Article ID: 1003-6326(2005)05-0971-07
Microstructure and properties of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites
GE Ji-ping(葛继平), ZHAO Hong(赵 红),
YAO Zai-qi(姚再起), LIU Shu-hua(刘书华)
(Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116028, China)
Abstract: The effects of intermediate annealings on the microstructure, the strength and the electrical resistivity of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites were studied. The results show that intermediate annealings favour the formation of uniform tiny fibres from the iron dendrites but they have no obvious effect on the strength of the composite. The bigger the strain is, the higher the strength is. As the strain increases, the resistivity increases due to the increase of interface density. Intermediate annealings result in notable decreasing resistivity due to the precipitation of the iron atoms from the Cu matrix and decrease of solute scattering resistivity. The doping with Zr improves the strength of the composite slightly and the ultimate tensile strength(UTS) increases about 10%. The colligated performances of deformation-processed Cu-11.5%Fe and Cu-11.5%Fe-Zr composites at strain η=5.37 are 64.6% IACS/752MPa and 61.4% IACS/824MPa respectively.
Key words: Cu-Fe alloy; deformation-processed; in-situ composite; strength; electrical resistivity CLC number: TB323
Document code: A
1 INTRODUCTION
Since Bevk et al[1] demonstrated that heavily drawn Cu-Nb alloys with 15%-20%Nb(volume fraction, %) can have good combination of strength and electrical conductivity, in-situ processed Cu-based composites, such as Cu-Nb[2], Cu-Ag[3], Cu-Cr[4] and Cu-Fe[5-8] alloys have been the subjects of considerable investigations. And Cu-Nb and Cu-Ag nanocomposite materials have been used in windings of high field pulsed magnets[2, 3]. These composites are usually fabricated by the so-called in-situ method, upon solidification of these two-phases (Cu-X) alloys, X dendrites form in copper matrix and the subsequent intensive transform into ribbon-like after very high drawing strains. It is believed that this ribbon morphology enhances the strength of these alloys and the limited solubility of the X element in copper allows the matrix to retain a high conductivity.
The Cu-Fe system is of particular interest because of the relatively low cost of iron compared with the other possible X components, and the phase equilibrium of Cu-Fe is similar to that of Cu-Nb and Cu-Cr. Iron is also bcc at room temperature. The flow stress of Fe is similar to that of Cu and cast Cu-Fe alloys can be drawn extensively at room temperature without breakage. Unfortunately, the higher resistivity of Cu-Fe alloys once made them less attractive for practical application. The studies show that the reduced conductivity on the given level of strength is a result of the relatively high solubility of iron in copper at high temperature, coupled with the slow kinetics of iron precipitation at low temperature. However, according to the data[9], the predicted equilibrium solubility of iron in copper is 1.25×10-6 at 250℃, and the conductivity of the copper matrix would be reduced only by 1% IACS. For this reason it is important to improve the conductivity of Cu-Fe alloys to remove as much iron from solid solution in the copper as possible.
There are two ways to realize this purpose. One is improving the preparation process of initial materials. If the Cu-Fe composites are processed at lower temperature, the solubility of Fe in the Cu matrix can keep sufficiently low so that the conductivity of composites is not obviously decreased. Jerman et al[5] demonstrated that the deformation-processed Cu-15%Fe(volume fraction) composites, prepared by powder metallurgical techniques under the condition of 2.5h at 475℃, have strength/electrical conductivity properties equivalent to that of Cu-Nb and Cu-Cr. But it needs especially preparation techniques and it will increase the cost. Another way is utilizing hot drawing. The precipitation kinetics would be enhanced by hot drawing in the temperature range of 200℃ to 400℃.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of thermo-mechanical treatment and the third element on the microstructure and physical properties of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites, and to examine the possible techniques that would accelerate the precipitation of Fe from Cu matrix and to optimize strength and electrical conductivity.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
Four compositions were chosen for investigation, namely, Cu-11.5%Fe, Cu-17.5%Fe and Cu-11.5%Fe-0.2%Zr. The initial ingots were prepared by induction melting in air. The ingots were about 25mm in diameter. After machining the rods with diameter of 22mm were drawn following two different routes:
A) Cold drawing: d22mm→d6mm→d3mm→d2mm→d1.5mm→d1mm→d0.8mm→d0.5mm →d0.3mm→d0.2mm.
