文章编号:1004-0609(2008)12-2196-06
磁控溅射氧化钒薄膜的相组成及性能
陈 爽1, 2,余志明1, 2,刘凤举1, 2,方 梅1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙410083;
2. 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙410083)
摘 要:采用反应磁控溅射法在玻璃基底上沉积氧化钒薄膜,分别利用X射线衍射 (XRD)、原子力显微镜(AFM)和红外光谱仪分析样品的物相、表面形貌和红外光透过率。结果表明:氧气体积分数低于15%时,薄膜为低价钒氧化物,高于20%时薄膜为V2O5;氧气体积分数等于15%时,溅射功率由150 W增加到200 W,薄膜中钒的价态变低;当溅射功率为250 W时,薄膜物相变成VO2。随着沉积时间从30 min增加到60 min,原子力显微分析显示VO2颗粒尺寸从约200 nm增加到400 nm;红外光透过率范围从55%~65%减小到45%~55%。
关键词:氧化钒;反应磁控溅射;红外透过率
中图分类号:TG 43 文献标识码: A
Phase compositions and property of VOx thin films by magnetron sputtering
CHEN Shuang, YU Zhi-ming, LIU Feng-ju, FANG Mei
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering of Ministry of Education, Changsha 410083,China)
Abstract: VOx thin films were produced on the substrates of glass by reactive magnetron sputtering. The phases, morphology and infrared transmittance were detected by X-ray diffractometer, atomic force microscopy and infrared spectrometer, respectively. The results show that, under the oxygen volume fraction φ(O2) of less than 15%, the films are vanadium oxides with low-valences. When φ(O2) is more than 20%, the films are V2O5. With φ(O2) of 15%, the average valence of vanadium becomes lower after the sputtering power increasing from 150 W to 200 W, and the films change to VO2 with the sputtering power of 250 W. While the sputtering time increases from 30min to 60min, the infrared transmittance of the VO2 films decreases from 55%?65% to 45%?55% and the size of grains increases from about 200 nm to 400 nm.
Key words: vanadium dioxides; reactive magnetron sputtering; infrared transmittance
VO2是一种具有广泛用途的热致相变材料,它在68 ℃左右发生低温半导体态到高温金属态的一级相变,晶格常数由低温单斜时的a=0.574 3 nm,b=0.451 7 nm,c=0.537 5 nm,β=122.61?变为高温金红石结构的a=b=0.453 nm,c=0.286 9 nm[1],并伴随有电导率和光透过率(特别是红外波段的光学透过率)的突变[2]。薄膜状的VO2在红外探测、非制冷红外成像、光电开关和智能窗等领域有广阔的应用前景[3?5] 。但钒的氧化物物相体系十分复杂,各种物相的晶体结构和性能有很大差异,使得制备单一物相的VO2薄膜非常困难[6]。目前制备VO2薄膜的主要方法有磁控溅射法[7]、真空蒸发法[8]、溶胶?凝胶法[9]和脉冲激光沉积法[10]等。袁宁一等[11]采用离子束增强沉积和溶胶?凝胶方法在SiO2/Si基底上制备的VO2薄膜开始相变温度分别为62和45 ℃,王利霞等[12]采用射频反应溅射法制备的VO2薄膜在温度52 ℃左右发生相变。本文作者采用磁控溅射法制备VO2薄膜,研究氧气体积分数(以下简称φ(O2)、溅射功率和沉积时间对薄膜物相和光学性能的影响,并讨论了其中的机理。
1 实验
