DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.09.036
高温氨气炭化制备氮掺杂炭干凝胶及其CO2吸附性能
刘斌,李立清,马卫武,李海龙,马先成,杨叶,唐琳,汪椿皓
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:以间苯二酚(R)和糠醛(F)为原料,通过溶胶-凝胶法、常压干燥法合成RF有机干凝胶,并在高温氨气氛下炭化制备氮掺杂炭干凝胶(ACXs)。采用热重分析仪、比表面积及孔径分析仪、扫描电镜、傅里叶红外光谱与X线光电子能谱对ACXs的表面物化性质进行表征;应用固定床等温吸附实验探讨ACXs对CO2的吸附性能。研究结果表明:高温氨气炭化后,ACXs比表面积和总孔容随着炭化温度升高而增大,温度越高,增加幅度越大;高温氨气炭化使材料表面形成氨基、吡咯氮、吡啶氮等含氮官能团,从而显著提高表面含氮量,有利于提高ACXs的CO2吸附性能;随着炭化温度升高,ACXs微球收缩变小,孔隙裂解、气化刻蚀效果增强,含氮量减少;氮的存在形态由氨基基团向吡啶基团转化,碱性含氮官能团减少,从而降低ACXs的CO2吸附能力;控制合理的氨气炭化温度,可以提高ACXs对CO2的吸附性能。
关键词:氮掺杂;炭干凝胶;吸附;NH3;CO2
中图分类号:TQ127.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)09-2536-08
Preparation of nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels carbonized by high-temperature with ammonia and its adsorption capacity for CO2
LIU Bin, LI Liqing, MA Weiwu, LI Hailong, MA Xiancheng, YANG Ye, TANG Lin, WANG Chunhao
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Organic xerogels were prepared by the sol-gel method and ambient drying method from polymerization of resorcinol with furfural, these xerogels were carbonized in ammonia atmosphere to obtain nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels (ACXs). The surface physical and chemical properties of the ACXs were characterized by thermogravimetry (TG), specific surface area and pore distribution analyzer (BET), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The isothermal adsorption performance of the ACXs for carbon dioxide was investigated with fixed-bed apparatus. The results show that after carbonization at high temperature in ammonia atmosphere, the BET specific surface area and total pore volume of ACXs increase with the increase of the carbonization temperature. The higher carbonization temperature is, the more