B) Cold drawing with intermediate annealings: d22mm →d6mm→ HT1→d3mm→ HT2→d2mm→ d1.5mm→HT3→d1mm→d0.8mm→d0.5mm→d0.3mm→d0.2mm.
HT is an intermediate annealing. Drawing reductions will be given in terms of logarithmic strain by η=ln(A0/Af), where A0 and Af is the initial and final cross-section area respectively. At last some samples were differently annealed in vacuum furnaces respectively.
The microstructure of the drawn and annealed wires were examined by SEM and TEM. To study the three-dimensional changes of Fe phase, a deep-etch technique was used to remove the Cu matrix prior to SEM observation, and the samples were immersed in HNO3 solution for approximately 20s.
Tensile tests were performed at room temperature with a strain rate of 2.5×10-4s-1. Fracture surfaces of the samples were examined by SEM to characterize fracture behavior. Standard four-probe technique was used to measure the resistivity by means of the direct current 100mA. The lengths of samples were 40-50mm.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Microstructure
The SEM images of as cast Cu-11.5%Fe and Cu-17.5%Fe alloys are shown in Fig.1. It can be found that the iron dendrites are evenly distributed in the Cu matrix and the average diameters of secondary arm of iron dendrites of Cu-11.5%Fe and of Cu-17.5%Fe alloys are 2.04±0.68μm and 1.95±0.41μm, respectively. It is confirmed that the microstructures only consist of α-Fe and Cu phases by XRD.
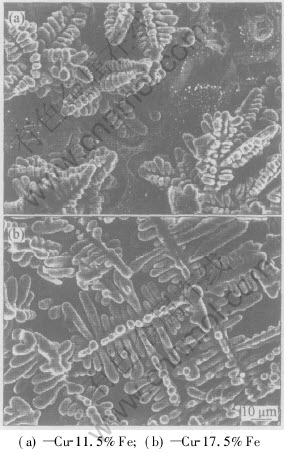
Fig.1 SEM micrographs of as-cast alloys (Cu matrix dissolved)
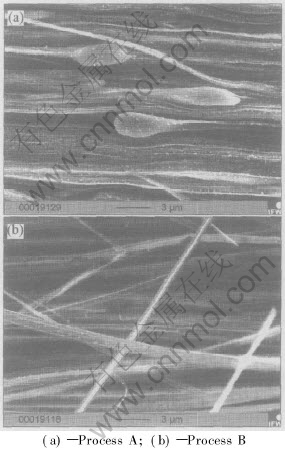
Fig.2 Longitudinal SEM micrographs of Fe filaments in Cu-11.5%Fe in-situ composites(η= 9.40)
Fig.2 shows the SEM images of longitudinal section of Cu-11.5%Fe alloys processed by routes A and B at η=9.40. Fig.2(a) shows that the deformation of iron dendrites is not uniform under room-temperature drawing, and there are still iron phases without full deformation. While under the same deformation strain, with the intermediate annealings, all iron dendrites are transformed into fibers (Fig.2(b)). Because of the high rigidity of iron phases, the deformation conducted directly at room temperature is slow, while fibres are easily formed after annealings, which can soften iron phases and accelerate the process of deformation. Obviously, annealings have favored fibrosing of the iron dendrites along drawing direction.
The TEM images of Cu-17.5%Fe alloy processed by route B at η=6.63 are shown in Fig.3. Fig.3(a) shows the structure of its longitudinal section, it is clear that all the fibres of Cu and Fe are growing along wire drawing direction. Fig.3(b) shows its transverse section, it illustrates that the iron fibres are in the form of flakes and curl. The bending structures are alternate distributions of iron fibres and copper fibres. It was pointed out that the appearance of the structure of iron fibers is due to the development of 〈110〉 fibre texture[7]. The development of 〈110〉 fiber texture causes sharp decrease in fiber thickness and comparatively small change in width. Therefore anisotropy deformation certainly results in bending structure, otherwise copper boundaries will be decorated by Fe fibres.
