Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3660-3665
Geostress measurements near fault areas using borehole stress-relief method
Ming-qing HUANG, Ai-xiang WU, Yi-ming WANG, Bin HAN
School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 4 December 2013; accepted 8 April 2014
Abstract: To minimize negative effects of geostress distribution on mining safety near the fault areas, the UPM40 triaxial geostress testing system was introduced to conduct in-situ geostress measurements at three sites and nine points by the borehole stress-relief method. The results of strain-confining pressure curves show that rock masses at the three measuring sites exhibit comprehensive linear elasticity in spite of various fissures or cracks within rocks. Horizontal and vertical stress components distribute discrepantly near the fault areas, and the maximum lateral pressure coefficient is as high as 6.15. The maximum principle stress ranges from 8.01 to 14.93 MPa, and stress directions are in the range of N78.07°W-N17.55°W. Geostresses near fault areas are dominated by the horizontal tectonic stresses, while the lower values, compared to those under similar geological conditions are due to stress release by the fault. Additionally, the fault and shear stress nearby are partially responsible for asymmetric elongation and southwesterly migration of orebodies.
Key words: fault areas; geostress distribution; borehole stress-relief method; lateral pressure coefficient; horizontal tectonic stress
1 Introduction
Geostress is one of the most important influential factors that govern the stability of underground engineering. A proper understanding of geostress distribution and variation is beneficial to mining design, roadway arrangements and supporting techniques [1,2]. Geostress often refers to initial rock stress that includes gravity stress and tectonic stress. Its magnitude and direction are usually affected by multiple factors such as mining depth, tectonics, lithology and blasting [3,4]. In the past few decades, researchers worldwide have carried out hundreds of researches with regard to geostress measurements, numerical simulations and theoretical calculations. In 2001, FUCHS and  [5] presented the world map of tectonic stresses after summarizing the global stress data, and pointed out the impacts of stresses on seismic hazard quantification and technological problems in underground openings managements. Similarly, ZHAO et al [6] reviewed the initial geostress measurement results in China up to 2007. They plotted a dispersed point chart of the ratios of the average horizontal geostress to the vertical geostress varying with depth, and stated the laws of geostress properties of magmatic rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. More recently, JING et al [7], WU et al [8], MA et al [9] and GUO et al [10] have presented detailed in-situ geostress measurements in various underground mines, and discussed control approaches to avoid hazards induced by rock stresses.
[5] presented the world map of tectonic stresses after summarizing the global stress data, and pointed out the impacts of stresses on seismic hazard quantification and technological problems in underground openings managements. Similarly, ZHAO et al [6] reviewed the initial geostress measurement results in China up to 2007. They plotted a dispersed point chart of the ratios of the average horizontal geostress to the vertical geostress varying with depth, and stated the laws of geostress properties of magmatic rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. More recently, JING et al [7], WU et al [8], MA et al [9] and GUO et al [10] have presented detailed in-situ geostress measurements in various underground mines, and discussed control approaches to avoid hazards induced by rock stresses.
The proceeding researches were mainly carried out in respect of intact, viscoelastic and homogenous rock masses, so as to minimize the negative effects of flabby and intricate geological structures on measuring precision. However, tectonics like faults are inevitable when designing underhand roadways and shafts. Fault is a typical tectonic, and represents a basal geological factor for geostress distribution [11]. On one hand, the formation and development of faults tend to disturb the mineralizing laws in mining areas. On the other hand, faults usually take great effect on tectonic stress, and therefore challenging the stability of underhand structures. Hence, geostress measurements near the fault areas are within the scope of design and operation considerations, especially for those mines with weak tectonics.
Geostress measurement methods currently include direct methods and indirect methods in terms of measuring principles [12]. The direct methods are realized by directly measuring multiple stresses by apparatus, and the initial rock stress is calculated according to its relationship with the tested multiple stresses. By recording indirect physical independent variables dynamically using sensor components, targeted parameters of the indirect methods can be calculated by the established formulas. Though indirect methods require more advanced apparatus, stricter technologies, longer performing time and higher costs compared with the direct methods, they tend to lead to more precise results. Among many indirect methods, the borehole stress-relief method is highlighted for its reliability and applicability. Thus, this method is accepted for geostress measurements in this work.
