DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.03.009
曲面变厚度编织CFRP微观形态与孔隙特征分析
李钊1, 2,周晓军1,杨辰龙1,陈越超1,李雄兵3
(1. 浙江大学 流体动力与机电系统国家重点实验室,浙江 杭州,310027;
2. 上海航天控制技术研究所,上海,201109;
3. 中南大学 CAD/CAM研究所,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘要:对曲面变厚度编织复合材料进行金相观察,分析纤维分布特点和主要缺陷类型,并对孔隙形态进行统计分析。研究结果表明:编织复合材料变厚度区纤维以90°铺层为主,0°铺层沿轮廓分布,且存在纤维层分裂现象;出现大量的富脂区,并有微裂纹存在,纤维层间有分层现象;孔隙主要分布在树脂区和层间,以小的球形为主,富脂区域容易出现集中孔隙;孔隙数量的增加是导致孔隙率增加的主要原因,随着孔隙率增加,孔隙长度、宽度和面积均增大,孔隙宽长比基本相同,孔隙形状因子减小,且当孔隙率大于1.5%时,形状因子减小加剧;孔隙长度、宽度与孔隙含量之间均存在近似对数正态关系。
关键词:编织复合材料;孔隙率;形态特征;富脂;形状因子
中图分类号:TB332,V258 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)03-0829-06
Microstructure and pore characteristics of braided CFRP with variable thickness
LI Zhao1, 2, ZHOU Xiaojun1, YANG Chenlong1, CHEN Yuechao1, LI Xiongbing3
(1. The State Key Laboratory of Fluid Power Transmission and Control, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China;
2. Shanghai Institute of Spaceflight Control Technology, Shanghai 201109, China;
2. CAD/CAM Institute, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: Analysis of distribution features of fibers and main defects was made, and the morphology of pore in hybrid fibers braided composite with variable thickness was statistically studied based on metallographic observation. The results show that the variable thickness area is filled with fibers of 90° laminate, and 0° laminate is displayed along the boundary with fiber division. Large area rich resin occurs with micro-crack, as well as layered between laminates. Small spherical pores mainly