砂岩储层中CO2-地层水-岩石的相互作用
王广华,赵静,张凤君,陶怡,杨潇瀛,王怀远
(吉林大学 地下水资源与环境教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春,130026)
摘要:利用高温高压反应釜模拟不同温度条件下CO2-地层水-砂岩间的相互作用,并观察反应前后样品形貌、分析质量和比表面积的变化,讨论反应液pH和各离子浓度的变化原因,进一步阐明CO2-地层水-砂岩相互作用过程中矿物的溶解和沉淀机制。研究结果表明,超临界CO2注入后,随着温度的升高,砂岩中可溶矿物(长石类)的溶蚀作用加剧;样品表面和孔隙中均有新物质生成,主要矿物为石英、高岭石、绿泥石和一些未知的含“C”硅铝酸盐。
关键词:CO2;地层水;砂岩;水-岩相互作用
中图分类号:X54 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)03-1167-07
Interactions of CO2-brine-rock in sandstone reservoir
WANG Guanghua, ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Fengjun, TAO Yi, YANG Xiaoying, WANG Huaiyuan
(Key Lab of Groundwater Resources and Environment, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China)
Abstract: The interaction among CO2-the underground water-rock was simulated at different temperatures with the high-temperature autoclave. The samples were observed using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the changes of quality and specific surface area were analyzed. At the same time, the changes of pH and the concentration of ions in the solution were analyzed in order to make the mechanism of the dissolution and precipitation of the minerals clear. The results show that after injection of supercritical CO2, the dissolution of the soluble minerals (feldspar) in the sandstone becomes easier with the increase of temperature. Some new minerals on the surface or in the pores of the sample can be found, such as quartz, kaolinite, chlorite and unknown aluminosilicate containing carbon.
Key words: CO2; formation water; sandstone; water-rock interaction
