固溶处理及挤压态Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr镁合金的显微组织与生物腐蚀行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第12期
论文作者:章晓波 巴志新 王章忠 薛亚军 王 强
文章页码:3797 - 3803
关键词:镁合金;锶;显微组织;生物腐蚀行为
Key words:magnesium alloy; strontium; microstructure; biocorrosion behaviors
摘 要:采用重力铸造制备Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr(x=0,0.4和0.7,质量分数,%)镁合金。为使组织均匀,对铸态合金进行了固溶处理,并对固溶处理后的合金进行热挤压。采用光学显微镜和扫描电子显微镜观察合金的组织;采用失重、析氢和Tafel极化法分析合金在模拟体液中的生物腐蚀行为。研究结果表明:随着Sr含量的增加,固溶处理态合金中的残余共晶相增加,挤压后晶粒显著细化。3种腐蚀性能测试方法均表明固溶处理态合金的耐蚀性能随Sr含量的增加而显著降低,而挤压态合金的耐蚀性能随Sr的加入而提高。然而,Tafel极化法获得的挤压态合金的腐蚀趋势和其他2种方法获得的趋势不同。
Abstract: Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys (x=0, 0.4 and 0.7, mass fraction, %) were prepared by gravity casting. Solution treatment was conducted on the as-cast alloys to homogenize microstructure, and hot extrusion was subsequently conducted. Microstructure was observed using an optical microscope and a scanning electron microscope. Biocorrosion behaviors of the alloy in simulated body fluid were analyzed by mass loss, hydrogen evolution and Tafel polarization experiments. The results show that the amount of residual eutectic phase of the solution treated alloys increases with increasing Sr addition, and the grains are significantly refined after hot extrusion. The corrosion resistance of the solution treated alloys deteriorates apparently with increasing Sr addition, while the corrosion resistance of the as-extruded alloys is improved with Sr addition. Nevertheless, the biocorrosion behavior of the as-extruded alloys obtained by Tafel polarization shows different trends from those obtained by the other two methods.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3797-3803
Xiao-bo ZHANG1,2, Zhi-xin BA1,2, Zhang-zhong WANG1,2, Ya-jun XUE1,2, Qiang WANG3
1. College of Materials Engineering, Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing 211167, China;
2. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials and Application Technology, Nanjing 211167, China;
3. Jiangsu Konsung Equipment Co., Ltd, Danyang 212300, China
Received 17 October 2013; accepted 23 October 2014
Abstract: Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys (x=0, 0.4 and 0.7, mass fraction, %) were prepared by gravity casting. Solution treatment was conducted on the as-cast alloys to homogenize microstructure, and hot extrusion was subsequently conducted. Microstructure was observed using an optical microscope and a scanning electron microscope. Biocorrosion behaviors of the alloy in simulated body fluid were analyzed by mass loss, hydrogen evolution and Tafel polarization experiments. The results show that the amount of residual eutectic phase of the solution treated alloys increases with increasing Sr addition, and the grains are significantly refined after hot extrusion. The corrosion resistance of the solution treated alloys deteriorates apparently with increasing Sr addition, while the corrosion resistance of the as-extruded alloys is improved with Sr addition. Nevertheless, the biocorrosion behavior of the as-extruded alloys obtained by Tafel polarization shows different trends from those obtained by the other two methods.
