
Solidification microstructures and mechanism of grain refinement of electrolytic low titanium Al alloys
WANG Ai-qin(王爱琴)1, 2, XIE Jing-pei(谢敬佩)2, LI Ji-wen(李继文)2,
LIU Zhong-xia(刘忠侠)1, WANG Wen-yan(王文焱)2, YAN Shu-qing(闫淑卿)1
1. Key Laboratory of Material Physics, Ministry of Education, Zhengzhou University,
Zhengzhou 450052, China;
2. School of Material Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology,
Luoyang 471003, China
Received 28 July 2006; accepted 15 September 2006
Abstract: The solidification microstructures and the mechanism of grain refinement of electrolytic low titanium Al alloys were investigated by means of the wedge-shaped sample, the directional solidification and the rapid solidification ribbon. The results show that the coarse columnar grains formed in pure Al are transformed into the equiaxed grains in electrolytic low titanium Al alloys. The grain refinement is resulted from the constitutional supercooling caused by Ti and heterogeneous nucleation of Al3Ti particles. Under the condition of normal cooling rate, the grains are refined by the increment of constitutional supercooling when the content of titanium is less than 0.2%. With the increment of content of titanium, the grains are mainly refined by heterogeneous nucleation of Al3Ti particles. The grain size is decreased with the increment of cooling rate. When the cooling rate is larger than 105 ℃/s, the grain size is decreased to 0.1-10 μm, the grain refinement is resulted from the larger cooling velocities mainly. After directional solidification, the equiaxed grains can be formed and the Ti element is distributed at the center of the grains.
Key words: Al3Ti particle; heterogeneous nucleation; constitutional supercooling; growth restriction factor; refinement mechanism
1 Introduction
According to the standard of American, proper Ti is almost demanded in Al casting alloys. The effect of Ti on strength and toughness is becoming more and more important. The new national standard of GB/T3190— 1996 are promulgated in 1996, and 0.3%Ti are demanded in Al alloys.
Ti is one of the most effective grain refinement elements in Al alloys[1-2]. The grain of alloys can be effectively refined if containing up to 0.3%Ti, which results in the improvement of mechanical properties. Ti is usually added into Al alloys by melting Al-Ti master alloys. Because of the master alloys must be melted at high temperature, it is necessary to control the melting temperature and holding time strictly, which results in the difficulty to the quality of alloys.
A new approach was put forward that electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys with 0.3%Ti could be produced in the industrial electrolyzer, and the in-situ Ti alloying of Al alloys was fulfilled by electrolysis[3-5]. Adding some Ti into Al alloys by electrolysis, the grain is refined and the second dendrites arm is shortened, the microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys are improved. In recent years, XIE et al[6], LIU et al[7], WANG et al[8] studied Al alloys automobile wheel with low-titanium content produced by electrolysis, effects of Ti content on wear resistance of the electrolytic low-titanium eutectic Al-Si piston alloys, wear resistance of Al-Si-Ti piston alloys produced by electrolysis, effect of Ti alloying manner and Ti content on microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 alloys, and the mechanical properties of 6063 alloys added Ti by electrolysis.
In order to apply the electrolytic low titanium aluminium alloys in industry, it is necessary to solve some important problems as follows: the solidification micro- structures under different cooling rates, the mechanism of grain refinement of electrolytic low titanium aluminium alloys, the relationship between the grain size and solute concentration, constitutional undercooling and cooling rate, and the conditions of heterogeneous nucleus.
In this study, the directional solidified aluminum bar, wedge-shaped sample and the rapid solidification ribbon are made from the electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys, and the solidification microstructures, the mechanism of grain refinement were investigated by directional solidification and rapid solidification.
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation of wedge-shaped sample
Pure Al, Al-0.3%Ti and the electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys were used in this paper, and the specimens were made in the furnace, then the melted alloys was poured into a wedge-shaped metal mold to get specimens. The dimension of the sample was given as 100 mm×120 mm×30/2 mm.