The aim of this work is to measure geostress near the ore-controlling fault areas and present geostress distribution laws. Firstly, three measuring sites are arranged in a fault area, whose tectonics properties directly deteriorate the mining safety. Secondly, the UPM40 triaxial geostress testing system and LUT triaxial strain gauges are introduced to perform the in-situ rock stress measurements. Thirdly, the geostress distribution characteristics and the relationship between geostress and regional tectonics in the fault areas are discussed along with the results of dual-axis experiments. The relative work has overcome serious challenges in borehole drilling and geostress measuring near fault areas, and some informative and conclusive geostress data are put forward, which is beneficial to practical mining.
2 Measuring sites and methods
2.1 Tectonics and fault
The geostress measurements were carried out in Mine III (Fig. 1). Strata belong to the old metamorphic rock series in early Proterozoic. This region experienced couples of tectonics movements, during which the reverse fault F8 formed across the mining region, and forced Mine III to derive from matrix Mine I. As a negative geological tectonic, fault F8 and its crushed zone were 15-32 m in width, and directly cut through the ore body. The ore body was embedded in stable ultrabasic rocks and parent rocks, the hanging wall was surrounded by fractured chlorite schist zones, whereas the footwall consisted of broken rock masses such as griotte, biotite gneissic rocks and mica quartz schist. Additionally, underground mining operations were all located within the footwall rock masses.
2.2 Measuring sites arrangement
Three boreholes (i.e. sites 1-3 in Fig. 2) were arranged in three parallel crosscut drifts near the ore-controlling fault F8. The mining depth was about 720 m, and the distances from fault F8 varied from 49.2 to 70.3 m (Table 1). To avoid the formation of secondary stress field induced by mining activities, the measuring sites were set tens of meters away from working operations.
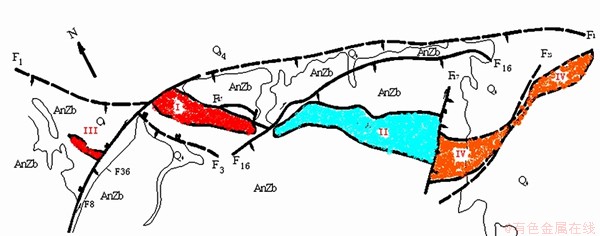
Fig. 1 Location and main tectonics distribution in mine areas
Table 1 Three measuring sites near ore-controlling fault areas
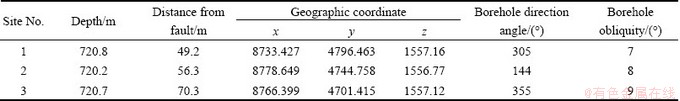
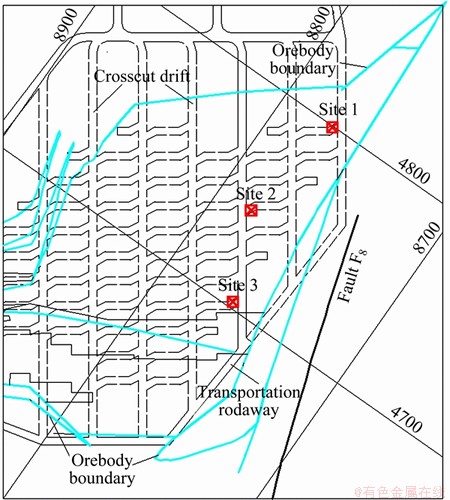
Fig. 2 Measuring sites arrangement near fault areas
2.3 Measuring apparatus and method
Geostresses were measured by UPM40 rock triaxial geostress testing system and the LUT triaxial strain gauges [13]. Each LUT triaxial gauge probe includes three groups of strain rosette pistons, whose fix angles along the axial direction are sequentially 270°, 30° and 150°. Each piston has two rosettes, and each rosette consists of two groups of orthogonal resistances strain gauges. Angles of four gauges along the probe axis are 90°, 45°, 0° and 135°, respectively (Fig. 3). The system has 20 galleries, and is able to automatically record and print the released strains of 20 measuring points. The data collecting system will automatically recognize and exclude the suspicious data to maintain the reliability of the maximal principal stress. In addition, the modified compensate circuit is able to eliminate the adverse effects of environmental temperatures on measuring precision. Other auxiliary equipments mainly consist of 1) oil-water separator, 2) portable dual-axis experimental equipment, usually operated in conjunction with strain gauges, 3) electricity temperature testing system and 4) aluminium alloyed install rods for connecting washing tools and installing tools.
