文章编号:1004-0609(2010)S1-s0641-06
不同变形量TA15钛合金的热处理行为
王玉会,李 艳,张旺峰,马济民
(北京航空材料研究院,北京100095)
摘 要:研究了TA15钛合金变形量大的d20 mm小棒材及变形量小的大锻件的热处理行为。结果表明:在750~920 ℃范围内,随着退火温度的升高,大锻件拉伸强度升高约100 MPa,小棒材拉伸强度先降后升,且升幅远小于大锻件的;920 ℃以上退火,二者强度都出现降低。随着退火温度的升高,小棒材中再结晶软化率先发挥作用,使拉伸强度降低;而830 ℃以上退火,β转变组织中次生α二次析出起到强化作用,二者抗拉强度均出现升高,但小棒材由于再结晶温度低,再结晶软化削弱了析出强化的作用。
关键词:TA15钛合金;热处理;变形程度;再结晶;析出强化
中图分类号:TG 146.23; TG 113.25 文献标志码:A
Heat treatment behavior of TA15 titanium alloy with different deformation degrees
WANG Yu-hui, LI Yan, ZHANG Wang-feng, MA Ji-min
(Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China)
Abstract: The heat treatment behavior of TA15 titanium alloys with different deformation degrees was studied with d20 mm bar and large forging as the representatives for large deformation and small deformation, respectively. The results show that tensile strength increment can be obtained to be 100 MPa for large forging. The tensile strength decreases and then increases for the bar, and the increment is far less than that of large forging when annealed at 750-920 ℃. Both tensile strengths decrease when annealed at temperature higher than 920 ℃. The decrease of the tensile strength for the bar is caused by the recrystallization softening effect with increasing the annealing temperature. The strengthening effect for the little bar and large forging is caused by the secondary phase precipitation from the transformed β above 830 ℃. The precipitation strengthening effect on the little bar is smaller than that of the large forging because of the recrystallization softening effect.
Key words: TA15 titanium alloy; heat treatment; deformation degree; recrystallization; precipitation hardening
TA15钛合金具有中等的室温强度、优良的高温性能和焊接性能,并可制成各种半成品,如棒材、板材、锻件、铸件及型材等,在航空、航天等领域得到广泛应用。该合金对应的俄罗斯牌号为BT20,按名义成分划归为近α型合金,采用的热处理制度为普通退 火[1-2]。随着需求的不断增加,锻件、棒材规格不断加大,为解决大规格棒材或大锻件强度余量不足的问题,有效的措施是把合金中α相和β相稳定元素含量取上限或中上限,其实际化学成分已落入α+β两相合金的范围[3-6]。
在工程实践中,不同的半成品(如小棒材、小锻件和大棒材、大锻件)变形量不同,甚至同一半成品(如大型复杂锻件)由于变形不均匀,不同部位的变形程度也存在差异。研究发现,不同变形量的半成品或变形量存在差异的半成品的不同部位,在同一温度下退火,有的强度高,有的强度则不足。变形程度不同,组织
与性能差异很大[7],因此,研究不同变形量的半成品的热处理行为,对挖掘材料潜力有重要的意义。本研究以大变形量的d20 mm小棒材和小变形量的大锻件(采用大规格棒材制成)作为典型代表,研究不同退火温度下的热处理行为及机理,从而为TA15钛合金热处理工艺的制定提供理论依据。
1 实验
实验用料取自d20 mm小棒材及d350 mm棒材制成的大锻件(投影面积超过0.78 m2),二者化学成分基本相同,见表1。热处理前d20 mm小棒材和大锻件的组织照片见图1。