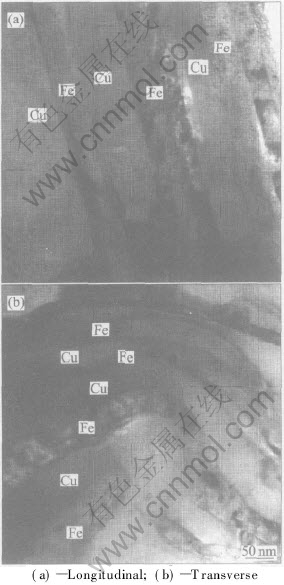
Fig.3 TEM micrographs of Cu-17.5%Fe in-situ composites at η=6.63
3.2 Strength
Fig.4 shows the relationship between the strength of the Cu-Fe alloys and deformation strain. It is clear that both ultimate tensile strength(UTS) and yield strength(YS) increase as deformation strain increases or the iron content increases. Intermediate annealings have no obvious effect on the change of strength.
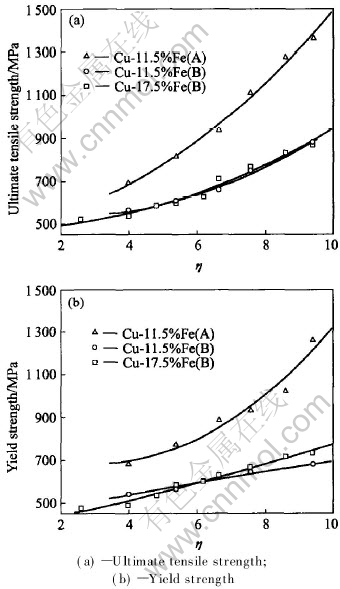
Fig.4 Effect of strain on strength of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites(B)
The correlations among UTS, YS, deformation strain and iron content are easy to be understood. The study on the strengthening of pure copper after plastic deformation demonstrated that the flow stress reached a saturated value of about 450-460MPa and basically kept stable as the deformation strain continuously increased. Such can be explained by an equilibrium between the production and the depletion of dislocations resulted from the occurrence of dynamic recovery and recrystallization[10]. The flow stress of iron phase is almost in linear relationship with the deformation strain[11], and the strength of iron phase is much bigger than that of copper phase[12]. Therefore, the main contribution to the strength of Cu-Fe in-situ composite is the enhancement of the strength of iron phase after plastic deformation. Intermediate annealings have no obvious effects on both UTS and YS of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite. Though it is clear that intermediate annealings contribute to the fibrosis of iron dendrites and result in the appearance of more tiny fibers(see Fig.2), which can enhance the strength of alloys, it may offset to the loss in strength caused by intermediate annealings.
Fig.5 shows the change of elastic modulus of different deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites. It is clear that elastic modulus is correlated with iron content, deformation techniques and deformation strains. Elastic modulus of Cu-11.5%Fe in-situ composite subjected to A process (direct room temperature wire-drawing) is bigger than that of the same composite subjected to B process (with intermediate annealings), because the iron phase is softened during the intermediate annealings.
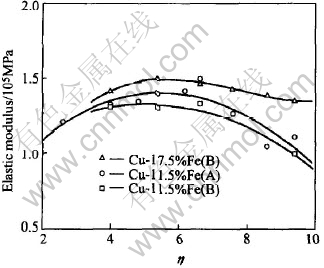
Fig.5 Elastic modulus of in-situ composites in tension as function of strain
Elastic modulus increases with increasing iron content, which is consistent with the generally accepted view that elastic modulus of Cu-Fe alloy is subjected to the rule of mixture. Since the elastic modulus of Fe is bigger than that of Cu, elastic modulus of the alloy is proportional to the Fe content. There were also some arguments that the elastic modulus of Cu-Fe alloy reaches a maximum value when the content of iron is 75% and then it decreased as the content increases[13]. Abnormal augment in elastic modulus is also observed when the iron content is over 75%. The content of Fe in our cases is far smaller than that of the crucial value; therefore the elastic modulus increases as the content of iron rises.
