DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.07.016
东营凹陷陡坡带盐斜229地区沙四上亚段砂砾岩油藏成藏控制因素
解强旺1,王艳忠1,操应长1,王淑萍2,李宇志3,王欣3,李桥1,葸克来1,弭连山4,郭迎春5
(1. 中国石油大学 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛, 266580;
2. 中国石油大学 石油工业训练中心,山东 青岛, 266580;
3. 中国石化胜利油田分公司 东辛采油厂,山东 东营,257061;
4. 中国石化胜利油田分公司 胜利采油厂,山东 东营,257000;
5. 中国石化胜利油田分公司 勘探开发研究院,山东 东营,257000)
摘要:东营凹陷盐斜229地区沙四上亚段埋深大于3 700 m近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层中发育大规模水层,与前期建立的“扇根封堵、扇中富集、扇缘疏导,中深层非油即干”的油气成藏理论矛盾。针对这一问题,通过地震剖面以及油藏剖面解释,综合运用薄片鉴定、阴极发光分析及荧光薄片观察等技术方法,对砂砾岩体的坡度、油水层展布、储集空间、成岩作用特征及差异性开展系统研究,总结砂砾岩油藏成藏控制因素。研究结果表明:储层以原生孔隙为主;碳酸盐胶结作用是主要的成岩事件。油层、水层和干层的储层特征存在差异,油层原生孔隙发育,碳酸盐胶结物含量少,以白云石胶结为主;水层及干层孔隙不发育,碳酸盐胶结物含量高,以铁白云石胶结为主。砂砾岩体的坡度控制早期石油充注的范围,早期石油充注抑制压实作用和晚期碳酸盐胶结作用,早期石油充注范围及运移路径决定晚期石油优先聚集区域。未发生早期石油充注的近泥岩部位碳酸盐胶结壳阻止晚期油充注,导致深层扇中发育大量水层。
关键词:东营凹陷;砂砾岩体;砂砾岩体坡度;碳酸盐胶结物;石油成藏;控制因素
中图分类号:TE122 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)07-1626-11
Control factors on the hydrocarbon accumulation of the Es4s reservoirs in Yanxie 229 area, Dongying Sag
XIE Qiangwang1, WANG Yanzhong1, CAO Yingchang1, WANG Shuping2,LI Yuzhi3, WANG Xin3, LI Qiao1, XI Kelai1, MI Lianshan4, GUO Yingchun5
(1. School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China;
2. Oil Industry Training Center of China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China;
3. Dongxin Oil Production Plant, Shengli Oilfield Company, SINOPEC, Dongying 257061, China;
4. Shengli Oil Production Plant, Shengli Oilfield Company, SINOPEC, Dongying 257000, China;
5. Exploration and Development Research Institute of Shengli Oilfield Company, SINOPEC, Dongying 257000, China)
Abstract: A large-scale water layer is developed in conglomerate reservoir of near-shore subaqueous fan in the Yanxie 229 area of Dongying Sag under the depth of 3 700 m. This is contradict with previous cognition that “Root fan can be used as caprock, oil is rich in middle fan, outer can be used as migration pathway, middle fan reservoirs is oil layer or dry layer”. Aiming at this problem, through seismic section and reservoir section interpretation, comprehensive application of thin-film identification, cathodoluminescence analysis and fluorescence observation, the slope of conglomerate body, distribution of oil and water layer, characteristics and differences of reservoir space and diagenesis were systematically studied. Control factors of petroleum accumulation in conglomerate reservoirs were summarized. The results show that primary pores are the main pore types. Carbonate cementation is the main diagenetic event. There are differences in reservoir characteristics in the oil layer, water layer and dry layer. Primary pores in the oil layer are developed, and the content of carbonate cementation is low, mainly dolomite cementation. The porosity of water layer and dry layer is not developed, and the content of carbonate cementation is high, mainly ankerite cementation. The area of early oil emplacement was controlled by the slope of conglomerate body. Compaction and late carbonate cementation is inhibited by early oil emplacement. Early oil emplacement range and migration path are the priority area of late oil accumulation. Carbonate cementation near mudstone where oil was not filled in early stage prevents oil charging in late stage, resulting in the development of large water layers in deep fan.
