文章编号:1004-0609(2010)07-1440-06
电渗析处理石煤提钒废水
包申旭1,张一敏1, 2,刘 涛1,陈铁军1
(1. 武汉理工大学 资源与环境工程学院,武汉 430070;
2. 武汉理工大学 矿物资源加工与环境湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430070)
摘 要:采用循环式电渗析器处理石煤提钒过程中产生的大量高盐度、富含重金属的酸性废水。结果表明:在不同电压条件下,淡水箱中的盐度在脱盐开始时变化显著,随着脱盐的进行,盐度变化逐渐趋于平缓;55 V时的平均脱盐速率为19.84 mg/(L?s),约为25V时脱盐速率的3倍;电流随时间都表现出先上升再下降的变化趋势,55 V时的单位能耗为25 V时的2倍。脱盐过程中,阴离子的脱除顺序为Cl-、SO42-。试验中单台循环式电渗析的最大淡水产率为78%,淡水可回收用于工业生产或排放。
关键词:电渗析;高盐废水;钒;石煤
中图分类号:X703.1 文献标志码:A
Electrodialytic treatment of wastewater produced in vanadium extraction from stone coal
BAO Shen-xu1, ZHANG Yi-min1, 2, LIU Tao1, CHEN Tie-jun1
(1. School of Resource and Environmental Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China;
2. Hubei Key Laboratory of Mineral Resources Processing and Environment, Wuhan University of Technology,
Wuhan 430070, China)
Abstract: The acid wastewater produced in vanadium extraction from stone coal was desalinated by electrolysis. The results show that, at different voltages, the salinities of solutions in diluate tank vary rapidly at the beginning of desalination but slowly with the proceeding of desalination. The average desalination rate is 19.84 mg/(L?s) at 55 V, which is nearly three times faster than that at 25 V. The trends of current identified by the feature increase at initial stage and decrease sharply later. The specific power consumption at 55 V is two times higher than that at 25 V. The anions are removed in the following order: Cl-, SO42-. The maximum water recovery of one electrodialysis unit can reach 78% and the diluate can be recycled in production or discharged.
Key words: electrodialysis; high-salt wastewater; vanadium; stone coal
石煤是我国特有的一种含钒资源。据统计,我国南方7省含钒石煤中V2O5的储量达1.197 9亿吨,是国内钒钛磁铁矿中V2O5的7倍,比其它国家V2O5的地质总储量还多[1-2]。随着钢铁、化工等行业对钒的需求逐年上升,利用石煤提取钒在我国正日益受到重 视[3-4]。由于钒在石煤中特殊的赋存状态,大部分石煤需经加盐焙烧才能保证钒具有较高的产率和回收率,但加盐焙烧工艺带来的主要问题就是会产生大量高盐度废水。大量随意排放这种高盐度、高矿化度水体会给环境造成很大的危害[5]。高含盐水体能加速电化学反应,严重腐蚀、损害生产设备;如排入农田,由于其含盐量大大高于农田灌溉用水标准[6],可造成土地盐渍化、土壤板结、农作物烂死,给生态环境和当地居民的生活以及工农业生产带来严重的负面影响。因此,对高盐废水进行综合处理,实现该类水体的二次利用或无害排放对于我国石煤资源的环境友好型开发利用具有重要的意义。
高盐废水的处理方法目前主要分为膜法和热法两大类,膜法由于能耗低、投资小和操作简单等优点在其中占主导地位[7-8]。反渗透和电渗析是目前应用最为广泛的膜法脱盐技术,但前者存在着对水质要求较高、淡水产率低、膜易结垢等缺点[9],而电渗析技术在这些方面具有较大的优势。因此,本文作者主要研究电渗析器对石煤提钒废水的处理,以期推动电渗析器在该类废水处理中的应用。
1 实验
1.1 试验仪器和方法
研究所用的循环式电渗析装置如图1所示。膜堆组装方式为一级二段式,采用钛涂钌电极,阴阳膜采用国产某新型异相离子交换膜,膜面积为160 mm× 520 mm,膜对数为50,湿阳膜厚约0.90 mm,湿阴膜厚约0.88 mm,隔板厚为1 mm。废水阳离子含量用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱仪(ICP-AES,Perkin- Elmer)测定;阴离子含量用离子色谱(DIONEX? ICS-1500) 测定;悬浮固体(SS)和化学需氧量(COD)的测定据《水和废水监测分析方法》[10];pH值用精密pH仪(上海精科 PHS-3C)测定;电导用电导率仪(上海精科DDS-307A)测定;溶液盐度通过电导-盐度标准曲线换算得到。

