文章编号:1004-0609(2008)08-1402-05
TiB2/Al喷丸形变层连续加热组织结构
栾卫志1,姜传海1,王浩伟1,嵇 宁2
(1. 上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200240;
2. LEMHE/ICMMO, UMR 8182, Université Paris-Sud 11, Orsay 91405, France)
摘 要:研究加热过程中TiB2/6351Al及其基体合金喷丸形变层组织结构的变化,利用X射线衍射线形分析方法计算不同加热温度和时间下的晶块尺寸和显微畸变。结果表明:喷丸使表层晶粒细化,织构消失并且在加热后不再出现;加热过程中,复合材料晶块长大速度低于基体材料,且复合材料显微畸变更易释放;喷丸过程中增强体周围产生的高密度位错使储存能提高,从而促进再结晶,但晶块的进一步长大因增强体的钉扎作用而受到阻碍;复合材料的热稳定性高于基体合金。
关键词:复合材料;晶块尺寸;显微畸变;线形分析;喷丸;连续加热
中图分类号:TG 115 文献标识码:A
Microstructures of shot peened layer on TiB2/Al at elevated temperatures
LUAN Wei-zhi1, JIANG Chuan-hai1, WANG Hao-wei1, V. JI2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China;
2. LEMHE/ICMMO, UMR 8182, Université Paris-Sud 11, Orsay 91405, France)
Abstract: The microstructures of 6351Al and TiB2/6351Al during heating process were investigated by X-ray diffractometry. Domain size and microstrain were calculated by modified Warren-Averbach method and Voigt method. The results show that the textures of both specimens are randomized by shot peening and do not appear again after any heat treatments. Domains grow during heat treatments, and the growth of domains in composite is slower than that of monolithic 6351Al alloy. The microstrain of composite is easier to release than that of the alloy. Higher density dislocation around reinforcements improves stored energy and promotes recrystallization while further domain growth is retarded. The thermostability of composite is higher than that of alloy.
Key words: composite; domain size; microstrain; line profile analysis; shot peening; continuous heating
金属基复合材料以其优异的性能,如高强度和高硬度等[1],而受到广泛的关注。喷丸可使晶体材料表层发生严重的弹塑性变形,形成组织强化层,从而有效地提高工件的表面硬度、疲劳强度和抗腐蚀等性 能[2?3],在工业中已经获得了广泛的应用。然而在加热条件下,喷丸形变层将发生再结晶、晶粒长大以及显微畸变降低等现象,从而削弱了组织强化效应。喷丸形变层的组织结构对保持喷丸工件的优良性能有重要的影响,考察升温条件下组织结构的变化具有实际意义。
X射线衍射(XRD)能够区分晶体材料中不同的相,从而可以对特定相进行分析。对于组织结构不均匀的材料如变形复合材料,X射线衍射分析得到的是统计结果。近年来,发展了一些先进的XRD线形分析方法,运用这些方法,可以迅速而准确的得到晶体材料组织结构的信息。目前对复合材料喷丸形变层在加热条件下显微结构的变化鲜有报导,本文作者利用X射线衍射线形分析方法,研究了TiB2/6351Al及其基体材料在不同温度下晶块尺寸和显微畸变的变化,比较了两种材料变化的差异,并探讨了引起变化的原因。
