按需喷射CuSn合金液滴的冷却速率及组织演变
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第7期
论文作者:徐轶 N. ELLENDT 黎兴刚 V. UHLENWINKEL U. FRITSCHING
文章页码:1636 - 1644
关键词:碰撞液滴;二次枝晶间距;冷却速率;热传导;按需喷射
Key words:impinging droplet; secondary dendrite arm spacing; cooling rate; heat transfer; drop on demand
摘 要:采用按需喷射方法制备不同粒径的Cu-6%Sn合金粉末,测量不同粒径条件下的二次枝晶间距,并且推导出半经验公式,建立二次枝晶间距与液滴冷却速率之间的数学关系,并利用光学显微镜和背散射电子显微镜观察液滴组织形貌。结果表明:枝晶特征取决于凝固速率、冷却介质以及飞行距离;液滴温度处于液相线与固相线之间,当液滴彼此发生碰撞时,由于碰撞引起热传导率提高,经过数学模型推导,发生碰撞的液滴冷却速率超过4×104 K/s,枝晶组织和晶粒明显细化。由于液滴内部温度梯度作用,枝晶沿碰撞方向生长。
Abstract: Different sized single droplets of Cu-6%Sn alloy were prepared by drop on demand (DOD) technique. The secondary dendrite arm spacing was measured and correlated with the droplet cooling rate by a semi-empirical formula. The microstructure of droplets was observed by optical microscopy (OM) and electro backscatter diffraction (EBSD). The dendrite feature of single droplets depends on solidification rate, cooling medium and flight distance. When droplets collide with each other at temperatures between solidus and liquidus, the dendrites and grains are refined obviously possibly because the collision enhances the heat transfer. The cooling rate of colliding droplets is estimated to be more than 4×104 K/s based on a Newton’s cooling model. The dendrites grow along the colliding direction because of the temperature gradient induced by the internal flow inside the droplets.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 1636-1644
Yi XU1, N. ELLENDT2, Xing-gang LI3, V. UHLENWINKEL2, U. FRITSCHING2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China;
2. Foundation Institute of Materials Science, Bremen University, Bremen 28359, Germany;
3. National Engineering and Technology Research Center for Nonferrous Metal Matrix Composites, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China
Received 22 April 2016; accepted 8 July 2016
Abstract: Different sized single droplets of Cu-6%Sn alloy were prepared by drop on demand (DOD) technique. The secondary dendrite arm spacing was measured and correlated with the droplet cooling rate by a semi-empirical formula. The microstructure of droplets was observed by optical microscopy (OM) and electro backscatter diffraction (EBSD). The dendrite feature of single droplets depends on solidification rate, cooling medium and flight distance. When droplets collide with each other at temperatures between solidus and liquidus, the dendrites and grains are refined obviously possibly because the collision enhances the heat transfer. The cooling rate of colliding droplets is estimated to be more than 4×104 K/s based on a Newton’s cooling model. The dendrites grow along the colliding direction because of the temperature gradient induced by the internal flow inside the droplets.
Key words: impinging droplet; secondary dendrite arm spacing; cooling rate; heat transfer; drop on demand
1 Introduction
Rapid solidification techniques have been extensively developed in the last decades as they enable to obtain an original microstructural and constitutional features in the final products which cannot be formed under conventional solidification processes [1]. Among the other methods, atomization is an innovative approach that is capable of producing droplets of controlled sizes with a relatively narrow distribution and a predictable cooling rate [2]. This technique has successfully atomized metallic materials such as aluminum, zinc, copper, cobalt, nickel and their alloys as well as steel [3].
The large deviations from thermodynamic equilibrium induced by rapid solidification significantly alter the solidification conditions compared with those obtained at or close to equilibrium. The final properties can be modified through microstructure morphology change [1], extended solute solubility, nonequilibrium phase formation [4] or structure refinement.