图1 循环式电渗析试验装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of experimental system of electrodialysis: 1—Electrodialysis stack; 2—Diluate tank; 3—Concentrate tank; 4—Electrode solution tank; 5—Pump; 6—Valve; 7—Flowmeter; 8—Manometer; 9—Recifier
1.2 废水特征
试验所用水样为湖北某石煤提钒厂产生的工业废水,水体的pH值约为4.5,SS含量高达670 mg/L,主要化学成分见表1。
表1 废水主要化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of wastewater (mg/L)

从表1可知,原水盐度很高,约为30 g/L,SS和重金属含量远远超过电渗析进水要求[11]。因此,需要采用石灰-纯碱-混凝沉淀法对原水进行预处理[12]。处理后废水pH为10.12,SS含量小于3 mg/L,COD含量为80 mg/L,其它主要化学成分见表2。
表2 预处理后废水中主要化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of wastewater after pre- treatment (mg/L)

对比表1和表2可以看出,石煤提钒废水经过石灰-纯碱-混凝沉淀法预处理后,重金属离子含量有明显的降低,废水中主要存在的是Na+、Cl-和SO42-等离子,满足电渗析进水要求。
2 结果与分析
2.1 盐度变化特征和脱盐速率
根据膜的技术要求,同时为了避免发生极化现 象[13],试验选定的膜堆电压分别为55、45、35和25 V。试验开始时,浓、淡水箱废水体积均为15L。由于膜存在浓差渗透,为保持浓、淡水箱中溶液体积平衡,淡水管的压力要稍高于浓水管的压力,淡水室和浓水室压力分别为0.08和0.07 MPa。浓、淡水室流量均为450 L/h。
图2所示为不同电压条件下淡水箱中废水盐度和膜堆电流随时间的关系。从图2可以看出,不同电压条件下废水盐度都随脱盐的进行呈现出单调的下降趋势,且在脱盐初期盐度变化显著,随着脱盐的进行,脱盐速率逐渐降低。
由于盐度在1 000 mg/L以下的水体不会对环境造成较大的危害,因此将废水脱盐到1 000 mg/L时即可回用于工业生产或排放。这一过程的平均脱盐速率定义为
 (1)
(1)
式中:v为平均脱盐速率,mg/(L?s);Cd为淡水箱盐度,mg/L;?t为脱盐时间,s。
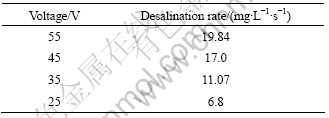
从表3可以看出,平均脱盐速率随电压的降低下降明显,25 V电压下的平均脱盐速率约为55 V电压下的33%。
2.2 电流变化特征和能耗
在相同的试验条件下,膜堆加电后每隔30 s记录
表3 不同电压下的平均脱盐速率
Table 3 Average desalination rate at different voltages
一次通过膜堆的电流值。从图2可以看出,循环式电渗析器在对高盐度水体的脱盐过程中,电流随时间呈现出先升高后降低的抛物线变化轨迹,最后电流趋向一恒定的最小值,这与其在苦咸水脱盐过程中电流随时间单调下降的特征有显著的区别[14]。根据欧姆定律,通过膜堆的电流I为
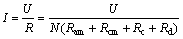 (2)
(2)
式中:U为加在膜堆上的电压,V;R为膜堆的总电阻,Ω;N为膜对数;Ram为阴膜电阻,Ω;Rcm为阳膜电阻,Ω;Rc为浓水室电阻,Ω;Rd为淡水室电阻,Ω。对于已选定的离子交换膜来所,Ram和Rcm