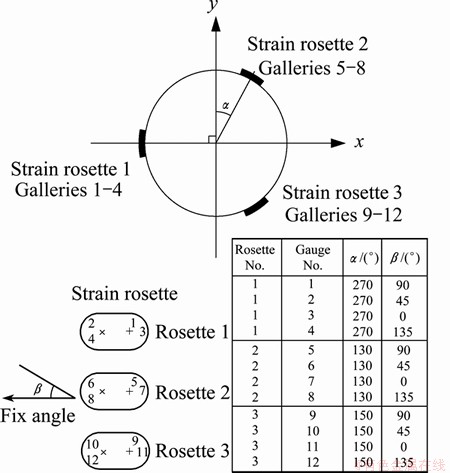
Fig. 3 Angles distribution of LUT triaxial strain gauges
The in-situ measurements were proceeded in several steps. Firstly, the d92 mm borehole was drilled and its depth was recorded. Secondly, a small oriented borehole was concentrically drilled from the bottom of the former borehole, and its diameter was 35 mm and length was about 20 cm. Thirdly, rock core was taken out of the oriented borehole followed by borehole cleaning with water and acetone, respectively. After checking the reliability of boreholes, the gauge was installed where strain rosettes were pasted. Furthermore, a cover hole (91 mm in outer diameter, 40 cm in length) was drilled at a constant rate to take out the rock core together with strain gauges. After that, the geostress testing system was connected to the rock core, and printed strain data very two minutes until the data kept stable. Finally, the dual-axis experiment was conducted to determine the rock elastic modulus and Poisson ratio of the rock.
2.4 Dual-axis experiments
Dual-axis experiments were conducted with the portable dual-axis experimental equipment. The polyethylene jacket was installed in the dual-axis tune, then hydraumatic oil was poured into the jacket, and the rock core was inserted into the tune concentrically. Confining pressures were loaded on the rock core in classified values varying from 0 to 7 MPa by a manual pump. When the recorder consistently printed strain values, strain-confining pressure curves were drawn. Following the thick cylinder theory, the elastic modulus E and Poisson ratio μ can be calculated by Eqs. (1) and (2).
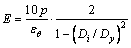 (1)
(1)
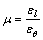 (2)
(2)
where p is the confining pressure, MPa; εθ and εl are the horizontal and vertical strains, respectively, %; Di and Dy are the inner and outer diameters of rock core, respectively, mm.
2.5 Geostress data processing
The LUT-str rock stress program was introduced to process measuring geostresses. After inputting parameters including borehole direction angles, dips, elastic modulus and released strains, the program automatically printed geostress data. These data consisted of six rock stress components and their standard errors, values, direction angles and dips of principle stresses.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Elastic modulus and Poisson ratio
Each measuring site was divided into three measuring points at different borehole lengths, and the final released strain was calculated as the average of three measuring points. Accordingly, the calculation of final elastic modulus and Poisson ratio followed the same pattern. Typical microstrain curves throughout the loading and unloading procedures at each measuring site are shown in Figs. 4-6, respectively.
