文章编号:1004-0609(2011)05-1151-08
高砷难处理金精矿细菌氧化-氰化提金
杨 玮1, 覃文庆1, 刘瑞强2, 任允超3
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;2. 山东黄金矿业(莱州)有限公司精炼厂,莱州 261441;3. 山东黄金集团烟台设计研究工程有限公司,烟台 264006)
摘 要:通过在高砷金精矿中配入不同比例的低砷碳酸盐型金精矿,使其所含硫、砷及铁等主要矿物成分含量发生变化,研究给矿中铁砷摩尔比对难处理高砷金精矿细菌氧化-氰化浸出效果的影响。结果表明:含砷金精矿中铁砷摩尔比直接影响细菌预氧化的效果,同时也影响细菌的活性和溶液中铁砷摩尔比的变化,给矿中铁砷摩尔比越高,溶液中的铁砷摩尔比也越高,且随着给矿中铁砷摩尔比的增加,溶液中铁砷摩尔比的变化幅度加大,给矿中铁砷摩尔比介于4.6~5.2之间,有利于细菌预氧化和氰化浸出,铁、砷氧化率分别由6.14%和7.38%提高到89.90%和93.60%,金、银浸出率分别由64.18%和35.93%提高到97.78%和88.83%,较好地改善细菌氧化效果,稳定和优化细菌预氧化过程。
关键词:高砷难处理金精矿;细菌氧化;氰化提金
中图分类号:TF80 文献标志码:A
Extraction of Au from high arsenic refractory gold concentrate by bacterial oxidation-cyanidation
YANG Wei 1, QIN Wen-qing 1, LIU Rui-qiang 2, REN Yun-chao 3
(1. School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. The Refinery of Shandong Gold Mining Co., Ltd., Laizhou 261441, China;
3. Engineering Design & Research Co. Ltd., Shandong Gold Group, Yantai 264006, China)
Abstract: Through blending low arsenic carbonate gold concentrate with different ratios into high arsenic-containing gold concentrate and changing the content of major ores, such as sulfur, arsenic and iron, the effect of iron-arsenic molar ratio on the bacteria oxidating-cyaniding extraction from high arsenic-containing refractory gold concentrate was investigated. The result shows that the iron-arsenic mole ratio of arsenic-containing gold concentrate has direct effect on the bacteria oxidation, bacteria activity and iron-arsenic molar ratio in solution. High iron-arsenic mole ratio in feeding results in high iron-arsenic ratio in solution. With iron-arsenic molar ratio increasing, the iron-arsenic ratio increases, and the frequency of change accelerates. The iron-arsenic ratio ranging from 4.6 to 5.2 is helpful to bacteria oxidizing-cyaniding extraction, the oxidation ratios of iron and arsenic increase to 89.90% and 93.60% from 6.14% and 7.38%, respectively. The extraction rate of gold and silver increase to 97.78% and 88.83% from 64.18% and 35.93%, respectively. Choosing appropriate iron-arsenic molar ratio can effectively improve the bacterial oxidation, stabilizes and optimize the process of bacterial pre-oxidation.