本实验采用直流反应磁控溅射法沉积薄膜。设备为沈阳中科仪生产的CSU?5001型多功能磁控溅射仪,其极限真空度为8×10?4 Pa。溅射气体和反应气体分别为纯度99.999%的Ar和O2,Ar和O2进气总流量为15 cm3/min,通过改变Ar和O2 的流量比来改变φ(O2),通过控制抽气量把腔体内Ar和O2总压强控制在2 Pa;靶材为纯度99.95%金属钒,尺寸为d60 mm×3 mm,靶到基底的距离为70 mm;基底为普通玻璃,基底经过丙酮浸泡5 min后放到蒸馏水中超声波清洗15 min;沉积薄膜前用氩气预溅射靶材5 min去除靶面的污染物。实验工艺参数如表1所列。
表1 实验参数
Table 1 Parameters of experiments

采用DMAX?2250 X射线衍射仪对薄膜进行物相分析,入射X射线选用Cu Kα,该仪器带有可加热的样品台。采用俄罗斯NTMDT公司生产的Solver P47多模式扫描探针显微镜(原子力显微镜)观察薄膜样品的表面形貌。采用AVATAR傅里叶红外光谱仪测试退火前后薄膜的透过率,波数范围为500~4 000/cm。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 氧化钒薄膜的物相分析
2.1.1 氧气体积分数对薄膜物相的影响
图1所示为Ⅰ组实验沉积的薄膜的XRD谱。从图中可以看出,φ(O2)为8%和10%时,薄膜的XRD谱表现为一个较强的非晶态漫衍射峰和一些微弱的低价钒氧化物的衍射峰。漫衍射峰是由非晶玻璃衍射造成的,薄膜主要由一些低价态钒氧化物组成;随着φ(O2)增大到15%,XRD谱出现V2O5和VO2的衍射峰,同时出现微弱的V3O7衍射峰,说明钒氧化物的价态增加,薄膜中物相主要为V2O5和VO2;当φ(O2)增大到20%和25%时,XRD谱上只有V2O5的衍射峰,薄膜的物相为V2O5。根据异质外延晶体生长理论,晶粒在基体上形核生长要受到表面能和界面应变能的控制[3]。玻璃基底为非晶态,钒氧化物与其不存在匹配关系,晶体形核主要受表面能的控制,各种晶粒都可能形核生长。φ(O2)较低时,钒可生成不同价态的氧化物,这些氧化物在玻璃上都能形核生长,所以玻璃基底上薄膜的物相复杂,结晶性能差,在XRD谱上表现为很多弱衍射峰。随着φ(O2)的增大溅射出来的钒原子进一步被氧化,薄膜物相由低价态的钒氧化物向高价态过渡,而且薄膜的衍射峰愈趋尖锐,表明薄膜的结晶性能变好。在高φ(O2)下,钒原子被充分氧化成为了最高价态的V2O5,衍射峰尖锐,薄膜结晶性很好。

图1 不同φ(O2)时玻璃上沉积VOx薄膜的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of VOx thin films deposited on glass with different oxygen volume fractions
2.1.2 溅射功率对薄膜物相的影响
图2和图3所示分别为Ⅱ组和Ⅲ组实验沉积的VOx薄膜的XRD谱。在φ(O2)为25%和20%时,随着功率的增大,薄膜的成分没有变化,全部为V2O5,但V2O5衍射峰的强度和数量随着功率的增大都有所增加,说明当φ(O2)增大到一定程度,而溅射功率在一定范围内改变时,薄膜的物相不再改变,但结晶性随溅射功率的增加而增强。这是因为溅射出来的钒原子全部被氧化成V2O5,溅射功率越大,被氧化生成的V2O5越多,越有利于V2O5薄膜的生长,薄膜的各个晶面都会长大,衍射强度增加,衍射峰数量增多。
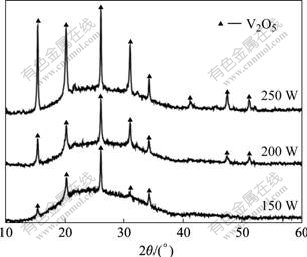
图2 φ(O2)为25%时不同溅射功率下薄膜的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of films with different sputtering power with φ(O2) of 25%
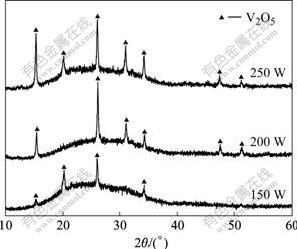
图3 φ(O2)为20%时不同溅射功率下薄膜的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of films with different sputtering power with φ(O2) of 20%
图4所示为Ⅳ组实验沉积的薄膜的XRD谱。当功率为150 W时,XRD谱上全为V2O5衍射峰,薄膜的物相为V2O5。当功率增大到200 W时,XRD谱中V2O5衍射峰的数量减少,出现VO2 和V3O7的衍射峰,说明钒氧化物的价态降低,薄膜中物相主要为V2O5和VO2。这是因为随着功率的增加,溅射出来的钒原子或原子团数量较多,不能被充分氧化成V2O5。当功率增大到250 W时,薄膜的XRD谱中只出现了VO2的衍射峰,薄膜的物相已变成了VO2。
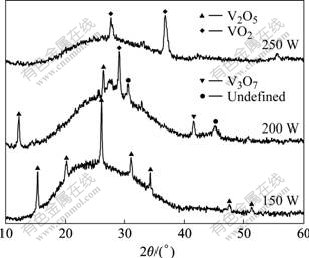
图4 φ(O2)为15%时不同溅射功率下薄膜的XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of films with different sputtering power with φ(O2) of 15%
2.1.3 沉积时间对薄膜物相的影响