1 实验
1.1 材料制备
实验材料为TiB2/6351Al原位生成复合材料及其基体合金,增强体体积分数为10%。根据文献[4?5]的方法制备复合材料,增强体颗粒尺寸为50~500 nm。复合材料和基体材料经挤压成棒材,线切割成20 mm×20 mm×5 mm的样品。在喷丸之前,样品经相同条件热处理,热处理工艺如下:530 ℃固溶110 min,室温水淬,170 ℃时效6 h。复合材料和基体合金的弹性模量分别为80 GPa和69 GPa,屈服强度分别为370 MPa和275 MPa。
1.2 实验方法
利用气动式喷丸机分别对两种样品进行喷丸处理,喷丸参数为:气体压力5.88×105 Pa,喷丸介质为玻璃弹丸,平均直径0.5 mm,喷丸时间5 min,A型Almen试片饱和弧高约0. 22 mm。为测定两种材料加热条件下组织结构的变化,喷丸样品在100~400 ℃之间加热,温度间隔25 ℃,每一温度下保温5 min。每一加热阶段结束后,将样品空冷至室温。借助Dmax/rC衍射仪进行X射线衍射谱线测定,管压40 kV,管流100 mA,Cu Kα辐射,扫描范围20?~90?,步长0.02?。
1.3 线形分析原理
分别利用Voigt方法[6]和 modified Warren- Averbach(MWA)方法[7?8]计算喷丸形变层的晶块尺寸和显微畸变。对于X射线衍射,晶块(镶嵌块)指晶体中X射线能够发生连续衍射的区域,这里主要是亚晶和位错胞,利用线形分析方法得到的晶块尺寸,是有效穿透体积内两种亚结构的平均尺寸。在Voigt方法中,各积分宽度(β)之间的关系为

当衍射线形的组成以Gaussian成分为主时,β f可以直接根据式(1)得到,称为Gaussian方法。在Voigt和Gaussian方法中,选用Al(111)和Al(311)衍射线形作为物理线形,用Si(111)和Si(331)衍射线形作为仪器线形,所有线形均扣除衍射背底并根据Rachinger方法去掉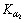 衍射峰。
衍射峰。
根据 UNG?R等[7?8]的理论,MWA方法的基本公式为

平均对比因子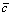 可以从文献[8?9]中计算出。假定从傅里叶数中得到的尺寸因子为L0,根据WANG等[10]的公式
可以从文献[8?9]中计算出。假定从傅里叶数中得到的尺寸因子为L0,根据WANG等[10]的公式

用这种方法得到的是面积权重各衍射方向平均晶块尺寸。在MWA方法中,选用与基体合金相同化学成分的材料作为标准样品,在450 ℃退火6 h,得到的线形作为仪器宽化线形,通过Stokes去卷积的方 法[11]求得A(L)。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 喷丸对织构的影响
图1所示为复合材料与合金加热条件下的XRD谱。从图中可以看出,未经喷丸处理的样品存在严重的织构。而喷丸后织构消失,且经加热处理后不再出现。用Harris的方法[12]计算织构系数(Tc)

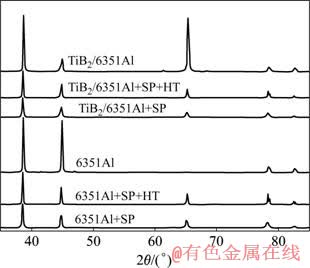
图1 喷丸及加热后样品的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of samples after shot peening (SP) and heat treatment (HT)
对于复合材料,(220)峰的织构系数为2.8,而对于合金材料,在(111)和(200)峰均存在织构,织构系数分别为1.4和2.5。
在喷丸过程中,高速运动的弹丸从不同方向撞击样品表面,引起表面材料产生不均匀塑性变形,结果使晶粒细化成等轴晶[13?14]并使晶界增加。变细的晶粒和晶界的增加使晶粒在进一步变形中更容易转动,通过这种方式,样品表层材料(X射线有效穿透深度内,约35 ?m)的织构被消除。喷丸后取向随机的细小晶粒,在加热长大后仍然保持随机取向,因而在X射线衍射谱线上未表现出存在织构。
2.2 加热对喷丸形变层组织结构的影响
随着温度的提高和加热时间的延长,晶块尺寸增大。选用与基体合金具有相同化学成分的材料作为标样,利用MWA方法计算出喷丸后TiB2/6351Al的晶块尺寸,其过程如下:1) 通过Stokes去卷积的方法,得到各衍射峰在各级傅里叶长度L时的傅里叶数实部A(L),结果如表1所示。2) 利用式(4)对表1中的数据进行计算,则得到对应不同L时傅里叶数实部的尺寸因素As(L),结果如表2所列。3) 利用式(5)和表2中的数据,通过最小二乘法,得到喷丸后复合材料表层的晶块尺寸为(49±1) nm。