the amplitude increases. Mainly nitrogen functional groups which are formed on the ACXs surfaces because of high-temperature carbonization in ammonia atmosphere are amino groups, pyrroles and pyridines. Nitrogen content of ACXs improves significantly, and the adsorption performance of ACXs for carbon dioxide also improves. With the increase of carbonization temperature, ACXs microspheres become smaller as a result of shrinkage, the pyrolysis and gasification process enhance remarkably, both leading the nitrogen content to decrease. Additionally, the presence of nitrogen forms is converted from amino groups to pyridine ones. The reduction of carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of ACXs is attributed to the decrease of alkaline nitrogen functional groups. The carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of ACXs can be advanced by controlling carbonization temperature in ammonia atmosphere.
Key words: nitrogen-doped; carbon xerogels; adsorption; NH3; CO2
随着能源需求日益增大,大量化石燃料的燃烧使温室气体CO2排放量日益增多,导致全球变暖问题日益严重[1]。用适宜的方法控制CO2的排放迫在眉睫[2]。通过捕获分离燃烧废气中的CO2是一种极具潜力的控制CO2排放技术。吸附法分离CO2具有能耗低、吸附量大且可再生重复使用等优点[3-4],其CO2吸附性能与吸附剂的物化性质密切相关。炭干凝胶是一种新型高聚物分子互相连接所形成的三维网络结构材料, 因具有比表面积大等优点而被受到广泛关注。 等[5]研究了炭干凝胶对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能,发现炭干凝胶微孔比表面积和微孔孔容的增加可以大大提高其对亚甲基蓝的吸附量;GORGULHO等[6]以间苯二酚和甲醛为原料,采用三聚氰胺和尿素为氮源,合成了氮掺杂炭干凝胶。DRAGE等[7]发现氮掺杂能显著提高炭干凝胶含氮官能团含量和表面碱度,有利于提高CO2吸附性能;SEVILLA等[8]在聚吡咯为炭前体的基础上,采用KOH活化法制备了氮掺杂多孔炭,显著提高了多孔炭的CO2吸附能力。他们使用含氮化合物作为炭前体制备氮掺杂材料,但主要研究了合成条件对材料影响,未涉及高温炭化过程中氨气氛掺氮方式、高温炭化条件对含氮官能团变化影响规律及其二氧化碳吸附作用机理。为此,本文作者采用溶胶-凝胶法、常压干燥法[9]制备有机干凝胶,以高温氨气炭化的方式引入氮源,获得氮掺杂炭干凝胶;采用固定床吸附实验测试其CO2吸附性能,分析氨气氛下炭化温度对氮掺杂炭干凝胶孔结构与表面物理化学性质的影响规律,探讨氮掺杂炭干凝胶表面含氮官能团和CO2之间可能的作用机理。