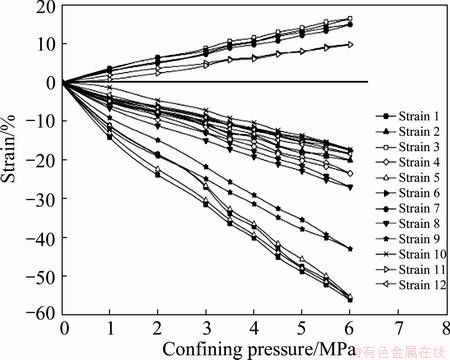
Fig. 4 Strain-confining pressure curves throughout loading and unloading procedures at site 1
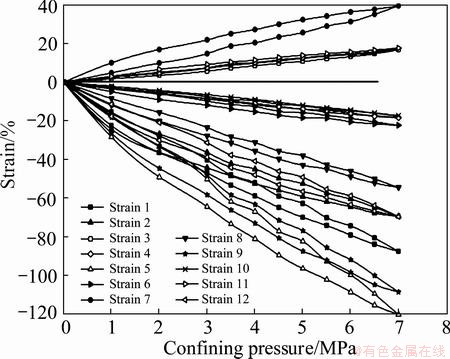
Fig. 5 Strain-confining pressure curves throughout loading and unloading procedures at site 2
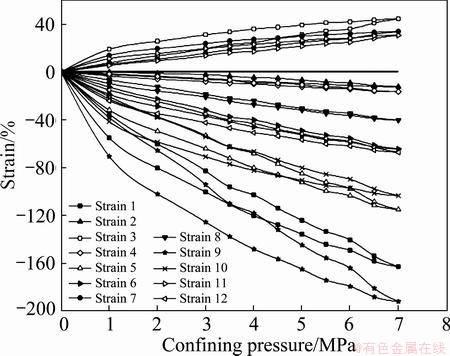
Fig. 6 Strain-confining pressure curves throughout loading and unloading procedures at site 3
Strains at measuring sites 1 and 2 increase approximately linearly with increasing loading and unloading confining pressures, whereas curves at site 3 exhibit tender circuitous variations. Generally, rock masses at three sites show comprehensive linear elasticity in spite of tiny fissures or cracks develop within rocks. Furthermore, the strain confining pressure curves suggest good pastes between strain rosettes and rock masses, and proper operations of strain gauges. The average values of elastic modulus and Poisson ration are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Average values of elastic modulus and Poisson ratio at three measuring sites

3.2 Stress components distribution
A discrepant distribution of horizontal and vertical stress components are observed in ore-controlling fault areas (Table 3). The data show that the maximum horizontal stresses are 1.64-4.18 times higher than the minimum values, whereas the ratio of the maximum horizontal stress to the vertical stress is as high as 9.92. The lateral pressure coefficient is an important indicator to geostress variation tendency, and lateral pressure coefficients are in the range of 0.7-4 in metamorphic rocks when the depths are less than 1000 m in mainland of China [7]. However, the lateral pressure coefficient at site 3 reaches 6.15 and is higher than the reported range, thus posing potential hazards for underground engineering induced by horizontal extrusion.
The maximum shear stress near the fault areas is 3.58 MPa, and this stress partially results in the depth unbalance of burial ore at two sides along the vertical axis. Meanwhile the second maximum shear stress is 3.43 MPa, and this horizontal stress induces the NE-SW ore strike. Additionally, the distribution of shear stresses at three sites shows good accordance with the ore elongation. As shown in Fig. 1, Mine III is long in east-west direction and narrow in south-north direction, and southwesterly migrates about 800 m from matrix Mine I.
3.3 Principle stress distribution
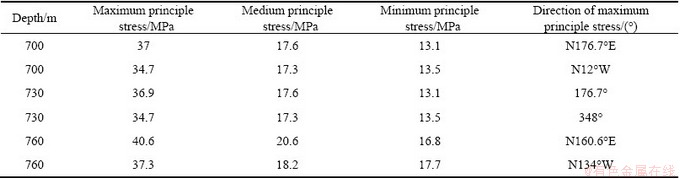
The stress tensor method was introduced to analyze the principle stress distribution. Table 4 shows the principle stress distribution at three measuring sites in Mine III. It can be seen from Table 4 that the maximum principle stresses range from 8.01 to 14.93 MPa, whilst their directions are in the range of 281.93°-342.45° (N78.07°W-N17.55°W). However, the maximum principle stresses, medium principle stresses and minimum principle stresses are accordingly lower than those under similar depths and mining conditions in neighboring mine areas (Table 5) [14,15]. In Mine III, fault F8 and its crushed zones separate the rock connectivity at both sides of the fault, and form a buffering zone for geostress conductivity. Hence, geostress is released and accumulated in the fault and its crushed zones.