表1 Stokes去卷积得到各衍射峰L不同时的A(L)
Table 1 A(L) vs L obtained by Stokes deconvolution
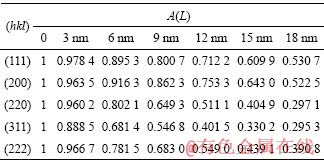
表2 对应各级傅里叶长度L时的尺寸因素傅里叶数As(L)
Table 2 Size Fourier coefficients As(L) vs L

利用与上述过程相同的处理方法,通过MWA方法可以得到两种材料喷丸后表层晶块尺寸在加热过程中的变化。作为对比,还用Voigt方法对晶块尺寸在加热过程中的变化进行了研究。两种方法得到的结果如图2和3所示,图中每一阶段的晶块尺寸用加热前的初始值进行了标准化处理。结果均表明,基体合金的晶块长大速度大于复合材料。用MWA方法计算,合金和复合材料在加热结束后晶块尺寸分别长大到初始值的16和4倍。而用Voigt方法计算的结果分别是12和8倍。两种结果之间的差异是由计算方法不同引起的,MWA方法得到的是面积权重各衍射方向平均晶块尺寸,而Voigt方法得到的是Al(111)衍射方向的平均晶块尺寸。

图2 晶块尺寸的变化
Fig.2 Variations of domain size during heat treatment (L0: domain size; L0S: domain size before heat treatment, calculated using MWA method)
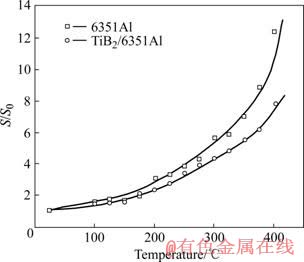
图3 Al(111)衍射方向晶块尺寸的变化
Fig.3 Variations of domain size of Al(111) reflection (S: domain size; S0: value before heat treatment, obtained from Voigt method)
形变过程中,增强体能够提高其周围基体材料局部形变量,从而提高储存能。当复合材料中增强体的尺寸较大时,增强体粒子为再结晶提供了更多的形核部位[15?17],从而促进了再结晶[18]。当增强体尺寸较小时,其周围基体材料仍然存在较多的储存能,但是细小增强体在再结晶过程中影响大角度晶界的形成及其迁移,晶块的长大因增强体粒子的钉扎作用而受到阻碍。因此,在相同的加热条件下,TiB2/6351Al的晶块尺寸比6351Al相对稳定。
加热也引起了显微畸变的降低,如图4所示。在Al(311)衍射方向上弹塑性各向同性,因而本研究选用Al(311)衍射峰,利用Voigt方法分别计算了两种材料显微畸变的变化。加热过程中显微畸变的变化均分为如下3个阶段:1) 缓慢下降阶段,25~225 ℃;2)急剧下降阶段225~300 ℃;3) 稳定阶段300~400 ℃。在前两个阶段,复合材料显微畸变下降比合金快。而在稳定阶段,复合材料显微畸变比基体合金略大,这主要是由于当温度从高温降至室温时,增强体和基体之间的热错配引起的[19],类似的结果在文献[20]中也有报道。从图5中还可以看出,复合材料显微畸变急剧下降的温度区间比基体合金略低,表明复合材料显微畸变更容易释放。
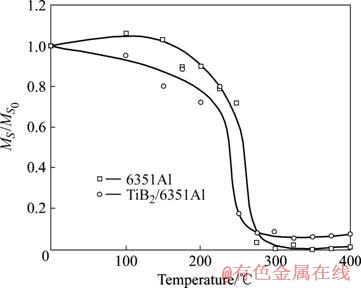
:
图4 加热过程中材料显微畸变的变化
Fig.4 Microstrain change of materials during heat treatment (MS: Microstrian; 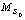 Microstrian before heat treatment, calculated using Viogt method according to Al(311) reflection profiles)
Microstrian before heat treatment, calculated using Viogt method according to Al(311) reflection profiles)
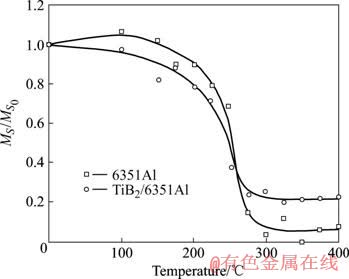
图5 加热过程中材料显微畸变的变化