图2 不同电压下淡水箱盐度和电流随时间的关系
Fig.2 Relationships among salinity, current and time in diluate tank at different voltages: (a) 55 V; (b) 45 V; (c) 35 V; (d) 25 V
为一定值,随时间变化的只是浓、淡水室的电阻Rc和Rd,浓水室的电阻Rc可以表示为
 (3)
(3)
式中:ρc为浓水室的电导率,S/m;d为隔板厚度,m;δ为膜表面能斯特(Nernst)扩散层厚度,m[15];A为有效膜面积,m2。由于ρc是溶液电解质浓度的函数,因此式(3)可以变换为
 (4)
(4)
同理,淡水室的电阻Rd可表示为
 (5)
(5)
式中:cc和cd分别为浓水室和淡水室溶液的摩尔浓度,mol/L;Λc和Λd分别为浓水室和淡水室溶液的摩尔电导率,S?m2?mol-1。
由于初始浓、淡水室电解质的浓度非常高,刚开始加电时,浓水室浓度开始升高,其电阻下降,虽然淡水室溶液浓度逐渐变小,但其摩尔电导率并非随浓度线性降低[16],淡水室的电阻在初期仍维持在较低的水平。此外,通电后,溶液的摩尔电导率会随温度的增加有一定的上升,膜堆总电阻变小,因此试验开始时通过膜堆的电流逐渐上升。随着脱盐的进行,淡水室电解质浓度不断下降,到一定程度时其电阻显著上升,这时淡水室电阻成为控制膜堆电流的主要因素,膜堆电流开始下降。到脱盐的末期,浓、淡水室盐度达到平衡,膜堆总电阻趋于稳定,通过膜堆的电流也达到恒定的最小值。
脱盐过程中单位电能消耗为[14]
 (6)
(6)
式中:E为单位能耗,kW?h?m-3;Vd为淡水箱中溶液的体积,m-3。
根据式(6)可以计算不同电压条件下,将淡水箱中废水的盐度降低到1 000 mg/L时的单位电能消耗,结果见表4。
由表4可知,单位脱盐能耗随膜堆电压的降低而降低,25 V时的单位能耗约为55 V时的50%,但其平均脱盐速率却只有55 V条件下的33%(见表3),因此,要根据脱盐的实际需求合理选择最佳电压条件。
表4 不同电压下的单位能耗
Table 4 Specific power consumption at different voltages

2.3 Cl-和SO42-的变化特征
图3所示为淡水箱中Cl-和SO42-浓度随时间的变化。从图3可见,不同电压下在脱盐初期,Cl-的含量下降非常明显,而SO42-的浓度相对变化较小;随着脱盐的进行,Cl-的脱除速度逐渐变小,而SO42-的含量在脱盐中期却变化较为显著,最终,Cl-和SO42-含量的变化都趋于稳定。本研究中,不同电压下阴离子的脱除顺序为Cl-、SO42-,这与SIRIVEDHIN等[17]对油田工业废水的脱盐研究结果不同,表明溶液中离子的存在形式和络合状态影响着其脱除速率。另外,离子交换膜的类型可能也是影响离子脱除速率的因素之一[18]。
2.4 pH的变化
图4所示为不同电压条件下淡水室pH值随时间的变化。由图4可见,不同电压下,淡水室pH值都随脱盐的进行而逐渐降低,这主要是由于淡水室水体中的OH-在电场力的作用下迁移到浓水室的缘故。pH值的变化规律与盐度的变化一致,高电压条件下的pH值的变化要远快于低电压条件下的pH值。到处理终点时,不同电压条件下淡水的pH值较为接近,均保持在9左右。
2.5 淡水产率
试验研究了在最大电压条件下(55 V),循环式电渗析处理该废水的最大淡水产率。脱盐过程中,当淡水室废水盐度降到1 000 mg/L后就换入原始废水,如此循环直到浓、淡水室废水盐度不再发生变化为止,此时测得浓水室的最大盐度为132.8 g/L。
单台循环式电渗析的淡水产率为
 (7)
(7)
式中:R为淡水产率;C0为原水盐度,mg/L;Cmax为浓水室最大盐度,mg/L。
根据式(7)可以计算出本研究中单台循环式电渗析器的最大淡水产率为78%。

图3 不同电压下淡水室Cl-和SO42-浓度随时间的变化
Fig.3 Changes of Cl- and SO42- concentration in diluate tank with time at different voltages: (a) 55 V; (b) 45 V; (c) 35 V; (d) 25 V