Key words: Dongying sag; glutenite; gradient of glutenite body; carbonate cement; oil accumulation; control factors
陆相断陷湖盆广泛发育的大量砂砾岩体紧邻生油中心分布,与深湖相烃源岩呈指状接触,有极佳的生储盖匹配关系,易于形成岩性油气藏或构造—岩性复合油气藏。近年来胜利、准噶尔、辽河、华北等油田均发现了大量的砂砾岩油藏[1]。东营凹陷为北陡南缓、北深南浅的半地堑型盆地,是中国东部典型的富油气断陷湖盆。东营凹陷陡坡带盐斜229地区近岸水下扇砂砾岩体勘探不断取得突破,2015年在该地区沙四上亚段上报控制储量380×104 t,2016年又新增控制储量337.7×104 t。东营凹陷陡坡带砂砾岩油气藏前期勘探开发过程中取得了“扇根封堵、扇中富集、扇缘疏导、中深层扇中非油既干”的认识[2]。近岸水下扇砂砾岩体扇根部位的垂向或侧向封堵层、扇中靠近泥岩层边部碳酸盐致密胶结壳以及多期扇体间湖相泥岩可作为封堵层[3],形成以物性封闭为主的成岩圈闭,扇根与扇中之间的突破压力差决定封堵油气的高度[4]。许多学者针对东营凹陷北带砂砾岩储层成岩作用、物性演化、油藏类型及油藏流体性质演化进行探讨[5-10],认为东营凹陷沙四上亚段(Es4s)中深层主要发育“扇根封堵”的砂砾岩岩性油气藏,扇中有效储层发育,是有利的油气聚集区。但是,盐斜229地区在近期勘探过程中发现中深层扇中储层发育大规模水层,这难以用前期的砂砾岩油藏成藏理论进行解释。本文通过地震剖面以及油藏剖面解释,剖析对比盐斜229地区和盐22地区的典型油藏剖面,归纳出盐斜229地区沙四上亚段储层油气成藏的控制因素,这有助于完善砂砾岩油藏成藏理论。
1 地质概况
东营凹陷是渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东南部的1个次级构造单元,是发育在太古界基岩之上的中新生代断陷湖盆。图1所示为区域地质概况图,由图1(a)可见:东营凹陷北以陈家庄凸起为界,南以鲁西隆起和广饶凸起为界,西以青城凸起为界,东以青坨子凸起为界。东营凹陷内部主要包括4个洼陷(民丰洼陷、利津洼陷、牛庄洼陷和博兴洼陷)和1个中央背斜带。如图1(b)所示:盐家地区位于东营凹陷北带东段民丰洼陷北部,自西向东发育盐16和盐18两大古冲沟 [3]。剖面上:东营凹陷是北陡南缓的半地堑盆地,从北向南可划分为5个次一级构造单元,依次为北部陡坡带、北部洼陷、中部背斜带、南部洼陷和南部缓坡带。如图1(c)所示,东营凹陷北部陡坡带是由陈南铲式边界断层控制,具有断坡陡峭、山高谷深、沟梁相间的古地貌[7,11]。盐斜229地区位于民丰洼陷北带盐16古冲沟的下方靠西的位置,北邻陈家庄凸起,南邻民丰洼陷。东营凹陷新生代沉积地层,从下往上依次包括孔店组(Ek)、沙河街组(Es)、东营组(Ed)、馆陶组(Eg)、明化镇组(Em)以及平原组(Ep);其中,沙河街组又分为沙四上亚段(Es4s)和沙四下亚段(Es4x)。盐斜229地区Es4s以近岸水下扇砂砾岩体沉积为主[12-13]。断陷湖盆陡坡带近岸水下扇在平面上呈无水道舌形体迁移摆动,以稳定泥岩为标志层[13],本次研究以砂砾岩体横向补偿沉积、迁移摆动模式为指导,由外扇向中扇、内扇进行沉积期次横向和纵向精细划分对比,划分出Es4s-1,Es4s-2,Es4s-3,Es4s-4,Es4s-5,Es4s-6,Es4s-7和Es4s-8共8期近岸水下扇。砂砾岩体是东营凹陷北带重要的油气储层[9],油源主要来源于沙四上烃源岩[14]。东营凹陷存在2期石油充注,分别对应于东营组沉积末期和馆陶组—明化镇组沉积期[15-16]。