Key words: magnesium alloy; strontium; microstructure; biocorrosion behaviors
1 Introduction
Biodegradable pure magnesium and its alloys are potential candidates for temporary bone implants due to their special characteristics, such as good biocompatibility, biodegradation, similar density and elastic modulus to those of human bone [1,2]. For the poor mechanical properties of pure Mg, some nutrient elements have been added into Mg as alloying elements [3]. Strontium is one of the normal alloying elements in Mg alloys, which can refine grains, improve mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and creep resistance of Mg alloys with suitable addition [4-6]. It was also reported that Sr could refine the precipitates, promote their solution [7] and weaken textures of Mg alloy during hot extrusion [8]. Moreover, Sr is a component of human bone and can promote the growth of osteoblasts and prevent bone resorption. Therefore, several Mg alloys with Sr addition have been studied as biodegradable materials in the last two years, and the primary results show that the Mg alloys with proper Sr addition are promising candidates for biodegradable implants [9-11]. Some reports indicate that the effect of Sr addition on the corrosion behavior of the Mg-Sr binary alloy under different conditions is different. GU et al [12] reported that the as-rolled Mg-Sr alloy with 2% Sr (mass fraction) exhibited the slowest corrosion rate, while BORNAPOUR et al [13] found that the as-cast Mg-Sr alloy with 0.5% Sr showed the slowest corrosion rate. Furthermore, ZHANG et al [14] indicated that the best corrosion resistance of the as-cast Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy was obtained from the alloy with 0.7% Sr addition [14]. Consequently, the effect of Sr addition on corrosion behavior of a novel Mg alloy cannot simply refer to the reports but need systemic study.
Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloys exhibit good mechanical properties, high corrosion resistance in simulated body fluid, uniform corrosion mode and acceptable biocompatibility, and thus are promising for bone fixture implant and cardiovascular stent applications [15-17]. In this work, for the desired performance of Sr on bone fixture applications, Sr was added in Mg-Nd-xSr-Zr alloys on the basis of the Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloys. Solution treatment and hot extrusion were conducted on the alloys to reveal effects of Sr addition and extrusion on microstructure and biocorrosion behaviors of the Mg-Nd-xSr-Zr alloys.
2 Experimental
Three alloys with nominal composition of Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr (x=0, 0.4 and 0.7, mass fraction, hereafter, denoted as A, B and C, respectively) were prepared with highly pure Mg, Mg-30%Nd, Mg-25%Sr and Mg-30%Zr (mass fraction) by gravity casting under a mixed protected atmosphere of CO2 and SF6. The melt was cast at 720 °C into a steel mould, which was preheated and coated with graphite paste. The ingots were solution treated at 540 °C for 12 h, and then quenched into water at room temperature (hereafter, denoted as A-T4, B-T4 and C-T4, respectively). The solution treated (T4) specimens were extruded into rods with the diameter of 20 mm at 350 °C with an extrusion ratio of 9 and extrusion speed of 50 mm/s (hereafter, denoted as A-E, B-E and C-E, respectively).
The as-extruded specimens for microstructure observation were cut parallel to the extrusion direction. All the solution treated and as-extruded specimens were polished with 600, 1200 grit papers and 3.5 μm diamond grinding paste, and then etched with acid solution (acid solution with 20 mL acetic acid + 1 mL nitric acid + 60 mL glycol + 19 mL distilled water for the T4 alloys, and acid solution with 10 mL acetic acid + 4.2 g picric acid + 70 mL ethanol + 10 mL distilled water for the as-extruded alloys). The microstructure of the alloys was observed using an optical microscope (OM) and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) in conjunction with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS).