等[5]研究了炭干凝胶对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能,发现炭干凝胶微孔比表面积和微孔孔容的增加可以大大提高其对亚甲基蓝的吸附量;GORGULHO等[6]以间苯二酚和甲醛为原料,采用三聚氰胺和尿素为氮源,合成了氮掺杂炭干凝胶。DRAGE等[7]发现氮掺杂能显著提高炭干凝胶含氮官能团含量和表面碱度,有利于提高CO2吸附性能;SEVILLA等[8]在聚吡咯为炭前体的基础上,采用KOH活化法制备了氮掺杂多孔炭,显著提高了多孔炭的CO2吸附能力。他们使用含氮化合物作为炭前体制备氮掺杂材料,但主要研究了合成条件对材料影响,未涉及高温炭化过程中氨气氛掺氮方式、高温炭化条件对含氮官能团变化影响规律及其二氧化碳吸附作用机理。为此,本文作者采用溶胶-凝胶法、常压干燥法[9]制备有机干凝胶,以高温氨气炭化的方式引入氮源,获得氮掺杂炭干凝胶;采用固定床吸附实验测试其CO2吸附性能,分析氨气氛下炭化温度对氮掺杂炭干凝胶孔结构与表面物理化学性质的影响规律,探讨氮掺杂炭干凝胶表面含氮官能团和CO2之间可能的作用机理。
1 实验
1.1 样品制备
将1 g间苯二酚(纯度99.5%,国药试剂)、0.043 g六次甲基四胺(纯度99.0%,国药试剂)和1.5 mL糠醛(纯度99.0%,光复化工)溶于100 mL无水乙醇(纯度99.7%,恒兴试剂)后密封,置于集热式磁力加热搅拌器(DF-I型,江苏省金坛市荣华仪器制造有限公司)中匀速搅拌3 h;在搅拌的同时将4 mL乙酸(纯度99.5%,国药试剂)以1 mL/min的速度逐滴加入上述溶液[10],搅拌完后静置4 h,将形成的淡黄色溶胶-凝胶置于75 ℃恒温水浴箱中固化48 h,得到深棕色有机湿凝胶,再将有机湿凝胶置于室内环境下自然干燥24 h,最后在真空干燥箱(DZF,北京市永光明医疗仪器厂)中在75 ℃下干燥12 h,所得样品为有机干凝胶。
氮掺杂炭干凝胶(ACXs)的炭化装置图如图1所示。将一定量的有机干凝胶放入内径为3 cm的石英管中,置于可精确控温(±0.1 ℃)的程序控温管式炉(GSL-1100X-S,合肥科飞商贸有限责任公司)中炭化。炭化过程分为升温、恒温和降温3个阶段,利用程序升温控制仪(AI-716P,厦门宇电自动化科技有限公司)控制温度以3 ℃/min的升温速度从室温升至目标温度(600,700,800,900 ℃),并恒温1 h,然后以3 ℃/min的降温速度降至300 ℃,最后自然冷却至室温。在升温和降温过程中采用高纯N2(99.999%)气氛保护,在恒温过程中使用NH3 (99.9%)气氛引入氮源。实验所用气体高纯N2和NH3均来自钢瓶(长沙高科气体有限公司),N2(100 mL/min)和NH3(100 mL/min)的流量以及进入管式炉的气氛均通过质量流量控制器(D07-19B,北京七星华创电子股份有限公司)精确控制(±1%)。所得样品记为ACXx,其中,后缀x表示炭化温度;同时,为了考察NH3对炭干凝胶的影响,设计1个空白实验,选取炭化温度为600 ℃,炭化全过程在高纯N2保护下进行,所得样品记为CX600。尾气采用0.1 mol/L的磷酸溶液处理。
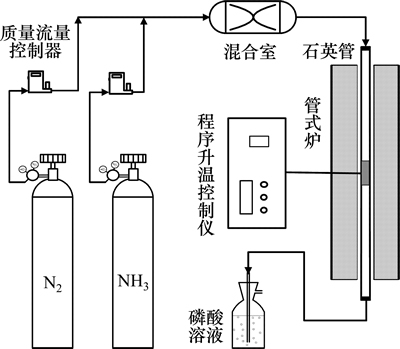
图1 炭化装置图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of carbonization
1.2 样品表征
在氮气氛围下利用热重分析仪(LABSYS TG, SETARAM, France)表征有机干凝胶的热重特性曲线,升温速率为10 ℃/min;采用比表面积及孔径分析仪(SA3100, BECKMAN COULTER, USA)测定77 K下高纯N2等温吸附线,得到炭干凝胶比表面积SBET(BET法)、微孔孔容Vmicro(t-Plot法)、中孔孔容Vmeso(BJH法)、大孔孔容Vmacro(BJH法)和总孔容Vtotal等物性参数;利用扫描电子显微镜(QUANTA200, FEI Instrument Co., NED)表征炭干凝胶表面微观形貌;利用傅里叶红外光谱仪(NEXUS670, Nicolet, USA)表征炭干凝胶表面官能团特性,扫描的波数范围为400~2 000 cm-1;采用X线光电子能谱仪(ESCALAB 250XI, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA)表征炭干凝胶表面元素含量及含氮官能团种类,放射源为Al Kα(hv=1 486.6 eV,其中,h为普郎克常数,v为光波频率),操作压力为10-6 Pa。