Together with undercooling and cooling rate, the resulting microstructure is process dependent. CHEN et al [5] investigated the microstructure evolution of atomized powders of Fe-dosed Al alloy, and studied the effect of Fe content on the dendrite growth direction. CIFTCI et al [6] quantified the amorphous fraction of atomized powders and computed the critical cooling rate of approximately 5000 K/s. ILBAGI and HANI [7] effectively utilized various 2D and 3D characterization techniques to investigate the effect of cooling rate on the phase fractions. KHATIBI DELSHAD and HENI [8] produced D2 tool steel powders using a drop tube-impulse atomization, measured the in-situ droplet velocity and droplet size, and deduced the droplet cooling rate using a thermal model of droplet cooling. BEDEL et al [1] investigated the development of the dendrite arms occurring in most droplets along (111) crystallographic axes, and discussed the impact of different processing parameters on the final distribution of dendrite morphologies. ELLENDT et al [9] used the impulse atomization for spray deposition, and compared different spray characteristics and impinging conditions of the droplets with gas atomization technique which is the common technique used for spray deposition. ZHAI and WEI [10] investigated the effect of substantial undercooling condition on the direct nucleation and growth of peritectic phase of Cu-70%Sn alloy.
Nowadays, the drop on demand (DOD) technique has attracted more and more attention from researchers as a kind of three-dimensional(3D) printing technology. In the present study, we aim to prepare single impinging Cu-6%Sn droplets, to investigate the dendrite feature, to calculate the effects of droplet diameter and flight distance on the cooling rate of single droplets based on the Newton’s cooling law. A semi-empirical formula will be derived to describe the relationship between dendrite arm spacing and droplet cooling rate.
2 Experimental
Drop on demand (DOD) experimental facility was set up in Bremen University where a liquid alloy jet emanating from a capillary can be destabilized when disturbed with a specific wave. The unit included a gas pulser which pushed the molten metal through a nozzle at the bottom of the graphite crucible. Nitrogen was used as impulse gas and cooling gas in this experiment. The Cu-6%Sn alloy was heated upto and held at 1150 °C in the crucible, and the melt temperature near the atomizing nozzle was recorded by a thermocouple immersed in the crucible. The impulses generated discontinuous streams of molten metal, which broke up into fine droplets subsequently. A video camera pointing at the crucible bottom recorded each single droplet.
Single droplets with a uniform diameter (d) of 320 μm can be obtained at a specific pulse frequency. The initial velocity of single droplets was 0.5 m/s. These droplets flew through a stagnant nitrogen gas atmosphere, fell into different beakers filled with two kinds of cooling medium, i.e., oil or water, and then solidified as spherical particles. These beakers were located at 0.22, 0.48 and 0.82 m away under the crucible bottom, respectively. The collected droplets samples in different beakers were marked by h1-o (0.22 m, oil), h1-w (0.22 m, water), h2-o (0.42 m, oil), h2-w (0.42, water), h3-o (0.82, oil) and h3-w (0.82 m, water), respectively. The heat transfer occurred between the static nitrogen gas environment and the droplets in the whole flight stage. The heat transfer intensified when these droplets fell into the cooling liquid.
Different sized droplets can be fabricated by the drop generator in a range between 220 and 741 μm. The secondary dendrite arm spacing of different sized droplets was measured, respectively, and was related to the droplet cooling rate based on the mathematical methods and experimental results. In addition, according to the calculated solidification rate of melt droplets, the distance between the deposit substrate and the crucible bottom was selected as 0.15 m where droplets consisted of solid and liquid phases when these droplets collided with each other. One purpose of the present contribution is to study the effect of impinging on the microstructure characteristics and the solidification rate of Cu-6%Sn alloys.
An optical microscope Olympus BX51 was used to take photomicrographs of samples of each particle size range. The characteristic lengths of secondary dendrite arm spacing and cell spacing were measured. More detailed observations of the microstructure were carried out using a JXA-8200 backscatter scanning electron microscope (BSEM). For each micrograph, four lines perpendicular to the growth direction of secondary dendrite were drawn across the particle microstructure. The number of cell/dendrite intercepts (n) was counted for a line of known length (l). Most of the secondary dendrite arm spacings (λ) were calculated using 40 lines to get a statistically meaningful value. The cell/dendrite spacing (λ) is then given by Eq. (1):
 (1)
(1)
3 Mathematical model
A mathematical droplet-cooling model based on the Newton’s cooling law was used to calculate thermal history of an alloy droplet during its free fall in a static gas. According to the formula derivation, the thermal history can be determined using the following Eq. (2):
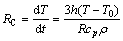 (2)
(2)
where h is the effective heat transfer coefficient and consists of the additive contribution of convection and conduction heat transfer mechanisms in the environment, the cooling rate (RC) greatly depends on the heat transfer coefficient between droplet surface and gas; T is the droplet surface temperature; T0 is the free stream gas temperature; ρ is the density of alloy material; cp is the specific heat capacity; and R is the powder particle radius. Because undercooling and microsegregation had a negligible effect on the calculated cooling rate [11], the effect of undercooling on the cooling rate and the microstructure is thus ignored in order to simplify the model. The release of latent heat is assumed to be a linear function of temperature between the liquidus and solidus temperature and treated as a change of specific heat during solidification.
