氟和氯在Mg(0001)表面吸附的密度泛函理论研究
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第6期
论文作者:段永华1$2
文章页码:1844 - 1852
Key words:first principles; halogens; F; Cl; Mg (0001) surface; adsorption energy
摘 要:采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的第一性原理研究低覆盖度F和Cl原子在Mg(0001)表面的吸附特性,分析F和Cl原子吸附在(2×2)Mg(0001)表面不同吸附位置的稳定性,讨论F和Cl原子在Mg(0001)表面的吸附。计算结果表明,在低覆盖度下,洞位是最稳定吸附位;电荷布居和态密度表明,电子从Mg原子转移至吸附原子F和Cl,从而形成吸附键,使Mg原子和吸附原子之间的相互作用增强,Cl和Mg原子之间的相互作用弱于F和Mg原子之间的相互作用。
Abstract: The adsorption of low-coverage of F and Cl adatoms on the Mg (0001) surface was investigated using first-principles calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT). The stability of the (2 × 2) structures formed by halogen atoms adsorbed at different sites was determined. The difference between the adsorption of F and Cl on Mg (0001) surface was also discussed. The calculation results show that hollow sites are the energetically most favorable at the low-coverage. It can be concluded from the Mulliken charges and density of states that electrons transfer from the substrate Mg atoms to the adatoms, which leads to the formation of adsorbate bond and further causes the stronger interaction between Mg atom and adatom. The interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weaker than the interaction between F and Mg.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1844-1852
Yong-hua DUAN1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. Key Lab of Advanced Materials of Yuanan Province, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China
Received 27 May 2013; accepted 1 April 2014
Abstract: The adsorption of low-coverage of F and Cl adatoms on the Mg (0001) surface was investigated using first-principles calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT). The stability of the (2 × 2) structures formed by halogen atoms adsorbed at different sites was determined. The difference between the adsorption of F and Cl on Mg (0001) surface was also discussed. The calculation results show that hollow sites are the energetically most favorable at the low-coverage. It can be concluded from the Mulliken charges and density of states that electrons transfer from the substrate Mg atoms to the adatoms, which leads to the formation of adsorbate bond and further causes the stronger interaction between Mg atom and adatom. The interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weaker than the interaction between F and Mg.
Key words: first principles; halogens; F; Cl; Mg (0001) surface; adsorption energy
1 Introduction
As the lightest non-ferrous materials of the practical metals, magnesium alloys have been widely used in the fields of aerospace, automotive, electronic information and civil appliances. However, magnesium alloys have the highest chemical and electrochemical activities, which lead to them prone to electrochemical corrosion in the humid atmosphere and marine environment containing the halogens [1]. The electrochemical reaction on the magnesium surface is so fast that the atomic scale study on the magnesium surface is difficult to solve by experiments. First-principles calculations based on the density functional theory have been confirmed to be a powerful tool to accurately investigate the physical and chemical properties of metal and compound surfaces [2-5]. The calculations provide a possibility to explain and predict the physical properties of surfaces which are previously inaccessible by experiments. At present, the investigation of adsorption on magnesium surface in atomic scale is concentrated on the Mg (0001) surface and atoms or small molecules adsorption on the Mg (0001) surface [6,7]. At coverage 0.25 monolayer (ML), K atoms adsorption on the surface at FCC-hollow site is most favorable while a substitution of Na atom in place of one of the Mg surface atoms is energetically most favored [8,9]. As for H atoms and H2O molecule, H atoms adsorption at the FCC-hollow sites and H2O molecule adsorption at the on-top sites are most favorable, respectively [10-12]. The compressive (negative) strains facilitate the formation of the H-Mg-H trilayers, a precursor of the transition to magnesium hydride, due to the fact that the lattice constant of H-Mg-H trilayer is shorter than that of pure Mg [13]. At lower H absorption (less than one monolayer), H atoms prefer to adsorb at on-surface FCC sites, and the bonding strength increases with the absorption due to the enhanced hybridization between H and Mg substrates [14]. In the respect of oxygen atoms adsorption on the Mg (0001) surface, it is found that there is a negative dissociation barrier in the process of oxygen dissociation on Mg (0001) surface and oxygen monomer adsorption to Mg (0001) is demonstrated to be on subsurface [15-17].
Halogen atoms adsorption on simple metal surface is considered a model for understanding more complicated systems under acid conditions. The theoretical investigations of halogen atoms adsorption and co-adsorption on metals, such as Al and Si, have shown a variety of phenomena that halogen atoms can form strong ionic bonds with the metal atoms on the surface [18]; adatoms will induce reconstruction of the substrate surface [19]; the halogen atoms are absorbed on the surface with no energy barrier [20]. Adsorption on magnesium surfaces is far less studied experimentally, to our knowledge. No atomistic first-principles calculations for halogen/magnesium system have been performed so far.
In this work, low-coverage (2 × 2) structures of fluorine and chlorine adlayers on Mg (0001) surface are investigated in order to obtain the adsorption position of halogen atoms and the interaction between halogen atoms and the Mg surface. The results are useful to further study the corrosion mechanism of Mg alloy under the environment containing halogens.
2 Computational
We applied first-principles methods based on the density functional theory (DFT) implemented in CASTEP (Cambridge sequential total energy package) code [21]. Ultrasoft pseudo-potentials were employed to represent the interactions between ionic core and valence electrons. The exchange-correlation energy was described by the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) of PBE scheme [22].