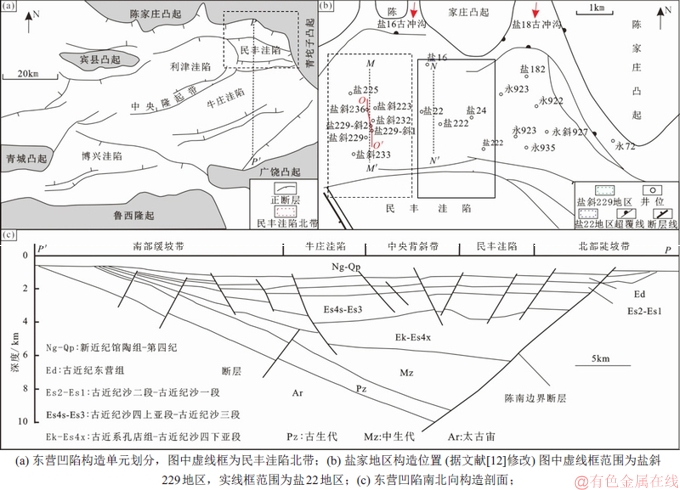
图1 区域地质概况
Fig. 1 Regional geological setting
2 油藏特征
2.1 砂砾岩扇体坡度特征
在三维地震数据体上,沿每1期次扇体走向方向选取地震剖面,依据近似法,将扇体顶面、水平距离△L以及垂直落差△H近似为直角三角形,如图2所示,△H和△L及坡度角β满足:
tanβ=△H/△L
因此,可以计算出近岸水下扇沉积体顶面坡度。依据该方法对盐斜229地区Es4s的8期砂砾岩扇体的沉积体顶面坡度角进行统计,发现每期砂砾岩体顶面与控盆断层水平距离大于3 km后变为扇缘,砂砾岩体顶面坡度变化不大,接近水平;因此,每期扇体只统计距离控盆断层3 km之内的坡度角。
图3所示为地震剖面上Es4s砂砾岩体坡度对比结果,以第4期次近岸水下扇为例,在过该期扇体的物源方向地震剖面上,盐斜229区块近岸水下扇扇体顶面坡度角为13.01°,而盐22地区近岸水下扇扇体展布平缓,近于水平。最终计算8期扇体的坡度角平均值,盐斜229地区各期砂砾岩体坡度角平均值为9.10°,而盐22地区各期砂砾岩体的平均坡度为3.10°。表1所示为坡度角定量统计结果,由表1可以看出:盐斜229地区Es4s沉积期形成的砂砾岩扇体坡度整体比盐22地区的大。
2.2 油水层展布
图4所示为典型油藏剖面图。由图4可见:盐斜229地区目前发现的油藏类型与盐22地区前期勘探过程中发现的油藏类型均为岩性油藏。扇根侧向封堵和垂向上泥岩层为有利的封堵层[3],石油紧邻扇根在有良好储集条件的位置聚集,盐斜229地区Es4s储层中油层主要分布深度为3 400~3 700 m,该范围内储层中不是油层的部位均为干层;深度大于3 700 m的Es4s储层中发育大量水层和干层,油层紧邻扇根分布;深度小于3 400 m储层中以水层为主。盐22地区深度范围为3 600 ~3 800 m的Es4s储层中“非油即干”[2],中深层并未发育水层。
图5所示为盐斜229地区和盐22地区Es4s储层中各主力含油层段的现今油层宽度。盐斜229地区Es4s储层中第6期次油层宽度为838.2 m,盐22地区第4,5,7期次含油层段储层的油层宽度分别为1 376.4, 1 619.2和1 511.9 m。
2.3 储层特征
图6所示为盐斜229地区Es4s油水层储层特征。由图6(a)可见:盐斜229地区Es4s储层发育原生孔隙和次生孔隙,原生孔隙是主要的孔隙类型。盐斜229地区Es4s油层物性好,孔隙度平均值为10.2%,渗透率平均值为5.2 mD,储集空间以原生粒间孔隙为主,原生粒间孔隙周围见残余油膜。由图6(b)可见:次生溶蚀孔隙。水层及含油水层孔隙度平均值为7.2%,渗透率平均值为2.6 mD,孔隙发育少,孔隙直径小,主要为少量溶蚀孔隙。干层物性差,孔隙度小于5%,渗透率小于1 mD,储集空间不发育。
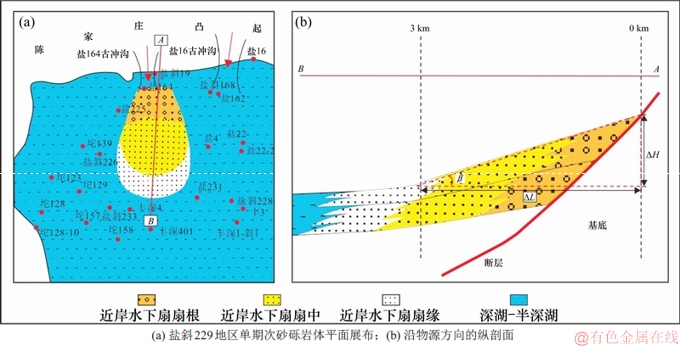
图2 砂砾岩扇体坡度角统计原理
Fig. 2 Statistical principle of gradient in glutenite body
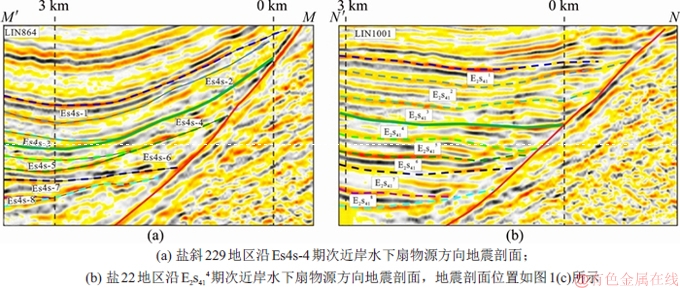
图3 Es4s砂砾岩体坡度对比
Fig. 3 Contrast of gradient in glutenite body in Es4s
