文章编号:1004-0609(2008)10-1749-07
铸造Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金的低温超塑性及其组织演变
肖代红,黄伯云
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点试验室,长沙410083)
摘 要:通过非自耗电弧熔炼及氩气保护浇铸,制备高Cr含量的Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金。采用金相观察、扫描电镜、透射电镜及高温拉伸测试等实验方法,研究铸态合金在800~1 000 ℃的超塑性变形能力及其变形机制。结果表明,高Cr合金化的铸造Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金显示出低温超塑性。在850 ℃的低温及应变速率1×10-4 /s时的最大伸长率为630%,应变速率敏感系数m达到0.51。在800~1 000 ℃的变形激活能为245 kJ/mol。合金的低温超塑性变形机制是由晶界扩散控制和β→γ相转变而协调的晶界滑动,b相在变形过程中起到了重要的作用。
关键词:钛铝合金;铸造;超塑性;显微组织
中图分类号:TG 146.23 文献标识码: A
Superplastic behavior and microstructure evolution of
as-cast Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb alloy at lower temperature
XIAO Dai-hong, HUANG Bai-yun
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb alloys with high Cr content were synthesized by non-consumable arc melting in argon atmosphere. Superplastic behavior and deformation mechanism of the as-cast alloy were investigated by optical microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and elevated-temperature tensile testing at temperatures ranging 800~1 000 ℃. The results show that the as-cast alloy with high Cr content reveals excellent lower temperature superplasticity with the maximum elongation-to-failure of 630% at 850 ℃ and strain rate of 1×10-4 /s, and the strain rate sensitivity exponent m is 0.51. The activation energy calculated is 245 kJ/mol. The dominant deformation mechanism of Ti-Al-Cr-Nb alloy with high Cr content between 800 ℃ and 1 000 ℃ is the grain boundary sliding controlled by volume diffusion. The presence of β phase and its transformation to γ phase during deformation are beneficial to the grain boundary sliding.
Key words: titanium aluminum alloy; casting; superplasticity; microstructure
TiAl基合金具有密度低、熔点高、高温强度及模量大、抗氧化性能及抗吸氢能力强等优点,是新一代发动机耐高温候选材料[1-3]。但TiAl基合金在室温时晶面滑移难以开动导致滑移数目不足,从而表现出室温脆性以及由此而产生的机加工困难,极大限制了它的发展。为此,有关TiAl基合金的近净型成型技术受越来越多的重视,其中超塑性成型技术是比较有吸引力的方法之一。