Elastic modulus goes up first and then down as the deformation strain increases, which is contrary to the results of Beusse et al[13] and Berk[1]. It was accepted that the change of elastic modulus was the integrated function of the stress and the fiber texture. Compression stress increases the elastic modulus while tensile stress decreases it[13]. When the plastic deformation becomes bigger, the fiber texture forms, hence elastic modulus along deformation direction reaches its maximum. The work done on the deformed Cu-Ag in-situ composite shows that when the deformation strain reached a certain value, the spacing between filaments comes to 50-60nm, elastic modulus decreases markedly[14]. It is supported by analysis when the structure of a material become fine enough, the dislocation density falls sharply, which in return results in the decline of the elastic modulus.
Fig.6 shows the stress-strain curves of in-situ composites. The strength of deformation-processed Cu-17.5%Fe in-situ composite is the highest at both cases (η=5.37 and η=7.57), while the strength of deformation-processed Cu-11.5%Fe in-situ composite is the lowest. It also shows that the doping with alloy elements Zr improves the strength of in-situ composite with a little expense of ductility of the in-situ composite. The UTS of Cu-11.5%Fe and Cu-11.5%FeZr are 603MPa, 752MPa and 663MPa, 924MPa at η=5.37 and η=7.57, respectively. In both cases, the doping with alloy elements Zr can increase the strength by about 10%.
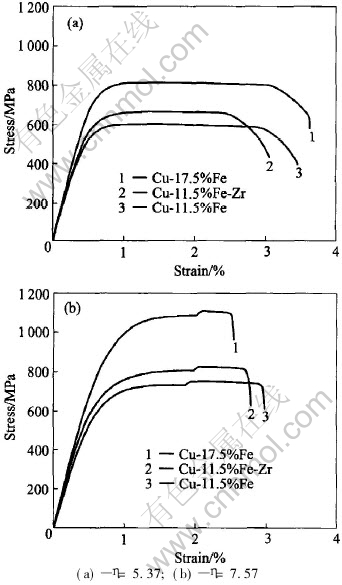
Fig.6 Stress—strain curves of as-drawn Cu-Fe in-situ composites
The fracture characteristics of alloy wires at η=5.37 show many fine dimples. The contractility of the fracture surfaces of the alloys are as follows: for Cu-11.5%Fe, ψ=64.8%; for Cu-17.5%Fe, ψ=50.5%; for Cu-11.5%FeZr, ψ=59.5%.
3.3 Resistivity
Fig.7 shows the correlation between the resistivity of Cu-Fe alloys and deformation strain. The resistivity of deformation-processed Cu-11.5%Fe in-situ composite without intermediate annealings is in linear relationship with deformation strain, and follows the equation:
ρ=5.3369+0.2411η
(η=2.6-9.4)(1)
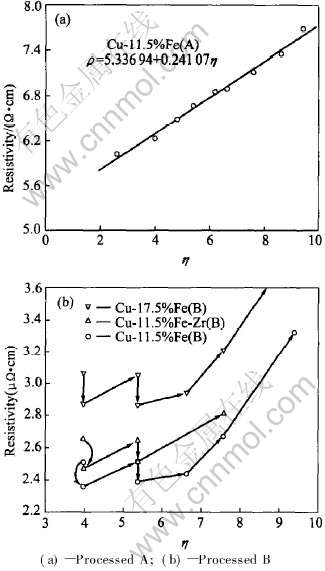
Fig.7 Resistivity vs strain for deformation-processed Cu-Fe alloy
The existence of dislocation results in an un-even electrical field, which in return intensifies the scattering of electrons and finally increases the resistivity. The degree of dislocation scattering depends on the arrangement of dislocation and the moving direction of electrons, which is proportional to the square of Burgers vector[15]. The contribution of dislocation of per unit length to resistivity is quite small, for example, ρD≈(1.0±0.2)×10-19Ω·cm3[16] or ρD≈1.3×10-19Ω·cm3[17] to the resistivity of pure Cu. The calculated contribution is about 0.10-0.13μΩ·cm to the resistivity of Cu-Fe in-situ composite. The interface scattering resistivity is an important contribution to the resistivity. The study on deformation-processed Cu base in-situ composite has pointed out that the dislocation density does not increase markedly as the strain increased after heavy deformation, so the decrease in the spacing between filaments is the main reason to the enhancement of the resistivity. Factually, interface scattering resistivity is noticeable, because of the inelastic scattering of conductive electrons[1, 18].