近年来,气候变化引起了人们对温室气体CO2的格外关注,特别是如何缓解“温室效应”已经成为全球面临的新挑战。据IPCC调查评估,到2100年,大气中CO2的质量浓度将达到540~970 mg/L,为工业革命前的2倍[1],会对全球气候、生态及人类生存等诸多方面带来极为不利的影响,为此,将CO2以超临界的状态注入到地下进行储存,从而阻止或减少CO2向大气中的人为排放,即CO2地质储存[2]。目前,CO2地质储存最为理想的场所主要有深部含盐水层,枯竭或开采到后期的油、气田以及不可开采的贫瘠煤层和海洋[3]。自20世纪70年代开始,欧美国家及日本已开展了大量有关CO2地质储存的理论研究和工程项目[4],他们的成功经验表明,CO2的地质储存是减少大气中CO2含量的有效措施之一。目前,我国有关CO2地质储存的研究工作才刚刚起步,对于CO2-地层水-岩石相互作用的研究较少。在此,本文作者利用储层中的地层水和岩芯,在实际储层压力和温度的条件下,通过CO2-地层水-岩石间相互作用的水热实验,研究超临界CO2对储层的改造、新矿物的生成以及地层水成分的变化,进一步探讨CO2地质储存的过程和机理,并为实际工程中CO2的地质储存提供一些有意义的参数。
1 实验研究
1.1 实验材料
实验样品:采自老石嘴山市三区井下岩芯,层位为石千峰组。实验前将岩芯样品加工成10 mm×10 mm×1 mm(长×宽×厚)的薄片,表面抛光。通过偏光显微镜观察,定名为长石石英砂岩,其主要化学成分(质量分数)及矿物组成含量(体积分数)分别见表1和表2。
实验溶液:根据该储层地层地层水的水分析资料所配置,水中主要离子及化学成分见表3。
1.2 实验设备
本实验采用大连通产高压釜容器制造有限公司生产的FYX-1型高压釜,配有连续取样装置,其容量为1.0 L,最高工作温度为350 ℃、压力为30 MPa。实验中,利用永磁旋转搅拌仪、恒温控制仪和气-液增压泵分别对实验的转速、温度和压力进行控制,实验装置流程如图1所示。
1.3 实验分析仪器
利用X线荧光光谱仪、X线衍射仪测定样品的化学成分及矿物组成;用电子天平精确称取样品质量,并用SSA-3200C型物理及化学吸附分析仪测定比表面积;同时,反应前后样品的表面特征及矿物组成用JSM-6700F型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察分析,并利用 INCAX-SIGHT型能谱议确认矿物种类及其主要化学成分。
在实验前、后,利用PHS-3C型pH计测量溶液pH的变化;用酸标准溶液滴定法测定HCO3-和CO32-的浓度;溶液中主要阳离子的测量,先用3%(质量分数)的HNO3调节反应液pH=2(防止沉淀),再用AA-6300C型原子吸收仪测定K+,Na+,Mg2+和Ca2+的浓度,最后,用7500A型ICP-MS测定Al3+和TFe浓度。
表1 样品中主要化学成分
Table 1 Chemical component of sample

表2 样品中矿物含量
Table 2 Mineral abundance in sandstone
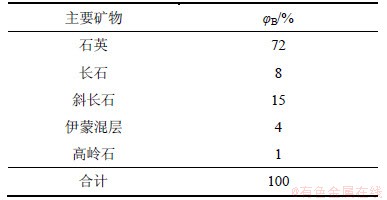
表3 实验前、后不同温度下溶液中的化学成分
Table 3 Solution chemical composition before and after experiment at different temperature

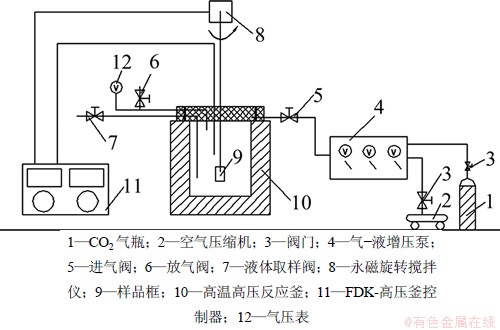
图1 实验装置图
Fig.1 Schematic of experimental equipment