The Monkhorst-Pack scheme was used for k-point sampling in the first irreducible Brillouin zone (BZ). For Mg primitive cell, we used 11 × 11 × 1 k-point mesh and the maximum cutoff energy was 400.0 eV for plane wave expansions after convergence tests. The optimized lattice parameters of Mg were a=0.3212 nm, c/a=1.621, which agreed well with the experimental values (a=0.321 nm, c/a=1.624) [23]. Based on the optimized Mg cell, we calculated a series of Mg (0001) surface slabs consisting of 1-9 atomic layers and vacuum region of 0.5-2.5 nm in order to obtain reasonable parameters of the slab. For Mg (0001) surface, we used 7 × 7 × 1 k-point mesh and the maximum cutoff energy was 400 eV after convergence tests (5 × 5 × 1, 6 × 6 × 1, 7 × 7 × 1, 8 × 8 × 1 k-point meshes and 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 eV cutoff energies were selected in the convergence tests; the total energy in the case of 7 × 7 × 1 k-point mesh and 400 eV cutoff energy is stabilized ). The difference of the surface energies of the 7, 8 and 9 layers Mg (0001) surfaces with 1.5 nm slab is less than 0.08 J/m2 and the relaxed 7-layer Mg (0001) surface is more stable, which shows that the suitable vacuum layer thickness and atomic layer number are 1.5 nm and 7 for Mg (0001) surface, respectively.
Four topmost Mg atomic layers fully relaxed while three lowermost Mg atomic layers were fixed in the 7-layer Mg (0001) surface slab with the vacuum thickness of 1.5 nm. The calculated relaxations for the four topmost atomic layers gave expansion of 1.98%, 1.02%, -0.36% and 0.004%, respectively. The three upper layers in our calculated four topmost atomic layers agreed well with the three topmost layers experimentally measured values of 1.9%, 0.8% and -0.4% at 100 K [24]. We employed low-coverage of 0.25 monolayer of fluorine and chlorine using a (2 × 2) Mg (0001) surface structure (Fig. 1). As shown in Fig. 1, F and Cl atoms were adsorbed on (2 × 2) Mg (0001) surface at four different adsorption sites which are on-top, FCC-hollow, bridge, and HCP-hollow, respectively. Adatoms and atoms of four topmost Mg layers were relaxed until the forces on all atoms were less than 0.001 eV/nm.

Fig. 1 Adsorption sites of Mg (0001) surface with 2 × 2 surface unit cell
The adsorption energies of different on-surface atoms sites are calculated from the following difference of total energies:
Ead=-(EHal/Mg(0001)-EMg(0001)-EHal) (1)
where Hal denotes halogen (F or Cl); Ead is the adsorption energy of halogen adsorbed on Mg (0001) surface; EHal/Mg (0001) and EMg (0001) are the total energies of the adsorbate covered Mg (0001) slab and a clean relaxed Mg (0001) slab, respectively; EHal is the total energy of a free halogens atom. Positive adsorption energy of absorption system corresponds to an exothermic process and a more stable halogen/Mg(001) surface than the clean Mg (0001) surface. Greater adsorption energy means a stronger adsorption action of halogen atoms-surface and a more stable adsorption structure.
The work function is the important properties of the metal surface. The work function Φ is a measurement of the minimum energy required to extract an electron from the surface of a solid and is defined as [25]
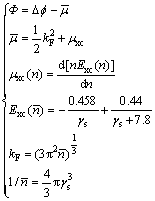 (2)
(2)
where Δf is the change in electrostatic potential across the dipole layer created by the spilling out of electrons on the surface and the value for Mg is 3.67 [25];  is the chemical potential of the electrons in the bulk metal reative to the mean electrostatic potential; kF is the bulk Fermi wave number; μxc is the exchange and correlation part of the chemical potential of an infinite uniform electron gas of density
is the chemical potential of the electrons in the bulk metal reative to the mean electrostatic potential; kF is the bulk Fermi wave number; μxc is the exchange and correlation part of the chemical potential of an infinite uniform electron gas of density 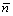 ; Exc is the exchange and correlation energy per particle of the uniform gas; γs is the Wigner-Seitz radius and γs of Mg is 2.65 [25].
; Exc is the exchange and correlation energy per particle of the uniform gas; γs is the Wigner-Seitz radius and γs of Mg is 2.65 [25].
The change in work function (△Φ) can well describe charge transfer caused by the adsorption. Based on the Helmholtz equation, the relationship between dipole moment μD and ΔΦ is [26]
μD=(12π)-1AΔΦ/θ (3)
where A is the surface area of the (1 × 1) Mg(0001) with the unit of  2; θ is the coverage and θ=0.25 in this work.
2; θ is the coverage and θ=0.25 in this work.
The effective radius of the adsorbate is calculated as follows:
rad=dnn–rMg (4)
where dnn is the adsorbate bond length and rMg is the metallic radius of bulk Mg (1.56  ) [27].
) [27].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 F on Mg (0001) surface
3.1.1 Adsorption energy
The calculated adsorption energies of F atom at different adsorption sites are listed in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1, the differences of adsorption energies of F atom in FCC-hollow, HCP-hollow and bridge sites are very small and remain within 0.18 eV. For low-coverage considered here, the adsorption energies of the FCC-hollow and HCP-hollow sites are similarly equal to 6.54 eV. The adsorption energy of F atom in the FCC-hollow or HCP-hollow sites is the highest while that in the on-top site is the lowest, indicating that the two hollow sites should be most favorable and the least favored adsorption position is the on-top site at 0.25 monolayer coverage. It is noted that the adsorption energy decreases with the F coordination number CF in FCC-hollow (CF=3), HCP-hollow (CF=3), bridge (CF=2), and on-top (CF=1) site. For the hollow-site adsorption of F atom, the F atom will interact with three Mg atoms and the adsorption energy is the sum of the interactions of one F atom and three Mg atoms. The interaction atom number of Mg is reduced to 2 and 1 when F atom adsorbs at bridge and on-top sites, respectively, indicating that the adsorption energy decreases due to the reduced interacted atom number.