在一定的条件下,TiAl基合金呈现明显的超塑性特征,但所表现出的超塑性一般为组织超塑性,也称为静态超塑性,而它要求材料具有细小而稳定的等轴组织,即所谓晶粒的三化(微细化、等轴化、稳定化)[4]。晶粒尺度一般在0.5~5 mm,最大不超过10 mm[5-7]。对于TiAl基合金而言,为了实现晶粒的细化而达到超塑性的要求,一般要对材料进行晶粒细化处理。处理方法主要采用热机械处理,即进行热挤压或锻造[8-10],这一过程既增加了工艺的复杂性,又增加了成本。另外,在超塑性加工工艺中,TiAl合金的变形速率比较低,表现出超塑性特征的温度范围比较高,一般在 1 000 ℃左右,在这种条件下,对工艺设备的要求比较高,同时又要防止材料的过度氧化等问题。因此,发展变形温度较低的超塑性TiAl基合金变得很重要。HUANG等[11-12]研究了低Cr合金化的Ti-48Al-2Cr- 0.2Mo合金的在800~900 ℃时的超塑性变形能力,得到的最大伸长率为300%~413%,并认为其变形机制是受晶界扩散控制。
研究表明,在Ti-Al合金中添加高含量(摩尔分数)的Cr (8%~20%),有助于提高合金的抗氧化性能[13-14],但对高Cr合金化的铸造Ti-Al合金的超塑性行为研究报道较少。为此,本文作者制备含高Cr的Ti-47Al-8Cr- 2Nb合金,并对其超塑性变形特征及机制进行探讨。
1 实验
研究用合金名义成分为Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb(摩尔分数),同时添加微量B与W。合金采用水冷铜坩埚电弧熔炼,氩气保护浇铸。铸锭通过线切割成高温拉伸所需的板状样,试样标距部分为8 mm×4 mm×1.4 mm,在带高温炉的岛津材料实验机上进行,测试温度范围为800~1 000 ℃,应变速率为2.5×10-5~1×10-4 /s。
为观察不同变形阶段的组织变化,部分试样拉伸到一定程度后停止并水淬。合金的组织观察在Polyvar-MET金相显微镜及JSM-6360型扫描电镜下进行。相分析的确定采用RIGAKU-3014X型X射线衍射仪和H-800型透射电子显微镜(TEM)。TEM样品从拉伸后的标距部分取出。为分析材料在变形温度范围是否发生其他转变,采用NETZSCH DSC 404型差热分析仪对铸态合金进行DSC分析,测试温度为400~1 200 ℃,升温速率为5 ℃/min。
2 结果
2.1 铸态组织
合金的铸态组织如图1所示,通过高Cr合金化由β凝固产生的铸态组织均匀细小,晶粒的边界从图中无法明确辨认(图1(a))。而通过X射线衍射分析发现合金中包含γ、β(B2)和α2这3种相。EDX分析显示,β(B2)相中含有高Ti和高Cr。TEM观察发现,合金组织主要由β和γ两相构成(图1(b)),其中具有较亮衬度的是γ相,黑灰色衬度的是β相,而α2在组织中很难发现,可能是含量很少的缘故。
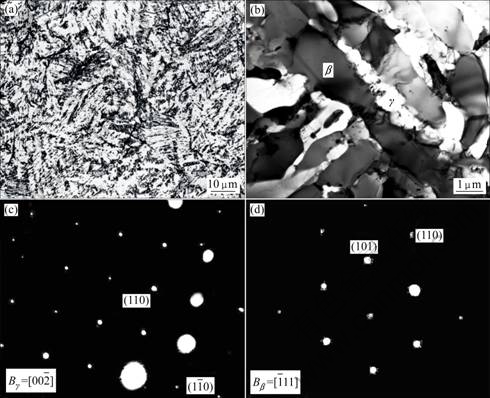
图1 铸态合金的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of as-cast alloy: (a) Optical microscope; (b) TEM bright-field image; (c) Diffraction pattern of γ; (d) Diffraction pattern of β
2.2 高温变形
铸态合金在800~1 000 ℃及应变速率为1×10-4 /s时的真应力—真应变曲线如图2(a)所示。在800 ℃变形时,样品几乎没有产生塑性变形,而在800 ℃以上,合金则表现出超塑性特征。在经过弹性变形后,样品产生应变硬化,但是过程非常短暂,并很快达到峰值应力。应变硬化没有持续很长时间,经过一个近似应变硬化和软化平衡的阶段,应力就逐渐开始下降,即应变软化占据了主导作用,直至样品断裂。这种曲线的变化趋势随温度的上升而逐渐趋于缓和,即在较高温度变形时后面的软化作用所导致的应力下降趋势渐缓,曲线也趋于平坦。并且从图2(b)中可以看出,合金的峰值拉伸应力随着变形温度的升高而逐渐下降。另外,在800 ℃变形时样品在几乎是弹性阶段就已发生断裂。根据拉伸曲线的变化趋势,此温度的峰值拉伸应力应该远高于850 ℃的应力水平。因此可以看出,在800 ℃到850 ℃之间合金的峰值应力下降很大,而在850 ℃以上应力减小的趋势明显减缓。由图2(b)可见,样品伸长率随温度的变化呈现另外一种趋势。在800 ℃时合金几乎未产生塑性变形,而在850 ℃时样品具有良好的超塑性变形能力,伸长率达到了630%,超过了文献[11-12]报道的结果。当继续提高温度,合金仍然表形出良好的塑性变形,而伸长率出现一定程度下降。但随着温度的提高,这种下降的趋势并不十分明显。