distribute in resin and layered, and concentration pores distribute in rich resin area. Increasing pore quantity is the main reason for increased porosity. While porosity increases, the average length, width and area of pores increase, but the ratio between width and length is unchanged. As well, the shape factor decreases, and it decreases faster when porosity is larger than 1.5%. Lognormal distribution relationships exist between length or width and porosity.
Key words: braided composite; porosity; morphology characteristics; rich resin; shape factor
编织复合材料具有异型件一次编织成型、结构不分层和整体设计灵活等特点,与层板复合材料相比,具有良好的力学性能、抗冲击和耐烧蚀性等优点,因而在航空领域如飞机螺旋桨、尾翼、火箭头锥以及非航空领域如坦克车和油罐车的桁架面板、汽车底盘、高尔夫球棒等都得到广泛应用[1-3]。由于编织材料的制造工艺特殊,并且在变厚度区域形状复杂,材料中会存在各种缺陷,从而对材料性能产生影响[4-5]。目前,针对复合材料的微观缺陷研究大都集中在层板复合材料,且多为平的层压板。高晓进等[6]对层板复合材料孔隙形态与超声衰减关系进行了研究;牟云飞等[7-8]对孔隙率进行了定量分析,并对复合材料进行三维建模;华志恒等[9-10]对平板复合材料进行了金相观察,并对孔隙率进行了统计分析;顾轶卓等[11-12]对变厚度层板和L型层板的缺陷类型进行了分析,并研究了缺陷形成机理。目前,人们对编织复合材料的研究大都集中在力学、拉伸、屈曲等性能分析方面[13-14],而相对于层板复合材料,对编织复合材料的孔隙率建模以及无损检测等方面的研究较少。为此,本文作者对曲面变厚度编织复合材料进行金相观察,对比层板复合材料,分析编织复合材料的微观形态和主要缺陷类型,并对孔隙率及孔隙形态特征进行统计分析。分析显示,编织复合材料结构和孔隙分布特点均与层板复合材料有很大不同,由于内部结构复杂,超声波在编织复合材料中的传播规律也较复杂,传统的孔隙率超声检测方法能否很好地适用于编织复合材料还有待进一步研究。本文研究结果可为正确建立编织复合材料孔隙率的超声检测模型、为编织复合材料超声检测新方法的提出和改进提供参考[15]。
1 实验材料与方法
1.1 试样
试样采用如图1所示泡沫芯夹层结构,上、下蒙皮材料为碳纤维/玻璃纤维混杂编织复合材料,其中外表面为曲面形状,内表面为不规则曲面,截面形状为变厚度曲面。
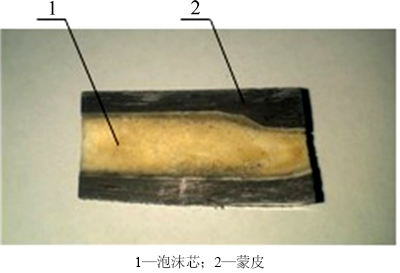
图1 泡沫芯夹层结构
Fig. 1 Structure of layered soap
1.2 实验方法