1.3 吸附实验
固定床吸附实验装置如图2所示,该装置由配气系统、恒温系统、吸附床和测试系统组成。配气系统包括高纯N2和标准CO2(10%和90%N2,体积分数)气体,均来自钢瓶,气体流量通过质量流量控制器精确控制(±1%)。吸附之前,打开控制阀1,将样品置于温度为80 ℃和N2(10 mL/min)气氛下脱气处理2 h,并利用气相色谱仪(SP-6890,山东鲁南瑞虹化工仪器公司)检测出口CO2浓度,当待检测不到CO2时,则认为脱气完毕;然后,关闭N2和控制阀1,同时打开控制阀2和标准CO2(10 mL/min)气体进行换气,并维持1 h,确保吸附实验开始时进气管路形成标准CO2气体气氛;最后,打开控制阀1且关闭控制阀2,开始实验。实验时,吸附柱进气浓度和出气浓度由气相色谱仪测定,待出气浓度和进气浓度相同,并保持30 min左右,则认为吸附已达平衡[11]。在每次实验中,将1 g炭干凝胶置于内径为1.1 cm、高度为18 cm的石英管吸附柱,填充高度为6 cm,占整个吸附柱高度的1/3。脱气温度和吸附温度用恒温水浴箱(DC1015,上海精密科学仪器有限公司)调节。
实验中,吸附温度均为293 K,进气流量均为10 mL/min,利用积分法分别测得5种炭干凝胶对CO2的平衡吸附量,并得到CO2的吸附穿透曲线。
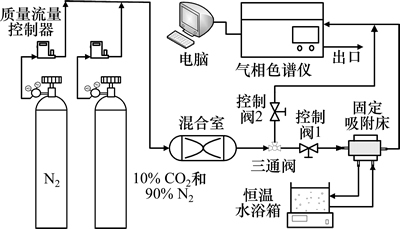
图2 固定床吸附实验装置
Fig. 2 Experiment device of fixed-bed adsorption
2 结果与讨论
2.1 有机干凝胶热重特性
图3所示为有机干凝胶在热解过程中的TG和相应的DTG曲线。由图3可知热解过程分为4个阶段:150 ℃之前的质量损失率(约18%)是表里物理吸附的乙醇和水蒸气的挥发所致[12];150~300 ℃之间的质量损失率为3%;300~800 ℃的质量损失率高达35%,这是材料造孔的主要温度阶段。材料在热解过程中释放了H2O,CO和CO2等小分子气体,这表明有机干凝胶框架结构开始瓦解,并形成具有丰富孔隙且互相连接的炭结构[13];在900 ℃以上存在约2%的质量损失率,这可能是孔内的气态热解产物缓慢释放的结果。由于NH3在高温条件下分解成自由基NH2以及NH的形式,然后与炭表面反应形成含氮官能团[14],结合KANG等[15]的高温氨气炭化方法,实验中炭化起始温度选为600 ℃。
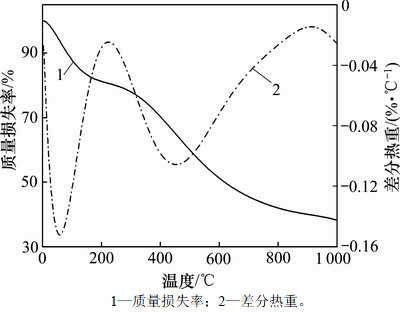
图3 有机干凝胶的热重特性曲线
Fig. 3 TG characteristic curves of organic xerogel
表1 ACXs的孔结构参数
Table 1 Pore structure parameters of ACXs
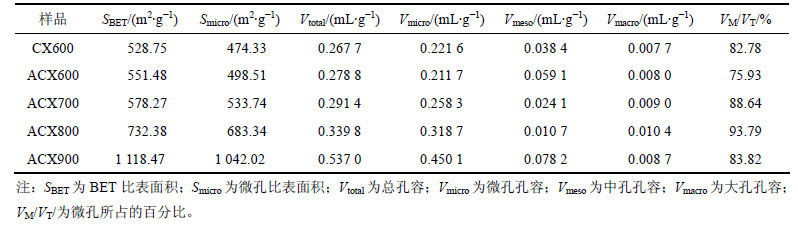
2.2 氨气炭化温度对炭干凝胶比表面积和孔结构的影响
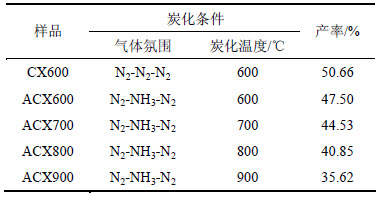
图4所示为炭干凝胶样品在77 K下的N2等温吸附曲线(其中,p为绝对压力,p0为大气压)。根据IUPAC分类,所有炭干凝胶样品的N2等温吸附线均属于I型等温吸附线,说明炭干凝胶样品内部结构主要以微孔为主。样品比表面积及孔结构参数如表1所示。从表1可见:炭干凝胶样品的比表面积和孔容均随着温度升高而增大,且温度越高,增加幅度越大,其中ACX900的比表面积、总孔容、微孔比表面积和微孔孔容均分别高达1 118.47 m2/g,0.537 0 mL/g,1 042.02 m2/g和0.450 1 mL/g。在高温氨气热解过程中,一方面,高温使有机干凝胶的骨架结构开始瓦解,并形成具有丰富孔隙且互相连接的炭结构[13],且温度升高促进微孔率(Vmicro/Vtotal)上升,但900 ℃时形成大量中孔导致微孔率又出现下降;另一方面,由于NH3的强烈刻蚀作用,不利于更多微孔的形成。对比CX600和ACX600可知:后者微孔率降低且中孔率大幅度增加,这可能是NH3的刻蚀作用促使部分微孔转化成了中孔。炭化条件和相应的产率(即有机干凝胶炭化后与炭化前的质量之比)见表2。炭化产率反映了温度和NH3刻蚀的综合结果。由表2可知:炭化产率随温度升高而降低,同时,ACX600比CX600质量损失率更高,表明NH3是导致额外质量损失的一种有效刻蚀剂[15]。