图5所示为Ⅴ组实验沉积的VO2薄膜的XRD谱。随着溅射时间由30 min增加到60 min,VO2衍射峰的强度增加,峰型愈趋尖锐。取图5中最强衍射峰的半峰宽,由Scherrer公式估算晶粒尺寸[7]
L=0.89λ/(?2θ?cos θ)
式中 L为晶粒尺寸,λ为X射线波长(本研究中取λ=0.154 05 nm),?2θ为尺寸效应产生的附加宽度,近似为半峰宽,θ为布拉格角。沉积时间为30 min和60 min时薄膜的晶粒大小分别约为17.8 nm和25.4 nm,说明随沉积时间延长薄膜的晶粒尺寸有所增大,结晶性更好。这是因为随沉积时间的延长,溅射粒子对基片的轰击累积能量,使基片的温度不断升高[13],提高了原子的扩散能力,原子不断迁移,晶粒进一步长大,结晶程度大幅度提高,所以衍射峰的强度增大。同时薄膜厚度增加,也导致XRD衍射峰的强度增加。

图5 不同沉积时间玻璃上VO2薄膜的XRD谱
Fig.5 XRD patterns of VO2 thin films deposited on glass with different sputtering times
2.2 VO2薄膜的表面形貌分析
图6所示为Ⅴ组实验沉积的VO2薄膜的AFM像。当沉积时间由30 min增加到60 min,图6中显示的颗粒尺寸由约200 nm增加到400 nm,随沉积时间增加,薄膜的颗粒明显增大。由Scherrer公式估算出的薄膜的晶粒约几十纳米,是AFM显示的晶粒度的十分之一,可见AFM显示的颗粒是很多细小的晶粒组成的。从图6中还可以看到比较大的孔洞,这可能是由于沉积薄膜时的阴影效应[14]造成的,当原子入射的方向被阴影遮蔽,薄膜中孔洞的数量将增加。使后续沉积粒子不能进入空隙处,进而引起薄膜组织内出现孔洞,会造成薄膜的粗糙度增加。图6(a)和(b)的均方根粗糙度分别为41.481 nm和91.935 nm,随沉积时间延长,孔洞加深,薄膜粗糙度明显上升。

图6 不同沉积时间下VO2薄膜的表面形貌分析
Fig.6 Morphologies of VO2 thin films with different sputtering times by AFM: (a), (a’) 30 min; (b) , (b’) 60 min
2.3 VO2薄膜的红外透过率
图7所示为Ⅴ组实验沉积的VO2薄膜的红外透过率。因为玻璃基底不能透过波数在500~2 000 /cm之间的红外光,如图7(a)所示,所以只考虑波数在2 000~ 4 000 /cm之间的红外光。沉积时间为30 min时薄膜的透过率的范围为55%~65%,沉积时间为60 min时透过率范围为45%~55%,随着沉积时间增大,薄膜的红外透过率减小。根据Lambert定律,光沿介质传播的强度随着传播距离呈指数衰减[15]:I=I0exp(?αd) (其中I0为入射光源强度,α为吸收系数,d为光传播的距离)。随着沉积时间的增加,薄膜的厚度增加,光的传播距离d增加,红外透过率减小。

图7 不同时间沉积玻璃上VO2薄膜红外透过率
Fig.7 Infrared transmittance of VO2 films on glass with different sputtering times
2.4 VO2薄膜相变
利用DMAX?2250 X射线衍射仪上的可加热样品台,分别在90、50和25 ℃对VO2薄膜进行了XRD分析。图8 所示为VO2薄膜在不同温度下的XRD谱。可见VO2薄膜在25和50 ℃时对应于2θ=36.691?的衍射峰基本没有变化;只有当温度上升到90 ℃时衍射峰移动较小角度到2θ=36. 639?。没有看到所期望的VO2薄膜发生单斜到四方金红石结构的相变过程。温度升高会造成晶体热膨胀,使晶面间距d变大,衍射角向小角度偏移。而对沉积制备的VO2薄膜未发生相变的原因,需要更深入的探讨。

图8 VO2薄膜在不同温度下的XRD谱
Fig.8 XRD patterns of VO2 thin films at different temperatures
3 结论
1) 200 W溅射功率下,φ(O2)低于15%时玻璃基底上薄膜物相为结晶性较差的低价钒氧化物,当φ(O2)高于20%时基底上的薄膜物相为V2O5。
2) 当φ(O2)为25%和20%时,溅射功率由150 W增大到250 W,薄膜的成分没有变化,全部为V2O5;当φ(O2)为15%、溅射功率为150 W时,玻璃基底上的相成分为V2O5,随着溅射功率增加到200 W时,薄膜中出现低于五价的钒氧化物,当溅射功率为250 W时,薄膜的物相变成四价的VO2。
3) φ(O2)为15%、功率为250 W时沉积VO2薄膜,随着沉积时间由30 min增加到60 min,VO2结晶性能有很大提高,AFM像显示的VO2颗粒尺寸从约200 nm增加到约400 nm;对于波数在2 000~4 000 /cm之间的红外光,沉积时间为30 min和60 min的VO2薄膜透过率范围分别为55%~65%和45%~55%。
REFERENCES
[1] 袁宁一. 氧化钒红外敏感膜和非致冷焦平面成像阵列研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院, 2002.