表1 盐斜229地区和盐22地区Es4s砂砾岩体坡度角统计
Table 1 Gradient statistics of glutenite body of Es4s formation in Yanxie 229 and Yan 22 area
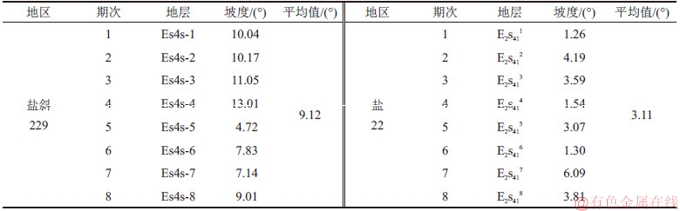
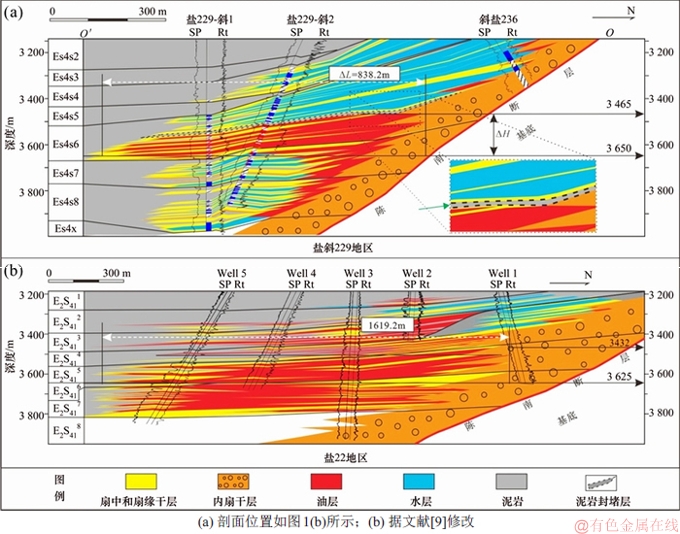
图4 典型油藏剖面图
Fig. 4 Typical reservoir profiles
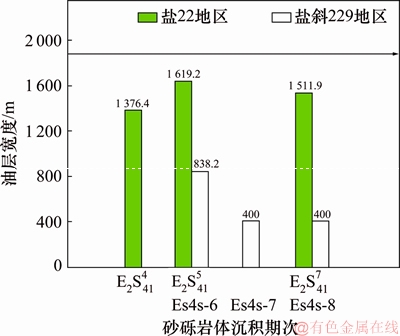
图5 Es4s储层现今油层宽度统计
Fig. 5 The statistics of oil distribution range of Es4s reservoirs
从如图6(c)~(f)可见:碳酸盐胶结作用是盐斜229地区Es4s储层中最主要的成岩作用类型,主要胶结物有方解石、白云石、铁方解石和铁白云石。方解石、白云石多呈分散状孔隙式胶结。油层中铁白云石含量(视域面积百分含量,下同)少,呈分散状分布于孔隙中。水层和干层中铁白云石多呈基底式胶结。图7所示为不同厚度单层砂体垂向上成岩作用特征。由如图7可见:砂泥岩界面处碳酸盐强烈胶结,远离砂泥岩界面,砂岩中碳酸盐胶结逐渐减弱。
图8所示为油层、水层荧光特征。由图8可见:盐斜229地区Es4s储层中可见赋存在粒间孔隙以及吸附在黏土杂基、胶结物上的原油和炭质沥青;炭质沥青主要以分散状态分布于粒间孔隙中;原油在紫外光下发黄色荧光和蓝色荧光;在同一视域下可见发黄色和蓝色2种荧光颜色,黄色荧光原油在孔隙中间分布,蓝色荧光原油围绕黄色荧光原油分布。不同性质的原油具有不同颜色的荧光,荧光颜色由红色→橙色→黄色→绿色→蓝白色演化,可以反映有机质成熟度不断提高。同时,研究区烃类包裹体在紫外光照射下可见黄色荧光和蓝色荧光。多种荧光颜色的原油及烃类包裹体,表明盐斜229地区Es4s储层中存在2期油充注[15-16],早期为成熟度低的黄色荧光油充注,晚期为成熟度高的蓝色荧光油充注。油层可见发黄色荧光和蓝色荧光原油,以发蓝色荧光原油为主,多存在于粒间孔隙中。水层及含油水层以发黄色荧光的油质沥青为主,多以浸染状侵入胶结物溶蚀孔隙中,并浸染杂基和胶结物。
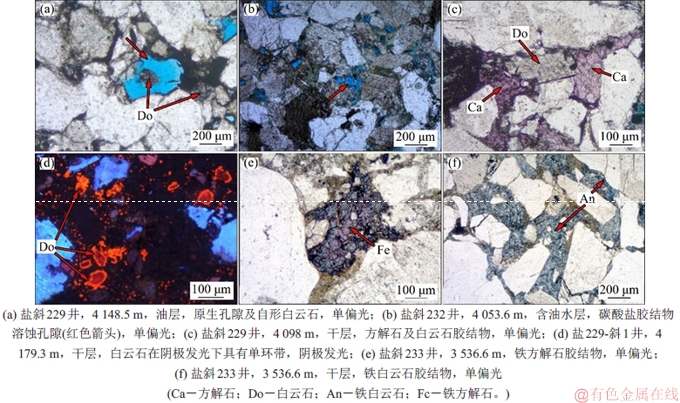
图6 盐斜229地区Es4s油水层储层特征
Fig. 6 The characteristic of reservoir of oil and water layer in Es4s reservoirs in Yanxie 229 area
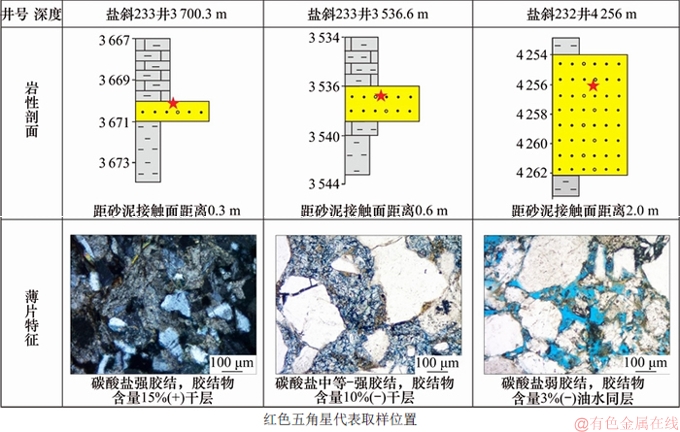
图7 不同厚度单层砂体垂向上成岩作用特征
Fig. 7 Diagenetic features of single sand layer with different thicknesses

图8 油层、水层荧光特征
Fig. 8 Fluorescence characteristics of oil layers and water layers
3 石油成藏控制因素
3.1 砂砾岩扇体的坡度控制早期石油充注范围