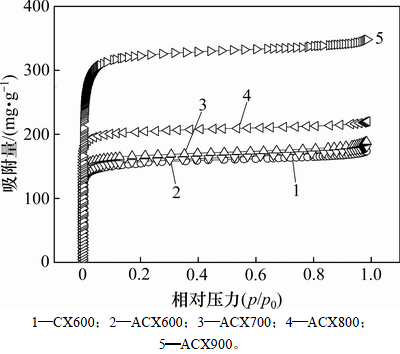
图4 ACXs样品在77 K下的氮吸附等温线
Fig. 4 Nitrogen adsorption isotherms for ACXs at 77 K
表2 炭化条件和产率
Table 2 Carbonization conditions and product yields
2.3 氨气炭化温度对炭干凝胶表面形貌的影响
图5所示为不同炭化温度条件下氮掺杂炭干凝胶样品的SEM图。由图5可知:在不同温度下,炭化的氮掺杂炭干凝胶具有相似的微球结构,这些微球粒子相互连接形成三维网络结构,这与 等[16]所得出的结果一致。由图5(a)可知:ACX600微球表面比较光滑,微球直径不一,在1~4 μm之间。由图5(b),(c)和(d)可观测到氮掺杂炭干凝胶微球有被刻蚀的痕迹,且随着炭化温度升高,氮掺杂炭干凝胶微球收缩变小[16],孔隙气化刻蚀增强,甚至造成炭干凝胶微球瓦解,产物进一步以小分子气体CO,NO和H2O等释放出去[13],导致氮掺杂炭干凝胶炭化产率减少(表2)和含氮量降低(表4)。
等[16]所得出的结果一致。由图5(a)可知:ACX600微球表面比较光滑,微球直径不一,在1~4 μm之间。由图5(b),(c)和(d)可观测到氮掺杂炭干凝胶微球有被刻蚀的痕迹,且随着炭化温度升高,氮掺杂炭干凝胶微球收缩变小[16],孔隙气化刻蚀增强,甚至造成炭干凝胶微球瓦解,产物进一步以小分子气体CO,NO和H2O等释放出去[13],导致氮掺杂炭干凝胶炭化产率减少(表2)和含氮量降低(表4)。
2.4 氨气炭化温度对炭干凝胶表面官能团的影响
图6所示为氮掺杂炭干凝胶样品的傅里叶红外光谱。由图6可知:CX600在1 580 cm-1处存在明显的吸收峰,这归因于苯环中C—C键的伸缩振动,当温度大于600 ℃时,该峰会由于化学反应而分解消失[12];而ACX600在1 560 cm-1和1 634 cm-1处形成2个峰,分别归因于由于氨气的作用而形成的—NH2和—NH[17],当达到700 ℃时,—NH2峰消失,且—NH峰变弱,同时,ACX800和ACX900无氨基峰;随着温度升高,在1 400 cm-1和1 600 cm-1之间出现一些微弱的峰,这来源于高温氨气炭化后形成的吡咯氮和吡啶氮等含氮官能团,表明—NH在800 ℃时完全分解或转化成吡啶氮;在1 060~1 150 cm-1处存在尖锐的吸收峰,这是C—O—C的不对称伸缩振动所致[18],这可能源于间苯二酚和糠醛聚合反应所形成的连接二者之间的醚键;此外,873 cm-1和810 cm-1处的吸收峰归因于C—H的伸缩振动[17],CX600在此处的峰最强,而ACX600峰变弱,且随着温度升高而消失,表明高温氨气炭化促进了C—H键的分解。综上所述,高温氨气炭化促进了苯环中C—C和C—H键的分解,炭干凝胶表面形成了新的更多的N—H、吡咯氮、吡啶氮等含氮官能团,且随着温度升高而分解。

图5 ACXs的SEM图
Fig. 5 SEM photographs of ACXs
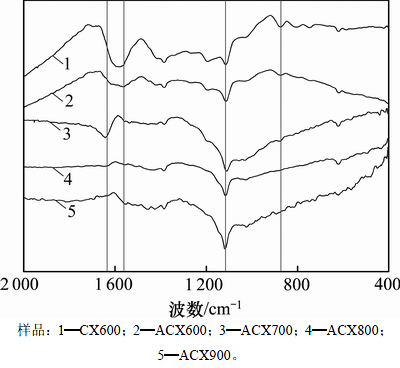
图6 ACXs的红外光谱
Fig. 6 FTIR spectra of ACXs
为了更深入地探讨ACXs表面含氮官能团的种类以及表面元素质量分数随温度升高的变化规律,对材料进行XPS表征。采用Gaussian方程拟合N 1s的XPS光谱,如图7所示。在N 1s光谱中,结合能位于398.5, 400.1,401.1和402.5 eV附近的特征峰,分别归因于吡啶氮(N-6)、吡咯氮(N-5)、质子化吡啶氮(N-Q)和氮氧化物(N-O)[19],;而ACX600样品中,结合能在399.5 eV处的峰来源于氨基[16],这与红外光谱分析结果一致,如图8所示。