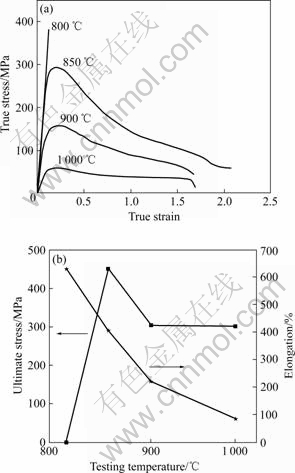
图2 合金的高温拉伸性能
Fig.2 Tensile properties of alloy after tensile testing at high temperature: (a) True stress—true strain curves; (b) Temperature dependence of ultimate stress and elongation
采用拉伸速度突变法[3],即Backofen法求m值,得出合金在850 ℃的平均应变速率敏感性因子m为0.51(图3(a))。这一值高于传统的采用热机械处理方式获得超塑性组织的TiAl基合金的m值(一般在0.3~0.4之间),表明所制备的含高Cr合金具有良好的超塑性特征。
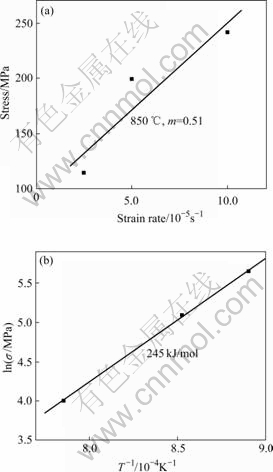
图3 应变速率敏感性m值(a)及超塑性激活能(b)的确定
Fig.3 Determination of strain-rate-sensitivity m (a) and activation energy Q (b)
超塑性变形过程与高温蠕变一般都在高温低速条件进行,属于热激活过程,而其激活能的测定也是建立在高温蠕变的基础上。它们在变形过程中伴随有扩散的发生,因此其变形速率、应力和温度关系都可以用Arrhenius型方程式表示[3]:

式中 A为材料和结构有关的常数,b为位错的柏氏矢量,d为平均晶粒直径,p为晶粒指数,R为摩尔气体常数, n为应力指数,其值为m-1(m为应力敏感性指数),Q为变形激活能,T为绝对温度。
通过进一步的简化可以得到下面的关系式:
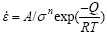
在实验中变形速率近似保持不变,所以可以得到:

式中 B为常数。以lns 对T-1作图,其斜率k为Q/nR,则Q=knR=Kr/m。因此得到高Cr合金化TiAl基合金超塑性变形的激活能(图3(b))为245 kJ/mol。这一值接近β-Ti的自扩散激活能(250 kJ/mol)[15],而略高于在低温超塑性变形过程中晶界扩散激活能(180~200 kJ/mol)[16]。
2.3 差热分析
从图2可知,合金在800~850 ℃呈现一种明显的转折特征;而DSC的分析结果发现(图4),合金在800~850 ℃存在一个吸热反应。前人对Ti-Al-Nb三元系的研究发现,β(B2)相的有序无序反应对合金的成分很敏感,对于富Nb成分转变温度约为600 ℃左右,而对于富Ti部分为1 182 ℃。由铸态合金显微组织的分析可知,组织中的β(B2)相含有高Ti和高Cr,所以以此推断,β(B2)相在800~850 ℃这个温度范围发生了有序无序转变。

图4 合金在400~1 200 ℃的DSC曲线
Fig.4 DSC curves from 400 ℃ to 1 200 ℃ for alloy
2.4 变形后的显微组织
试样在850 ℃及应变速率为1×10-4 /s变形15%后的显微组织如图5(a)所示,在变形15%后的初始时期发生了动态再结晶,原来具有一定取向的条带状晶粒组织(图1)被细小的等轴晶粒组织所代替,并且这些细小的等轴晶粒一般在原来的条带晶粒组织的晶界处出现的频率比较大,表明晶界是再结晶形核的主要部位。另外,变形期间各相不仅发生了动态再结晶,而且原来铸态组织中的β相也发生了相转变。从图5(b) 和(c)中可知,与β相临近的γ相逐渐向β相晶粒内部渗透,由此产生β和γ相界面迁移,一个原来的β晶粒逐渐被附近的γ相所“挟开”,分割(箭头所示)。这与超塑性Zn-Al共析合金中在变形中产生的变化类似。
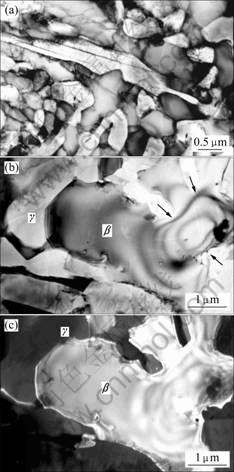
图5 在850 ℃变形15%后组织的TEM像
Fig.5 TEM images of microstructure after 10% deformation for alloy at 850 ℃: (a) TEM graph image of alloy; (b) and (c) Grain boundary morphologies between β and γ phases