研究区存在2期石油充注,为探究砂砾岩沉积体坡度对每期石油充注的影响,定量恢复并对比盐斜229地区和盐22地区Es4s各主力含油层早期油充注的宽度。通过视厚度与压实系数的倒数相乘获得每个层段的原始厚度[19],再利用回剥法[20]将目的层段之上的地层剥去,计算东营组沉积末期扇根的古埋深。结合前人建立的封堵油柱高度随深度变化曲线[3,9],得出东营组沉积末期(早期油气充注末期[15]) 2个地区早期石油充注末期扇根的封堵油柱高度H,运用前文中统计的2个研究区的平均坡度β,结合前文中坡脚计算公式,反推东营组沉积末期(早期油)油充注宽度。(注:该油充注宽度为油源供应充足条件下早期油可能形成的最大范围,后文中早期油充注宽度均以此为标准)。依据上述原理统计2个地区沉积时期大致相同的主力含油层段沉积体的早期油充注宽度,如图9(a)所示,盐斜229地区的早期油充注的宽度依然小于盐22地区的宽度。
盐斜229地区Es4s砂砾岩体的坡度角大于盐22地区同时期砂砾岩体的坡度,如图9(a)所示:盐斜229地区的现今油层宽度和早期石油充注的宽度均小于盐22地区的宽度,表明坡度会影响每期石油范围,进而影响晚期石油充注,早期石油充注范围及运移路径决定晚期石油优先聚集区域。在坡度较陡的背景下,石油运移过程中所受浮力较大,石油在浮力的作用下沿垂向上叠置的砂砾岩向上倾方向运移[21-22],在有扇根封堵和垂向泥岩封堵形成的有效圈闭(即第6期次砂砾岩体)中聚集,第6期次砂砾岩体顶部有近5 m厚的泥岩层(图4(a)),可作为有效的垂向封堵层[3]。因此,盐斜229地区Es4s储层中油主要在第6期次砂砾岩体扇中富集。另外,盐22地区的现今油层宽度大于早期油充注宽度,而盐斜229地区第7和第8期次砂砾岩储层中现今油层宽度小于早期油充注理论最大宽度。进一步统计盐斜229地区扇根古封堵油柱高度(东营组沉积末期封堵能力)、现今油柱高度以及现今扇根可封堵油柱高度。由图9(b)可见:第7,8期次砂砾岩扇根古封堵油柱高度和现今封堵油柱高度均大于现今储层中的油柱高度。结果表明:盐斜229地区Es4s储层中深层存在大量水层并不是扇根封堵能力所致。经进一步分析发现:第6,7和8期次砂砾岩体垂向上叠置连片,垂向连通性好,不易形成有效圈闭,因此,早期石油充注只在扇根附近形成少量油聚集(图4(a))。
3.2 早期石油充注保护储层
盐斜229地区Es4s储层中存在2期油气充注,分别为早期黄色荧光油充注和晚期蓝色荧光油充注(图8(e),(f)),分别对应于东营组沉积末期和馆陶—明化镇组沉积期[15-16]。研究区早期油充注时期储层处于中成岩A1期[23]。储层经历了一定的压实和溶蚀作用(图6(b)),颗粒呈点—线接触,保留有一定的原生孔隙;可见长石溶蚀现象。但是,早期油气充注进一步保护原生粒间孔隙[24-26]。油层中孔隙发育,多以原生粒间孔隙为主,孔隙周缘可见残余的油膜(图6(a))。水层和干层中由于没有发生油气聚集,进一步发生压实作用,导致原生孔减少,只保留少量溶蚀型微孔(图6(c))。
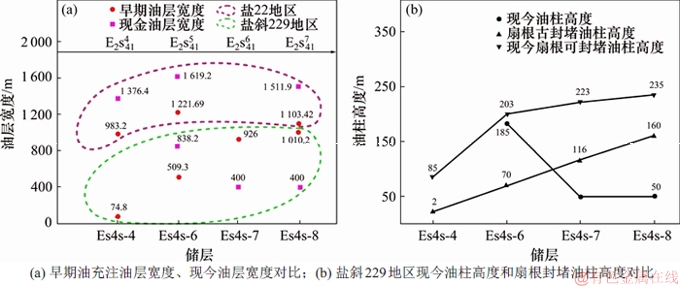
图9 油层宽度及扇根封堵能力统计
Fig. 9 The statistics of Oil distribution range and inner fans’ sealing ability
此外,油层碳酸盐胶结物含量少,主要为白云石胶结物,水层及含油水层的碳酸盐胶结物的含量高,白云石含量与油层差别不大,但铁白云石含量高于油层。干层中铁白云石多呈基底式胶结(图6(f))。深层碎屑岩储层碳酸盐胶结物主要为外部来源,即来源于临近泥岩,搬运方式以平流为主;外源平流供应物质的水润湿/油润湿砂岩,高含油饱和度情况下,水相相对渗透率非常低,胶结物通过孔隙水平流传输进入砂岩基本停止[26-30],从而抑制碳酸盐胶结作用。石油充注会抑制铁白云石的胶结[24-25,27],同时,这一过程受石油充注时间等因素控制。石油充注早于胶结作用或与胶结作用同时发生才能抑制胶结作用,石油充注越早、抑制效果越明显[5,27,31]。MA[32]等认为:白云石的沉淀温度为50~74 ℃;铁白云石的沉淀温度为96 ~137 °C。而东营凹陷烃类包裹体同期的盐水包裹体的均一温度主峰区为70~92 ℃和108~128 ℃[15]。白云石形成时间早于第1期石油充注,没有受到石油充注的影响,因此,油层、水层以及含油水层的白云石含量差异不明显。