1.4 实验步骤
(1) 按图1所示流程图对实验设备进行连接。
(2) 将砂岩样品用蒸馏水冲洗、烘干(65 ℃,24 h)、称质量,测其比表面积。
(3) 将一定数量的样品及实验溶液(750 mL)放入反应釜内,密闭。通过气-液增压泵通入超临界CO2,使釜内压力到达16 MPa,在不同温度下反应72 h。
(4) 反应结束后,冷却至室温,打开反应釜,将样品取出,用蒸馏水冲洗3~5次、烘干(65 ℃,24 h)、称质量,进行比表面积测定和扫描电镜分析;反应液用一次性针管取出装入无污染的塑料瓶中,进行化学成分测定。
2 结果与讨论
CO2是一种“活性气体”[5],易溶于水形成H2CO3。特别是超临界CO2,其密度接近于液体,黏度低,扩散系数高[6],因此,具有良好的传质能力,可加快反应速率,增加溶液的酸度。在 CO2-地层水-岩石体系中,伴随着超临界CO2的注入,CO2先扩散进入砂岩含水层孔隙,与地层水形成弱酸性流体,再与含水层岩石发生一系列复杂的物理和地球化学反应,进而引起储层物性、成分和地层水的组成发生变化。
2.1 储层成分的变化
2.1.1 矿物的溶蚀
矿物与水接触时发生的溶解反应分为全等溶解和非全等溶解[7] 。长石在酸性介质下发生非全等溶解[8],即在其溶解过程中,一部分离子被溶解进入溶液,另一部分转变成新的矿物。实验中储层中长石主要成分为钾长石、钠长石和钙长石,在超临界CO2流体作用下发生的溶蚀反应如下[9]:
2KAlSi3O8+9H2O+2H+→2K++Al2Si2O5(OH)4+4H4SiO4 (1)
2NaAlSi3O8+H2O+CO2→2Na++2HCO3-+Al2Si2O5(OH)4+4SiO2 (2)
CaAl2Si2O8+H2CO3+H2O→CaCO3+Al3++Al2Si2O5(OH)4 (3)
通过CO2流体与岩石反应前后样品表面特征的观察,发现75 ℃时长石类矿物微弱溶蚀(图2(a)),石英和黏土矿物相对稳定。随着温度的升高,长石类矿物溶蚀加剧,石英和黏土矿物也开始发生微弱溶蚀,如200 ℃时长石类矿物沿双晶方向发生强烈溶蚀,溶出一些平行排列的深沟(图2(b));石英溶蚀成破碎状,表面出现了一些溶孔(图2(c));伊-蒙混层呈层状溶蚀(图2(d))。因此,可以说明超临界CO2注入后,随着温度的升高,岩石的溶蚀强度逐渐增强,且可溶的成分也逐渐增多。
2.1.2 新生矿物的沉淀
反应后矿物表面生成新矿物的扫描电镜照片如图3所示。其能谱数据见表4。由图3和表4可知:不同温度下均有新矿物生成, 如75 ℃下有球形的过渡态石英生成(图3(a));100 ℃下发现呈书页状集合体存在的高岭石(图3(b));150 ℃下溶坑中析出了晶型不太规则的新矿物(图3(c)),能谱分析其主要组成元素O,C,Fe和Si。可能为菱铁矿中间态;200 ℃下还观察到氧化亚铁(图3(d))和叶片状的绿泥石生成(图3(e))。
如果反应时间足够长,实验中“C”和阳离子(Fe2+,Mg2+,Ca2+等)的硅铝酸盐可能以方解石、菱镁矿、菱铁矿、铁白云石等CO2捕获矿物的形式沉淀析出[10],即发生CO2的矿物捕获。进一步说明CO2-水-岩石相互间的地球化学作用除了会使岩石发生溶蚀反应外,在特定条件下还会在岩石表面或孔隙中形成新的碳酸盐,使CO2以碳酸盐矿物的形式稳定存在,从而实现CO2地下的永久储存。
2.2 样品比表面积的变化
实验前后不同温度下岩石的质量和比表面积如表5所示。由表5可知:实验后岩石质量减少,比表面积(单位质量物质的总表面积)变大,说明超临界CO2注入使岩石中的一些可溶性矿物(如长石类和黏土类矿物)发生了溶蚀。