图6所示为样品变形100%后的显微组织。可以看出在大变形量之后,合金的显微组织变得非常均匀和等轴化并接近球化,而且组织中γ相所占比例比初始组织中的大。另外,合金经过大变形量之后,在某些晶粒中还可以看到位错结构(图6(b)箭头所示),但是位错的密度不大。
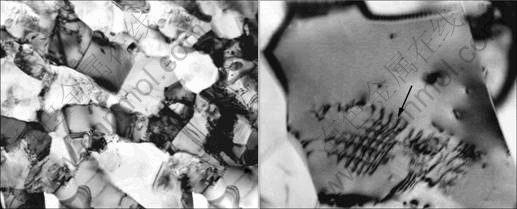
图6 合金在850 ℃变形100%后的细晶等轴组织
Fig.6 Fine equiaxed microstructure (a) and low density of dislocations (b) after 100% deformation at 850 ℃
合金在不同温度变形后的断口形貌图如7所示,可以看出在800 ℃变形时,断口组织中有较多的解理表面,断裂主要是穿晶解理形式(图7(a)),而在850 ℃变形时,基本上没有解理平面,断裂以沿晶断裂为主(图7(b))。并且从不同温度的断口形貌中还可以发现,随着变形温度的提高,经过大变形量变形后在晶界处的空洞发生由少到多,由小到大(图7(c)和7(d))的 变化。
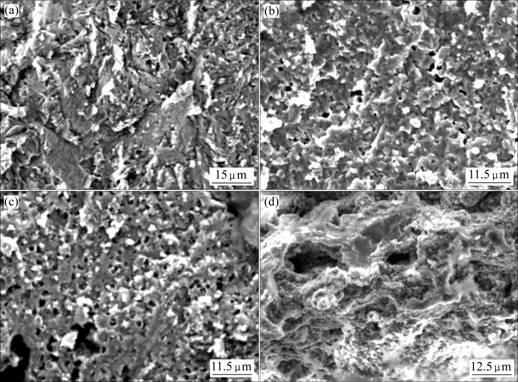
图7 在不同温度变形后的断口表面形貌
Fig.7 Fracture surfaces morphologies after deformation at different temperatures: (a) 800 ℃; (b) 850 ℃; (c) 900 ℃; (d) 1 000 ℃
3 讨论
前人的研究发现,TiAl基合金发生超塑性变形的温度一般在1 000 ℃以上[17-18]。要降低超塑性变形温度,目前较普遍的方法是细化晶粒,即把晶粒从微米级细化至亚微米级,这就需要复杂的工艺。还有一种就是引入亚稳态的β相,但是相关的报导比较少。本实验结果表明,通过β稳定元素Cr合金化,可以兼顾这两个方面的作用,首先由β凝固获得均匀细小的铸态组织,另外得到的铸态组织中由于强β稳定元素Cr的作用,所以含有较多的β相。同时,大多数的超塑性TiAl基合金的应变速率一般小于10-4 /s[17-18],大于这个数值会导致较差的伸长率。这主要是因为超塑性过程往往涉及到一些协调过程,如体扩散和晶界扩散,在较高的应变速率下,这些协调过程无法及时进行而导致了较早的断裂。
图5及图6表明,Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金在超塑性变形过程中晶粒发生球化,晶界圆弧化。这种现象与很多材料在超塑性变形过程中的变化相似。而对细晶超塑性材料产生这种现象的解释,研究者讨论的最多的是晶界滑动过程。因为超塑性材料在变形后一般会产生比本身原始尺寸大几倍甚至几十倍的变形量,要达到这么大的变形量而又使材料内部不发生明显的空洞,并使晶粒的形状保持等轴,比较合理的解释就是晶粒在变形过程中发生了相对移动。在Ti-47Al-8Cr- 2Nb合金超塑性变形过程中,晶界滑动过程同样也起了重要的作用。但是它所伴随的控制或协调过程却是多个因素的共同作用。
首先,晶界滑动本身可以作为一种协调过程来填充由于晶界滑动而产生的晶粒之间的空洞,这就是由GIFKING所提出的晶粒转出模型[19]。但是,由简单的估算可以发现,这种过程在实际变形中不是所有晶粒都可以发生的。因为基于这种模型,样品的变形量可以由样品标距段宽度和晶粒尺寸计算出,而高Cr合金化TiAl基合金的初始组织十分细小,由此估算出的结果远大于实际观察,所以其他控制过程一定在起作用。从热激活分析发现,在变形过程中的激活能与晶界扩散激活能接近,因此可以判断在变形过程中,晶界扩散是主要的扩散机制,可能也是一种控制机制。原子在晶界扩散的实质是界面处错配位错的正负攀移,而正是由于界面位错运动的快慢决定了界面的移动快慢,决定了晶界的形状变化和晶界滑动能否顺利进行。
其次,从DSC的分析结果以及前人的研究可知,合金中富集Ti和Cr的β(B2)相在高于800 ℃的温度发生了有序无序转变。而在高温变形时,这些较软的β(B2)相发挥了重要作用,它类似于在粘性晶界滑动理论中论述的高温晶粒边界无序状态所起到的对变形的作用。VANDERSCHUEREN认为β相可以增加晶界的结合,从而避免在滑动过程中形成空洞导致提前断裂[20]。但从本次研究来看,由于存在有序无序的转变,在800 ℃以上β相是一种较软的亚稳相,所以更可能的作用是作为一种“润滑剂”,有利于晶界的滑动;并且β相的有序无序转变也有利于扩散的进行,从而使晶界滑动顺利进行。