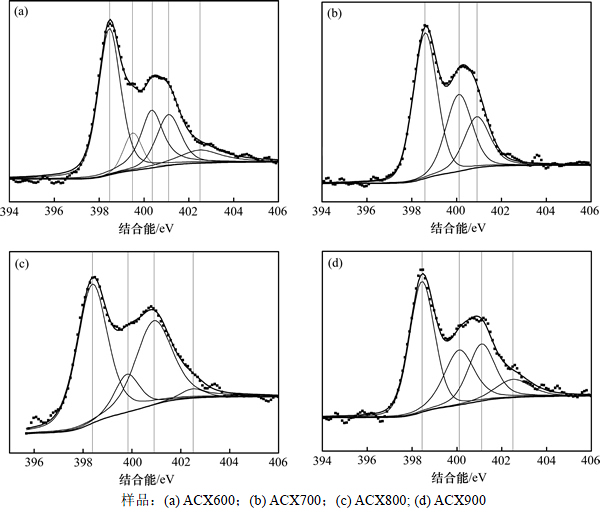
图7 ACXs中N元素的XPS能谱图
Fig. 7 N1s XPS spectra of ACXs
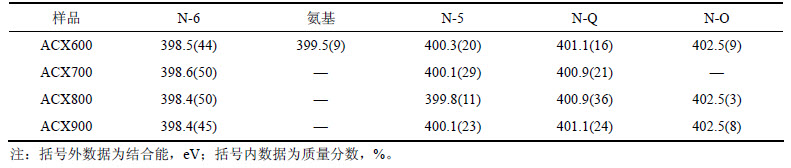
根据XPS结果,计算氮掺杂炭干凝胶表面5种含氮官能团的质量分数,结果如表3所示。由表3可知:4种氮掺杂炭干凝胶的吡啶氮质量分数(44%~50%)均相近,几乎占含氮官能团总量的一半,仅ACX600样品含有少量(9%)氨基。这表明当温度为600 ℃时,氨气分解成自由基NH和NH2之后,自由基与炭干凝胶表面发生反应,且在炭干凝胶表面上形成有利于酸性CO2气体吸附的氨基基团[14];其他样品中没有氨基,因为在700 ℃时,炭干凝胶开始脱氧脱氢,氨基脱氢,且N-O脱氧,并向吡咯氮转化,导致其质量分数有所增加(29%),且随着温度升高,吡咯氮的质量分数略减少,而质子化吡啶质量分数有所增大,即在高温条件下,吡咯氮向吡啶氮转化,氮元素进入炭干凝胶的主体结构,并最终形成稳定的质子化吡啶,从而导致其质量分数增加[6]。氮氧化物质量分数随温度升高出现先下降后略有增加的趋势,这主要是在较低温度下,氮基团的脱氧脱氢造成氮氧化物质量分数降低,在高温条件下,有机干凝胶里面原有的氧元素与不稳定的吡啶氮反应结合成新的氮氧化物,致使氮氧化物质量分数增加[15]。综上所述,随着炭化温度升高,氮元素在炭干凝胶中的存在形式发生改变。
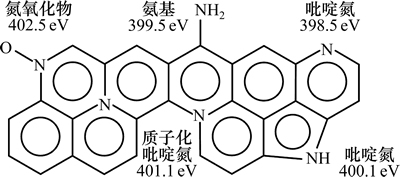
图8 ACXs中含氮官能团峰值位置
Fig. 8 Peak positions of nitrogen functionality in ACXs
表3 ACXs含氮官能团结合能和质量分数
Table 3 Binding energies and relative concentrations of nitrogen functionalities in ACXs
2.5 炭干凝胶CO2等温吸附性能
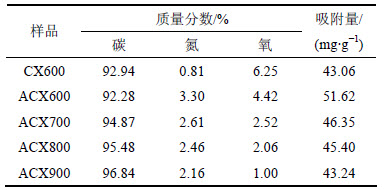
不同氮掺杂炭干凝胶样品对CO2的吸附穿透曲线如图9所示。不同样品的CO2饱和吸附量如表4所示。从表4可见:CX600样品对CO2的吸附量为43.06 mg/g,ACX600的吸附量为51.62 mg/g,比CX600提高19.88%,表明含氮官能团在CO2吸附过程中发挥着重要作用;ACX700,ACX800和ACX900的CO2吸附量分别为46.35,45.40和43.24 mg/g,所有的ACX系列样品均表现出比CX600更强的CO2吸附能力,但吸附性能随着炭化温度升高而下降。这表明高温氨气炭化在炭干凝胶表面所形成的含氮官能团有利于酸性CO2气体吸附[20];由于含氮量越高,表面碱度越大,而酸性CO2气体优先吸附在孔表面的碱性位,并与含氮官能团发生化学反应,使其相互间的作用力加强,提高了氮掺杂炭干凝胶对CO2的吸附能力[20]。但碱性含氮官能团随温度升高而减少,CO2吸附量随之降低。可能的反应机理[21]为CO2与含氮官能团反应可生成氨基甲酸酯:
CO2+2RNH2 NH4++R2NCOO- (1)
NH4++R2NCOO- (1)
CO2+2R2NH R2NH2++R2NCOO- (2)
R2NH2++R2NCOO- (2)
CO2+2R3N R4N++R2NCOO- (3)
R4N++R2NCOO- (3)
由表4可知:CX600样品中含有少量氮元素,这部分氮元素可能来自于合成有机干凝胶所使用的六次甲基四胺;通入氨气炭化以后,ACX600样品中氮元素质量分数显著增加至3.30%,且CO2吸附量达到最大;氮掺杂炭干凝胶的氮元素质量分数随着炭化温度继续升高而减小,CO2吸附量也随之减小。这是因为随着炭化温度升高,炭干凝胶表面有利于酸性CO2气体吸附的碱性含氮官能团减少,导致CO2吸附量减小[7]。