铁白云石形成时间晚于第1期充注时期。在扇缘薄层砂体和扇中近泥岩的储层中,由于受原始组构以及压实作用的影响,物性较差[33],早期油难以充注到该类储层中,储层中含油饱和度低,铁白云石可以持续胶结[19],导致物性进一步变差,在近泥岩位置形成胶结壳,如图10(a)中(1),(3)和(4)对应位置。对于扇中远离砂泥接触面的位置(图7(c)),一方面,由于原始物性好[3],另一方面,受到早期黄色荧光油充注的保护,储层物性较好,晚期油更倾向补充到这类储层中,抑制了铁白云石的胶结,如图10中(3)对应位置。所以,水层和干层中铁白云含量高于油层,并且水层和干层只有黄色荧光油(图8(c)),然而,油层中可见黄色荧光和蓝色荧光油(图8(e))。油层、水层和干层的储集特征差异以及碳酸盐胶结物含量的差异表明早期油充注对储层的保护作用是油层中孔隙发育的控制因素。
在原始组构和成岩作用改造下,近岸水下扇扇缘是有利的输导层,扇中是有利的储集层,内扇是有利的封堵层[2]。研究区砂砾岩扇体坡度陡,油运移过程中所受浮力大,深湖相泥岩生成的油会沿着扇缘输导层向上倾方向有垂向和侧向封堵条件的扇中储层中聚集。深层为未发生油充注的水层,由于没有石油对原生孔的保护作用以及对碳酸盐胶结的抑制作用,储层中靠近泥岩部位发生强烈铁白云石胶结,并且越靠近砂泥接触面胶结作用越强(图7,图10)。当砂层过薄时,储层中孔隙就会全部被铁白云石占据而成为干层,如图10中(3)对应位置。在晚期石油发生充注时,近泥岩部位形成的碳酸盐胶结壳会阻止晚期油充注。而早期石油充注路径会成为后期石油充注的优势运移通道[34-35],晚期石油会更多的补充到早期石油充注的含油水层中。因此,在深层扇中厚砂层中部就会存在大量被碳酸盐胶结壳包裹的水层,如图10中(4)对应位置。
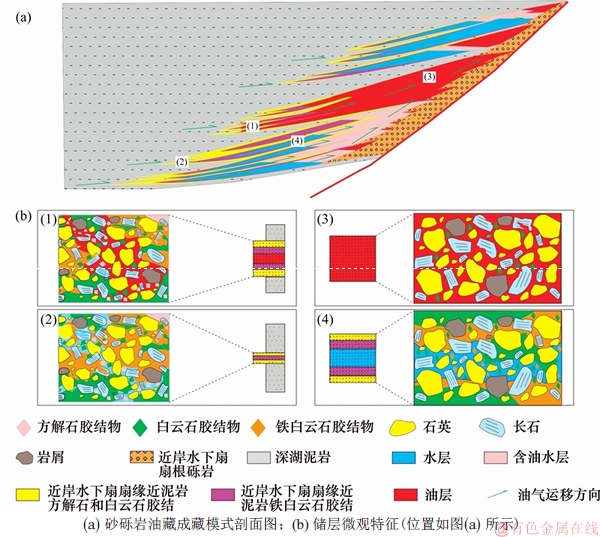
图10 盐斜229地区沙四上亚段砂砾岩油藏成藏模式
Fig. 10 Accumulation models of Es4s reservoirs in Yanxie 229 area
4 结论
1) 碳酸盐胶结是盐斜229地区Es4s储层主要的成岩作用,白云石和铁白云石是主要的碳酸盐胶结物。油层、水层、干层中白云石含量相差不大,油层中铁白云石含量远少于水层和干层中的含量。
2) 盐斜229地区Es4s砂砾岩储层成藏主要受砂砾岩扇体的坡度和早期油充注控制,近岸水下扇砂砾岩体坡度控制了第1期油有效充注的范围,受早期石油充注保护的储层,压实和胶结作用弱,储集空间以原生粒间孔为主。早期石油充注范围控制着晚期油的充注。
3) 盐斜229地区Es4s储层中深层存在大量水层并不是扇根封堵能力所致,储层中未发生石油充注的近泥岩部位碳酸盐胶结壳阻止晚期石油充注,导致深层扇中存在大量水层。
参考文献:
[1] 刘向君, 熊健, 梁利喜, 等. 玛湖凹陷百口泉组砂砾岩储集层岩石力学特征与裂缝扩展机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 83-91.