2.2 Preparation of directional solidified sample
The influence of Ti on morphology of dendrite crystal was studied by mean of the directional solidification. The prefabricated bars were put into corundum tubular pot with d16 mm in outer diameter, wall thickness of 2 mm, and they were putted into directional solidified apparatus to heat. The furnace temperature was 760 ℃ for 30 min, and the sample was drawn downwards with constant speed of 80 mm/h and stationary temperature. After draw for 50 mm, the sample was quickly quenched into liquid of gallium-indium alloys. The dimension of sample was d12 mm. The length was 200 mm. The temperature gradient of freezing interface was 2.3 ℃/mm. The freezing speed was 80 mm/h.
2.3 Rapid solidification ribbon sample
Two groups of electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys, one was Al-0.2%Ti alloys and the other was Al-0.3%Ti, were used to make the rapid solidification ribbon samples, and the sample was made in single-roller rotary machine. Diameter of roller was d400 mm; rotational speed was 1 600 r/min; nitrogen pressure was 0.06 MPa; thickness of ribbon sample was 0.3 mm.
2.4 Measurement of chemical composition
The chemical composition of the sample was analyzed with Metalscan 2500 spectrometer. The analyses of the sample were given, and the average of the sample was gotten by computer.
2.5 Analyses of microstructure
The microstructures of sample were examined by using JSM-5610LV electron microscope with EDS, OLYMPUS-BX51 microscope and TEM.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of cooling rate on microstructure
The microstructure of wedge-shaped sample of Al-0.3Ti alloys is shown in Fig.1. Because of the fast chilling, the cooling velocity reaches 300 ℃/s at a distance of 10 mm from the wedge tip, equiaxed grains are formed (Fig.1). With the increment of distance from the wedge tip, the grain size grows up. In other words, the microstructure of Al-Ti binary alloys gets more finer with the increment of cooling velocity (Fig.2). The grain size of wedge-shaped sample is decreased with the increment of Ti content (Fig.3).
The microstructure of the electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys with 0.3%Ti is shown in Fig.4(a), the diffraction patterns of α(Al) and Al3Ti are shown in Figs.4(b) and (c), and the morphology of Al3Ti particles is like short stick.
The microstructure after rapid solidification processing is shown in Fig.5. When the cooling velocity can be as high as 105 ℃/s, the grain size becomes smaller and there is no difference between 0.2%Ti and 0.3%Ti. The grain sizes of the two kinds of Al alloys are less than 0.1-10 μm. The Al3Ti phases can be found in electrolytic low-titanium Al alloys with 0.3%Ti (Fig.6), and the (111) crystal face of α(Al) has a better lattice matching with (112) crystal face of Al3Ti phase, and the calculated result shows that the misfit degree is 0.98%, so that the grain refinement is resulted from the bigger cooling velocity mainly.
3.2 Influence of Ti on constitutional supercooling
The dendrites are mostly common microstructures in cast alloys, especially in wide crystallizing range alloys. The mechanical properties are influenced by the micrograph, size and distribution of dendrite largely, especially the size of the secondary dendrite spacing[9].
There are two mechanisms of grain formation in casting. One is the nucleation at the wall of the casting[10], and the other is in the bulk of melt. The reasons to activate the nucleation of the melt are the constitutional supercooling and the growth restriction. For the difference of solubility of Ti in the solid and liquid, Ti migrates from to the front of the solid though the diffusion. The directional solidification microstructures of the alloys with 0.18%Ti show that the vertical section is columnar crystal, and Ti distributes at the center of the columnar crystal and at the dendritic arm (Fig.7). The cross section is equiaxed crystal, and Ti distributes at the center of the grain(Fig.8). With the reduction of Ti content in front of the solid, the constitutional supercooling is formed, therefore the rate of the nucleation is increased. In addition, the growth restriction increases the time of solidification, there will be more nucleus of crystallization are formed and activated.