Table 1 Adsorption energy, adsorbate height zad, bond length dnn, change in work function △Φ, dipole moment μD and adatom effective radius rad for F atom
3.1.2 Geometric structure
The adsorbate height which is defined as a vertical distance between the adsorbate and the average position of the top Mg atomic layer, decreases followed by the order: hollow, bridge and on-top structures from Table 1. The calculated adsorption energies of F in FCC-hollow and HCP-hollow sites are similar to the others. This means that their vertical distances of the adsorbate to the surface (zad) should be nearly the same. Both of the adsorbate heights of F atom in FCC and HCP-hollow site are 0.91  . The bond length of F adsorbed in the FCC-hollow and HCP-hollow site on Mg (0001) surface is 2.09
. The bond length of F adsorbed in the FCC-hollow and HCP-hollow site on Mg (0001) surface is 2.09  . For the bridge and top-site adsorption, the bond lengths are 1.98
. For the bridge and top-site adsorption, the bond lengths are 1.98  and 1.83
and 1.83  , respectively, and they are smaller than hollow-site adsorption which is related to the adsorption site. In hollow-site adsorption the F atom is located upon the center of the triangle formed by three Mg atoms in uppermost Mg atomic layer, while the F atoms are located upon the center of two Mg atoms and one Mg atom in the bridge and top sites, respectively. Although the adsorbate moves close to the uppermost Mg atomic layer, the adsorbate height in hollow-site adsorption is still higher than that in bridge and top sites. So, the bond length in hollow-site adsorption is larger than that in bridge and top sites.
, respectively, and they are smaller than hollow-site adsorption which is related to the adsorption site. In hollow-site adsorption the F atom is located upon the center of the triangle formed by three Mg atoms in uppermost Mg atomic layer, while the F atoms are located upon the center of two Mg atoms and one Mg atom in the bridge and top sites, respectively. Although the adsorbate moves close to the uppermost Mg atomic layer, the adsorbate height in hollow-site adsorption is still higher than that in bridge and top sites. So, the bond length in hollow-site adsorption is larger than that in bridge and top sites.
As an important property of the metal surface, the calculated work function of the clean Mg (0 0 0 1) surface is 3.33 eV which is slightly smaller than the experimental result of 3.66 eV [28]. Generally, the work function calculated by GGA method is slightly smaller than that by the LDA method or experimental value [29]. With adsorption of F atom, the work function and the dipole moment per adatom increase. The reason for the increase of the work function with adsorption of F atom is that, when the F atom adsorbed on the Mg (0001) surface, electrons transfer between the Mg surface atoms and F atom, causing that the F adatom has negative charges and Mg (0001) surface possesses positive charges, thereby forming a surface dipole moment. The largest increase of work function is noticed for adsorption at the on-top site, while the smallest increase occurs at the FCC-hollow site which is approximately 1/20 that at the on-top site.
The ionic binding between F and Mg atoms obviously shortens the effective atomic radius of F (rF) which is 0.57  [30]. Since a strong ionic bond is formed between Mg atom and F atom, the two atoms close each other under the binding force, resulting in the effective atomic radius of F atom decreasing. The effective radius of the adsorbate varies from 0.53
[30]. Since a strong ionic bond is formed between Mg atom and F atom, the two atoms close each other under the binding force, resulting in the effective atomic radius of F atom decreasing. The effective radius of the adsorbate varies from 0.53  at FCC-hollow site to 0.27
at FCC-hollow site to 0.27  at on-top site.
at on-top site.
The difference of changes in the middle two Mg atomic positions within the same layer in Fig. 2 is less than 0.01  , and thus the lateral Mg atoms are not considered in this work. In response to the presence of the adsorbate atom, the three atoms of each relaxed layer of Mg (0001) surface move vertically together with the corresponding adsorbate atom. The rumples of Mg layers when F atom adsorbed at different adsorption sites on the p (2 × 2) Mg (0001) surface are shown in Fig. 2. The adsorption in different adsorption sites leads the interlayer distance to change. The interlayer distance refers to the average position of the relaxed Mg atomic layer.
, and thus the lateral Mg atoms are not considered in this work. In response to the presence of the adsorbate atom, the three atoms of each relaxed layer of Mg (0001) surface move vertically together with the corresponding adsorbate atom. The rumples of Mg layers when F atom adsorbed at different adsorption sites on the p (2 × 2) Mg (0001) surface are shown in Fig. 2. The adsorption in different adsorption sites leads the interlayer distance to change. The interlayer distance refers to the average position of the relaxed Mg atomic layer.