YUAN Ning-yi. Study of vanadium oxide thin films for infrared sensitivity and uncooled IR focal plane array[D]. Shanghai: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2002.
[2] 卢 勇, 林理彬, 何 捷, 卢铁城. VO2薄膜γ辐照过程的变价和退火现象[J]. 功能材料, 2002, 33(1): 73?75.
LU Yong, LIN Li-bin, HE Jie, LU Tie-cheng. Valence variation and annealing effect in VO2 thin films during γ-ray irradiation[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2002, 33(1): 73?75.
[3] 刘艳辉, 孟 亮, 张秀娟. 薄膜生长基底对FeS2晶体取向的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2004, 18(14): 373?379.
LIU Yan-hui, MENG Liang, ZHANG Xiu-juan. Efect of substrate structures on crystal orientation of the FeS2 thin films[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 18(14): 373?379.
[4] 袁宁一, 李金华, 林成鲁. 氧化钒薄膜的结构、性能及制备技术的相关性[J]. 功能材料, 2001, 32(6): 572?575.
YUAN Ning-yi, LI Jin-hua, LIN Cheng-lu. Relativity among struetures,properties and preparation of vanadium oxides thin films[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2001, 32(6): 572?575.
[5] KIVAISI R T, SAMIJI M. Optical and electrical properties of vanadium dioxide films prepared under optimized RF sputtering conditions[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 1999, 57(2): 141?152.
[6] 丰世凤, 宁桂玲, 王 舰, 林 源. 二氧化钒薄膜制备研究的最新进展[J]. 化工进展, 2007, 26(6): 814?818.
FENG Shi-feng, NING Gui-ling, WANG Jian, LIN Yuan. Recent progress of research on VO2 thin film[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2007, 26(6): 814?818.
[7] 王银玲, 李美成, 赵连成. 磁控溅射氧化钒薄膜的相成分及电阻?温度特性[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 18(4): 1077?1080.
WANG Yin-ling, LI Mei-cheng, ZHAO Lian-cheng. Phase compositions and resistance-temperature characteristic of VOx thin films by magnetron sputtering[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 18(4): 1077?1080.
[8] 尚 东, 林理彬, 何 捷, 王 静, 卢 勇. 特型二氧化钒薄膜的制备及电阻温度系数的研究[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 42(3): 523?527.
SHANG Dong, LIN Li-bin, HE Jie, WANG Jing, LU Yong. Preparation and TCR characterization of VO2(B) thin films[J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Natural Science Edition, 2005, 42(3): 523?527.
[9] 江少群, 马欣新, 孙明仁. 溶胶?凝胶制备二氧化钒薄膜的价态研究[J]. 中国表面工程, 2005, 2: 39?43.
JIANG Shao-qun, MA Xin-xin, SUN Ming-ren. Study on chemical states of VO2 thin films prepared by Sol-gel method[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2005, 2: 39?43.
[10] RAJENDRA KUMAR R T, KARUNAGARAN B, MANGALARAJ D, NARAYANDASS S K, MANORAVI P, JOSEPH M, GOPAL V. Pulsed laser deposited vanadium oxide thin films for uncooled infrared detectors[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2003, 107(1): 62?67.
[11] 袁宁一, 李金华, 李 格. IBED和Sol-gel制备方法对二氧化钒薄膜性能的影响[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2003, 8(5): 88?89.
YUAN Ning-yi, LI Jin-hua, LI Ge. Effect of IBED and sol-gel methods on electrical properties of VO2 thin films[J]. Journal Harbin Univ Sci Tech, 2003, 8(5): 88?89.
[12] 王利霞, 李建平, 何秀丽, 高晓光. 二氧化钒薄膜的低温制备及其性能研究[J]. 物理学报, 2006, 55(6): 2846?2851.
WANG Li-xia, LI Jian-ping, HE Xiu-li, GAO Xiao-guang. Fabrication of vanadium dioxide fi1ms at low temperature and researches on properties of the fi1ms[J]. ACTA Physics Sinica, 2006, 55(6): 2846?2851.
[13] 曲敬信, 汪泓宏. 表面工程手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1998: 377.
QU Jing-xin, WANG Hong-hong. Surface engineering manual [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1998: 377.
[14] 唐伟忠. 薄膜材料制备原理、技术及应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2003: 178?186.
TANG Wei-zhong. The preparation theory, technology and application of thin film materials[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2003: 178?186.
[15] 郭永康. 光学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005: 357.
GUO Yong-kang. Optics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005: 357.
收稿日期:2008-03-26;修订日期:2008-06-26
通讯作者:余志明,教授;电话:0731-8830335;E-mail: zhiming@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 陈爱华)