Key words: high arsenic refractory gold concentrate; bacterial oxidation; cyaniding gold extraction
随着易处理黄金资源的日渐枯竭,难处理含金矿石成重要的可用资源,其处理技术也成为我国黄金生产发展的瓶颈。大多数矿石之所以难处理是因为金呈细粒或微细粒被包裹在硫化物中,在氰化过程中不能与氰化物接触[1]。高砷金矿是公认的难处理矿石,其中金绝大部分包裹在黄铁矿和毒砂中,难以与氰化物直接接触[2], 直接氰化的回收率低。 在我国,难选冶含砷金矿占相当大的比例,砷为氰化浸金的主要干扰元素之一,金矿石中砷的原生矿物是毒砂,而大多数难浸金精矿中的主要砷矿物也是毒砂[3]。这类金精矿采用机械磨矿等普通方法很难使金颗粒解离,因此,在浸金前必须进行预处理,目前预处理的方法主要有培烧、加压氧化和细菌氧化3大技术。细菌氧化预处理技术因具有成本低、能耗小、污染少且设备简单易于操作等特点而更具有竞争力[4-7],越来越受到人们的关注。
生物提金工艺利用氧化亚铁硫杆菌,氧化黄铁矿和毒砂等金属矿物,使被矿物包裹的金颗粒裸露,能充分与浸金溶剂接触而有利于浸出,可使金的回收率大幅提高,但影响生物提金的因素很多,归结起来主要有3类:生物因素、矿物因素和工艺因素[8]。在矿物因素中,矿物含砷量的大小直接影响细菌氧化的效果(目前金精矿含砷的高低并没有统一划分标准,本文作者结合国内外主要金精矿的细菌氧化处理厂生产实际,界定含砷量在8%以上的为高砷金精矿),对于含砷量高的原料,细菌氧化也有其局限性,因此,有关学者针对高砷金精矿的细菌氧化-氰化提金开展大量的研究工作,包括浸矿机理、菌种筛选驯化、核心反应器及工艺条件等方面。如金世斌等[9]对金精矿生物氧化过程中砷的氧化行为研究后指出,生物氧化过程中毒砂中砷主要被Fe3+氧化,是间接作用的生物氧化过程,氧化液中As3+含量与试样的砷含量有关;杨洪英等[10-11]研究氧化亚铁硫杆菌SH-2T氧化毒砂的机理,并采用HQ20211嗜热菌对含砷11.78%金精矿的氧化预处理, 金的回收率大大提高;罗志雄等[12]对中度嗜热嗜酸铁氧化菌MLY和嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans,At.f ) 氧化处理含砷金精矿的机理及浸矿效果进行了研究;戴红光[13]研究用中温菌预氧化-氰化浸出湖北某难浸高砷高硫金精矿;柳建设等[14]设计了实验室规模的气升式生物反应器,用于高砷难处理金精矿的细菌氧化预处理;崔日成等[15]研究了pH 值对浸矿细菌的活化以及金精矿脱砷的影响;佟琳琳等[16]通过不同矿浆浓度的细菌氧化预处理实验, 发现含砷金精矿细菌氧化渣的金浸出率随着矿浆浓度的增大而降低;李万全等[17]和李育林等[18]研究了含砷难处理金精矿在不同磨矿细度、细菌接种量、氧化时间、氧化温度及通气量工艺条件下的预氧化效果,但目前尚未见通过改变给料中各种矿物成分的配比来提高难处理高砷金精矿细菌氧化-氰化浸出效果的系统研究。本文作者根据原料中硫、砷及铁等主要成分和黄铁矿及毒砂等主要矿物的不同,考察给矿及溶液中的砷铁摩尔比对河北某高砷金精矿的细菌预氧化及氰化浸出过程的影响,为指导生产实践提供操作依据。
1 实验
1.1 矿样
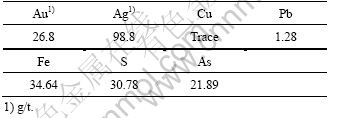
试验用矿样取自河北某高砷矿,该矿石中金属矿物主要为黄铁矿、毒砂、方铅矿、磁黄铁矿及少量的黄铜矿、闪锌矿、黑钨矿、辉锑矿等。脉石矿物主要为石英,其次为绿泥石、斜长石、云母、方解石和磷灰石等。主要载金矿物为黄铁矿、毒砂和石英,金粒的嵌存状态主要为赋存于黄铁矿及石英中的包裹金和赋存于黄铁矿、毒矿及石英的晶隙间的晶隙金,且多与毒砂连生。矿样的主要元素化学成分分析结果如表1所列。从化学分析可以看出,该矿砷、铁、硫的含量比较高,占87.31%,其中硫化物含量近30%,属于典型的高砷高硫金精矿。
表1 高砷金精矿化学成分分析