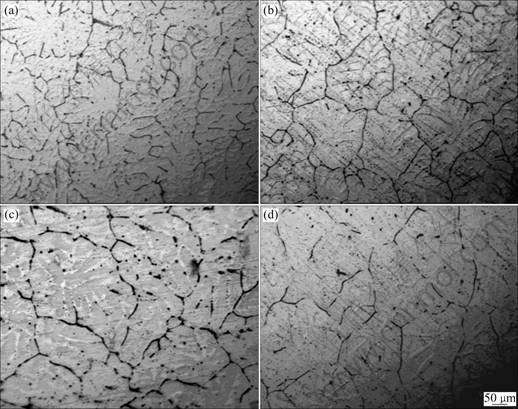
Fig.1 Solidification microstructures of wedge-shaped sample with 0.3%Ti: (a) 10 mm from wedge tip; (b) 30 mm from wedge tip; (c) 50 mm from wedge tip; (d) 70 mm from wedge tip
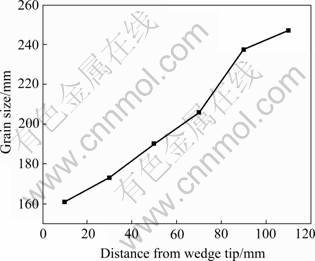
Fig.2 Relationship between grain size and distance from wedge tip
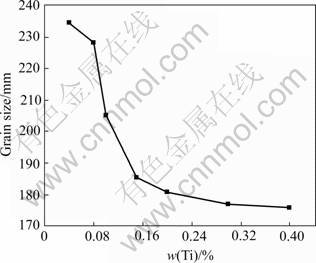
Fig.3 Change of grain size with Ti content at 70 mm from tip
There are two parameters which have been used to quantify the effects of solute on the grain size: the growth restriction factor Q=mlc0(k0-1), and the constitutional supercooling P=mlc0(k0-1)/k0. Where ml is the gradient of the liquid slope, c0 is the concentration of solute in a binary alloys, k0 is the partition coefficient. The values of P and Q of typical factors are listed in Table 1.
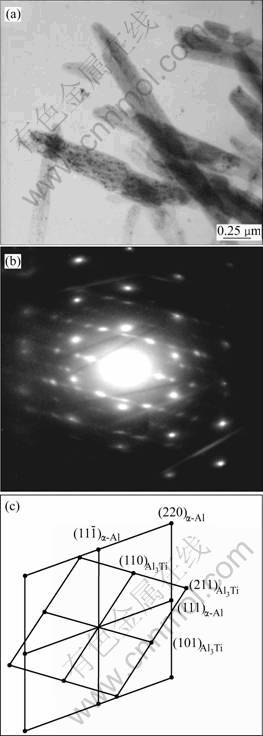
Fig.4 TEM micrographs showing primary Al3Ti particles with Al-0.3%Ti alloys: (a) Al3Ti particles; (b) Diffraction pattern; (c) Scaling of diffraction pattern
P has been used by Spittle and Sadli for evaluate the effects of solute elements to the grain size. By analysing the growth of a dendrite, RAPPAZ and THEVOZ[11] developed the following equation:
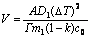
where A is a constant, Γ is the Gibbs-Thomson parameter, Dl is the diffusion coefficient of the solute in the liquid, V is the growth rate of dendrite tip, and ΔT is the liquid-solid temperature range.
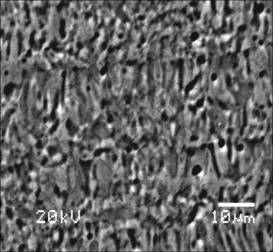
Fig.5 SEM image of Al-0.3%Ti alloys by simply-roller fast solidification method
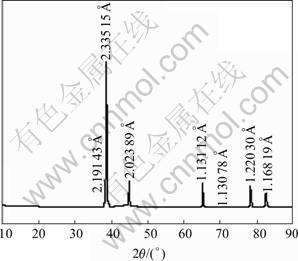
Fig.6 XRD pattern of Al-0.3%Ti alloys
Table 1 Value of P and Q of typical element in Al alloys
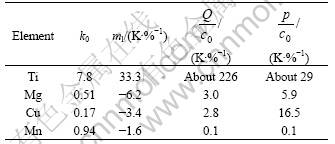
The growth rate of dendrite tip is inversely proportional to the growth restriction factor. With the increment of growth restriction factor, the solidification time is increased, and more nucleus are formed.