For small droplets (diameter ≤ 1 mm) in flight, the effective heat transfer is dominated by convection. The effects of radiation will be taken into account [12]. The convective and conductive components of hcg are functions of the thermophysical properties of the cooling medium, the size of the droplet and its relative velocity with the gas. The general form of the semi-empirical equations for calculating the effective heat transfer coefficient is given by [13]
 (3)
(3)
where Nusselt number (Nu) is averaged over the entire droplet surface, kg is the conductivity of the film at temperature T and d is the droplet diameter. The velocity and temperature in the gas boundary layer surrounding the droplet are decisively related with the Reynolds (Re) and the Prandtl (Pr) numbers. Equation (4) was used to calculate the Nusselt number, which is based on the Whitaker correlation and modified by ILBAGI et al [14]:
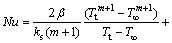
 (4)
(4)
Equations (5) and (6) give the formulation used for the calculation of the Prandtl and the Reynolds numbers, respectively.
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
where μ∞/μs is the ratio between the viscosity at the gas temperature to that at the droplet surface temperature; Tt and T∞ are the surface and gas temperature, respectively; ks, kg, cpg, ρg and μg are the surface conductivity, the gas conductivity, the gas heat capacity, the gas density and the gas viscosity, respectively; β and m are constants. The software Matlab is used to solve the above equations numerically. The experimental parameters in the whole experiment process and thermophysical properties of the experimental materials are listed in Table 1. The default parameters values used in the simulation and calculation are listed in Table 2.
Based on the physical model, the cooling rate is defined as the ratio of the difference between liquidus and solidus temperatures to the time needed to cool the material from liquidus temperature to solidus temperature:
 (7)
(7)
where TL is liquidus temperature at the time tL, TS is solidus temperature at the time tS. Based on the Newton’s free fall law, the single droplets movement is described by
 (8)
(8)
where h is the movement distance, v0 is the initial velocity of single droplet, g is the acceleration of gravity, t is the movement time.
Table 1 Thermophysical properties and experimental parameters of Cu-6%Sn

Table 2 Default parameters values used in simulations
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Effect of droplets size on cooling rate
Different sized single droplets are produced under the action of different generator frequencies. Different sized droplets have different initial velocities due to the working principle of atomization. An existing model for the droplet cooling [13] is used to characterize the temperature and velocity of droplets in flight as shown in Fig. 1. According to the observation of high speed camera, the initial velocities of different sized droplets are recorded. For example, the initial velocities of four groups of droplets with diameters of 182, 319, 601 and 801 μm are 1.8, 1, 0.5 and 0.2 m/s, respectively. The droplet velocity is increased to the maximum value by the combined action of gravity and air drag. Larger droplets need more time to cool from liquidus to solidus temperature because the path of convective and conductive heat loss from the surface and the interior of the droplet extends. The time of tL and tS increases with the increase of droplets diameter, and the value of △t=tL-tS increases with the increase of droplet diameter.
4.2 Relation between secondary dendrite arm spacing and cooling rate
The cooling rates of different sized single droplets are shown in Fig. 2. The cooling rate decreases gradually with the increase of droplet diameter. Dendrite spacing has a linear relation to the cooling rate of single alloy droplets during the cooling procedure [12,14]. In order to study the influence of collisions on the cooling rate of droplets, the secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) of different sized droplets is measured. The relationship between particle size and solidification microstructure is shown in Fig. 2. With the increase of droplet size, SDAS increases. Smaller droplets have higher cooling rates, and the development of dendrite arms is restrained to some extent.