实验采用超声反射法对不同蒙皮处的试块进行检测,选取超声衰减系数不同的6个试块,对每个试块的2个侧面(变厚度面)和1个端面进行处理:首先分别采用水磨砂纸100#1、金相砂纸W50(01),W14(03)和W5(06)按由粗到细的顺序进行打磨,之后用高速水流进行冲洗,然后在抛光机上进行粗抛和精抛,直至被观察面没有划痕并且光滑清晰为止,再次进行冲洗并晾干,最后在金相显微镜上对每个试块的3个面进行观察拍照。1次拍摄完成之后,将试块的3个面各磨掉一定厚度,再按上述过程进行表面处理,进行下一次观察拍照。对每个试块进行3次表面处理,每次处理后随机拍摄20~30张照片,对拍摄的照片采用专业金相分析软件进行孔隙分析和统计。
实验采用江苏南光电子科技有限公司提供的NK-5000型倒置金相显微镜,图片分析采用NK-100金相分析软件,孔隙率参照GB/T 3365—2008[16]测定。编织复合材料微观形态见图2。
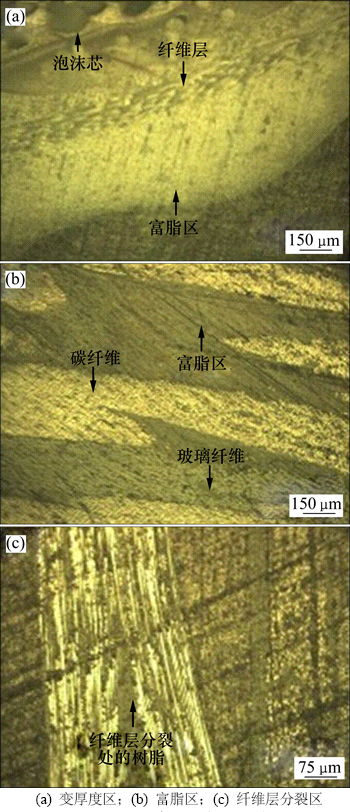
图2 编织复合材料微观形态
Fig. 2 Microstructures of braided composite
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 纤维分布特点
由于制造工艺的差异,编织复合材料与层板复合材料在微观结构上有很大不同。
如图2(a)所示,在变厚度截面上,编织复合材料纤维以90°铺层为主,0°铺层集中在中部和变厚度一侧;变厚度侧由90°铺层纤维和树脂填充,0°铺层纤维走向与厚度变化方向相一致,以起到固定形态的作用。而层板复合材料变厚度区主要是由于层数不同而形成,纤维层厚度基本相同。材料以碳纤维为主,中间混编有玻璃纤维,碳纤维直径小于玻璃纤维直径;玻璃纤维主要集中在材料外侧,以提高材料的抗冲击能力。如图2(b)所示,编织复合材料纤维层轮廓形态各异,纤维层边界多呈不规则曲面,且纤维层走向各异,靠近中部的0°铺层纤维易出现分裂现象,如图2(c)所示纤维层由1层分为2层。层板复合材料纤维层分布则相对均匀,层与层间基本平行。
2.2 富脂和分层
与层板复合材料相比,编织复合材料树脂含量较高,富脂主要存在于以下3个区域:图2(a)所示为变厚度侧靠近泡沫芯的富脂区域,图2(b)所示为交织的纤维束之间的富脂区域,图2(c)所示为纤维分裂处的富脂区域。这些区域易出现纤维分布不均以及纤维难以完全填充的现象,因而在成型过程中树脂容易在这些区域堆积形成富脂区。此外,由于富脂区强度低,当受冲击和长期疲劳时容易产生微裂纹,如图3所示,而裂纹的存在将使该区域材料的力学性能大大降低。
此外,纤维层间易产生分层现象,如图4所示。由于纤维分布不均,纤维层间容易产生应力集中而形成分层。分层是先进复合材料中最严重的缺陷类型,它通过降低材料的压缩强度和刚度影响结构的完整性。
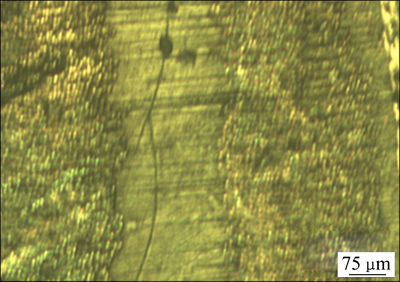
图3 富脂区的微裂纹
Fig. 3 Micro-crack in rich resin area
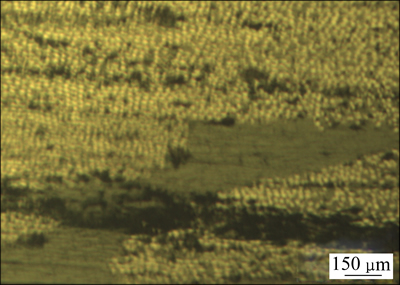
图4 纤维层间的分层
Fig. 4 Layered between laminates
2.3 孔隙形态
编织复合材料中的孔隙多分布在树脂区,以球形孔隙为主,同时也存在扁平状孔隙以及其他不规则形状的孔隙(如图5(a)所示),并且富脂区容易出现大面积集中孔隙(如图5(b)所示)。孔隙形成的原因有很多种,树脂浸润性差空气难以挤压出去、树脂中的低分子组分在加工过程中挥发以及固化过程中树脂的化学反应产生的挥发物,均可造成树脂中孔隙出现。
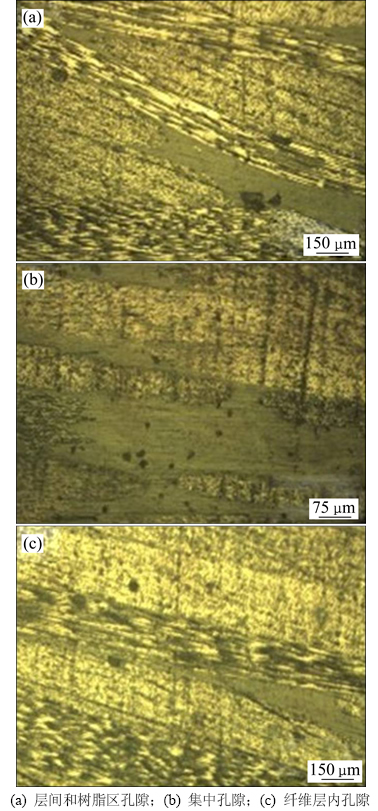
图5 孔隙形态特征
Fig. 5 Morphologies of pores