但样品质量的变化率和比表面积的变化率随着温度的升高先变大后变小,这种现象可能由原生矿物的溶蚀和次生矿物的沉淀共同作用所引起。在CO2-地层水-岩石形成的弱酸性体系中,当温度小于100 ℃时,矿物主要表现为溶蚀作用,且随着温度的升高,溶蚀作用加剧,从而使样品比表面积的变化率与温度呈正相关;当温度大于100 ℃时,随着温度的升高,矿物的溶蚀作用加剧,同时矿物表面或孔隙中开始有新矿物沉淀(图3(e)和图3(f)),从而使样品比表面积的变化率降低。
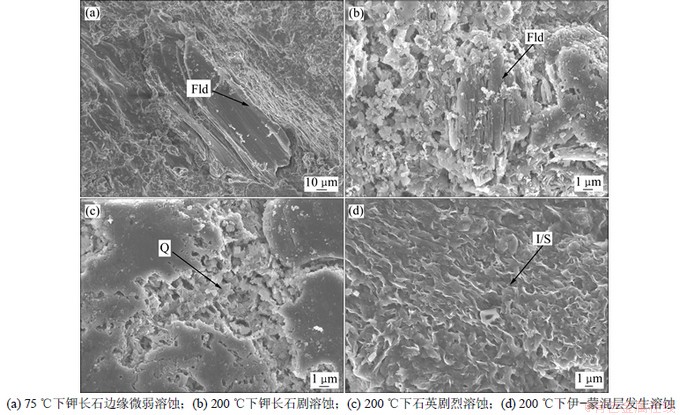
图2 反应后矿物溶蚀的电镜照片
Fig.2 SEM images of erosion after reaction
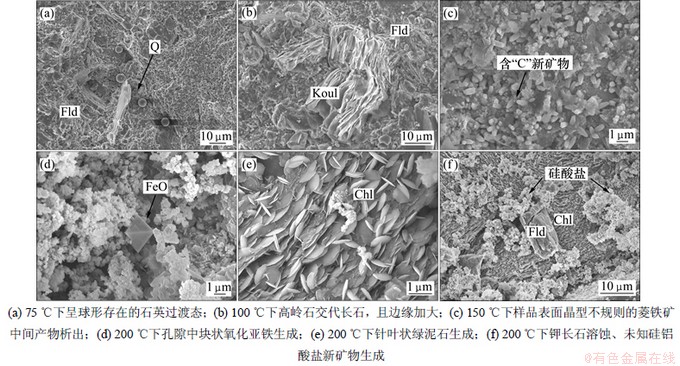
图3 反应后矿物表面生成新矿物的电镜照片
Fig.3 SEM images of new mineral after reaction
表4 反应后矿物表面生成的新矿物及其能谱数据
Table 4 Energy spectrum of educt from surface of sample at different experimental temperatures
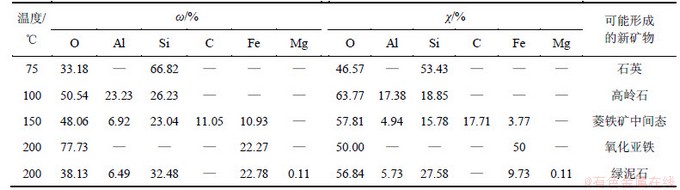
表5 实验前后不同温度下岩石的质量和比表面积
Table 5 Rock mass and specific surface area at different experimental temperatures

CO2注入储层后与地层水、岩石发生的溶蚀作用,增大了岩石的比表面积,甚至形成了溶蚀孔隙,为CO2地质储存提供了有利的空间。
2.3 反应液成分的变化
2.3.1 溶液总矿化度的变化
从反应液中总矿化度含量的变化(表3)可以看出,随着温度的升高,CO2流体对砂岩样品的溶蚀程度逐渐增强,使反应液中的离子浓度增大,总矿化度变大。尽管实验中发现有新矿物析出,但它们只能使个别离子浓度降低,而对总矿化度的影响很小;特别是反应液中非成矿离子浓度的增加(如K+和Na+),进一步说明较短时间内,矿物的溶解速率大于沉淀速率。
2.3.2 阳离子质量浓度的变化
从表3可以看出:超临界CO2注入后,反应液中K+和Na+质量浓度随温度升高而增大,说明样品中的长石类矿物易发生溶蚀反应,而且溶蚀程度随温度的升高逐渐增强。
一些有关CO2地质储存的数值模拟结果表明:伴随着CO2流体的注入,溶液中的Ca2+会转变为碳酸盐沉淀[11-12],从而使Ca2+质量浓度降低。但本实验中Ca2+质量浓度随温度的升高明显增加,一方面说明钙长石的溶蚀强度加剧,另一方面也说明该反应条件下,短时间内不利于方解石、白云石等含钙碳酸盐的形成。
但是,在高温下(温度高于150 ℃),反应液中TFe和Al3+质量浓度明显降低,结合反应后样品的扫描电镜可知,高温条件下易形成含Fe新矿物和一些未知的硅铝酸盐新矿物。特别是150 ℃时发现的富“C”含铁矿物(图3(d)),说明了CO2地质储存的可行性和稳定性。
2.3.3 阴离子质量浓度的变化
由表3可知:实验后溶液中HCO3-的质量浓度明显比实验前的高,说明CO2注入后,多数会以离子态(HCO3-和CO32-)存在于溶液中;随着温度的升高,溶液中HCO-的质量浓度先降低后增加,这和溶液中TFe质量浓度的变化相似,说明随着温度的升高,溶液中溶出的Fe2+与HCO3-反应生成了FeCO3难溶碳酸盐,但由于实验时间较短,并没有以矿物(菱铁矿)的形式在样品表面沉淀;但当温度高于200 ℃时,生成的碳酸盐络合物不稳定,发生了溶解,即CO2+H2O+ FeCO3=Fe(HCO3)2[9],从而使HCO-的质量浓度增大。结合Worden[13]关于菱铁矿形成的温度在100~200 ℃的论述,推断本实验菱铁矿的形成温度可能在150 ℃左右。因此,在CO2地质储存的实际工程中,要选择合适的深度。