第三,组织的观察分析发现,在变形中发生了β→γ的相变,相变的驱动力可能来自变形过程中的应力集中。这是因为在变形中总是存在一些晶界取向不利于晶界滑动的晶粒,而在这些晶粒的边界产生应力的集中,从而导致这种转变的发生,使β和γ相界面的迁移。这种现象与在Zn-Al共析合金中的现象类 似[21],产生的结果往往是β相被“挟开”,使晶粒取向更有利于变形。
以上分析表明β相在变形中发挥了重要的作用,正是由于β相的这两种作用从而使伸长率从800 ℃到850 ℃产生较大的跳跃。
但是上面所讨论的晶界滑动在变形的开始阶段并不能够顺利的启动和进行。因为从初始组织(图1(b))中可以看出,晶粒的许多位向并不是总是有利于变形的方向。所以必须进行某种转化,而通过组织观察可以发现这种转化是通过动态再结晶完成的(图5(a))。发生动态再结晶之后,组织主要由等轴的晶粒构成,而这种组织形态为晶粒传出和晶界滑动的启动提供了良好的前提。
4 结论
1) 由β凝固所得到的铸造Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金具有良好的超塑性。在变形温度850 ℃及应变速率10-4 /s下的伸长率达到630%。与其他的超塑性TiAl基合金相比,它具有较低的变形温度。
2) 铸造Ti-47Al-8Cr-2Nb合金的超塑性变形机制是由晶界扩散控制和β→γ相转变而协调的晶界滑动。另外在变形初期,发生了动态再结晶,使初始的那些不利于变形的组织形态发生了转化,成为更加均匀的等轴组织,从而为晶界滑动的启动提供了良好的前提。
3) β相在变形过程中起到了重要的作用,主要体现在两个方面。首先在高于800 ℃时发生了有序无序转变,而转变之后的β相是较软的亚稳相,它有利于晶界的滑动和扩散过程。另外在变形过程中还通过β→γ相变来松弛晶界应力集中来协调变形。正是由于在组织中存在较高含量β相的这两种作用才使合金表现出良好的变形能力。
REFERENCES
[1] 张永刚, 韩雅芳, 陈国良. 金属间化合物结构材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001.
ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang. Structural intermetallics[M]. Beijing: Defense Industry Press, 2001.
[2] KIM Y W. Scale-up of ingot metallurgy wrought TiAl[C]// NATHAL M V, DAROLIA R, LIU CT, MARTIN PL, MIRACLE DB, WAGNER R, YAMAGUCHI M eds. Structural Intermetallics 1997. Warrendale: TMS, 1997. 20-25.
[3] 张 伟, 刘 咏, 黄劲松, 刘 彬, 贺跃辉. 高铌TiAl高温合金的研究现状与展望[J]. 稀有金属快报, 2007, 26(8): 1-6.
ZHANG Wei, LIU Yong, HUANG Jin-song, LIU Bin, HE Yue-hui. Research progress and prospects for refractory TiAl Alloy with high Nb content[J]. Rare Metals Letters, 2007, 26(8): 1-6.
[4] 刘 勤. 金属的超塑性[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1989: 50-56.
LUI Qin. Superplasticity in metals[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 1989: 50-56.
[5] IMAYEV R M, KAIBYSHEV O A, SALISHCHEV G A. Mechanical behavior of fine grained TiAl intermetallic compound-Ⅱ. Ductile-brittle transition[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40(3): 589-595.