纤维层间以及纤维和树脂间存在球形和扁平形孔隙,孔隙较小时多为球形(如图5(c)所示),这些地方为纤维搭接处,在制造过程中纤维束难以完全填充因而容易夹杂空气,同时,由于应力不同孔隙形状也存在差异;而当孔隙较大时,基本呈现出扁平状。经观察发现,大面积扁平形孔隙数量较少,小的球形孔隙占主要部分。此外,纤维层内也存在孔隙,以圆形或不规则形的小空隙为主,且大多分布在90°铺层的碳纤维中(如图5(c)所示),玻璃纤维及0°铺层纤维中孔隙含量较少。
2.4 孔隙分布统计
对拍摄到的金相照片进行分析和统计,所得结果如表1所示,其中统计参数包括孔隙长度、宽度、面积、周长以及宽长比和形状因子,其中形状因子定义为
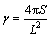 (1)
(1)
式中: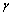 为孔隙的形状因子;S为孔隙的截面面积;L为孔隙的周长。孔隙的形状因子表征了孔隙形状的不规则程度和孔隙的形态特征,孔隙的宽长比是孔隙宽度和长度的比值,孔隙的宽长比表征了孔隙趋向扁平形状的程度。
为孔隙的形状因子;S为孔隙的截面面积;L为孔隙的周长。孔隙的形状因子表征了孔隙形状的不规则程度和孔隙的形态特征,孔隙的宽长比是孔隙宽度和长度的比值,孔隙的宽长比表征了孔隙趋向扁平形状的程度。
从表1可以看出:随着孔隙率的增加,孔隙的面积、长度和宽度均存在增大趋势,但与层板复合材料相比,长度增加范围较小,而宽度增加范围较大;当孔隙率从0.62%增加到2.37%时,长度平均值增加了51%,宽度平均值增加了56%,而当层板复合材料孔隙率从0.8%增加到2.8%时,长度平均值增加了164%,宽度平均值几乎不变[9]。由此可知:随着孔隙率的增加,孔隙的整体尺寸均增大,孔隙在各个方向均有增大趋势,而非只沿某一方向如长度方向发展。此外,随着孔隙率增加,一些大面积孔开始出现,以扁平型和椭圆形为主,但数目较少。
经统计,随着孔隙率的增加,孔隙数目也逐渐增多,并且当孔隙率大于1.5%时,孔隙数目增加的速度变大,孔隙率与孔隙数量的关系曲线如图6所示。以试块1和试块5为例,二者统计的图像数量相同,而试块5的孔隙数量比试块1的孔隙数量多1.85倍,在孔隙平均面积变化不大的情况下,孔隙数目的增多是造成孔隙率增大的主要原因。
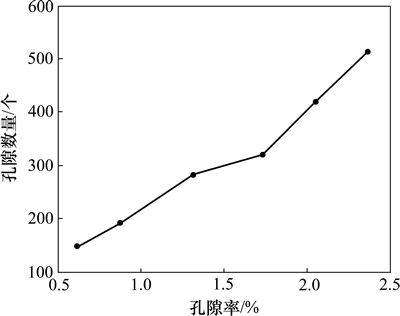
图6 孔隙率与孔隙率的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between porosity and pores rate
宽长比、形状因子与孔隙率关系曲线见图7。如图7中曲线1所示,各种孔隙率下孔隙的平均宽长比基本相同,孔隙形态基本相似。其主要原因是孔隙多发生在树脂区,孔隙受到的各向压力均匀。而层板复合材料由于孔隙多发生在层间,随着孔隙面积的增大,受层间挤压的影响,孔隙长度变化明显,扁平型孔隙逐渐增多,从而使孔隙宽长比发生明显变化。
由图7中曲线2可以看出:孔隙形状因子随孔隙率的增加呈下降趋势,且当孔隙率大于1.5%时,形状因子下降明显。由于当孔隙率较小时,孔隙以小的圆形孔隙为主,孔隙形状比较规则,且孔隙多出现在树脂间,随着孔隙率的增大,树脂间形成密集孔隙,小孔隙逐渐靠近,并有部分连接在一起形成不规则的孔隙,但仍以小的球形孔隙为主;而当孔隙率较大时,一些大的不规则孔隙开始出现并且数量增多,特别是纤维层间开始出现扁平形长孔隙,因而使孔隙形状因子明显减小。
表1 孔隙统计特征
Table 1 Statistical characteristics of pores
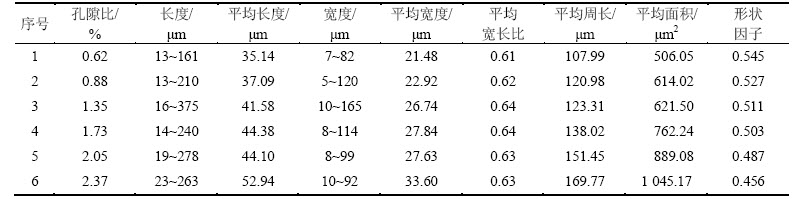
图7 宽长比、形状因子与孔隙率关系曲线