Table 1 Chemical composition in high arsenic gold concentrate (mass fraction, %)
1.2 菌种
试验用菌种TCJ采自山东某黄金冶炼企业,该组合菌种开始最高耐砷浓度为12 g/L,在生产中要求进料矿浆浓度为20%,含砷最好不超过6%,经过企业几年来的运行及驯化,该菌种的耐砷能力可以达到15 g/L。
1.3 试验方法
细菌氧化试验在5 L搅拌氧化槽中进行,采用莱宁A1000搅拌桨,通过DRZ-5型实验室细菌氧化反应罐夹套加热温度控制器进行温度控制,通过ZW-0.6/7立式空气压缩机、2 M气瓶、自力式压力调节阀和LZB-10型玻璃转子流量计进行充其量的控制。
细菌氧化试验基本条件如下:磨矿细度小于38 μm占86%,矿浆浓度为10% ,温度为40 ℃,充气量为0.4 m3/h,搅拌速度为900 r/min,用浓硫酸调矿浆pH值为2.0,当pH值稳定后加入营养物和接种物,接种物取自现场氧化槽溢流矿浆静置后的固体沉淀物,加入量为50 g,营养物加入量为硫酸铵2 g、磷酸氢二钾1 g、硫酸镁1 g。
试验中用上海精科雷磁仪器厂生产的pHB-4型便携式酸度计测量浸出体系的pH 值,用甘汞参比电极和金属铂电极测定浸出体系的氧化还原电位,浸出液中总铁的浓度用原子吸收光谱测定,Fe2+浓度用重铬酸钾滴定法测定,采用次亚磷酸盐滴定法测定液砷浓度。
氰化浸出试验在XTD-5L型搅拌浸出槽中进行,试验基本条件如下:浸出矿浆浓度为40%,氰化钠浓度为0.7%,浸出pH值在11.5以上,浸出时间为48 h。
2 实验结果
2.1 高砷矿直接氰化与细菌氧化试验
2.1.1 高砷矿直接氰化试验
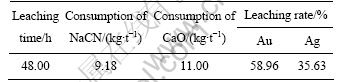
为了考察该高砷金精矿的浸出性能,对其在磨矿细度为粒度小于38 μm的占86%时进行直接氰化试验,试验结果如表2所列。
由表2可以看出,粒度小于39 μm的金有一半被氰化钠直接浸出来,而且氰化钠和石灰的消耗量较小,但是直接氰化浸出48 h,金浸出率仅为58.96%,银的浸出率为35.63%,属于典型的高硫高砷难浸矿石。
表2 高砷矿直接氰化浸出结果
Table 2 Results of ore with high arsenic content by direct cyanide leaching
2.2 高砷矿细菌氧化-氰化浸出试验
对此高砷矿直接氰化回收率太低,因此,对其进行预氧化,氧化渣再进行氰化浸出,判断是否可以提高金银浸出率。矿样细菌氧化过程中氧化还原电位、pH值、液体中铁、砷浓度及铁、砷氧化率随时间变化的曲线如图1和2所示。
由图1可知,此高砷矿的细菌氧化过程中,经过312 h氧化,矿浆氧化还原电位由290 mV上升到368 mV,上升得非常缓慢,而且pH值几乎也没变化。图2所示为高砷矿液体中铁砷浓度及氧化率变化曲线。由图2可知,矿浆中液体铁由最初的558 mg/L上升为2 158 mg/L,铁的氧化率仅为6.14%;液体砷由最初的188.41 mg/L上升为1 627 mg/L,砷的氧化率为7.38%,说明在这段时间内矿样几乎没有被氧化,因此,对该高砷矿直接进行细菌氧化效果不佳。对该氧化渣进行氰化浸出试验,试验结果如下:金浸出率64.18%,银浸出率35.93%,氰化钠消耗10 kg/t,浸出率也只是略有提高,浸出效果较差。

图1 高砷矿电位及pH值随时间的变化曲线
Fig.1 Variation curves of potential and pH value with time of ore with high arsenic content

图2 高砷矿液体中铁砷浓度及氧化率变化曲线
Fig.2 Variation curves of iron-arsenic concentration and oxidation ratio in ore liquid with high arsenic content
2.2 混矿降砷细菌氧化试验
