖南省重大科技专项(2006SK1002);湖南省科技计划重点项目(2007SK2006)
通讯作者:柴立元,教授,博士;电话:0731-8836921;E-mail: lychai@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 杨 兵)