The specimens with a size of 19 mm in diameter and 3.5 mm in thickness were polished for corrosion behavior experiments in simulated body fluid (SBF) at (37±0.5) °C. The composition of SBF contains NaCl (8.0 g/L), KCl (0.4 g/L), NaHCO3 (0.35 g/L), CaCl2 (0.14 g/L), MgCl2·6H2O (0.1g/L), Glucose (1 g/L), Na2HPO4·2H2O (0.06 g/L), KH2PO4 (0.06 g/L) and MgSO4·7H2O (0.06 g/L) [18]. The biocorrosion behaviors of the alloys were evaluated by mass loss test, hydrogen evolution test and Tafel polarization experiment. Prior to the immersion experiment, the mass of the specimens was weighted, the diameter and thickness of the specimens were measured, and the pH value of the SBF was adjusted to 7.4 with HCl or NaOH. The ratio of surface area (cm2) to SBF solution volume (mL) is 1:30. The hydrogen was collected by a burette placed on top of a funnel with a specimen in the center of the funnel. SBF was renewed every 24 h and the immersion experiment lasted for 120 h on the basis of the approximate corrosion rate of the alloys according to the ASTM G31-72. After immersion for 120 h, the specimens were cleaned with acid solution (200 g/L Cr2O3+10 g/L AgNO3) for 5 min to remove corrosion products on the surface of the specimens. The morphologies of the immersed specimens were observed by SEM. The Tafel polarization curves of the alloys were measured in SBF at (37±0.5) °C. The standard calomel electrode in saturated KCl solution was used as the reference electrode and the counter electrode was a high purity platinum grid. The Tafel polarization curves were recorded at a scan rate of 1 mV/s in the range from -0.25 mV to 0.3 mV vs the saturated calomel electrode (SCE).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 shows the optical microstructures of the Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys under T4 condition. The A-T4 alloy is mostly composed of equiaxed α-Mg grains, and minor second phase can be observed in the grain boundaries, which is not dissolved sufficiently during solution treatment, as shown in Fig. 1(a). With the addition of Sr, except for the equiaxed α-Mg grains, the discontinuous second phase is observed in the grain boundaries and increases with increasing Sr addition. It is known that the maximal solubility of Sr in Mg is only about 0.11%. The addition of Sr in alloys B and C are 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively. Sr cannot be dissolved into Mg matrix completely, and thus, it exists as the second phase in the grain boundaries. In addition, the grain size of the T4 alloys shows only slight decrease with increasing Sr addition.

Fig. 1 Optical microstructures of solution treated Mg-2.2Nd- xSr-0.3Zr alloys
Grey circles filled with numerous fine particles can be seen in the center of the α-Mg grains for the alloys B-T4 and C-T4, as shown in Figs. 1(b) and (c). Figure 2 shows the SEM image of the in B-T4 alloy and the EDS results of the different parts of the microstructure. It indicates that the bright second phase consists of Mg, Sr and Nd. The XRD analysis reveals that Mg41Nd5 and Mg17Sr2 are formed in the as-cast alloy B [14]. A large number of fine bright particles can be observed in the center of the α-Mg grains, which seem a little dark by OM, as shown in Fig. 1. Composition analysis indicates that the fine bright particles are rich in Zr element, and the edge of the grains (α-Mg) mainly consists of Mg and a little Nd and Zr.
The OM images of the as-extruded Mg-2.2Nd- xSr-0.3Zr alloys parallel to the extrusion direction are presented in Fig. 3. The microstructure of the alloys is refined significantly after hot extrusion. The precipitated grains, which can hardly be observed by OM, are also formed after extrusion. Generally, three kinds of grains are formed in the as-extruded alloys: relatively coarse grains with the grain size of 8-16 μm, fine grains with the grain size of 1-6 μm, and tiny grains located in the black strips, which can hardly be observed. It indicates that the completely dynamic recrystallization occurs during hot extrusion, and the non-uniform distribution of the plastic deformation energy results in the inhomogeneous grains. It seems that the grain size of the as-extruded alloy decreases slightly and the black strips with tiny grains increase apparently with increasing Sr addition. BORKAR and PEKGULERYUZ [19] reported that Mg17Sr2 precipitates in Mg alloy extrusion can act as nucleation sites for particle stimulated nucleation and also help in the restriction of grain growth during recrystallization by pinning grain boundaries, which can explain the refined microstructure of the alloys with Sr addition.
3.2 Corrosion behaviors
The corrosion rates of the T4 and as-extruded alloys are shown in Fig. 4. As for the T4 alloys, the corrosion rate increases obviously with increasing Sr addition. As for the as-extruded alloys, the corrosion rates of the alloys B and C with Sr addition are slower than that of the alloy A without Sr. Moreover, the corrosion rate of the alloy A-E is faster than that of the alloy A-T4, while the corrosion rates of the alloys B-E and C-E are slower than those of the alloys B-T4 and C-T4 accordingly.