图4 不同电压下淡水室pH随时间的变化
Fig.4 Changes of pH in diluate tank with time at different voltages
3 结论
1) 石煤提钒废水的重金属离子浓度、SS含量和
盐度较高,利用石灰-纯碱-混凝沉淀法对进行预处理后,可有效除去其中的重金属离子和SS,但对去除盐度没有效果。经石灰-纯碱-混凝沉淀法预处理后的废水可以满足电渗析的进水要求。
2) 电渗析脱盐过程中,在不同的电压条件下,淡水箱盐度呈单调下降的趋势,且盐度在脱盐开始时下降明显,随着脱盐的进行,盐度变化逐渐趋于稳定;电流随时间呈现出先升高后降低的特征;25 V时的单位能耗约为55 V时的50%,但平均脱盐速率却只有55 V条件下的33%。
3) 不同电压条件下,Cl-浓度在脱盐初期变化显著,随着脱盐进行而逐渐趋于稳定,SO42-浓度开始变化较小,在脱盐中期变化明显,最后与Cl-一样趋于稳定。阴离子的脱除顺序为Cl-、SO42-。淡水箱的pH值随时间不断降低,到脱盐终点时pH从10.12下降到9左右。本研究中单台电渗析的最大淡水产率为78%,淡水可回用于工业生产或排放。
REFERENCES
[1] 包申旭, 张一敏, 刘 涛, 陈铁军. 全球钒的生产、消费及市场分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2009, 18(7): 12-15.
BAO Shen-xu, ZHANG Yi-ming, LIU Tao, CHEN Tie-jun. The production, consumption and market analysis of vanadium in the world [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2009, 18(7): 12-15.
[2] 宾智勇. 石煤提钒研究进展和五氧化二钒的市场状况[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2006, 22(1): 16-20.
BIN Zhi-yong. Progress of the research on extraction of vanadium pentoxide from stone coal and the market of the V2O5 [J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 22(1): 16-20.
[3] 冯其明, 何东升, 张国范, 欧乐明, 卢毅屏. 石煤提钒过程中钒氧化和转化对钒浸出的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(8): 1348-1352.
FENG Qi-ming, HE Dong-sheng, ZHANG Guo-fan, OU Le-ming, LU Yi-ping. Effect of vanadium oxidation and conversion on vanadium leaching in extraction process of vanadium from stone coal [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1348-1352.
[4] HE D S, FENG Q M, ZHANG G F, OU L M, LU Y P. An environmentally-friendly technology of vanadium extraction from stone coal [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20: 1184-1186.
[5] PATTERSON R A. Wastewater quality relationships with reuse options [C]// Proceedings of 1st World Water Congress of the International Water Association (Conference Preprint Book 8), 2000. Paris, France: International Water Association, 2000: 205-212.
[6] GB 5084—2005. 中华人民共和国国家标准——农田灌溉水质标准[S].
GB 5084—2005. Standards for irrigation water quality of National Standard of the People’s Republic of China [S].
[7] WALHA K, AMAR R B, FIRDAOUS L, QU?M?NEUR F, JAOUEN P. Brackish groundwater treatment by nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis in Tunisia: Performance and cost comparison [J]. Desalination, 2007, 207: 95-106.
[8] 高从堦, 陈益棠. 纳滤膜及其应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(S1): 310-316.
GAO Cong-jie, CHEN Yi-tang. Nanofiltration membrane and its application [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(S1): 310-316.
[9] RAHARDIANTO A, SHIH W Y, LEE R W, COHEN Y. Diagnostic characterization of gypsum scale formation and control in RO membrane desalination of brackish water [J]. J Memb Sci, 2006, 279: 655-668.
[10] 魏复盛. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. (第四版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 220-222.
WEI Fu-sheng. Standard methods for water and wastewater monitoring and analysis [M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Press, 2002: 220-222.
[11] 时 钧, 袁 权, 高从堦. 膜技术手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2001: 468.
SHI Jun, YUAN Quan, GAO Cong-jie. The handbook of membrane technology [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2001: 468.
[12] 丁晓涛, 张一敏, 包申旭. 石煤提钒酸性高盐重金属废水的预处理研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2010. (已接收)
DING Xiao-tao, ZHANG Yi-min, BAO Shen-xu. Study on treatment of acid waste water containing heavy metal ions from vanadium extraction from stone coal by lime neutralization and coagulation-sedimentation [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2010. (accepted)
[13] TANAKA Y. Current density distribution, limiting current density and saturation current density in an ion-exchange membrane electrodialyzer [J]. J Membr Sci, 2002, 210: 65-75.
[14] ORTIZ J M, SOTOCA J A, EXP?SITO E, GALLUD F, GARC?A-GARC?A V, MONTIEL V, ALDAZ A. Brackish water desalination by electrodialysis: Batch recirculation operation modeling [J]. J Membr Sci, 2005, 252: 65-75.
[15] NIKONENKO V V, PISMENSKAYA N D, ISTOSHIN A G, ZABOLOTSKY V I, SHUDRENKO A A. Description of mass transfer characteristics of ED and EDI apparatuses by using the similarity theory and compartmentation method [J]. Chem Eng Process, 2008, 47: 1118-1127.
[16] LIDE D R. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics [EB/OL]. Internet Version 2007, (87th Edition). http:/www.hbcpnetbase. com.
[17] SIRIVEDHIN T, McCUE J, DALLBAUMAN L. Reclaiming produced water for beneficial use: Salt removal by electrodialysis [J]. J Membr Sci, 2004, 243: 335-343.
[18] POURCELLY G. Conductivity and selectivity of ion exchange membranes: Structure correlations [J]. Desalination, 2002, 147: 359-361.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家博士后科学基金资助项目(20080440967); “十一五”国家科技支撑计划课题资助项目(2007BAB15B02)
收稿日期:2009-07-22;修订日期:2009-12-28
通信作者:张一敏,教授,博士;电话:027-87212127; E-mail: zym126135@126.com