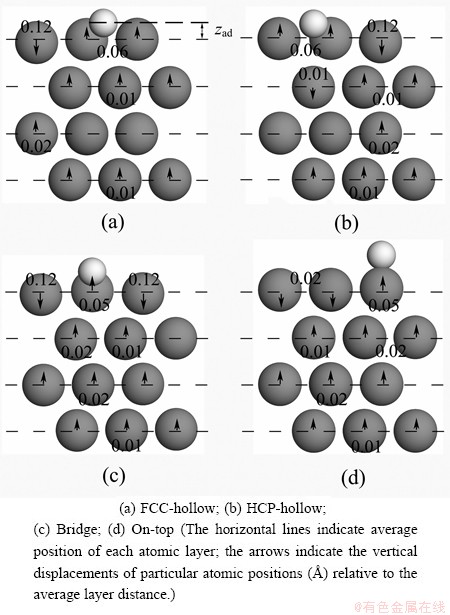
Fig. 2 Rumpling pattern for different adsorption positions of F atom on Mg (0001) surface
For F adsorption at FCC- and HCP-hollow sites, all interlayer separations contract and there are two nearest neighbor and one secondary neighbor Mg atoms on the topmost layer around the F adatom as shown in Fig. 2. The interaction between F adatom and Mg atoms is different, that is, the two nearest neighbor Mg atoms are pushed up by 0.06  while the secondary neighbor Mg atom is pushed down by 0.12
while the secondary neighbor Mg atom is pushed down by 0.12  . By calculating the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD), the distances of d12, d23, d34 and d45 (the changes of two adjacent Mg atomic layers by relaxation) are contracted slightly by 3.02%, 0.39%, -0.39% and 0.39%, respectively.
. By calculating the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD), the distances of d12, d23, d34 and d45 (the changes of two adjacent Mg atomic layers by relaxation) are contracted slightly by 3.02%, 0.39%, -0.39% and 0.39%, respectively.
F adsorption at the bridge site leads to a decrease of the topmost interlayer as well and the contraction is 0.01  smaller than that of FCC- or HCP-hollow. The distance of d12 contracts by 2.64% while the distance of d23 is unchanged. For the on-top site adsorption, the uppermost layer increases by 1.13% (0.03
smaller than that of FCC- or HCP-hollow. The distance of d12 contracts by 2.64% while the distance of d23 is unchanged. For the on-top site adsorption, the uppermost layer increases by 1.13% (0.03  ) and there is a very small expansion of d34 and d45.
) and there is a very small expansion of d34 and d45.
It also can be seen from Fig. 2, different from the Na and K adsorption on the Mg (0001) surface [8], in all considered cases the F atom pushes up the nearest Mg atoms while the furthest away Mg atoms are pushed down. The changes in the relaxation of deeper layers are much smaller.
3.1.3 Net Mulliken charge
The formation of the Mg (0001) surface induces the changes in the charges of surface atoms with respect to bulk Mg. According to the Mulliken population analysis [31], we obtained the atomic charges on the clean Mg (0001) and F/Mg (0001) surface. The results are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Net Mulliken charges for F atom adsorption on Mg (0001) surface
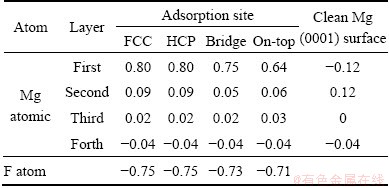
For the clean Mg (0001) surface, the charges of the first, second, third, and forth Mg atomic layers are -0.12, 0.12, 0, and -0.04, respectively. When F atom is adsorbed on the (0001) surface, the charges on the surface are distributed again. It is obvious that the charge of the first Mg atomic layer increases obviously, while the charges of the second and third Mg atomic layers are slight and the charge of the forth Mg atomic layer is unchanged from Table 2. This indicates that the electron charge mainly transfers from the uppermost Mg atomic layer to the adatoms. For the hollow-site adsorption of F atom, the charge of the first Mg atomic layer is 0.80, while the charges reduce to 0.75 and 0.64 in the bridge and top sites adsorption, respectively. The change trend in charge is similar to that in adsorption energy. The negative charges of F atoms also indicate the ionic character of F—Mg bond.
3.1.4 Density of states
The partial density of states (PDOS) for the clean Mg (0001) surface and F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface are shown in Fig. 3 (a). For the clean Mg (0001) surface, the PDOS is composed of one evident band ranging from -7 eV to Fermi level which is dominated by Mg 3s and 2p orbitals.
In the case of F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, the hybridization arises between F 2p orbital and Mg 3s orbital from -7 eV to the Fermi level. The Mg 3s orbital is full-filled with electrons while the F 2p orbital is unfilled, which lead to electrons transfer from Mg 3s orbital to F 2p orbital and final form adsorbate bonds. For F adsorption in FCC- or HCP-hollow, the hybridization between F 2p orbital and Mg 3s orbital from -7 eV to the Fermi level causes the band of isolated F atom broadening, further forming bonding state and anti-bonding state from -7 eV to Fermi level, as shown in Fig. 3 (b). The difference between the DOS of the clean and the adsorbate-covered surfaces (ΔN) (ΔN>0 means bonding states mentioned by TODOROVA et al [32]) clearly reveals the F-Mg bonding and anti-bonding states. For F atom adsorption at hollow site, the bonding state is mostly occupied by electrons in Fig. 3(b), indicating that the interaction between F and Mg atoms is strong and the adsorption energy of F adsorption in hollow-site is up to 6.54 eV. For the bridge-site adsorption, the bonding state and anti-bonding state move close to Fermi level. Moreover, the peak intensity of bonding state is weakening, revealing that the interaction between F and Mg atoms is weaker than that between FCC- and HCP-hollow sites. The adsorption energy of F adsorption at bridge site reduces to 6.36 eV. The adsorption of F at on-top site leads to an obvious change in DOS that the peak intensity of bonding state is the weakest and not evident. This indicates that the interaction between F and Mg atoms is the weakest with the adsorption energy dropping to 5.49 eV at on-top site.