Fig.9 shows the directional solidification micro- structures of the electrolytic low titanium alloys with 0.3%Ti and 0.5%Ti in vertical directional section respectively. The microstructure of Al alloys with 0.3%
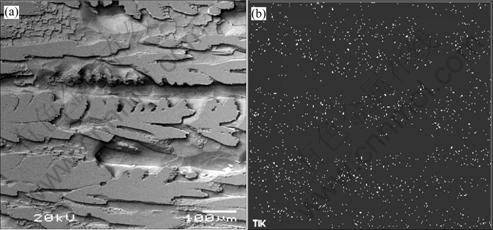
Fig.7 Surface scan of Ti and directional solidification microstructures in vertical section of Al alloys with 0.18%Ti: (a) Solidification microstructure; (b) Surface scanning of Ti

Fig.8 Directional solidification microstructures and surface scan of Ti in cross section of Al alloys with 0.18%Ti: (a) Solidification microstructure; (b) Surface scanning of Ti
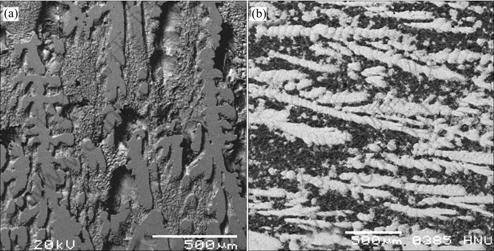
Fig.9 Solidification microstructures in vertical section: (a) 0.3%Ti; (b) 0.5% Ti
Ti is mainly columnar crystal, and the microstructure of Al alloys with 0.5%Ti is flourishing dendrite. It is confirmed that with the increment of Ti, the compositional supercooling degree is raised, and the crystallizing range of the alloys is enlarged, therefore the dendrite branch becomes flourishing.
Fig.10 shows that the directional solidification microstructures of the electrolytic low titanium Al alloys with 0.3% and 0.5%Ti in cross directional section are mainly equiaxed crystal. The petal-like equiaxed crystals are refined with the increment of Ti content, and the content of Ti in the center of the petal is higher than that in the boundary.
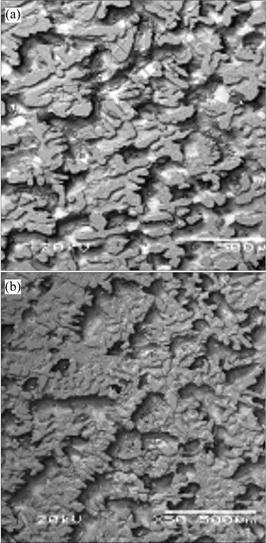
Fig.10 Solidification microstructures in cross section of low- titanium Al alloys: (a) 0.3%Ti; (b) 0.5%Ti
3.3 Mechanism of grain refinement
Titanium is one of the most effective grain refinement elements in electrolytic Al-Ti binary alloys[12-13]. The grain of alloys can be effectively refined when the composition of Ti is less than 0.2%. The grain refinement is resulted from increment of the compositional supercooling caused by Ti additions. With the increase of content of titanium, Al3Ti particles are formed, and the heterogeneous nucleus of Al3Ti is also a main reason of refining alloys in the electrolytic low-titanium aluminum alloys[14]. The distribution of Ti in Al alloys is homogeneous and Al3Ti is formed during cooling, the nucleus formation can be based on the closest packing plane of atom. Because of the diffusion of Ti is lower, Al3Ti phase grows uniformly on each crystal plane. At last Al3Ti phase forms fine block, it can exist stably in the electrolytic low-titanium aluminum alloys during the subsequent freezing. Distributed Al3Ti particles have a better lattice matching with α(Al), therefore they become the core of heterogeneous nucleus.