LIU Xiangjun, XIONG Jian, LIANG Lixi, et al. Rock mechanical characteristics and fracture propagation mechanism of sandy conglomerate reservoirs in baikouquan formation of Mahu sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 83-91.
[2] 隋风贵, 操应长, 刘惠民, 等. 东营凹陷北带东部古近系近岸水下扇储集物性演化及其油气成藏模式[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(2): 246-256.
SUI Fenggui , CAO Yingchang, LIU Huimin, et al. Physical properties evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of Paleogene nearshore subaqueous fan in the Eastern North margin of the Dongying depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(2): 246-256.
[3] 马奔奔, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等. 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层岩相与物性关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(2): 495-506.
MA Benben, CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong, et al. Relationship between lithofacies and physical properties of sandy conglomerate reservoirs of Es4s in yanjia area, Dongying depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2015, 45(2): 495-506.
[4] 刘惠民, 刘鑫金, 贾光华. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带深层砂砾岩扇体成岩圈闭有效性评价[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(5): 7-14.
LIU Huimin, LIU Xinjin, JIA Guanghua. Evaluation on trap effectiveness for deep fan diagenetic trap in the northern steep slope zone of Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(5): 7-14.
[5] 王永诗, 王勇, 朱德顺, 等. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩优质储层成因[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(2): 28-36.
WANG Yongshi, WANG Yong, ZHU Deshun, et al. Genetic mechanism of high-quality glutenite reservoirs at the steep slope in northern Dongying sag[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(2): 28-36.
[6] 宋国奇, 刘鑫金, 刘惠民. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩体成岩圈闭成因及主控因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6): 37-41, 113.
SONG Guoqi, LIU Xinjin, LIU Huimin. Study on genetic mechanism and controlling factors of conglomerate diagenesis trap in northern Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(6): 37-41, 113.
[7] 隋风贵. 断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩扇体成藏动力学特征: 以东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(4): 335-340.
SUI Fenggui . Characteristics of reservoiring dynamic on the sand-conglomerate fanbodies in the steep-slope belt of continental fault basin: a case study on Dongying depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(4): 335-340.
[8] 马奔奔, 操应长, 王艳忠. 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段储层低渗成因机制及分类评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(12): 4277-4291.
MA Benben , CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong. Genetic mechanisms and classified evaluation of low permeability reservoirs of Es4s in Yanjia area, Dongying depression[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2014, 45(12): 4277-4291.
[9] WANG Yanzhong, CAO Yingchang, MA Benben, et al. Mechanism of diagenetic trap formation in nearshore subaqueous fans on steep rift lacustrine basin slopes: A case study from the Shahejie Formation on the North slope of the Minfeng Subsag, Bohai Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Science, 2014, 11(4): 481-494.
[10] 李桥, 王艳忠, 操应长, 等. 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层分类评价方法[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(4): 812-823.
LI Qiao, WANG Yanzhong, CAO Yingchang, et al. Classified evaluation of sand-conglomerate reservoir of the upper section of the fourth member of shahejie formation in yanjia area, Dongying depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(4): 812-823.
[11] 孔凡仙. 东营凹陷北带砂砾岩扇体勘探技术与实践[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
KONG Fanxian. Exploration technique and practice of sandy-conglomeratic fans in the northern part of Dongying depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
[12] 宋明水, 李存磊, 张金亮. 东营凹陷盐家地区砂砾岩体沉积期次精细划分与对比[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 781-789.
SONG Mingshui, LI Cunlei, ZHANG Jinliang. Fine division and correlation of conglomerate sedimentary cycles in Yanjia area of Dongying depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 781-789.
[13] CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong, GLUYAS J G, et al. Depositional model for lacustrine nearshore subaqueous fans in a rift basin: the Eocene shahejie formation, Dongying sag, Bohai bay basin, China[J]. Sedimentology, 2018, 65(6): 2117-2148.
[14] 卢浩, 蒋有录, 薄冬梅, 等. 东营凹陷永安镇—盐家地区油源特征分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(6): 39-42, 113.
LU Hao, JIANG Youlu, BO Dongmei, et al. Oil and source rock correlation of Yong'anzhen—YanJia region in Dongying depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2008, 15(6): 39-42, 113.
[15] 朱光有, 金强, 戴金星, 等. 东营凹陷油气成藏期次及其分布规律研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2): 209-215.
ZHU Guangyou, JIN Qiang, DAI Jinxing, et al. A study on periods of hydrocarbon accumulation and distribution pattern of oil and gas pools in Dongying depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2): 209-215.
[16] 蒋有录, 刘华, 张乐, 等. 东营凹陷油气成藏期分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(3): 215-218, 259.
JIANG Youlu, LIU Hua, ZHANG Yue, et al. Analysis of petroleum accumulation phase in Dongying sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(3): 215-218, 259.
[17] BURRUSS R C. Practical aspects of fluorescence microscopy of petroleum fluid inclusions[J]. Society of Economic Paleontologists & Mineralogists, 1991: 25(1): 1-7.