3.2 Cl on Mg (0001) surface
3.2.1 Adsorption energy
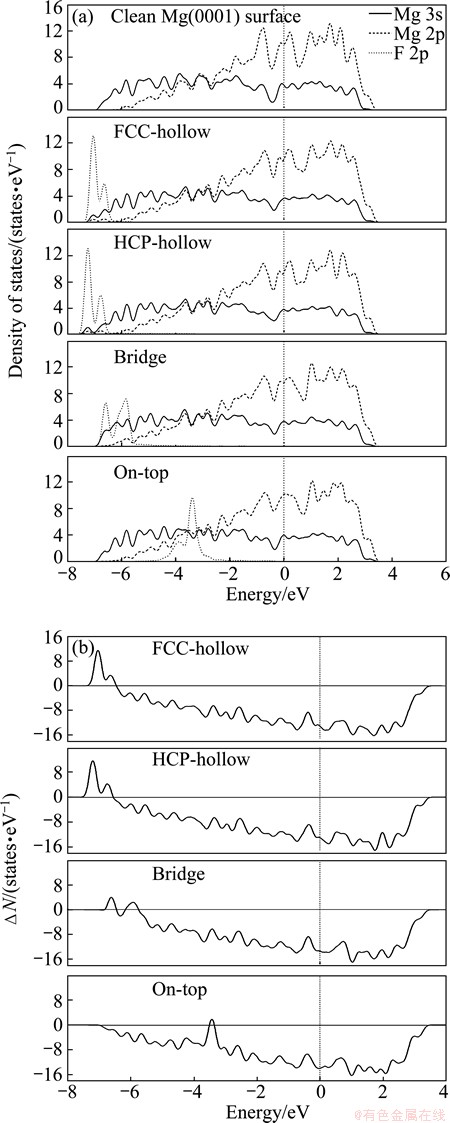
Fig. 3 Partial density of states of clean Mg (0001) surface and F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface at different adsorption sites (a) and corresponding differences of DOS (b)
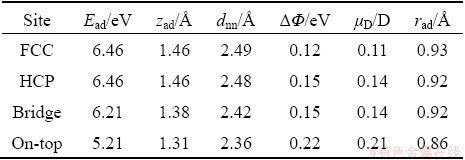
In order to obtain a chemical trend for different halogens, a similar series of calculations were repeated for chlorine adsorbate. The calculated adsorption energies of Cl atoms adsorbed at different sites are shown in Table 3. Similar to F atoms, the two more favored positions for Cl atoms adsorption are FCC- and HCP-hollows. Compared with the adsorption of F atom, the adsorption energy of Cl atom at corresponding adsorption site is smaller than that of F atom, and the larger radius of Cl (steric) and less electronegativity compared with F can be attributed to the difference of Mg—Cl and Mg—F, indicating that the interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weaker than that between F and Mg atoms. The decrease trend of adsorption energy with the Cl coordination number CCl is followed by 3 (FCC-hollow), 3 (HCP-hollow), 2 (bridge), and 1 (on-top).
Interestingly, compared with the adsorption of F atom, the adsorption energy of Cl atom at corresponding adsorption site is smaller than that of F atom, indicating that the interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weaker than that between F and Mg atoms. It also reveals that the binding between F atom and Mg (0001) surface is stronger than Cl atom. This suggests that MgF2 protective film is easier to form and more stable than MgCl2 on Mg surface, and further the corrosion velocity of Mg alloy in F-containing solution is smaller than that in Cl-containing solution. It is agreement with the corrosion behaviors of Mg-Li alloy [1] and AZ91D magnesium alloy [33] in F, Cl, Br and I halide solutions, which increases in the order of F atom adsorbed on the surface is more negative than that of Cl atom. The more negative charge also indicates that the bond length of F-Mg is shorter than that of Cl-Mg as listed in Table 1 and Table 3.
Table 3 Adsorption energy, adsorbate height zad, bond length dnn, change in work function △Φ, dipole moment μD and adatom effective radius rad for Cl atom
3.2.2 Geometric structure
The height of adsorbed Cl atom, bond length, changes in work function, dipole moment and effective radius are presented in Table 3. At both F and Cl on-top sites adsorption, the work function changes and dipole moments are the largest among all four adsorption sites considered. For a bridge site the values of △Φ and μD are the second larger followed by HCP-hollow site, and FCC-hollow site possesses the least values.
The degeneracy in the adsorption energy of the Cl adsorbate in hollows, bridge and top sites is also reflected in the corresponding geometric structures. As can be seen in Table 3, the adsorbate height is almost the same for hollows, bridge and on-top sites with a difference within 0.15  . The adsorption height and bond length of Cl adsorption on Mg (0001) surface are larger than those of F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, while the adsorption energy is opposite. This reveals that the adsorption affinity of F atom on Mg (0001) surface is larger than that of Cl atom in the corresponding adsorption position. For Cl/Cu (111) system the adsorption height and bond length for FCC-hollow are 1.86
. The adsorption height and bond length of Cl adsorption on Mg (0001) surface are larger than those of F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, while the adsorption energy is opposite. This reveals that the adsorption affinity of F atom on Mg (0001) surface is larger than that of Cl atom in the corresponding adsorption position. For Cl/Cu (111) system the adsorption height and bond length for FCC-hollow are 1.86  and 2.144
and 2.144  , respectively [34]. Generally, for Cl/Mg (0001) system the adsorption height for FCC-hollow position is lower by about 0.4
, respectively [34]. Generally, for Cl/Mg (0001) system the adsorption height for FCC-hollow position is lower by about 0.4  than that for Cl/Cu(111) system. The bond lengths for Cl/Mg (0001) and Cl/Cu (111) systems are very similar. It is the longest for FCC-hollow and the shortest for on-top site.
than that for Cl/Cu(111) system. The bond lengths for Cl/Mg (0001) and Cl/Cu (111) systems are very similar. It is the longest for FCC-hollow and the shortest for on-top site.