Fig. 7 Relationship among width/length, shape factor and pores rate
分别对单个样本的孔隙长度和宽度进行统计分析,结果如图8和图9所示,图中孔隙长度和宽度的统计间隔为10 μm,孔隙率为统计区间内孔隙数量占孔隙总数的百分比。从图8和图9可以看出:孔隙长度和宽度表现出对数分布的特征;随着孔隙率的增大,孔隙长度和宽度的平均值变大,且随着孔隙率的增大,长度和宽度较大的孔隙逐渐增多。该统计规律与层板复合材料相似,并且当取孔隙长度和宽度的自然对数作为横坐标、取孔隙率作为纵坐标作图时,统计结果呈现出高斯分布,由此可知孔隙长度、宽度与孔隙率之间均存在近似对数正态分布关系。图10所示为试块5取孔隙长度和宽度的对数为横坐标时的统计结果。
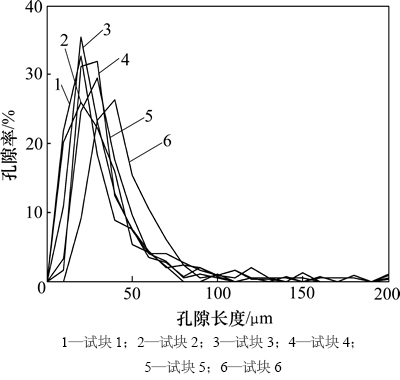
图8 各个试块孔隙长度分布图
Fig. 8 Statistical characteristics of pore length
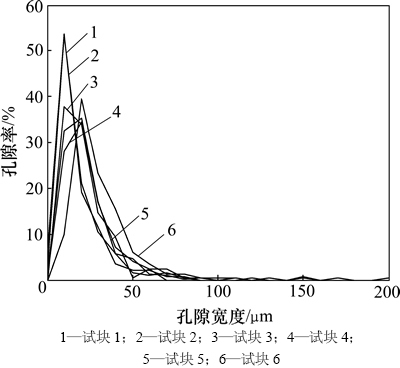
图9 各个试块孔隙宽度分布图
Fig. 9 Statistical characteristics of pore width
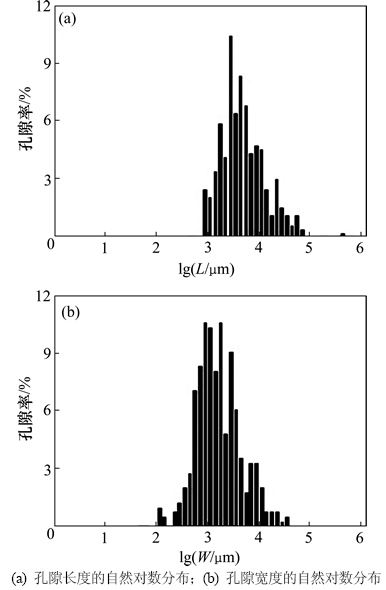
图10 试块5孔隙长度L和宽度W的自然对数分布图
Fig. 10 Statistical characteristics of nature log of pore length and width of sample 5
3 结论
1) 编织复合材料变厚度面纤维以90°铺层为主,变厚度侧由90°铺层纤维填充、0°铺层纤维固定形状;纤维层轮廓各异,0°铺层纤维易发生分裂现象。
2) 编织复合材料易出现富脂区域,且富脂区容易出现微裂纹,纤维层间有分层现象。
3) 孔隙主要分布在树脂区和层间,以小的球形孔隙为主,富脂区域容易出现集中孔隙。
4) 随着孔隙率的增加,孔隙平均长度、宽度和面积有小幅度增加,但仍以球形为主,孔隙数量的增加是导致孔隙率增加的主要原因,且当孔隙率大于1.5%时,孔隙数目增加得更快;随着孔隙率的增加,孔隙长度、宽度和面积均增大,孔隙宽长比基本相同,孔隙形状因子减小,且当孔隙率大于1.5%时,形状因子减小加剧;孔隙长度、宽度与孔隙含量之间均存在近似对数正态分布关系。
参考文献:
[1] Dexter H B. Innovative textile reinforced composite materials for aircraft structures[C]// Seattle: Proc of the 28th Int SAMPE Technical Conf. 1996: 404-416.
[2] Bilisik K. Three-dimensional braiding for composites: A review[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2013, 83(13): 1414-1436.
[3] Mouritz A P, Bannister M K, Falzon P J, et al. Review of applications for advanced three-dimensional fibre textile composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1999, 30(12): 1445-1461.