4 Conclusions
1) Titanium is one of the most effective grain refinement elements in electrolytic Al-Ti binary alloys when the cooling velocity is less than 103 ℃/s. The grain size is decreased with the increment of Ti content. When the cooling velocity can be as high as 105 ℃/s, there is no change in the grain size as the increase of titanium content, the grain refinement is resulted from the bigger cooling velocity mainly.
2) As the increment of Ti content, the compositional supercooling degree is raised, and crystallizing range of the alloys is enlarged, therefore the dendrite branch becomes flourishing.
3) When the content of Ti is less than 0.2%, the grain refinement is resulted from the compositional supercooling. With the increment of Ti content, the grains are mainly refined by heterogeneous nucleation of Al3Ti particles.
References
[1] ZHANG Ming-jie, QIU Zhu-xian, DI Hong-li. A few problems of aluminum alloys produced by electroly in electrolysis bath [J]. Light Metals, 1987: 29-30.
[2] ZHAO Heng-xian. Thermodynamics of Al interalloys produced by electrolysis [J]. Light Metals, 1983: 26-28.
[3] QIU Zhu-xian, YU Ya-xin, ZHANG Ming-jie, ZHAO Yong-wei. Produce Al-Ti alloys in the electrolysis bath [J]. Light Metals, 1986: 32-35.
[4] YANG Guan-qun, GU Qing-shong, LIU Gao-xing, WANG Xiao- feng. Aluminum ore treating and produce directly Al-Si-Ti alloys by electrolytic(1) [J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1993, 6: 19-20.
[5] LIU Zhi-yong, WANG Ming-xing, WENG Yong-gang, SONG Tian-fu, XIE Jing-pei, HUO Yu-ping. Grain refinement effect of Al based alloys with low titanium content produced by electrolysis [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2002, 12(6): 1122-1124.
[6] XIE Jing-pei, LI Ji-wen, LIU Zhong-xia, WANG Ai-qin, WENG Yong-gang. The investigation on aluminum alloys automobile wheel with low titanium content produced by electrolysis [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 475: 317-320.
[7] LIU Zhong-xia, SONG Tian-fu, XIE Jing-pei, WANG Ming-xing, LIU Zhi-yong, WENG Yong-gang. Production and grain refinement of direct electrolytic low Ti aluminium alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(5): 1258-1261. (in Chinese)
[8] SONG Mu-sheng, LIU Zhong-xia, LI Ji-wen. Effect of Ti alloying manner and Ti content on microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(10): 1729-1735. (in Chinese)
[9] LI Shuang-shou, ZHOU Yao-feng, ZENG Da-ben. Transmissibility on microstructure of material and its use in Al alloys [J]. Foundry, 1999, 8: 53-54.
[10] MCCARTNERY D G. Grain refining of aluminium and its alloys using inoculants [J]. Inter Meter Rev, 1989, 34(5): 247-249.
[11] RAPPAZ M, THEVOZ P H. Solute diffusion model for equiaxed dendritic growth [J]. Acta Metall, 197, 35: 1487-1489.
[12] LIU Zhong-xia, SONG Tian-fu, XEI Jing-pei, XIE Jing-pei, WANG Ming-xing, LIU Zhi-yong, WENG Yong-gang. Production and grain refinement of direct electrolytic low-titanium aluminium alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(5): 1257- 1258. (in Chinese)
[13] MOHANTY P S, GRUZLESKI J E. Mechanism of grain refinement in aluminium [J]. Acta Mater, 1995, 43: 2001-2004.
[14] LEE C T, CHEN S W. Quantities of grains of aluminium and those of TiB2 and Al3Ti particles added in the grain-refining process [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, A325(1): 242-243.
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project(0621000600) supported by the Innovation Fund for Outstanding Scholar of Henan Province, China
Corresponding author: WANG Ai-qin; Tel: +86-379-64231269; E-mail: aiqin_wang888@163.com