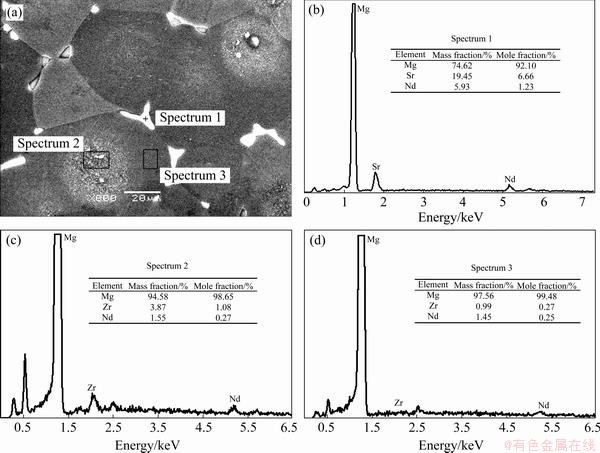
Fig. 2 SEM image of alloy B-T4 and EDS results of different areas
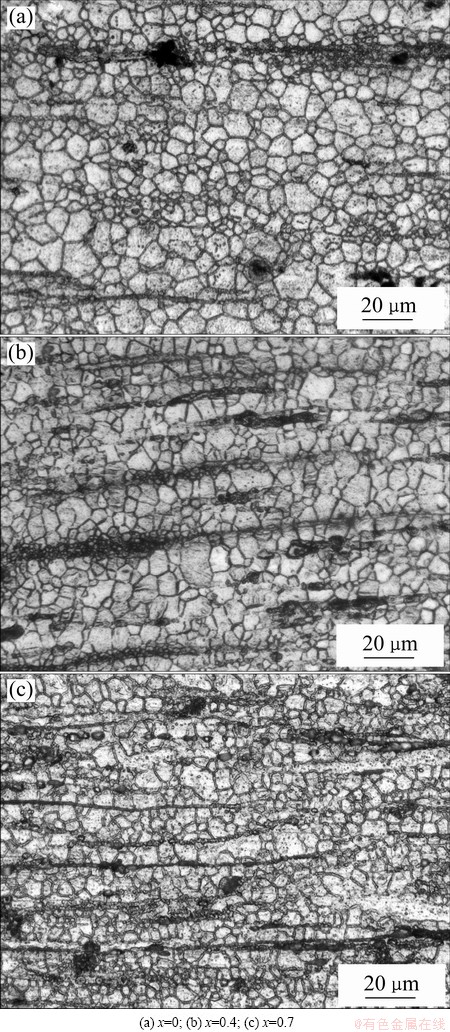
Fig. 3 Optical microstructures of as-extruded Mg-2.2Nd- xSr-0.3Zr alloys
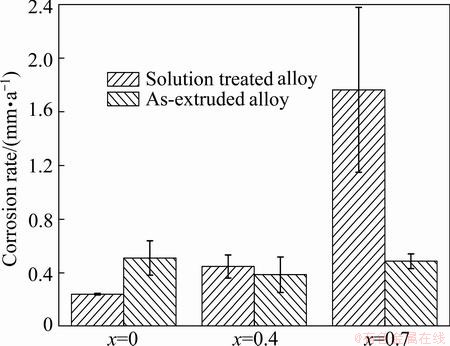
Fig. 4 Corrosion rate of Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys immersed in SBF for 120 h
The hydrogen evolution volumes of the T4 and as-extruded alloys as a function of the immersion time are plotted in Fig. 5. It presents that the hydrogen evolution volume of the alloys A-T4 and B-T4 shows general increase with prolonging immersion time, while the hydrogen evolution volume of the alloy C-T4 is higher during the first and the second 24 h than the following immersion time. The higher hydrogen evolution volume of the alloy C-T4 during the first 48 h is probably due to the more second phase, which causes severe micro-galvanic corrosion. The total hydrogen evolution volume of the three alloys follows the order: A-T4 The corrosion morphologies of the solution treated and as-extruded alloys are presented in Figs. 6 and 7, respectively. It is found that the alloys exhibit relatively uniform corrosion, which is desired for biodegradable implant applications. The corrosion surface of the alloy A-T4 is relatively smooth, and numerous pits located in the grains and grain boundaries, and some micro cracks located in the grain boundaries can be observed on the surfaces of the alloys B-T4 and C-T4. The corrosion potential of the second phase is more positive than that of the α-Mg matrix, and thus, the second phase could be protected for micro-galvanic corrosion. Therefore, the pits and micro cracks are probably caused by the peeling of the second phase during cleaning the corroded specimens with acid solution.