[4] Chambers A R, Earl J S, Squires C A, et al. The effect of voids on the flexural fatigue performance of unidirectional carbon fibre composites developed for wind turbine applications[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2006, 28(10): 1389-1398.
[5] Hagstrand P O, Bonjour F, Mason J A E. The influence of void content on the structural flexural performance of unidirectional glass fibre reinforced polypropylene composites[J]. Compos Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2005, 36(5): 705-714.
[6] 高晓进, 张峥. CFRP中孔隙几何形貌与超声衰减系数关系的研究[J]. 材料工程, 2012(7): 59-63.
GAO Xiaojin, ZHANG Zheng. Research of the relationship between pore morphology and ultrasonic attenuation coefficient in CFRP[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2012(7): 59-63.
[7] 牟云飞, 林莉, 郭广平, 等. CFRP随机孔隙模型及孔隙率超声检测数值模拟[J]. 材料工程, 2010(1): 54-57.
MU Yunfei, LIN Li, GUO Guangping, et al. CFRP random pores model and numerical simulation of porosity ultrasonic testing[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2010(1): 54-57.
[8] 田宏涛. 碳纤维复合材料孔隙几何形貌定量分析与研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012: 23-52.
TIAN Hongtao. Quantitative analysis and investigation on geometrical morphology of pore in CFRP[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. College of Materials Science and Engineering, 2010: 23-52.
[9] 华志恒, 周晓军, 刘继忠. 碳纤维复合材料(CFRP)孔隙的形态特征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2005, 22(6): 103-107.
HUA Zhiheng, ZHOU Xiaojun, LIU Jizhong. Morphology of pores in carbon fiber reinforced plastics[J]. Acta Material Compositae Sinica, 2005, 22(6): 103-107.
[10] 刘继忠, 蒋志峰, 华志恒. 含孔隙形态分布特征的孔隙率超声衰减测试建模[J]. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(2): 67-71.
LIU Jizhong, JIANG Zhifeng, HUA Zhiheng. A morphoogical study based ultrasonic attenuation model of carbon fiber reinforced plastics porosity testing[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26(2): 67-71.
[11] 顾轶卓, 张佐光, 李敏, 等. 复合材料变厚层板热压成型缺陷类型与成因实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(2): 41-46.
GU Yizhuo, ZHANG Zuoguang, LI Min, et al. Experimental study on type and cause of defects in variable thickness composite laminates during hot pressing process[J]. Acta Material Compositae Sinica, 2008, 25(2): 41-46.
[12] 邓火英, 张佐光, 顾轶卓. L形层板真空袋成型缺陷的实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(4): 34-39.
DENG Huoying, ZHANG Zuoguang, GU Yizhuo, et al. Experimental research on defects of L-shape laminates in vacuum-bag process[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2007, 24(4): 34-39.
[13] 刘建, 张永振, 杜三明, 等. PTFE编织复合材料摩擦特性研究[J]. 材料工程, 2012(8): 69-72.
LIU Jian, ZHANG Yongzhen, DU Sanming, et al. Study on friction characteristics of PTFE braided composites[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2012(8): 69-72.
[14] Wang Baolai, Fang Guodong, Liang Jun, et al. Failure locus of 3D four-directional braided composites under biaxial loading[J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2012, 19(3/4): 529-544.
[15] 胡宏伟, 李雄兵, 杨岳, 等. CFRP复杂型面构件的孔隙率超声检测方法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(4): 1315-1319.
HU Hongwei, LI Xiongbing, YANG Yue, et al. Method of inspecting porosity in CFRP with complex surface by ultrasonic[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(4): 1315-1319.
[16] GB/T 3365—2008, 碳纤维增强塑料孔隙含量和纤维体积含量试验方法[S].
GB/T 3365—2008, Carbon fiber reinforced plastics: Determination of void content and fiber volume content[S].
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2014-04-10;修回日期:2014-06-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51075358,51005252,61271356);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(201001011200155);浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(LY14E050013) (Projects(51075358, 51005252, 61271356) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(201001011200155) supported by the PhD Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China; Project(LY14E050013) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China)
通信作者:周晓军,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事检测、车辆及信号处理研究;E-mail: cmeesky@163.com