2.3.4 反应液中pH的变化
从图4可以看出:当超临界CO2流体注入后,溶液pH随着温度的升高呈上升趋势,并且始终呈弱酸性。该变化过程可用碳酸的生成和解离平衡来解释,即CO2+H2O H2CO3
H2CO3 H++HCO3-[14]。首先,CO2溶于水形成碳酸,溶液酸性变强。其次,CO2在地层水中的溶解度随着温度和矿化度的升高而变小[15];同时,岩石溶蚀的程度也随着温度的升高而加剧,消耗大量的H+,使平衡向右移动;但在50 ℃以上时,碳酸的解离平衡常数却随着温度的升高而降低,酸性变得愈来愈弱[16],不能为反应提供足够多的H+,因此,引起溶液酸性变弱,pH逐渐升高。
H++HCO3-[14]。首先,CO2溶于水形成碳酸,溶液酸性变强。其次,CO2在地层水中的溶解度随着温度和矿化度的升高而变小[15];同时,岩石溶蚀的程度也随着温度的升高而加剧,消耗大量的H+,使平衡向右移动;但在50 ℃以上时,碳酸的解离平衡常数却随着温度的升高而降低,酸性变得愈来愈弱[16],不能为反应提供足够多的H+,因此,引起溶液酸性变弱,pH逐渐升高。
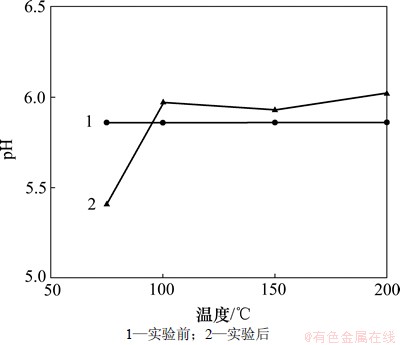
图4 不同温度下反应液pH的变化
Fig.4 Variation of pH in residual solution at different experimental temperatures
3 结论
(1) 在超临界CO2体系中,随着温度的升高,矿物的溶蚀、溶解强度加剧,比表面积变大,为碳酸盐等难溶矿物的沉淀析出和CO2地下的转移、储存提供了有利的空间,有助于CO2的地质储存。
(2) 在150 ℃下发现富“C”未知硅铝酸盐,说明了CO2地质储存的可行性。但在200 ℃反应时,高温下菱铁矿等固碳矿物会发生晶型转化,甚至溶解作用;也进一步表明CO2地质储存中,要选择合适的深度。
(3) 在实验温度范围内,砂岩样品比表面积的变化量随着温度的升高而减小,说明该条件下生成的绿泥石等矿物减少了样品的孔隙;进一步说明该过程有利于CO2的地质储存,同时也会对CO2的迁移起到一定的阻碍作用。
参考文献:
[1] Grimston M C, Karakoussis V, Fouquet R, et al. The european and global potential of carbon dioxide sequestration in tackling climate change[J]. Climate Policy, 2001, 1(2): 155-156.
[2] Holloway S. Underground sequestration of carbon dioxide available greenhouse gas mitigation option[J]. Energy, 2005, 30: 2318-2333.
[3] Xu T F, Kharaka Y K, Doughty C, et al. Reactive transport modeling to study changes in water chemistry induced by CO2 injection at the Frio-I Brine Pilot[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 27(1):153-164.