由以上试验可以看出,当金精矿中砷的含量过高时,很难进行细菌氧化,因此,需要降低试样中砷的含量,这可以通过配矿来实现。
2.2.1 配矿的选择
配矿种类的选择有基于两个原则:1) 含砷较低;2) 容易被细菌氧化,以实现在和高砷矿按照一定比例配入后降低原料中砷的同时,可以较快启动细菌氧化反应。根据该原则选择了另一含砷金精矿,为便于区分,以下称之为配矿,其主要元素含量、直接氰化及细菌氧化氰化浸出情况分别如表3、表4和图3所列。
表3 配矿的化学成分分析
Table 3 Chemical composition of core blending (mass fraction, %)
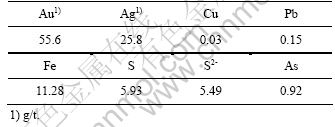
表4 配矿直接氰化浸出和细菌氧化后的浸出结果
Table 4 Results of direct cyanide leaching and leaching after bacterial oxidation for blending ore
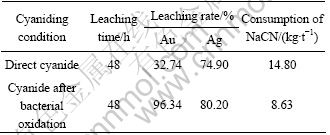

图3 配矿电位及铁砷氧化率随时间的变化曲线
Fig.3 Variation curves of potential and iron-arsenic oxidation ratio with time for blending ore
由表3、表4及图3可知,该金精矿中含硫化物较低,不到6%,配矿的直接氰化回收率都比较低,金和银的浸出率分别只有32.74%和74.90%;在其细菌氧化过程中,矿浆氧化还原电位及铁、砷的浓度都一直处于上升状态,铁、砷氧化率也不断提高;对细菌氧化后的氧化渣进行氰化,金、银浸出率分别提高到96.34%和80.20%,充分说明配矿的细菌预氧化效果较好,配矿很适合进行细菌氧化处理。
由表4可知,配矿经细菌预氧化后,其中金的浸出率提高很多,达到96.34%,但是由于该配矿含有大量的碳酸盐,在预氧化过程中消耗大量的硫酸,耗酸量达320 kg/t,因此,尽管其浸出率较高,从经济角度考虑,还是无法单一采用此矿进行生产。
生产实际中,在保证细菌氧化及金氰化浸出效果的前提下,尽可能减少配矿的比例,因此,按照高砷矿与混矿铵质量比为1:2、1:3、1:5和1:8的比例进行试验。
2.2.2 混矿细菌氧化试验
将高砷矿与配矿分别按照质量比为1:2、1:3、1:5和1:8进行混合后化验分析,为便于区分,简称为不同比例混矿,其主要元素的含量如表5所列。不同比例混矿细菌氧化过程中氧化还原电位及铁、砷氧化率随时间变化的曲线如图4~6所示。
表5 不同比例混矿中主要元素含量
Table 5 Main elements contents in mix ore with different blending ratios (mass fraction, %)

由图4~6可知,高砷矿经配矿后,无论是矿浆电位还是铁和砷的氧化率均大幅改善,细菌氧化效果大幅度提高,其中质量比1:5混矿的效果最佳,其氧化还原电位、铁和砷的氧化率都高于其他比例混矿的,所用的氧化时间最短,氧化速率最快(曲线斜率最大),其次是质量比为1:8、1:3和1:2的混矿矿样。
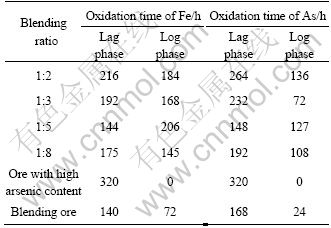
由以上试验可以看出,高砷矿、配矿及不同比例混矿时铁与砷的氧化时间是不同的,结果如表6所列。
尽管延迟期和对数期没有严格的划分依据,但还是能看出一些规律,由表6可以看出,质量比1:5混矿对细菌活性的影响也相对最小,主要表现在这种比例混矿细菌氧化铁的延迟期最短为144 h,对数期最长为206 h;氧化砷的延迟期最短为148 h,对数期相对较长,为127 h;同时由表中可以看出,TCJ菌氧化砷时对数期比氧化铁时的对数期要短。

图4 不同比例混矿电位变化曲线
Fig.4 Variation curves of potential for mix ore with different blending mass ratios