对比分析ACX900和 CA600可知:ACX900的比表面积、总孔容和含氮量均比CX600的高,且从FTIR和XPS表征可以看出ACX900中氮元素的存在形式发生了改变,而二者对CO2的吸附能力差不多。由此认为:氮掺杂炭干凝胶对CO2的吸附能力与其含氮量不呈线性关系,CO2的吸附能力关键取决于氮的存在形式[22]。
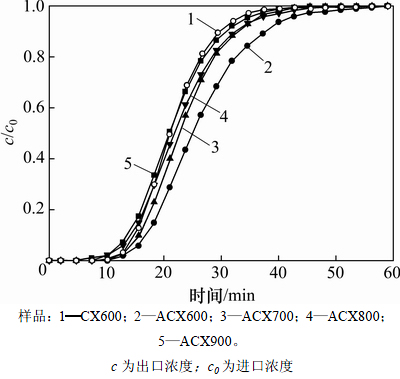
图9 不同炭化温度下氮掺杂炭干凝胶对CO2的吸附穿透曲线
Fig. 9 Breakthrough curves of CO2 onto ACXs at different carbonization temperatures
表4 ACXs样品表面元素质量分数和吸附量
Table 4 Surface elemental contents and adsorption capacity of ACXs
3 结论
1) 以间苯二酚和糠醛为原料,乙酸为催化剂,通过溶胶-凝胶法、常压干燥法,经高温氨气炭化合成了氮掺杂炭干凝胶,并在其表面引入了氨基、吡咯氮和吡啶氮等含氮官能团。
2) 随着炭化温度升高,氮掺杂炭干凝胶微球收缩变小,孔隙裂解、气化刻蚀效果增强,导致含氮量减少;氮元素在氮掺杂炭干凝胶表面的存在形态由氨基基团向吡啶基团转化。
3) 高温氨气炭化在炭干凝胶表面所形成的碱性含氮官能团有利于酸性CO2气体吸附。但碱性含氮官能团随温度升高而减少,CO2吸附量随之降低。
参考文献:
[1] HOSSEINI S, MARAHEL E, BAYESTI I, et al. CO2 adsorption on modified carbon coated monolith: effect of surface modification by using alkaline solutions[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 324: 569-575.
[2] JANG D I, PARK S J. Influence of nickel oxide on carbon dioxide adsorption behaviors of activated carbons[J]. Fuel, 2012, 102(9): 439-444.
[3] TAN Y L, AZHARUL ISLAM A, ASIF M, et al. Adsorption of carbon dioxide by sodium hydroxide-modified granular coconut shell activated carbon in a fixed bed[J]. Energy, 2014, 77: 926-931.
[4] OLAJIRE A A. CO2 capture and separation technologies for end-of-pipe applications:a review[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(6): 2610-2628.
[5]  C A, CONTRETRAS M S,
C A, CONTRETRAS M S,  A, et al. Effect of CO2 activation of carbon xerogels on the adsorption of methylene bule[J]. Adsorption, 2012, 18(3/4): 199-211.
A, et al. Effect of CO2 activation of carbon xerogels on the adsorption of methylene bule[J]. Adsorption, 2012, 18(3/4): 199-211.
[6] GORGULHO H F, GONCALVES F, PEREIRA M F R, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels[J]. Carbon, 2009, 47(8): 2032-2039.