[6] SHAGIEV M, SENKOV O, SALISHCHEV G, FROES F. High temperature mechanical properties of a submicrocrystalline Ti-47Al-3Cr alloy produced by mechanical alloying and hot isostatic pressing[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2000, 313: 201-208.
[7] NIEH T G, HSIUNG L M, WADSWORTH J. Superplastic behavior of a powder metallurgy TiAl alloy with a metastable microstructure[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(2): 163-170.
[8] IMAYEV V M, IMAYEV RM, SALISHCHEV G A. On two stages of brittle-to-ductile transition in TiAl intermetallic[J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8(1): 1-6.
[9] LEE W B, YANG H S, KIM K W, MUHKERJEE A K. Superplastic behavior in a two-phase TiAl alloy [J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1993, 29, 1403-1408.
[10] 苏喜孔, 李树索, 韩雅芳, 李臻熙, 徐向俊, 徐丽华, 林均品, 陈国良. 热锻开坯对高铌TiAl合金微观组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 1410-1514.
SU Xi-kong, LI Shu-suo, HAN Ya-fang, LI Qin-xi, XU Xiang-jun, XU Li-hua, LIN Jun-pin, CHEN Guo-liang. Effect of hot forging on microstructure of TiAl alloy containing high Nb[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 1410-1514.
[11] HUANG Bai-yun, ZHANG Jun-hong, HE Yue-hui, LIU Yong, SUN Jian, WU Jian-sheng. Superplastic behavior of TiAl based alloy at relatively low temperature ranging from 800 ℃ to 1 075 ℃[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2002, 12 (2): 577-581.
[12] 张俊红, 黄伯云, 贺跃辉, 孟力平. TiAl基合金低温超塑性变形的力学行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(2): 442-446.
ZHUANG Jun-hong, HUANG Bai-yun, HE Yue-hui, MENG Li-ping. Mechanical behaviors of TiAl alloy during low temperature superplastic deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(2): 442-446.
[13] 周春根, 杨 颖, 宫声凯, 徐惠彬. Cr在Ti-Al-Cr合金抗高温氧化过程中的作用研究[J].航空学报, 2001, 21(1): 73-77.
ZHOU Chun-gen, YANG Yin, GONG Sheng-kai, XU Hui-bin. Mechanism of Cr effect for improvement of oxidation resistance of Ti-Al-Cr alloys[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2001, 21(1): 73-77.
[14] DONG Zi-qiang, JIANG Hui-ren, FENG Xiao-ran, WANG Zhong-lei. Effect of Cr on high temperature oxidation of TiAl [J].Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(S3): 2004-2008.
[15] NAKAJUMA H, KOIWA M. Diffusion in titanium[J]. ISIJ International, 1991, 31(8): 757-767.
[16] IMAYEV R M, SALISHCHEV G A, SENKOV O N, IMAYEV V M, SHAGIEV M R, GABDULLIN N K, KUZNETSOV A V, FROES F H. Lower-temperature superplasticity of titanium aluminides[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 300(1/2): 263-277.
[17] 黄伯云, 贺跃辉, 邓忠勇. 热变形TiAl基合金的超塑性行为[J]. 金属学报, 1998, 34(11): 1173-1177.
HUANG Bai-yun, HE Yue-hui, DENG Zhong-yong. Superplasticity behaviors of thermally deformed TiAl based alloys[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 1998, 34(11): 1173-1177.
[18] SUN J, WU J S, HE Y H. Superplastic properties of a TiAl based alloy with a duplex microstructure[J]. J Mater Sci, 2000, 35(19): 4919-4922.
[19] GIFKINS R C. Grain rearrangements during superplastic deformation[J]. J Mater Sci, 1978, 13(9): 1926-1936.
[20] VANDERSCHUEREN D, NOBUKI M, NAKAMURA M. Superplasticity in a vanadium alloyed gamma plus beta phased Ti-Al intermetallic[J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1993, 28: 605-610.
[21] NAZIRI H, PEARCE R, Henderson-Brown M, HALE K F. Microstructural-mechanism relationship in the zinc/aluminium eutectoid superplastic alloy[J]. Acta Metall, 1975, 23(4): 489-496.
基金项目:中国博士后科学基金资助项目(20070410986);中南大学博士后科学基金资助项目(20070401)
收稿日期:2008-03-17;修订日期:2008-06-02
通讯作者:肖代红,副研究员,博士;电话:0731-8836773;E-mail: daihongx@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)