Dip angles of the maximum principle stresses at sites 1 and 3 are lower than 20°, which indicates that the tectonics stress field is dominated by the horizontal stress. The dip angle at site 2, however, is approximately vertical (76.24°), suggesting that an inclined stress exists and the stress is possibly influenced by regional hidden tectonics. Generally, the geostress near fault F8 is dominated by horizontal tectonic stress in light of principle stresses distribution at three measuring sites. These results are in agreement with the results in Ref. [15].
Table 3 Stress component distribution at three measuring sites
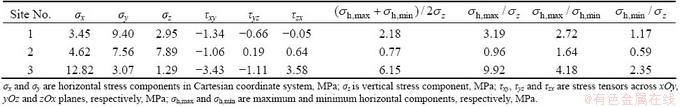
Table 4 Principle stress distribution at three measuring sites in Mine III
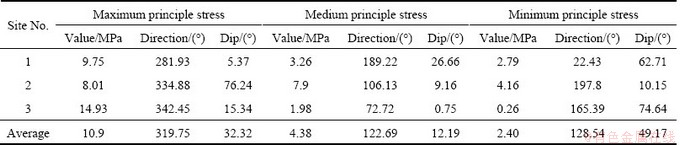
Table 5 Principle stress distribution under similar geological conditions in neighboring Mine II
3.4 Relationships between geostress and regional tectonics
An old and a new tectonic traces have sequentially formed due to historical tectonic movements in mining areas, and their oriented directions are N50°-55°W and east-west, respectively [15]. The motive force of tectonic movements is mainly horizontal tectonic stress in terms of geomechanics views, and the stress direction is perpendicular to the tectonic trace orientation. As discussed in Sections 3.2 and 3.3, the dominated tectonic stress is horizontal or approximately horizontal, and these tectonic stresses control the ground pressure. Because of the distribution of horizontal tectonic stresses, the hanging wall of reverse fault F8 moves towards northwest and the footwall moves towards southeast, whereas shear movements also occur. The measured geostresses are closely related to the regional tectonics, indicating that the measuring results are reliable.
4 Conclusions
1) The strain confining pressure curves throughout the loading and unloading procedures at each measuring site indicate that rock masses at three sites show comprehensive linear elasticity in spite of tiny fissures or cracks developing within rocks therein. The average elastic modulus values are in the range of 6787.74-30569.44 MPa and Poisson ratio is in the range of 0.22-0.29.
2) Horizontal and vertical stress components distribute discrepantly near the fault areas according to the borehole stress-relief method. The maximum horizontal stresses are 1.64-4.18 times higher than the minimum values, and the lateral pressure coefficients are in the range of 0.77-6.15, whereas the high shear stress near the fault area is partially responsible for ore asymmetric elongation and migration.
3) The maximum principle stresses range from 8.01 to 14.93 MPa, and their directions are in the range of N78.07°W- N17.55°W. Geostress near the fault F8 is dominated by horizontal tectonic stress. The lower stresses compared to those under similar geological conditions are due to stress release by the fault and its crushed zones.
References
[1] LI J, FAN P X, WANG M Y. Failure behavior of highly stressed rocks under quasi-static and intensive unloading conditions [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 5(4): 287-293.
[2] YAO Jin-rui, MA Chun-de, LI Xi-bing, YANG Jin-lin. Numerical simulation of optimum mining design for high stress hard-rock deposit based on inducing fracturing mechanism [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2241-2247.