The effective radius of Cl adsorbate depending on the corresponding site is bigger than that for F/Mg (0001) system. According to the adsorption energy, absorption height and bond length, the ionic binding between F and Mg atoms is larger than that between Cl and Mg atom. The atomic radii of F and Cl atoms are 0.57  and 0.97
and 0.97  [35], respectively; the effective radii of F and Cl atoms are 0.53
[35], respectively; the effective radii of F and Cl atoms are 0.53  at 0.93
at 0.93  at FCC-hollow site adsorption, respectively. The effective radii of F and Cl atoms decrease by 6.49% and 4.54%, respectively. The reported values of effective radius for K/Mg (0001) and Na/Mg (0001) [8] are larger than those for F/Mg (0001) and Cl/Mg (0001). This is due to a larger atomic radius of K and Na compared with F and Cl.
at FCC-hollow site adsorption, respectively. The effective radii of F and Cl atoms decrease by 6.49% and 4.54%, respectively. The reported values of effective radius for K/Mg (0001) and Na/Mg (0001) [8] are larger than those for F/Mg (0001) and Cl/Mg (0001). This is due to a larger atomic radius of K and Na compared with F and Cl.
Similar to the F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, the variations in the average interlayer distance are limited to the uppermost layer. For the Cl/Mg (0001) system the model of Mg atomic layer relaxations is different for each layer. Both F and Cl adsorptions at FCC-hollow site (Fig. 2(a) and 4(a)) cause the largest rumpling of the uppermost layers. From Fig. 4, Cl adsorption in FCC-hollow causes the nearest Mg atoms to push up by 0.06  while the furthest away Mg atom to push down by 0.16
while the furthest away Mg atom to push down by 0.16  . The rumpling of the uppermost Mg atomic layer is the largest (0.22
. The rumpling of the uppermost Mg atomic layer is the largest (0.22  ) at the considered sites, followed by HCP-hollow (0.17
) at the considered sites, followed by HCP-hollow (0.17  ), bridge and on-top sites (0.14
), bridge and on-top sites (0.14  ). Although the contractions of deeper layers are slightly increased or decreased, the changes in the relaxation of deeper layers are still much smaller relative to the uppermost layer.
). Although the contractions of deeper layers are slightly increased or decreased, the changes in the relaxation of deeper layers are still much smaller relative to the uppermost layer.
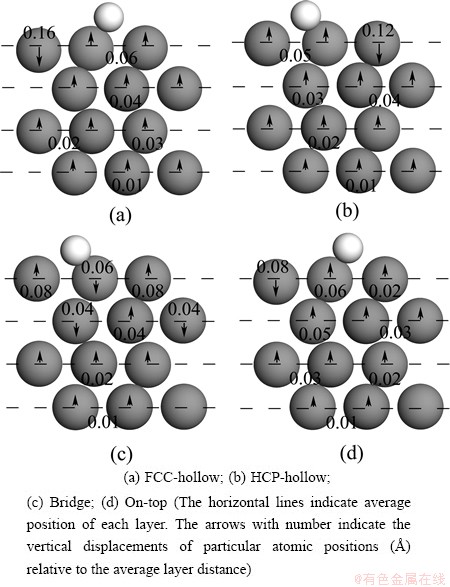
Fig. 4 Rumpling pattern for different adsorption positions of Cl atom on Mg (0001) surface
3.2.3 Net Mulliken charge
As the same as F adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, the charge of the first Mg atomic layer in the hollow-site adsorption of Cl atom possesses the largest value followed by the bridge and top sites (Table 4). However, the electronegativity of F (3.98) is greater than that of Cl (3.16) [36], resulting in the fact that F atom obtains electrons from Mg atom easier than Cl atom when these two halogens adsorbed on Mg (0001) surface. So the charge of F atom adsorbed on the surface is more negative than that of Cl atom. The more negative charge also indicates that the bond length of F-Mg is shorter than that of Cl-Mg as listed in Table 1 and Table 3.
Table 4 Net Mulliken charges for Cl atom adsorption on Mg (0001) surface
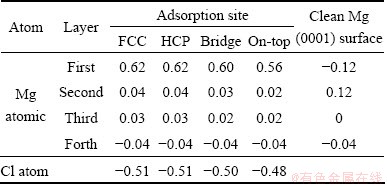
3.2.4 Density of states
Figure 5(a) shows the partial density of states (PDOS) for the clean Mg (0001) surface and Cl adsorption on Mg (0001) surface. Similar to the F absorbate, for Cl adsorption on Mg (0001) surface, the hybridization from -6.4 eV to Fermi level between the full-filled Mg 3s orbital and the unfilled Cl 3p orbital leads to forming adsorbate bonds. From Cl adsorption in FCC- and HCP-hollows, bridge to on-top sites, the bonding state moves to Fermi level as shown in Fig. 5(b). The peak intensity of bonding state decreases and the area of bonding state reduces, revealing that the interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weakening and the weakening trend is FCC-hollow, HCP-hollow, bridge and on-top sites. Moreover, PDOS of the Cl 3p orbital below the Fermi level were also analyzed. It is found that the bonding electron numbers of the Cl 3p orbitals at FCC- and HCP-hollows, bridge, and on-top sites are 5.833, 5.830, 5.801 and 5.799 between -6.4eV and the Fermi level, respectively. Larger bonding electron number corresponds to stronger charge interaction [37], that is, the stability of adsorption structure should be more stable. Hence, the adsorption energy of Cl adsorption in FCC-hollow is 6.46 eV and reduces to 5.21 eV in on-top site.