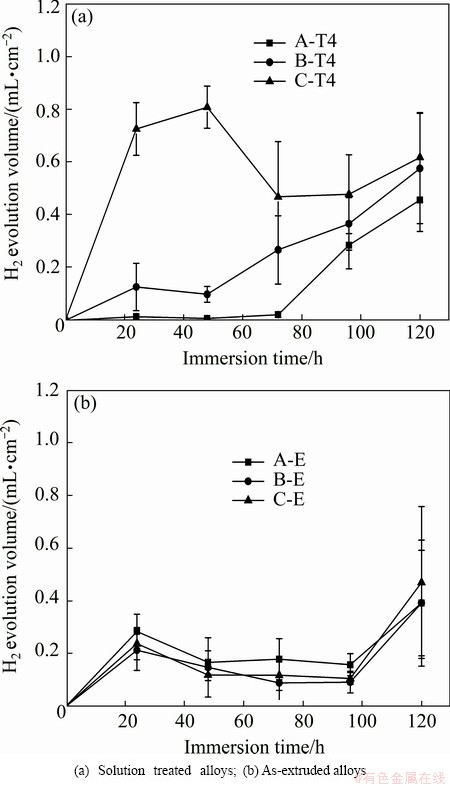
Fig. 5 H2 evolution volume of Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys immersed in SBF for 120 h
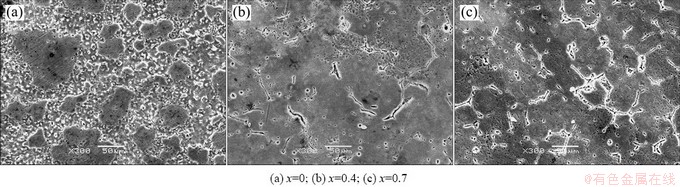
Fig. 6 Corrosion morphologies of solution treated Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys after cleaning corrosion products
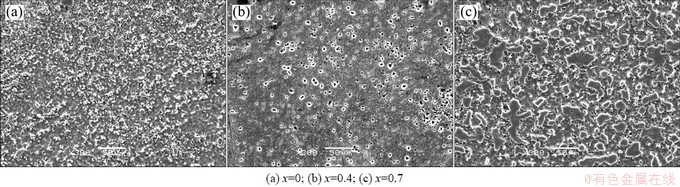
Fig. 7 Corrosion morphologies of as-extruded Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys after cleaning corrosion products
The corrosion surface of the alloy A-E is much more uniform than that of the alloy A-T4 due to the much finer microstructure. Micro cracks cannot be observed from the surfaces of the alloys B-E and C-E because the second phases are refined by hot extrusion and precipitated as fine particles. Consequently, a large number of pits are observed in the alloys B-E and C-E. Furthermore, the pits in the alloy C-E are much tinier than those in alloy B-E, suggesting that the precipitate size of Mg17Sr2 decreases with more Sr addition.