Fig. 1 Velocity (a) and temperature (b) of different sized droplets in flight

Fig. 2 Cooling rate RC,L/S and secondary dendrite arm spacing of different diameter droplets
For SDAS versus particle diameter, the relationship is given by
 (9)
(9)
where RC,L/S is the cooling rate of melt droplet during solidification stage and λ represents the SDAS. The constants a and n can be derived by comparing the dendrite arm spacing to the cooling rate. Figure 3 shows the measured SDAS as a function of the calculated cooling rate for the Cu-6%Sn melt droplets.

Fig. 3 Relationship between lg(RC,L/S/s-1) and lg λ
Figure 3 shows a well-fit correlation between the cooling rate and the SDAS. Based on the regression analysis, the relational expression is shown as y=1.4449- 0.3138x, i.e., together with the squared R value R2= 0.9274. According to the formula of lg λ=lg a+blg(RC,L/S), the relationship between SDAS and cooling rate is described as
 (10)
(10)
4.3 Effect of cooling medium and flight distance on solidified microstructure
Based on the mathematical model and the atomization process parameters, the thermal history of a single droplet with a diameter of d=320 μm is described using the Matlab program, as shown in Fig. 4. At the time t=0, the droplet locates at the crucible bottom, and the droplet temperature is equal to the melt temperature. At the time tL, the droplet temperature reduces to the liquidus temperature TL. At the time tS, the droplet temperature reduces to the solidus temperature TS. The slopes of temperature curve from TL to TS varied due to the latent heat of crystallization. The difference between liquidus time tL and solidus time tS reflects the solidification rate to some extent. According to the thermophysical parameters and the calculated results, the difference between solidus temperature and liquidus temperature is TL-TS=130 K and the required time is △t=tL-tS=0.1385 s. Based on Eq. (7), the cooling rate of the droplet is about 938.6 K/s.

Fig. 4 Temperature and flight distance of single droplet with time
The flight trajectory of the droplet is shown in Fig. 5. The red curve displays the flight distance with time. The h0, h1, h2 and h3 represent four setting flight distances. The mark of h0 indicates the position where these droplets collide with each other at the time t0 and the flight distance is less than or equal to 0.15 m. The marks of h1, h2 and h3 indicate that the droplets fly distances of 0.22, 0.48 and 0.82 m, respectively, and these single droplets are collected in the beakers filled with oil or water.
The evolution of dendrite microstructure of droplet depends on the change of cooling rate. Figure 5 shows the dendrite feature of single droplets cooled by oil or water at different flight distances. The microstructures of droplets obtained at different flight distances and from different cooling media show similar dendrite growth morphologies. The nucleation position locates inside the droplet and a clear network of primary and secondary dendritic arms is visible. The nucleation sites and the dendrites growth orientations are random.
Based on the calculated solidification time, the time t1 corresponding to the flight distance of h1 is between tL and tS, as shown in Fig. 5, and it indicates that solid phase and liquid phase coexist in droplets at the moment when the droplets fall into the cooling medium. The heat flow increases when these droplets are immersed in the cooling water or oil in the beakers, and the convective and conductive heat losses from the surface and the interior of the droplets become severer. The measured average SDASs of h1-w, h2-w and h3-w samples are 3.9, 4.8 and 4.9 μm, respectively. The measured average SDASs of h1-o, h2-o and h3-o samples are 3.5, 4.6 and 4.7 μm, respectively. The heat exchange between droplets and media is influenced by the type of medium, thus affecting the dendrite growth direction and topography. Once the droplets enter into the liquid medium, the cooling rate of droplets increases sharply and a rapid solidification occurs, which restrain the dendrite growth and result in dendrite refinement. SDAS of single droplets cooled by water is larger than that of those cooled by oil because the vapor of water reduces the heat transfer.
4.4 Effect of collision on microstructure and cooling rate
Figure 6 shows the grain characteristics of impinging droplets. The particle shape reflects the solidification process during the collision. It is considered reasonably that the spherical particle had already solidified before the binary droplets collided with each other. The irregular-shaped particle formed from the deformed droplet, which, in liquid state or semi-liquid state, collided with the solidified droplet. Figure 6(b) implies that the grain size in the irregular-shaped particle has been refined obviously, possibly because the collision enhances the heat transfer in the deformed droplet.