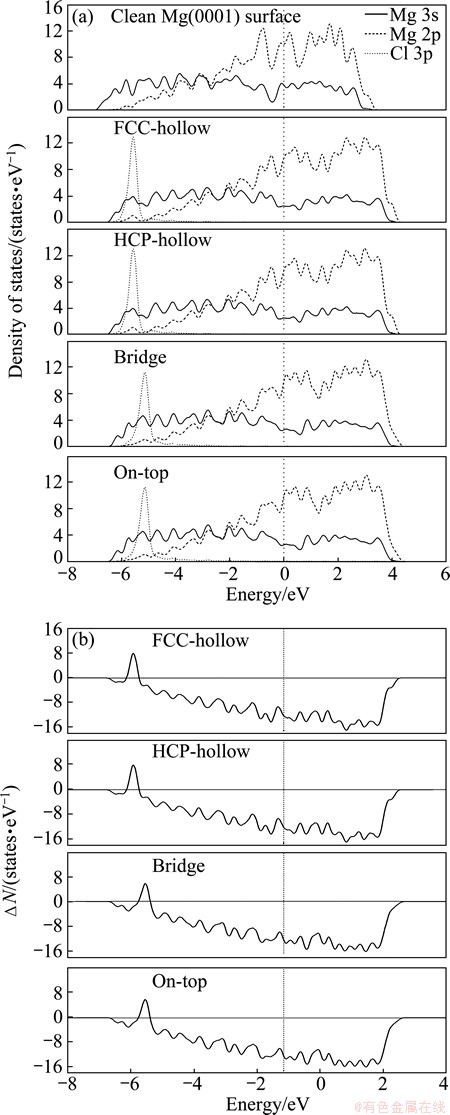
Fig. 5 Partial density of states of clean Mg (0001)surface and Cl adsorption on Mg (0001) surface at different adsorption sites (a) and corresponding differences of DOS (b)
4 Conclusions
1) The hollow site is the energetically most favorable for the F and Cl adatoms considered with the adsorption energies of 6.54 eV and 6.46 eV, respectively.
2) The adsorption energy of Cl atom at the corresponding adsorption site is smaller than that of F atom, which indicates that the interaction between Cl and Mg atoms is weaker than that between F and Mg atoms and the bond length of F—Mg is shorter than that of Cl—Mg.
3) It can be concluded from the Mulliken charges and density of states that the electron transfer from the substrate Mg atom to the adatom leads to the formation of adsorbate bond, which further causes the stronger interaction between Mg atom and adatom.
References
[1] MA Yi-bin, LI Ning, LI De-yu, ZHANG Mi-lin, HUANG Xiao-mei. Corrosion behavior of Mg-14-1Al-0.1Ce alloy in NaX (X=F, Cl, Br and I) solutions [J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2011, 23(6): 467-470. (in Chinese)
[2] WANG L, FANG L H, GONG J H. First-principles study of TiC (110) surface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 170-174.
[3] FANG L H, WANG L, GONG J H, DAI H S, MIAO D Z. First-principles study of bulk and (001) surface of TiC [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(5): 857-862.
[4] QIAN Y, HAMADA I, OTANI M, IKESHOJI T. Inhibition of water dissociation on a pitted Pt (111) surface: First principles study [J]. Catalysis Today, 2013, 202: 163-167.
[5] QIN Z, XIONG Z, QIN G, WAN Q. Behavior of aluminum adsorption and incorporation at GaN (0001) surface: First-principles study [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(19): 194307.
[6] CHEN M, CAI Z Z, YANG X B, ZHU M, ZHAO Y J. Theoretical study of hydrogen dissociation and diffusion on Nb and Ni co-doped Mg (0001): A synergistic effect [J]. Surface Science, 2012, 606(13): L45-L49.
[7] LILLEODDEN E. Microcompression study of Mg (0001) single crystal [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 62(8): 532-535.
[8] KIEJNA A, OSSOWSKI T, WACHOWICZ E. Alkali metals adsorption on the Mg(0001) surface [J]. Surface Science, 2004, 548(1): 22-28.
[9] OSSOWSKI T, KIEJNA A. Low-coverage K adsorption on Mg(0001) surface [J]. Surface Science, 2004, 566-568: 983-988.
[10] WU Guang-xi, ZHANG Jie-yu, WU Yong-quan, LIU Jing, CHOU Kou-chih. First-principles study of hydrogen adsorbed Mg (0001) surface [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metal, 2007, 17: 280-287. (in Chinese)
[11] LUO Zhi-cheng, ZHANG Guo-yin, LIANG Ting, LI Dan, ZHU Sheng-long. First-principles study on water adsops on Mg surface [J]. Journal of Shenyang Normal University: Natural Science, 2010, 28(2): 189-192. (in Chinese)
[12] WU G X, LIU S X, ZHANG J Y, WU Y Q, LI Q, CHOU K C, BAO X H. Density functional theory study on hydrogenation mechanism in catalyst-activated Mg (0001) surface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(2): 383-388.
[13] TANG J J, YANG X B, CHEN M, ZHU M, ZHAO Y J. First-principles study of biaxial strain effect on hydrogen adsorbed Mg (0001) surface [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(28): 14943-14949.
[14] JIANG T, SUN L X, LI W X. First-principles study of hydrogen absorption on Mg (0001) and formation of magnesium hydride [J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(3): 035416.