Fig.5 Microstrain change of materials during heat treatment (MS: Microstrian; 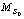 Microstrian before heat treatment, obtained from Gaussian method according to Al(311) reflection profiles)
Microstrian before heat treatment, obtained from Gaussian method according to Al(311) reflection profiles)
XRD实测线形是由物理线形和仪器线形卷积而成,进一步研究表明,Al(311)衍射线形的组成主要是Gaussian (大于87%)。原因是在本实验条件下,仪器线形的Gaussian成分大(82%),另一个原因是由于喷丸样品(包括退火样品)晶块尺寸在X射线有效穿透深度内大小并不均匀,而呈一定的Gaussian分布。作为对比,用Gaussian方法计算出两种材料显微畸变的变化,结果如图5所示。对比图4和图5发现,二者的变化规律基本相同。
形变金属中,显微畸变主要由位错引起,因为位错不仅是主要的晶体缺陷,也是其他缺陷的主要组成成分,或在他缺陷中起重要的作用[21?22]。喷丸能在很大程度上提高位错密度,在重复变形过程中,复合材料中的增强体粒子往往成为位错的沉积源[23]。已有研究认为,增强体粒子周围的高密度位错能够促进再结晶[17, 24],而再结晶晶核的生长主要依赖形变储存 能[25]。高密度位错意味着高的贮存能,在加热过程中,贮存能释放,成为再结晶的驱动力。增强体周围的高密度位错和更多的形核部位使复合材料的显微畸变在加热条件下更容易降低。
形变金属再结晶是热力学过程,包括形核和长大两个过程,其影响因素主要是加热温度和时间。在本实验条件下,显微畸变在225~300 ℃温度区间急剧降低,表明在该温度区间发生再结晶行为,其对应的时间区间为30~45 min,由于时间间隔较短,晶块长大的速度不如显微畸变降低的速度明显。对于复合材料而言,由于增强体的钉扎作用,晶块长大的速度更小,表明复合材料的热稳定性比基体合金高。
REFERENCES
[1] KURUVILLA A K, PRASAD K S, BHANUPRASAD V V, MAHAJAN Y R. Microstructure-property correlation in Al/TiB2 (XD) composites[J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1990, 24(5): 873?878.
[2] 高玉魁. 喷丸对Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al钛合金拉-拉疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(1): 60?63.
GAO Yu-kui. Influence of shot peening on tension-tension fatigue properties in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 60?63.
[3] 胡兰青, 李茂林, 王 科, 刘 刚, 卫英慧, 许并社. 铝合金表面纳米化处理及显微结构特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(12): 2016?2020.
HU Lan-qing, LI Mao-lin, WANG Ke, LIU Gang,WEI Ying-hui, XU Bing-she. Microstructure and characterization of surface nanocrystallization of aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(12): 2016?2020.
[4] YI Hong-zhan, MA Nai-heng, LI Xian-feng, ZHANG Yi-jie, WANG Hao-wei. High-temperature mechanics properties of in situ TiB2p reinforced Al-Si alloy composites[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 419(1/2): 12?17.