The intermediate annealings were applied in order to improve the deformation capability and conductivity of the deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite. Fig.7(b) shows the correlation between the resistivity of Cu-Fe alloys and deformation strain with intermediate annealings. The higher the iron content, the higher the resistivity of alloys. The increment in resistivity of alloys with different iron content are similar when deformation strain is the same. It can also be seen that the resistivity decreased 0.10-0.30μΩ·cm for d3(η=3.98) and d1.5(η=5.37) alloy wires after HT2 and HT3 intermediate annealing respectively. Alternative intermediate annealings and deformation processing creat a surrounding of higher temperature, more empty sites and higher dislocation density respectively, which accelerates to the diffusion of the iron atoms from the Cu base. The precipitation of iron atoms from Cu base results in the decrease of solute scattering resistivity[19]. The separated iron particles are slowly deformed into fibres during the later deformation process and unlikely generate comparable separation strain field resistivity. On the other hand, intermediate annealings also helps to diminish the defects by recovery and recrystallization, hence lowers the defect scattering resistively. The colligate effects result in decreasing in resistivity of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite after intermediate annealings.
Fig.8 shows the curves of the resistivity of the deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite vs the thickness of copper phase (spacing of Fe fibres). When the thickness is bigger as the thickness decreases, the increase in resistivity is slack, while it increases sharply with the thickness smaller. This is so called size effect, which was first advanced by MacDonald[20]. All these analyses are in agreement with that the proportional dependence of resistivity of Cu-11.5%Fe alloy on deformation strain due to the increase in both interface scattering resistivity and dislocation scattering resistivity with the increase of deformation strain.
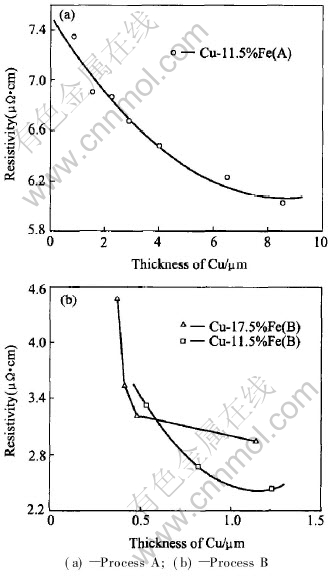
Fig.8 Resistivity of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite plotted vs thickness of Cu
As for the effect of iron content on the resistivity, it can be understood in three aspects. Firstly, the resistivity of Fe is much higher than that of copper. As the iron content increases, its corresponding volume percentage increases as well. The total resistivity of the Cu-Fe alloy becomes bigger either in series-or applied parallel-connection theories. Secondly, the iron content in copper matrix increases as the total iron content of the alloy increased. Thirdly, within a certain range, the higher the iron content is, the more the Cu-Fe interfaces appear, and consequently the higher resistivity is.
It is clear that impurity scattering resistivity ρimp and interface scattering resistivity ρint are the main reasons for increasing the resistivity of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composite. Since deformation process is a necessary procedure to prepare alloy wires, it is hard to reduce the amount of interfaces. As for Cu-Fe in-situ composite, it is reasonable to choose suitable thermo-mechanical treatment to lower the solubility of iron in copper phase.
4 CONCLUSIONS
1) Intermediate annealings contribute to the fibrosis of iron dendrites and result in the appearance of more tiny fibers.
2) The bigger the strain is, the higher the strength of deformation-processed Cu-Fe in-situ composites is. Intermediate annealings have no obvious effect on the strength of the composite.
3) As the strain increases, the resistivity increases due to increase in interface density. Intermediate annealings result in notable decreasing in resistivity of the composite due to the lower solubility of iron in copper phase.
4) The doping with Zr improves the strength of the composite slightly and the UTS increases about 10%.