本研究采用的热处理制度为750~950 ℃, 1 h,AC。热处理后加工成标准的拉伸试样,然后进行力学性能测试和组织观察,在Instron-4507实验机上测定试样的拉伸性能,在FEI Quanta600扫描电子显微镜上进行组织观察与分析。
表1 TA15钛合金半成品的主要化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of semi-finished product of TA15 alloy (mass fraction, %)

2 结果与分析
2.1 退火温度对拉伸性能的影响
图2给出了退火温度对小棒材及大锻件拉伸性能的影响规律。由图2可以发现:在750~920 ℃时,随着退火温度的升高,大型模锻件的强度呈上升趋势,其中抗拉强度σb增加约100 MPa,而屈服强度σ0.2在800 ℃开始下降,在840 ℃附近出现谷值;小棒材的强度呈现先降后升的规律,但升幅远小于大锻件的,且其屈服强度在830 ℃附近也出现微小的谷值。920

图1 TA15钛合金半成品退火前的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of semi-finished product of TA15 alloy before annealing: (a) d 20 mm bars; (b) Large forging

图2 退火温度对TA15钛合金半成品室温拉伸性能的影响
Fig.2 Effect of annealing temperature on room temperature tensile properties of semi-finished product of TA15 alloy: (a) Tensile strength; (b) Ductility
℃之后,小棒材及大锻件的强度均随退火温度的升高而下降,尤其是屈服强度有明显下降。在整个温度区间,小棒材的拉伸塑性随温度的升高变化不大,而大锻件的断面收缩率在920 ℃以后出现较大降幅。
2.2 退火温度对显微组织的影响
图3和图4给出了不同退火温度下小棒材及大锻件的显微组织(样品取自拉伸试样的螺纹部分)。小棒材的组织要比相应温度下的大锻件细小,且初生α相
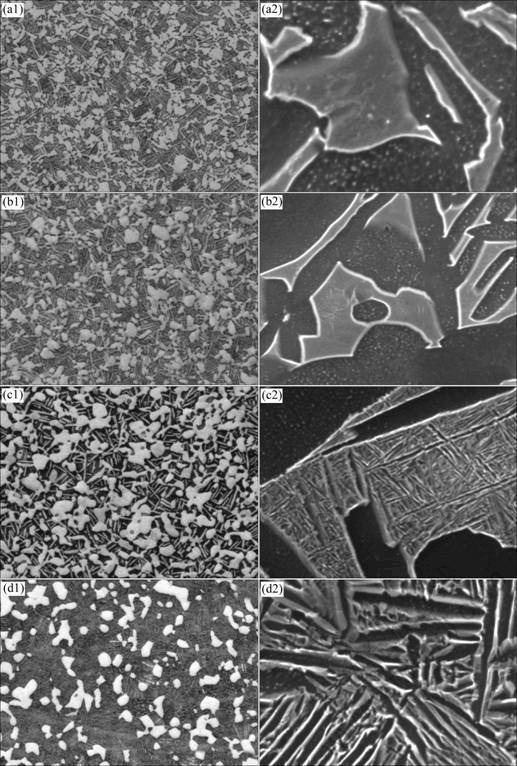
图3 小棒材不同温度退火后的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of little bar after annealing at different temperatures (holding time 1 h): (a1, a2) 800 ℃; (b1, b2) 830 ℃; (c1, c2) 900 ℃; (d1, d2) 950 ℃

图4 大锻件不同温度退火后的显微组织
Fig.4 Microstructures of large forging after annealing at different temperatures (holding time 1 h) : (a1, a2) 800 ℃; (b1, b2) 840 ℃; (c1, c2) 890 ℃; (d1, d2) 950 ℃
含量较多。二者均为典型的双态组织,并且都经历了β转变组织中次生α相析出、长大及粗化的过程。到达950 ℃时,小棒材及大锻件都产生了全新的β转变组织,如图3(d1)和4(d1)所示。
800℃退火时,在小棒材的β转变组织中尚观察不到明显的次生α相析出;当退火温度升高到830 ℃,其亚稳β相内局部析出细小的次生α相(见图3(b2));随着退火温度的进一步升高,亚稳β中细小、次生α相也相应出现局部析出增多、大量析出、析出长大的过程;达到900 ℃时,次生α相已明显长大(见图3(c2));达到950 ℃退火时,次生α相明显粗化(见图3(d2))。大锻件的情况类似,其次生α相局部析出、析出明显长大及粗化的温度分别为840 ℃(见图4(b2))、890 ℃(见图4(c2))及950 ℃(见图4(d2))。
3 讨论
本研究中TA15合金Mo当量已达3.4,实际上属于两相合金的范围。化学成分调整后的TA15合金在退火时除了发生回复和再结晶外,还会发生亚稳定β相的分解。回复和再结晶是一个软化过程,亚稳定β相分解析出弥散的α相是强化过程,所以退火半成品的性能在很大程度上取决于退火温度下这两种因素哪种起主导作用。并且随着退火温度的变化,这两种因素不是一成不变的,即在某个温度下强化起主导作用,而在另一个温度下可能软化起主导作用。
变形金属中的畸变能是再结晶的驱动力。小棒材变形量大,总畸变能高,能形成再结晶核心的区域很多,在830 ℃之前退火已发生充分的再结晶,使强度降低。对于大锻件,一般火次多、每火变形量小及冷却速度低等因素使得其再结晶温度明显高于小棒材的,在回复阶段亚稳定β相的分解已占主导地位,强度得到提高。在830~920 ℃时,小棒材和大锻件的亚稳β相中次生α相的析出强化均起到了主导作用。但是小棒材在830 ℃以后β析出强化带来的曲线升幅却远远小于大锻件的(见图2(a)),这主要是由于小棒材中再结晶软化作用大于大锻件中的,从而削弱了析出强化的作用。920 ℃以后退火,原本起强化作用的次生α相明显长大、粗化(见图3(d2),4(d2)),导致小棒材和大锻件的强度降低。总体来说,在整个温度区间,再结晶软化在小棒材的退火过程中一直发挥着至关重要的作用。