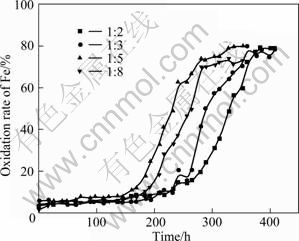
图5 不同比例混矿中铁氧化率的变化曲线
Fig.5 Variation curves of iron oxidation rate in mix ore with different blending mass ratio
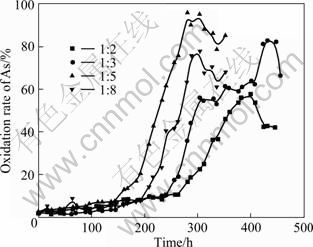
图6 不同比例混矿中砷氧化率的变化曲线
Fig.6 Variation curves of arsenic oxidation ratio for mix ore with different mass ratios
表6 各种矿样中铁、砷的氧化时间
Table 6 Oxidating time of iron and arsenic in various ore samples
2.2.3 混矿细菌氧化后氰化浸出试验
对上述比例混矿氧化渣进行氰化浸出试验,试验结果如表7所列。
由表7可以看出,不同质量比的混矿在经过细菌氧化之后进行氰化浸出,相对单独的高砷矿或者配矿来说,浸出率提高很多,说明氧化预处理效果明显,但是不同质量比混矿中金、银的浸出率相差不大,因此,细菌氧化速率的快慢和氧化时间的长短就显得尤为重要,另外,氰化钠作为氰化浸出的主要成本构成,其单耗相差还是比较大,综合来讲,质量比1:5混矿的浸出率和氰化钠单耗都较为合适。
表7 不同比例混矿氧化渣氰化浸出结果
Table 7 Cyanide leaching of oxidizing tailings in mix ore with different blending mass ratios

3 分析与讨论
在生物氧化过程中作为主要载金矿物的黄铁矿和毒砂可能会发生以下主要氧化还原反应[19-22]:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
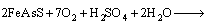
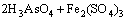 (4)
(4)
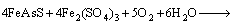
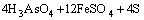 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
由以上反应可知:1) 在细菌氧化还原黄铁矿及毒砂的过程中,黄铁矿的氧化是一个产酸反应,毒砂的氧化是一个耗酸反应,并且生成As3+。在一定条件下,Fe3+可以将As3+氧化成As5+,在这些反应过程中,关键控制因素是细菌的活性、体系的氧化还原电位和pH,直接影响反应的持续性和砷的价态及转化;2) Fe3+与被氧化的矿物进行化学反应。氧化产生的Fe2+由细菌氧化为Fe3+后,再进入反应中循环,维持着生物氧化过程;3) 砷先以As3+的状态进入溶液中,含砷高的精矿As3+在整个氧化过程中占主导作用,而含砷低的精矿中只是在氧化的初始阶段占主导作用,当初始阶段黄铁矿存在量较大时,As3+迅速被氧化为As5+;4) 黄铁矿是决定生物氧化过程中砷的氧化状态的主要因素,尽管Fe3+是强氧化剂,但不能直接将As3+氧化成As5+,而需与黄铁矿共同作用才能氧化成As3+;5) As3+对细菌的抑制能力远大于As5+对细菌的抑制能 力[9-11] 。
高砷矿中由于含砷高,在整个氧化过程中,As3+在溶液中占主导作用,对细菌产生较强的抑制作用,使其失去活性,接种物中的Fe3+氧化矿物生成的Fe2+无法被细菌氧化为Fe3+,因此,高砷矿的生物氧化过程无法持续循环进行,主要表现为氧化过程电位上升得非常缓慢,以及pH值变化很小,说明溶液中的Fe3+和Fe2+的摩尔比基本没有变化,氧化过程中没有发生S被氧化为硫酸或者Fe2+被氧化为Fe3+的情况,从而造成溶液pH值降低,即高砷矿的细菌氧化没有办法启动。