5) The colligate performances of deformation-processed Cu-11.5%Fe and Cu-11.5%Fe-Zr composites at η=5.37 are 64.6% IACS/752MPa and 61.4% IACS/824MPa, respectively.
Acknowledgements
The work was finished at Leibniz-Institute of Solid State and Materials Research Dresden, Germany. The authors pay their sincere thanks to Professor Ludwig Schultz and Professor Jürgen Eckert for their generous supports.
REFERENCES
[1]Bevk J, Harbison J P, Bell J L. Anomalous increase in strength of in situ formed Cu-Nb multifilamentary composites [J]. J Appl Phys, 1978, 49: 6031-6038.
[2]Snoeck E, Lecouturier F, Thilly L, et al. Microstructural studies of in situ produced filamentary Cu/Nb wires [J]. Scripta Materialia, 1998, 38(11): 1643-1648.
[3]Sakai Y, Schneider-Muntau H J. Ultra-high strength, high conductivity Cu-Ag allow wires [J]. Acta Metall, 1997, 45: 1017-1023.
[4]Lee K L, Whitehouse A F, Withers P J, et al. Neutron diffraction study of the deformation behaviour of deformation processed copper-chromium composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 348(1-2): 208-216.
[5]Jerman G A, Anderson I E, Verhoeven J D. Strength and electrical conductivity of deformation-processed Cu-15vol% Fe alloys produced by powder metallurgy techniques [J]. Metall Trans, 1993, A24: 35-42.
[6]Go Y S, Spitzig W A. Strengthening in deformation-processed Cu-20%Fe composites [J]. J Mater Sci, 1991, 26: 163-171.
[7]Biselli C, Morris D G. Microstructure and strength of Cu-Fe in situ composites after very high drawing strains [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44: 493-504.
[8]Hong S I, Song J S. Strength and conductivity of Cu-9Fe-1.2X(X= Ag or Cr) filamentary microcomposite wires [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, 32A: 985-991.
[9]Hansen M, Anderko K. Constitution of Binary Alloy(2nd Ed) [M]. New York, 1958. 580-581.
[10]Thilly L, Véron M, Ludwig O, et al. High-strength materials: in-situ investigations of dislocation behaviour in Cu-Nb multifilamentary nanostructured composites [J]. Philos Mag, 2002, A82: 925-942.
[11]Langford G, Cohen M. Strain hardening of iron by severe plastic deformation [J]. Transactions of the ASM, 1969, 62: 623-638.
[12]Funkenbusch P D, Courtney T H. Microstructural strengthening in cold worked in situ Cu-14.8vol%Fe composites [J]. Scripta Metall, 1981, 15: 1349-1354.
[13]Beusse R, Boecker W, Bunge H J. Anomalies of young modulus in highly deformed iron-copper composites [J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 27: 767-770.
[14]Frommeyer G, Wassermann G. Microstructure and anomalous mechanical properties of in situ-produced silver-copper composite wires [J]. Acta Metall, 1975, 23: 1353-1360.
[15]Rossiter P L. The Electrical Resistivity of Metals and Alloys [M]. UK: Cambridge University Press. 1987.
[16]Kaveh M, Wiser N. Deviations from Matthiessens rule for the electrical resistivity of dislocations [J]. J Phys F Met Phys, 1986, 16: 795-802.
[17]Brown R A. A comparison of two theories of dislocation resistivity [J]. J Phys F: Metal Phys, 1977, 7(11): 297-230.
[18]Raabe D. Simulation of the resistivity of heavily cold worked Cu-20wt%Nb wires [J]. Comput Mater Sci, 1995, 3: 402-412.
[19]Hong S I, Song J S, Kim H S. Thermo-mechanical processing and properties of Cu-9Fe-1.2Co microcomposite wires [J]. Scripta Mater, 2001, 45: 1295-1300.
[20]MacDonald D K C. Metallic conduction-the “internal size-effect” [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1951, 42(7): 756-761.
Received date: 2005-02-17; Accepted date:2005-07-15
Correspondence: GE Ji-ping, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-411-84106686; E-mail:ge@dlru.edu.cn
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)