[7] DRAGE T C, ARENILLAS A, SMITH K M, et al. Preparation of carbon dioxide adsorptions from the chemical activation of urea-formaldehyde and melamine-formaldehyde resins[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(1/2): 22-31.
[8] SEVILLA M,  P, FUERTES A B. N-doped polypyrrole-based porous carbons for CO2 capture[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(14): 2781-2787.
P, FUERTES A B. N-doped polypyrrole-based porous carbons for CO2 capture[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(14): 2781-2787.
[9] WU D C, FU R W, ZHANG S T, et al. Preparation of low-density carbon aerogels by ambient pressure drying[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(10): 2033-2039.
[10] TIAN H Y, BUCKLEY C E, PASKEVICIUS M, et al. Acetic acid catalysed carbon xerogels derived from resorcinol-furfural for hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(11): 671-679.
[11] 李立清, 石瑞, 顾庆伟, 等. 改性活性炭吸附二氯乙烷性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(4): 1701-1707.
LI Liqing, SHI Rui, GU Qingwei, et al. Adsorption properties of modified activated carbon for 2-dichloroethane[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(4): 1701-1707.
[12] TIAN H Y, BUCKLEY C E,  S, et al. Preparation, microstructure and hydrogen sorption properties of nanoporous carbon aerogels under ambient drying[J]. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(47): 475605.
S, et al. Preparation, microstructure and hydrogen sorption properties of nanoporous carbon aerogels under ambient drying[J]. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(47): 475605.
[13] WU D C, FU R W, YU Z Q. Organic and carbon aerogels from the NaOH-catalyzed polycondensation of resorcinol-furfural and supercritical drying in ethanol[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2005, 96(4): 1429-1435.
[14]  J, SKRODZEWICZ M, MORAWSKI A W. High temperature ammonia treatment of activated carbon for enhancement of CO2 adsorption[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2004, 225(1): 235-242.
J, SKRODZEWICZ M, MORAWSKI A W. High temperature ammonia treatment of activated carbon for enhancement of CO2 adsorption[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2004, 225(1): 235-242.
[15] KANG K Y, LEE B I, LEE J S. Hydrogen adsorption on nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels[J]. Carbon, 2009, 47(4): 1171-1180.
[16]  M, MORENO-CASTILLA C, CARRASCO-
M, MORENO-CASTILLA C, CARRASCO-  F, et al. Surface chemistry, porous texture, and morphology of N-doped carbon xerogels[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(1): 466-470.
F, et al. Surface chemistry, porous texture, and morphology of N-doped carbon xerogels[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(1): 466-470.
[17]  J. Enhanced adsorption of phenol from water by ammonia-treated activated carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 135(1): 453-456.
J. Enhanced adsorption of phenol from water by ammonia-treated activated carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 135(1): 453-456.
[18] 宋剑飞, 李立清, 姚小龙, 等. 复合氧化改性活性炭的物性及其对甲苯的吸附性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(5): 1732-1739.
SONG Jianfei, LI Liqing, YAO Xiaolong, et al. Characteristics of activated carbon modified by composite oxidation and its adsorption capacity for toluene[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(5): 1732-1739.
[19] LONG D H, ZHANG J, YANG J H, et al. Chemical state of nitrogen in carbon aerogels issued from phenol-melamine- formaldehyde gels[J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(9): 1253-1269.
[20] LEE S Y, JANG D I, BAE S T, et al. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-enriched mesoporous carbon for carbon dioxide capture[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(23): 12347-12352.
[21] MENG L Y, CHO K S, PARK S J. Effect of heat treatment on CO2 adsorption of ammonized graphite nanofibers[J]. Carbon Letters, 2010, 11(1): 34-37.
[22] 钱旦, 郝广平, 李文翠. 含氮多孔炭的制备及其在二氧化碳吸附中的应用[J]. 新型炭材料, 2013, 28(4): 267-272.
QIAN Dan, HAO Guangping, LI Wencui. Synthesis of a nitrogen-doped porous carbon monolith and its use for CO2 capture[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2013, 28(4): 267-272.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2016-10-11;修回日期:2016-12-18
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21376274);国家科技支撑计划项目(2015BAL04B02);APEC科技产业合作基金资助项目(313001022) (Project(21376274) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015BAL04B02) supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China; Project(313001022) supported by Cooperation Fund of APEC Science and Technology Industry)
通信作者:李立清,博士,教授,从事空气污染控制研究;E-mail: liqingli@hotmail.com