The polarization curves of both the solution treated and as-extruded alloys are shown in Fig. 8. It reveals that the corrosion potentials of the alloys both at solution treated state and at as-extruded state have apparent differences. It is known that the corrosion potential of materials just suggests the corrosion tendency in view of thermodynamics, the more negative corrosion potential means easier to be corroded. However, the corrosion rate of the alloys is determined by the corrosion current density but not the corrosion potential. The current densities of the alloys are evaluated by Tafel extrapolation. The current densities of the alloys A-T4, B-T4 and C-T4 are 44.2, 60.7 and 1050 μA/cm2, respectively, and those of the alloys A-E, B-E and C-E are 122, 97.7 and 40.6 μA/cm2, respectively. The results reveal that the corrosion rates of the solution treated alloys follow the order: A-T4<B-T4<C-T4, which is consistent with the results obtained by mass loss and hydrogen evolution experiments. Nevertheless, the corrosion rates of the as-extruded alloys obtained by Tafel extrapolation follow the order: C-E<B-E<A-E, which do not agree with the corrosion results obtained by mass loss or hydrogen evolution experiments.
The corrosion rates of the solution treated alloys evaluated by three methods present the same trend: A-T4<B-T4<C-T4. The grain sizes of the three solution treated alloys show no obvious difference, therefore, the increased corrosion rate with increasing Sr addition is ascribed to the second phases. Second phases have a tendency to cause micro-acceleration of the corrosion of α-Mg matrix if they distribute discontinuously, and they can also provide a barrier and restrict corrosion of Mg alloys if they distribute continuously [20,21]. Consequently, the increased and discontinuously distributed second phases in alloys B-T4 and C-T4 are responsible for the increased corrosion rate. The corrosion rates of the alloys B and C after hot extrusion are slower than those under solution treated condition according to the results obtained by mass loss and hydrogen evolution tests. The microstructure is refined significantly after hot extrusion, and the second phases seem to be much less than those in the T4 alloys. As a consequence, the improved corrosion resistances of the alloys B and C after hot extrusion are attributed to the grain refinement and the reduction of the second phases. However, the corrosion rate of the alloy A after hot extrusion is much higher than that under T4 condition for all the three methods. As described above, the microstructure of the alloy A-T4 is nearly composed of α-Mg grains, while some precipitated grains are formed after hot extrusion. It is known that the refined grains can restrict the corrosion while the precipitates will accelerate the corrosion due to micro-galvanic corrosion. The corrosion rate of the alloy is determined by the factor which plays the dominating role of the corrosion. Therefore, the accelerated corrosion rate in the alloy A after hot extrusion may be attributed to the overwhelming negative role caused by the precipitates.
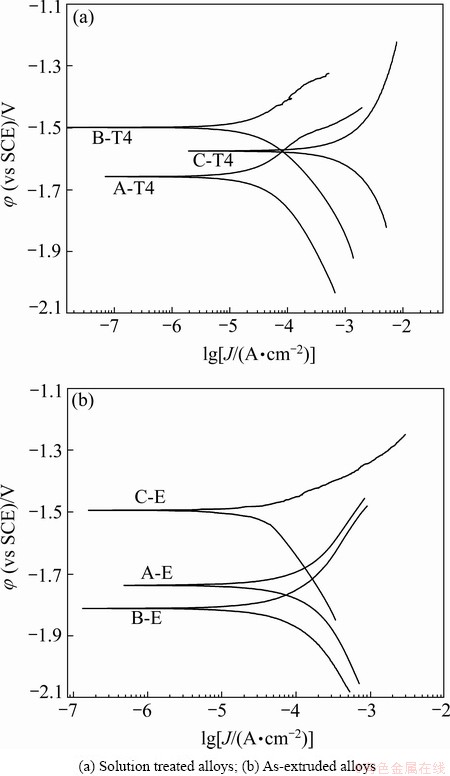
Fig. 8 Polarization curves of Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys
Moreover, according to the results obtained by Tafel polarization test, the corrosion rate of the alloy B-T4 is slower than that of the alloy B-E, and the corrosion rate of the alloy B-E is higher than that of the alloy C-E, which is adverse to the results obtained by mass loss and hydrogen evolution tests. The Tafel extrapolation technique essentially provides a measurement of the corrosion rate at a particular time over which the measurement was carried out soon after specimen was immersed in solution, and the corrosion rates have not been related to steady state corrosion. While the mass loss and hydrogen evolution tests are relatively long-term tests. Therefore, the deviations of the corrosion rates are observed for the Tafel polarization test compared with those for the mass loss and hydrogen evolution tests. The deviations of the corrosion rate of Mg alloys between Tafel polarization test and mass loss test/hydrogen evolution test were also reported by SHI et al [20]. And thus, for evaluating corrosion behavior of Mg alloys by Tafel extrapolation method, at least one of the other measurement methods, i.e., mass loss test or hydrogen evolution test, is strongly recommended.