低砷矿中含砷低,As3+只是在氧化的初始阶段占主导作用,并且由于黄铁矿的存在As3+迅速被氧化为As5+,因此,细菌没有受到强烈抑制而活性好,Fe3+氧化矿物生成的Fe2+被细菌氧化为Fe3+,所以氧化反应持续进行,在氧化开始电位上升较慢但仍处于上升阶段。
由于Fe3+需与黄铁矿共同作用才能氧化As3+,而配矿的硫化物含量较低不到6%,因此,随着氧化的进行,As3+的浓度有一个积累的过程,当达到一定值时,细菌尽管在低砷环境中,但活性仍受到As3+的影响,由于TCJ菌的耐砷能力较强,在适应一段时间后又恢复活性,因此在配矿的氧化开始反应阶段,砷的氧化率先上升后下降又上升出现反复。总体来说,尽管低砷矿的细菌氧化反应能够启动和进行,但是由于其硫化物含量较少,碳酸盐含量较多,因此,铁和砷的氧化率并不是很高,铁的氧化率65.63%,砷的氧化率55.96%,尽管铁砷氧化率不高,但由于配矿碳酸盐含量大,在pH值为2的条件下,预氧化后还是让金暴露,因此,金的浸出率并不低。
将高砷矿和配矿按照一定比例混合后,尽管只是一个简单的物理混合过程,但可以较好地解决两种单独原料预氧化中存在的问题:一是含砷量降低,有利于细菌的生存和活性恢复,细菌可以选择性地先吸附在低砷的配矿矿物表面,Fe3+将矿物氧化后产生的Fe2+被细菌氧化为Fe3+,并为细菌提供能量,这样氧化反应能够启动;二是高砷矿中硫化物含量高,其中的黄铁矿可以弥补低砷配矿中黄铁矿含量不高的缺陷,在有黄铁矿存在的条件下,As3+被氧化成As5+,从而减少对细菌的抑制,更有利于细菌氧化,因此,混矿后的铁和砷的氧化率都普遍高于单一的高砷矿或者配矿。
由试验可知,含砷金精矿中各种矿物的比例直接影响着细菌预氧化的效果,根据原料中硫、砷及铁等主要成分和黄铁矿及毒砂等主要矿物的不同,按一定比例进行混合配料会改善原料的细菌预氧化效果。通过混矿试验可以看出,高砷矿和配矿的质量比为1:5时,各项指标最好。综合整个试验中高砷矿、配矿及各种混矿的铁砷摩尔比与铁砷硫氧化率、金银浸出率及氰化钠单耗的关系曲线如图7所示。
由图7可知,给矿中铁砷摩尔比在4.6~5.2之间时,铁砷氧化率及金银浸出率都比较好,因此,在配料时要注意高砷矿与配矿的质量比,使给矿中的铁砷摩尔比介于此范围,亦有利于细菌预氧化和氰化浸出。
为了考察试验中溶液中的铁砷摩尔比变化情况,绘制高砷矿、配矿以及各种混矿的溶液中铁砷摩尔比对时间变化曲线如图8所示。
由图8可知,给矿中铁砷摩尔比高,溶液中的铁砷摩尔比也高,同时随着给矿中铁砷摩尔比的增加,溶液中铁砷摩尔比变化的幅度加大,变化频率加快。因此,给料中铁与砷的摩尔比不仅影响As3+的氧化,同时也会影响溶液中铁砷摩尔比的变化,从而影响溶液中砷酸铁的稳定性。

图7 不同给矿铁砷摩尔比与氧化率Fe/As摩尔比、浸出率及氰化钠单耗的关系曲线
Fig.7 Variation curves of oxidation rate of As, Fe, S and leaching rate of Au, and consumption of NaCN with mole ratio of Fe to As in feeding
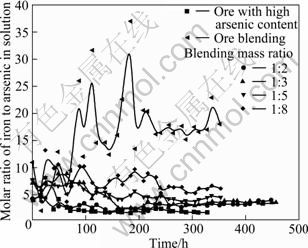
图8 不同给矿溶液中铁砷摩尔比变化曲线
Fig.8 Variation curves of iron-arsenic molar ratio in different ore feeding liquids
4 结论
1) 通过配入合适的原料处理高砷矿,可以改善细菌氧化效果,并且获得较好的技术经济指标,但是配料时需要考虑不同原料中硫、砷及铁等主要成分和黄铁矿、毒砂等主要矿物的组成,按照一定的比例混合,以保证给料中各种主要矿物的比例在合适的水平上,试验高砷矿配矿的适宜质量比为1:5。
2) 含砷金精矿给矿中的铁砷摩尔比不同会影响细菌的活性和溶液中的铁砷摩尔比,选择合适的给矿铁砷摩尔比有利于细菌预氧化过程的稳定和优化,试验高砷矿配矿铁砷摩尔比在4.6~5.2之间较为合适。