[15] FRANCIS M F, TAYLOR C D. First-principles insights into the structure of the incipient magnesium oxide and its instability to decomposition: Oxygen chemisorption to Mg (0001) and thermodynamic stability [J]. Physical Review B, 2013, 87(7): 075450.
[16] BUNGARO C, NOGUERA C, BALLONE P, KRESS W. Early oxidation stages of Mg(0001): A density functional study [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 79(22): 4433-4436.
[17] SCHRODER E, FASEL R, KIEJNA A. O adsorption and incipient oxidation of the Mg(0001) surface [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 69(11): 115431.
[18] WU Xiao-xia, WANG Qian-en, WANG Fu-he, ZHOU Yong-song. First-principles study on chemisorption of Cl on γ-TiAl(111) surface [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(10): 7278-7284. (in Chinese)
[19] ZHANG Rong, HUANG Kui-you, ZHANG Pan, CHEN Shu-han. Study on density functional theory of Cl- adsorption on Al(100) surface [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2010, 15(5): 433-438. (in Chinese)
[20] OKADA H, INAGAKI K, GOTO H, ENDO K, HIROSE K, MORI Y. First-principles molecular-dynamics calculations and STM observations of dissociative adsorption of Cl2 and F2 on Si(0 0 1) surface [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 515(2): 287-295.
[21] SEGALL M D, LINDAN P J D, PROBERT M J, PICKARD C J, HASNIP P J, CLARK S J, PAYNE M C. First-principles simulation: ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2002, 14(11): 2717-2744.
[22] MARLO M, MILMAN V. Density-functional study of bulk and surface properties of titanium nitride using different exchange- correlation functionals [J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(4): 2899-2907.
[23] AMONENKO V M, IVANOV V Y, TIKHINSKII G F, FINKELV A. X-ray study of solubility of impurities in beryllium [J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography, 1962, 14: 852-856.
[24] SPRUNGER P T, POHL K, DAVIS H L, PLUMMER E W. Multilayer relaxation of the Mg (0001) surface [J]. Surface Science, 1993, 297(1): L48-L54.
[25] LANG N D, KOHN W. Theory of metal surface: work function [J]. Physical Review B, 1971, 3(4): 1215-1223.
[26] LI W X, STAMPFL C, SCHEFFLER M. Oxygen adsorption on Ag(111): A density-functional theory investigation [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65: 075407.
[27] SONG G S, STAIGER M, KRAL M. Some new characteristics of the strengthening phase in β-phase magnesium–lithium alloys containing aluminum and beryllium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 371(1): 371-376.
[28] MICHAELSON H B. The work function of the elements and its periodicity [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(11): 4729-4733.
[29] LEUNG T C, KAO C L, SU W S, FENG Y J, CHAN C T. Relationship between surface dipole, work function and charge transfer: Some exceptions to an established rule [J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 68(19): 195408.
[30] GANDHI S R, BENZEL M A, DYKSTRA C E. Role of electron correlation and polarization functions in the energy difference between cis-and trans-1, 2-difluoroethylene [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1982, 86(16): 3121-3126.
[31] LIU D L, DENG J G, JIN Y Z, HE C. Adsorption of atomic oxygen on HfC and TaC(110) surface from first principles [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 261: 214-218.
[32] TODOROVA M, REUTER K, SCHEFFLER M. Oxygen overlayers on Pd (111) studied by density functional theory [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(38): 14477-14483.
[33] HEAKAL F El-TAIB, FEKRY A M, FATAYERJI M Z. Influence of halides on the dissolution and passivation behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy in aqueous solutions [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(5): 1545-1557.
[34] MATAI K, HASHIZUME T, LU H, JEON D, SAKURAI T. STM of the Cu(111)1 × 1 surface and its exposure to chlorine and sulfur [J]. Applied Surface Science, 1993, 67(1): 246-251.
[35] SCHNEIDER J, WOLFENSONO A, BRUNETTI A, de NUNESL A O. NQR and Raman spectroscopy study of-dichlorobiphenyl [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 1996, 8(21): 3909.
[36] SCHAFFER J P, SAXENA A, ANTOLOVICH S D, SANDERS T H, WARNER S B. The science and design of engineering materials [M]. Chicago: Irwin, 1995.
[37] FU C L, WANG X, YE Y Y, HO K M. Phase stability, bonding mechanism, and elastic constants of Mo5Si3 by first-principles calculation [J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(2): 179-184.
段永华1,2
1. 昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 昆明理工大学 云南省新材料制备与加工重点实验室,昆明 650093
摘 要:采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的第一性原理研究低覆盖度F和Cl原子在Mg(0001)表面的吸附特性,分析F和Cl原子吸附在(2×2)Mg(0001)表面不同吸附位置的稳定性,讨论F和Cl原子在Mg(0001)表面的吸附。计算结果表明,在低覆盖度下,洞位是最稳定吸附位;电荷布居和态密度表明,电子从Mg原子转移至吸附原子F和Cl,从而形成吸附键,使Mg原子和吸附原子之间的相互作用增强,Cl和Mg原子之间的相互作用弱于F和Mg原子之间的相互作用。
关键词:第一性原理;卤族元素;F;Cl;Mg(0001)表面;吸附能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51201079) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012Z099) supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Department of Education of Yunnan Province, China; Project (KKSY201251033) supported by the Scientific Research Foundation for Introduced Talents of KMUST, China
Corresponding author: Yong-hua DUAN; Tel: +86-871-65136698; E-mail: duanyh@kmust.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63262-3