Fig. 5 Dendrite features of single droplets from different cooling media and different flight distances

Fig. 6 Grain characteristics of impinging droplets
The dendrite growth and the microstructure feature of a single droplet depend on the cooling rate and the cooling medium. Figure 7 compares the dendrite characteristics of impinging and non-impinging droplets. Figure 7(a) shows a perfect spherical particle. The heat exchange occurs between the droplets and the nitrogen gas in flight. The effective heat transfer is merely dominated by convection with the gas environment. The dendrite randomly grows under the solid-liquid transformation condition.
Figure 7(c) shows the local details of dendrite microstructure at the high magnification of the marked zone in Fig. 7(a). A clear network of dendritic arms is visible. Second, tertiary arms can be developed in the cross section from the primary arms. The measured value of secondary dendrite arm spacing is equal to 3.5 μm. Fig. 7(b) shows the microstructure feature of irregular particles. These droplets are deformed when droplets collide with each other during solidification process. Compared with non-impinging droplets, the dendrites of impinging droplets are obviously fine, and the measured average lamellar dendrite arm spacings are less than 1μm. These droplets collide with each other at the time t0, and the flight distance is less than 0.15 m at this time. The deformation-induced internal flow may enhance the heat conduction inside the deformed droplet, thus resulting in a cooling rate increase and thereby a fine microstructure.

Fig. 7 Dendrite feature

Fig. 8 Dendrite growth direction of impinging droplets

Fig. 9 Relationship between microstructure and cooling rate
In addition, collision could affect the dendrite growth direction during solidification process. Figure 8(a) shows the dendrite feature of three impinging droplets. Depending on the droplets deformation degree, the dendrite microstructure reveals a significant difference. One droplet collides with two droplets, and both droplets deform greatly. Dendrites growth of one droplet sample shows a distinct preferred direction as marked by the arrows. This is similar to the directional solidification in cast process. Heat transfer is more intense near the contact surface of impinging droplets, so dendrites firstly begin to solidify on the droplets contact surface, and then grow along the colliding direction to lamellar structure due to the influence of the internal temperature gradient in the droplet. The dendrites show an obvious growth orientation, as shown in Fig. 8(b).
Based on Eq. (10) of  , for the Cu-6%Sn alloy droplets, the best-fit relationship between microstructure and cooling rate is calculated for the metastable conditions, as shown in Fig. 9. It shows that the spacing between the arms is inversely proportional to the cooling rate. From the microstructural analysis and heat flow modeling described earlier, the cooling rate depends on the effective heat transfer coefficient. The dendrite arm spacing increases with a decrease of cooling rate.
, for the Cu-6%Sn alloy droplets, the best-fit relationship between microstructure and cooling rate is calculated for the metastable conditions, as shown in Fig. 9. It shows that the spacing between the arms is inversely proportional to the cooling rate. From the microstructural analysis and heat flow modeling described earlier, the cooling rate depends on the effective heat transfer coefficient. The dendrite arm spacing increases with a decrease of cooling rate.
The range of SDAS of different sized Cu-6%Sn droplets is from 2.8 to 4.7 μm. Based on the relationship between cooling rate and SDAS, the droplet cooling rate ranges from 1511 to 290 K/s. When single droplets collide with each other, the dendrite growth is restrained by the enhanced heat transfer and the dendrites are refined obviously to lamellar structure. Lamellar dendrite arm spacing of impinging droplets is less than 1μm, and the cooling rate is calculated as 4×104 K/s.
5 Conclusions
1) Single Cu-6%Sn droplets are produced in droplet generator. The droplet diameter ranges in 220-741 μm, which is controlled by the pulse frequency. Secondary dendrite arm spacing increases with an increase of droplet diameter. The secondary dendrite arm spacing is correlated with the droplet cooling rate by the expression of λ=aRC-n with constants a=27.85 and n=0.3138, respectively.
2) Dendrites and grains of single impinging droplets are refined obviously, possibly because the internal flow induced by the droplets collision enhances the heat transfer. Cooling rate of impinging droplets is estimated with more than 4×104 K/s by the Newton’s cooling model. The dendrites grow along the colliding direction in which a temperature gradient may be built because of the collision-induced internal flow in the droplet.