[5] TJONG S C, MA Z Y. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites[J]. Mater Sci Eng R, 2000, 29(3/4): 49?113.
[6] LANGFORD J I. A rapid method for analysing the breadths of diffraction and spectral lines using the voigt function[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1978, 11: 10?14.
[7] UNGAR T, BORBELY A. The effect of dislocation contrast on X-ray line broadening: A new approach to line profile analysis[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1996, 69(21): 3173?3175.
[8] UNGAR T, BORBELY A, RIBARIK G, BORBELY A. Crystallite size distribution and dislocation structure determined by diffraction profile analysis: principles and practical application to cubic and hexagonal crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2001, 34(3): 298?310.
[9] UNGAR T, DRAGOMIR D, REVESZ A, BORBELY A. The contrast factors of dislocations in cubic crystals: The dislocation model of strain anisotropy in practice[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1999, 32(5): 992?1002.
[10] WANG Yu-ming, LEE Shan-san, LEE Yen-chin. X-ray line profile analysis of deformed Al[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1982, 15(1): 35?38.
[11] STOKES A R. A numerical Fourier-analysis method for the correction of widths and shapes of lines on X-ray powder photographs[C]// Proceeding of the Physical Society, 1948: 382?391.
[12] BARRETT C S, MASSALSKI T B. Structure of Metals[M]. Oxford: Pergamon, 1980: 204?224.
[13] LU Ke, LV Jian. Nanostructured surface layer on metallic materials induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 375/377: 38?45.
[14] WANG K, TAO N R, LIU G , LU K. Plastic strain-induced grain refinement at the nanometer scale in copper[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(19): 5281?5291.
[15] INEM B. Dynamic recrystallization in a thermomechanically processed metal matrix composite[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1995, 197(1): 91?95.
[16] MANNA R, SARKAR J, SURAPPA M K. Effect of second phase precipitates on recovery and recrystallization behaviour of cold-worked Al2024-SiCp composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1996, 31(6): 1625?1631.
[17] FERRY M, MUNROE P R. Recrystallization kinetics and final grain size in a cold rolled particulate reinforced Al-based MMC [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2004, 35(9): 1017?1025.
[18] YOO Y C, JEON J S, LEE H I. The effect of SiC whiskers on the hot-deformation behavior of SiCw/Al2124 composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1997, 57: 651?654.
[19] 姜传海, 王德尊, 姚忠凯. 颗粒增强金属基复合材料热错配应力分析[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(5): 555?560.
JIANG Chuan-hai, WANG De-zun, YAO Zhong-kai. Analysis of thermal mismatch stress in the particle reinforced composite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2000, 36(5): 555?560.
[20] 李建林, 江东亮, 谭寿洪. 原位生成SiC/TiSi2纳米复合材料的组织结构[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(8): 893?896.
LI Jian-lin, JIANG Dong-liang, TAN Shou-hong. Study on microstructure of in situ produced SiC/TiSi2 nanocomposite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(8): 893?896
[21] UNGAR T. Microstructural parameters from X-ray diffraction peak broadening[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51(8): 777?781
[22] UNGAR T. Dislocation densities, arrangements and character from X-ray diffraction experiments[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001(309/310): 14?22.
[23] HUMPHREYS F J, KALU P N. Dislocation-particle interactions during high temperature deformation of two-phase aluminum alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Materialia, 1987, 35(12): 2815? 2829.
[24] CAVALIERE P, VANGELISTA E E. Isothermal forging of metal matrix composites: Recrystallization behaviour by means of deformation efficiency[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(2): 357?362.
[25] POUDENS A, BACROIX B. Recrystallization textures in Al-SiC metal matrix composites[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1996, 34(6): 847?855.
基金项目:白玉兰科技人才基金资助项目(2007B071)
收稿日期:2007-12-05;修订日期:2008-04-07
通讯作者:姜传海,教授,博士;电话:021-34203095-8211;E-mail: wzluan@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑 陈爱华)