[4] 江怀友, 沈平平, 罗金玲, 等. 世界二氧化碳埋存技术现状与展望[J]. 能源与环境, 2010, 32(6): 28-32.
JIANG Huaiyou, SHEN Pingping, LUO Jinling, et al. Research status and prospects of carbon dioxide sequestration technique[J].Energy and Environment, 2010, 32(6): 28-32.
[5] 曲希玉, 刘立, 马瑞, 等. CO2流体对岩屑长石砂岩改造作用的实验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2008, 38(06): 959-964.
QU Xiyu, LIU Li, MA Rui, et al. Experiment on debris-arkosic sandstone reformation by CO2 fluid[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2008, 38(06): 959-964.
[6] 杨俊兰, 马一太, 曾宪阳, 等. 超临界压力下CO2流体的性质研究[J]. 流体机械, 2008, 36(1): 53-57.
YANG Junlan, MA Yitai, ZENG Xianyang, et al. Study on the properties of CO2 fluid at supercritical pressure[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2008, 36(1): 53-57.
[7] 蔡进功, 谢忠怀, 田芳, 等. 济阳坳陷深层砂岩成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(1): 84-88.
CAI Jingong, XIE Zhonghuai, TIAN Fang, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of deep sandstones in Jiyang depression[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2002, 23(1): 84-88.
[8] 李汶国, 张晓鹏, 钟玉梅, 等. 长石砂岩次生溶孔的形成机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(2): 220-223.
LI Wenguo, ZHANG Xiaopeng, ZHONG Yumei, et al. Formation mechanism of secondary dissolved pores inarcose[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2005, 26(2): 220-223.
[9] 朱子涵, 李明远, 林梅钦, 等. 储层中CO2-水-岩石相互作用研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(1): 104-112.
ZHU Zihan, LI Mingyuan, LIN Meiqin, et al. Review of the CO2-water-rock interaction in reservoir[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(1): 104-112.
[10] Gunter W D, Wiwchar B, Perkins E H. Aquifer disposal of CO2-rich greenhouse gases: Extension of the time scale of experiment for CO2-sequestering reactions by geochemical modeling[J]. Mineral Petrol, 1997, 59: 121-140.
[11] Xu T F, Apps J A, Pruess K. Mumerical simulation of CO2 disposal by mineral trapping in deep aquifers[J]. Applied Geochmistry, 2004, 19: 917-936.
[12] Xu T F, Apps J A, Pruess K. Mineral sequestration of carbon dioxide in a sandstone-shale system[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 217: 295-318.
[13] Worden R H. Dawsonite cement in the Triassic Lam Formation, Shabwa basin, Yemen: A natural analogue for a potential mineral product of subsurface CO2 storage for greenhouse gas reduction[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23: 61-77.
[14] 朱焕来, 曲希玉, 刘立,等. CO2流体-长石相互作用实验研究[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(3): 697-706.
ZHU Huanlai, QU Xiyu, LIU Li, et al. Study on interaction between the feldspar and CO2 fluid[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(3): 697-706.
[15] 范泓澈, 黄志龙, 袁健, 等. 高温高压条件下甲烷和二氧化碳溶解度试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 35(2): 6-11.
FAN Hongche, HUANG Zhilong, YUAN Jian, et al. Experiment on solubility of CH4 and CO2 at high temperature and high pressure[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Science and Technology, 2011, 35(2): 6-11.
[16] Johnson J W, Oelkers E, Helgeson H C. Software package for calculating the standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species and relations among them as functions of temperature and pressure[J]. Geosci, 1992, 18: 899-947.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2012-03-20;修回日期:2012-07-15
基金项目:中国地质调查局项目(1212011120048)
通信作者:张凤君(1957-),男,吉林农安人,博士,教授,从事水处理技术研究;电话:0431-88498717;E-mail: zhangfengjun@jlu.edu.cn