大锻件及小棒材在830~840 ℃附近出现屈服强度的谷值(见图2(a)),这可用亚稳β相分解来解释:分解过程可促使合金在较低应力下进行塑性变形,而引起屈服强度的急剧降低。800~840 ℃退火后,当最大量亚稳定β相固定下来时,大锻件的抗拉强度与屈服强度之差从800 ℃的88 MPa达到840 ℃的123 MPa,而小棒材的也从72 MPa增加到87 MPa。这种屈服强度出现谷值的现象普遍存在于两相合金的热处理过程,如BT9、BT14、BT25、BT28、BT33等合金的淬火 中[1]。
观察图3(d2)和4(d2)可以发现: 在950 ℃退火时,大锻件的初生α相含量已下降到约为10%,这正是大锻件在920 ℃以后断面收缩率ψ下降(见图2(b))的原因;而小棒材的初生α相含量始终在20%以上,塑性基本保持不变。可见,断面收缩率与初生α相含量有密切关系,这一结论与TC4的研究结果相似。对于TC4合金,当初生α相含量为20%~80%时,断面收缩率始终保持在40%以上;当初生α相含量少于20%时,断面收缩率开始下降[2]。
4 结论
1) 在750~920 ℃范围内,随着退火温度的升高,大锻件拉伸强度升高约100 MPa,d20 mm小棒材拉伸强度先降后升,且升幅远小于大锻件;920 ℃以上退火,二者强度都出现降低。
2) 在830~920 ℃退火,TA15合金d20 mm小棒材及大锻件亚稳定β相中次生α相的析出强化占主导地位, d20 mm小棒材的再结晶软化削弱了其析出强化作用。
3) d20 mm小棒材再结晶温度低,在整个温度区间再结晶软化一直发挥着重要作用。
REFERENCES
[1] 鲍利索娃 E A. 钛合金金相学[M]. 陈石卿译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1986: 120.
БΟΡИСВА E A. Metallography of titanium alloys [M]. CHEN Shi-qin, transl. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1986: 120.
[2] 王金友, 葛志明, 周彦邦. 航空用钛合金[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 1985: 208.
WANG Jin-you, GE Zhi-ming, ZHOU Yan-bang. Aeronautical titanium alloys [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1985: 208.
[3] 张旺峰, 曹春晓, 李兴无, 马济民, 朱知寿. β热处理TA15钛合金对力学性能的影响规律[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004, 33(7): 768-770.
ZHANG Wang-feng, CAO Chun-xiao, LI Xing-wu, MA Ji-min, ZHU Zhi-shou. Effect of β heat treatment on mechanical properties of TA15 titanium alloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(7): 768-770.
[4] FILIP R, KUBIAK K, ZIAJIA W. The effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties of two-phase titanium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 133: 84-89.
[5] FAN Rong-hui, ZHU Ming, HUI Song-xiao, LI De-fu, SHEN Jian. Influence of heat treatment on microsturcture and damage tolerance property in Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: s482-s485.
[6] 沙爱学, 李兴无, 储俊鹏. TA15钛合金的普通退火[J]. 稀有金属, 2003, 27(1): 213-215.
SHA Ai-xue, LI Xing-wu, CHU Jun-peng. Common annealing of TA15 alloy [J]. Rare Metals, 2003, 27(1): 213-215.
[7] ZHU Jing-chuan, WANG Yang, LIU Yong, LAI Zhong-hong, ZHAN Jia-jun. Influence of deformation parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA15 titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: s490-s494.
(编辑 杨 兵)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613803)
通信作者:王玉会; 电话: 010-62496627;E-mail: wyhnoah@126.com