4 Conclusions
1) The amount of second phases of the solution treated Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys increases with the increase of Sr addition. The bright particles in the center of the α-Mg grains of the solution treated alloys observed by SEM are Zr-enriched compounds.
2) The microstructure is refined significantly by hot extrusion due to dynamic recrystallization. Relatively coarse grains, fine grains and the tiny grains located in the black strips are observed from the as-extruded microstructure. The grain sizes decrease slightly with increasing Sr addition for the as-extruded alloys.
3) The corrosion rates of the solution treated alloys increase with increasing Sr addition due to the increased second phases. The corrosion rate of the as-extruded alloy without Sr addition is higher than those with Sr addition. The solution treated alloy without Sr addition exhibits much better corrosion resistance compared with the as-extruded alloy, while the as-extruded alloys with Sr addition exhibit better corrosion resistance compared with the solution treated alloys.
4) The corrosion rates of the alloys obtained by mass loss and hydrogen evolution tests are consistent, but show some deviations from those obtained by Tafel polarization. Therefore, mass loss and/or hydrogen evolution tests are recommended to accompany with Tafel polarization test to study the corrosion rate of the Mg alloys.
References
[1] MANIVASAGAM G, SUWAS S. Biodegradable Mg and Mg bases alloys for biomedical implants [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30(5): 515-520.
[2] ZHENG Y F, GU X N, WITTE F. Biodegradable metals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2014, 77: 1-34.
[3] LI Nan, ZHENG Yu-feng. Novel magnesium alloys developed for biomedical applications: A review [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2013, 29(6): 489-502.
[4] LOU Yan, BAI Xing, LI Luo-xing. Effect of Sr addition on microstructure of as-cast Mg-Al-Ca alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(6): 1247-1252.
[5] CHEN Gang, PENG Xiao-dong, FAN Pei-geng, XIE Wei-dong, WEI Qun-yi, MA Hong, YANG Yan. Effects of Sr and Y on microstructure and corrosion resistance of AZ31 magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(4): 725-731.
[6] CHENG R J, PAN F S, JIANG S, LI C, JIANG B, JIANG X Q. Effect of Sr addition on the grain refinement of AZ31 magnesium alloys [J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2013, 23(1): 7-12.
[7] CHENG R J, PAN F S, JIANG S, JIANG X Q, LI C. Effect of minor Sr on precipitates in AZ31 magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2013, 29(2): 219-225.
[8] BORKAR H, GAUVIN R, PEKGULERYUZ M. Effect of extrusion temperature on texture evolution and recrystallization in extruded Mg-1%Mn and Mg-1%Mn-1.6%Sr alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 555: 219-224.
[9] CIPRIANO A F, ZHAN T, JOHNSON I, GUAN R, GARCIA S, LIU H. In vitro degradation of four magnesium-zinc-strontium alloys and their cytocompatibility with human embryonic stem cells [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2013, 24(4): 989-1003.