References
[1] BEDEL M, REINHART G, BOGNO A, GANDIN C, JACOMET S, BOLLER E, NGUYEN H, HANI H. Characterization of dendrite morphologies in rapidly solidified Al-4.5 wt.% Cu droplets [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 89: 234-246.
[2] HANI H. Single fluid atomization through the application of impulses to a melt [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 326: 92-100.
[3] HANI H. Why is spray forming a rapid solidification process [J]. Mat.-wiss. u.Werkstofftech, 2010, 41: 555-561.
[4] ILBAGI A, HENI H, PHILLION A B. Phase quantification of impulse atomized Al68.5Ni31.5 alloy [J]. Journal of Material Science, 2011, 46: 6235-6242.
[5] CHEN Jian, ULF D, CUI Min-bao, MONIQUE C D, HANI H. Microstructure evolution of atomized Al-0.61 wt pct Fe and Al-1.90 wt pct Fe alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2011, 42: 557-567.
[6] CIFTCI N, ELLENDT N, BARGEN R, HENI H, MADLER L, VOLKER U. Atomization and characterization of a glass forming alloy {(Fe0.6Co0.4)0.75B0.2Si0.05}96Nb4 [J]. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2014, 394-395: 36-42.
[7] ILBAGI A, HANI H. 3D quantitative characterization of rapidly solidified Al-36 Wt Pct Ni [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45: 2152-2160.
[8] KHATIBI DELSHAD P, HENI H. The robustness of the two-colour assumption in pyrometry of solidifying AISI D2 alloy droplets [J]. Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech, 2014, 45: 736-743.
[9] ELLENDT N, SCHMIDT R, KNABE J, HENI H, UHLENWINKEL V. Spray deposition using impulse atomization technique [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 383: 107-113.
[10] ZHAI Wei, WEI Bing-bo. Direct nucleation and growth of peritectic phase induced by substantial undercooling condition [J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 108:145-148.
[11] ARVIND P, HENI H. Droplet cooling in atomization sprays [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43: 5930-5941.
[12] HANI H,VINCENT B, RALF S, CHUCK W, DMITRI M, CHARLES G, GERARD L, VOLKER U. Droplet solidification of impulse atomized Al-0.61Fe and Al-1.9Fe [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2010, 49: 275-292.
[13] WISKEL J B, HENI H, MAIRE E. Solidification study of aluminum alloys using impulse atomization: Part1: Heat transfer analysis of an atomized droplet [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2002, 41: 97-110.
[14] ILBAGI A, HENI H, PHILLION A B. Phase quantification of impulse atomized Al68.5Ni31.5 alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46: 6235-6242.
徐 轶1,N. ELLENDT2,黎兴刚3,V. UHLENWINKEL2,U. FRITSCHING2
1. 西南交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,成都 610031;
2. Foundation Institute of Materials Science, Bremen University, Bremen 28359, Germany;
3. 北京有色金属研究院 复合材料国家工程技术中心,北京 100088
摘 要:采用按需喷射方法制备不同粒径的Cu-6%Sn合金粉末,测量不同粒径条件下的二次枝晶间距,并且推导出半经验公式,建立二次枝晶间距与液滴冷却速率之间的数学关系,并利用光学显微镜和背散射电子显微镜观察液滴组织形貌。结果表明:枝晶特征取决于凝固速率、冷却介质以及飞行距离;液滴温度处于液相线与固相线之间,当液滴彼此发生碰撞时,由于碰撞引起热传导率提高,经过数学模型推导,发生碰撞的液滴冷却速率超过4×104 K/s,枝晶组织和晶粒明显细化。由于液滴内部温度梯度作用,枝晶沿碰撞方向生长。
关键词:碰撞液滴;二次枝晶间距;冷却速率;热传导;按需喷射
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51301143) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2014M560727) supported by the National Postdoctoral Foundation of China; Project (2015GZ0228) supported by the Sichuan Province Science-Technology Support Plan, China; Project (2682014CX001) supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project of SWJTU University, China
Corresponding author: Yi XU; Tel: +86-28-87600782; E-mail: xybwbj@swjtu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60186-9