[3] OUYANG Zhen-hua, LI Chang-hong, XU Wan-cai, LI Hao-jie. Measurements of in situ stress and mining-induced stress in Beiminghe Iron Mine of China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2009, 16(1): 85-90.
[4] LU W B, YANG J H, YAN P, CHEN M, ZHOU C B, LUO Y, JIN L. Dynamic response of rock mass induced by the transient release of in-situ stress [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2012, 53(1): 129-141.
[5] FUCHS K,  B. World stress map of the earth: A key to tectonic processes and technological applications [J]. Natur wissenschaften, 2001, 88(9): 357-371.
B. World stress map of the earth: A key to tectonic processes and technological applications [J]. Natur wissenschaften, 2001, 88(9): 357-371.
[6] ZHAO De-an, CHEN Zhi-min, CAI Xiao-lin, LI Shuang-yang. Analysis of distribution rule of geostress in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(6): 1265-1271. (in Chinese)
[7] JING Feng, SHENG Qian, ZHANG Yong-hui, LIU Yuan-kun. Statistical analysis of geostress distribution laws for different rocks [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(7): 1877-1883. (in Chinese)
[8] WU Man-lu, MA Yu, LIAO Chun-ting, LEI Yang, GAO Zhi, QU Ming-yi. Study on recent state of stress in depth 1000 m of Jinchuan mine [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(S2): s3785-s3790. (in Chinese)
[9] MA Chun-de, XU Ji-cheng, CHEN Feng, ZUO Yu-jun. Research on in-situ stress measurement and its distribution law in Dahongshan iron mine [J]. Metal Mine, 2007, 374(8): 42-46. (in Chinese)
[10] GUO Z B, JIANG Y L, PANG J W, LIU J W. Distribution of ground stress on puhe coal mine [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2013, 23(1): 139-143.
[11] LIU Zhi-xiang, DANG Wen-gang, HE Xian-qun, LI Di-yuan. Cancelling ore pillars in large-scale coastal gold deposit: A case study in Sanshandao gold mine, China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(10): 3046-3056.
[12] WU L, XU C M, WU S L, SHI L. Geostress measurement and rock burst prediction analysis for a deep-buried long and large high-speed railway tunnel [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 256-259: 1359-1364.
[13] PENG Kang, LI Xi-bing, WAN Chuan-chuan. Safe mining technology of undersea metal mine [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(3): 740-746.
[14] CAI Mei-feng, QIAO Lan, YU Bo, WANG Shuang-hong. Results and analysis of in-situ stress measurement at deep position of No.2 mining area of Jinchuan nickel mine [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1999, 18(4): 414-418. (in Chinese)
[15] WANG Fu-yu, GAO Qian, ZHANG Zhou-ping. Law of in-situ stress in Jinchuan diggings and research on prediction model based on artificial neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(S2): s2601-s2606. (in Chinese).
套孔应力解除法测量断层区域地应力
黄明清,吴爱祥,王贻明,韩 斌
北京科技大学 土木与环境工程学院,北京 100083
摘 要:为了减小断层区域地应力分布对采矿安全性的影响,采用套孔应力解除法及UPM40三轴应变地应力测量系统开展断层区域3处9点的地应力现场测量。结果表明,尽管岩石内部孔裂隙较发育,从岩芯围压-应力曲线仍可看出3处测量点岩石表现出较好的线弹性。断层区域的水平及垂直应力分量在不同方向上存在明显差异,最大侧压系数高达6.15,最大主应力为8.01~14.93 MPa,应力方向为N78.07°W~N17.55°W。断层区域地应力以水平构造应力为主,由于断层及其破碎带的应力释放,其数值比类似地质区域的应力值低。此外,断层及其区域剪切力部分导致了矿体的非对称延伸及西南向偏移。
关键词:断层区域;地应力分布;套孔应力解除法;侧压系数;水平构造应力
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Projects (50934002, 51104011) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012BAB08B02) supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program during the 12th Five-year Plan of China
Corresponding author: Yi-ming WANG; Tel: +86-10-62332264; E-mail: ustbwym@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63512-3