[10] BRAR H S, WONG J, MANUEL M V. Investigation of the mechanical and degradation properties of Mg-Sr and Mg-Zn-Sr alloys for use as potential biodegradable implant materials [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012, 7: 87-95.
[11] BERGLUND I S, BARA H S, DOLGOVA N, ACHARYA A P, KESELOWSHY B G, SARNTINORANONT M, MANUEL M V. Synthesis and characterization of Mg-Ca-Sr alloys for biodegradable orthopedic implant applications [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2012, 100(6): 1524-1534.
[12] GU X N, XIE X H, LI N, ZHENG Y F, QIN L. In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(6): 2360-2374.
[13] BORNAPOUR M, MUJA N, SHUN-TIM D, CERRUTI M, PEKGULERYUZ M. Biocompatibility and biodegradability of Mg-Sr alloys: The formation of Sr-substituted hydroxyapatite [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(2): 5319-5330.
[14] ZHANG X B, HE X C, XUE Y J, WANG Z Z, WANG Q. Effects of Sr on microstructure and corrosion resistance in simulated body fluid of as-cast Mg-Nd-Zr magnesium alloys [J]. Corrosion Engineering, Science and Technology, 2014, 49(5): 345-351.
[15] ZHANG X B, YUAN G Y, WANG Z Z. Mechanical properties and biocorrosion resistance of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy improved by cyclic extrusion and compression [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 74: 128-131.
[16] ZHANG Xiao-bo, MAO Lin, YUAN Guang-yin, WANG Zhang-zhong. Performances of biodegradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy for cardiovascular stent [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(6): 1300-1305. (in Chinese)
[17] ZHANG Xiao-bo, XUE Ya-jun, WANG Zhang-zhong. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure, mechanical properties and in vitro degradation behavior of as-extruded Mg-2.7Nd-0.2Zn-0.4Zr alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(10): 2343-2350.
[18] ZHANG Xiao-bo, YUAN Guang-yin, WANG Zhang-zhong. Biocorrosion properties of as-cast Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(4): 905-911. (in Chinese)
[19] BORKAR H, PEKGULERYUZ M. Microstructure and texture evolution in Mg-1%Mn-Sr alloys during extrusion [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(4): 1436-1447.
[20] SHI Z, LIU M, ATRENS A. Measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using Tafel extrapolation [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(2): 579-588.
[21] ZHAO M, LIU M, SONG G, ATRENS A. Influence of the beta-phase morphology on corrosion of the Mg alloy AZ91 [J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(7): 1939-1953.
章晓波1,2,巴志新1,2,王章忠1,2,薛亚军1,2,王 强3
1. 南京工程学院 材料工程学院,南京 211167;
2. 江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室,南京 211167;
3. 江苏康尚医疗器械有限公司,丹阳 212300
摘 要:采用重力铸造制备Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr(x=0,0.4和0.7,质量分数,%)镁合金。为使组织均匀,对铸态合金进行了固溶处理,并对固溶处理后的合金进行热挤压。采用光学显微镜和扫描电子显微镜观察合金的组织;采用失重、析氢和Tafel极化法分析合金在模拟体液中的生物腐蚀行为。研究结果表明:随着Sr含量的增加,固溶处理态合金中的残余共晶相增加,挤压后晶粒显著细化。3种腐蚀性能测试方法均表明固溶处理态合金的耐蚀性能随Sr含量的增加而显著降低,而挤压态合金的耐蚀性能随Sr的加入而提高。然而,Tafel极化法获得的挤压态合金的腐蚀趋势和其他2种方法获得的趋势不同。
关键词:镁合金;锶;显微组织;生物腐蚀行为
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51301089) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (BK20130745) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China; Project (13KJB430014) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province, China; Project supported by the Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, China
Corresponding author: Xiao-bo ZHANG; Tel: +86-15951722675; E-mail: xbxbzhang2003@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63535-4