[18] EADINGTON P I, HAMILTON P I, BAI GP.Fluid history analysis: a new concept for prospect evalution[J].The APEA Journal, 1991, 31(1): 282-294.
[19] 边凤青. 东营凹陷沙四段-孔店组剥蚀厚度与原型盆地的恢复[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学海洋地球科学学院, 2009: 20-33.
BIAN Fengqing. The restored eroded thickness and prototype basin of Kongdian formation and the fourth member of the Shahejie formation in Dongying depression[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. College of Marine Geosciences, 2009: 20-33.
[20] 邵新军, 刘震. 沉积盆地地层古埋深的恢复[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1999, 26(3): 33-35.
SHAO, Xinjun; Liu Zhen. Restoration of the paleoburial depth of strata in deposition basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26(3): 33-35.
[21] 李明诚. 石油与天然气运移研究综述[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(4): 3-10, 109-117.
LI Mingcheng. An Overview of hydrocarbon migration research[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(4): 3-10, 109-117.
[22] 卓勤功, 隋风贵, 银燕, 等. 济阳坳陷地层油气藏油气运移动力与方式探讨[J]. 油气地球物理, 2006, 4(4): 36-40, 44.
ZHUO Qingong, SUI Fenggui , YIN Yan, et al. Hydrocarbon migration agent and fashion of the stratigraphic reservoir in Jiyang depression[J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 2006, 4(4): 36-40, 44.
[23] 纪友亮, 高崇龙, 刘玉瑞, 等. 高邮凹陷阜一段油气充注对储层物性演化的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(1): 133-139.
JI Youliang, GAO Chonglong, LIU Yurui, et al. Influence of hydrocarbon charging to the reservoir property in 1st member of funning formation in Gaoyou depression[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2015, 43(1): 133-139.
[24] SAIGAL G. C., BJ RLYKKE K., LARTER S. The effects of oil emplacement on diagenetic processes: examples from the fulmar reservoir sandstones, central North sea: geologic note (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76: 1024-1033.
RLYKKE K., LARTER S. The effects of oil emplacement on diagenetic processes: examples from the fulmar reservoir sandstones, central North sea: geologic note (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76: 1024-1033.
[25] TAYLOR T R, GILES M R, HATHON L A, et al. Sandstone diagenesis and reservoir quality prediction: Models, myths, and reality[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(8): 1093-1132.
[26] BUKAR M. Does oil emplacement stop diagenesis and quartz cementation in deeply buried sandstone reservoirs[D]. Liverpool: University of Liverpool, Department of Earth, Ocean and Ecological Sciences, 2013:36,54.
[27] GUO Xiaowen, LIU Keyu, JIA Chengzao, et al. Effects of early petroleum charge and overpressure on reservoir porosity preservation in the giant Kela-2 gas field, Kuqa depression, Tarim Basin, northwest China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(2): 191-212.
[28] WORDEN R H, OXTOBY N H, SMALLEY P C. Can oil emplacement prevent quartz cementation in sandstones?[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 1998, 4(2): 129-137.
[29] NEVEUX L, GRGIC D, CARPENTIER C, et al. Influence of hydrocarbon injection on the compaction by pressure-solution of a carbonate rock: An experimental study under triaxial stresses[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 55: 282-294.
[30] EHRENBERG S N, MORAD S, LIU Yaxin, et al. Stylolites and porosity in A lower cretaceous limestone reservoir, onshore Abu Dhabi, U.A.E[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2016, 86(10): 1228-1247.
[31] RAMM M. Porosity-depth trends in reservoir sandstones: theoretical models related to Jurassic sandstones offshore Norway [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1992, 9(5): 553-567.
[32] MA Benben, ERIKSSON K A, CAO Yingchang, et al. Fluid flow and related diagenetic processes in a rift basin: Evidence from the fourth member of the Eocene Shahejie Formation interval, Dongying depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(11): 1633-1662.
[33] 马奔奔, 操应长, 王艳忠,等. 渤南洼陷北部陡坡带沙四上亚段成岩演化及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(1):170-182.
MA BenBen , CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong, et al. Diagenetic evolution and its influence on physical properties of reservoir in the northern steep zone of the Bonan Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(1):170-182.
[34] 公言杰, 柳少波, 刘可禹, 等. 致密油充注过程中储层润湿性变化对含油性影响: 以川中侏罗系致密油为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(4): 423-429.
GONG Yanjie, LIU Shaobo, LIU Keyu, et al. Influence of reservoir wettability changes on oil-bearing features during tight oil accumulation: A case study of Jurassic tight oils in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(4): 423-429.
[35] 张发强, 罗晓容, 苗盛, 等. 石油二次运移优势路径形成过程实验及机理分析[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(2): 159-167.
ZHANG Faqiang, LUO Xiaorong, MIAO Sheng, et al. Experiments on oil migrating in a limited pathway and the mechanism analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(2): 159-167.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2018 -08 -30; 修回日期: 2018 -11 -08
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金面上资助项目(41772137);国家科技重大专项(2016ZX05006-003-003);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(17CX05009, 15CX08001A)(Project(41772137) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2016ZX05006-003-003) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Foundation; Projects(17CX05009, 15CX08001A) supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:王艳忠,副教授,从事沉积学、储层地质学研究;E-mail: wangyanzhong1980@163.com