REFERENCES
[1] FRASER K S, WALTON H, WELLS J A. Processing of refractory gold ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1991(4): 1029-1041.
[2] 杨洪英, 范 金, 崔日成, 巩恩普. 难处理高砷金矿的细菌氧化-提金研究[J]. 贵金属, 2009, 30(3): 1-3.
YANG Hong-ying, FAN Jin, CUI Ri-cheng, GONG En-pu. Study on bacterial oxidation-extraction gold of refractory gold ore[J]. Precious Metals, 2009, 30(3): 1-3.
[3] EHRLICH H L. Past, present and future of biohydrometalhrgy[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2/3): 127-134.
[4] AKCIL A. Potential bioleaching developments towards commercial reality: Turkish metal mining’s future[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2004, 17(3): 477-480.
[5] CABRAL T, IGNATIADIS I. Mechanistic study of the pyrite-solution interface during the oxidative bacterial dissolution of pyrite (FeS2) by using electrochemical techniques[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2001, 62(1/4): 41-64.
[6] TIPRE D R, DAVE S R. Bioleaching process for Cu-Pb-Zn bulk concentrate at high pulp density[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 75: 37-43.
[7] WATLING H R. The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 84(1/2): 81-108.
[8] 杨丽丽, 杨洪英, 范有静,王大文, 朱长亮, 孙会兰. 难处理金矿石细菌氧化的影响因素研究[J]. 贵金属, 2007, 28(1): 58-62.
YANG Li-li, YANG Hong-ying, FAN You-jing, WANG Da-wen, ZHU Chang-liang, SUN Hui-lan. Study on influencing factors of bacterial oxidation of refractory gold ores[J]. Precious Metals, 2007, 28(1): 58-61.
[9] 金世斌, 马金瑞, 郝福来. 金精矿生物氧化过程中砷的氧化行为初探[J]. 黄金, 2009, 30(8): 41-43.
JIN Shi-bin, MA Jin-rui, HAO Fu-lai. Preliminary discussion on the arsenic oxidization behavior in gold concentrate biologic oxidization process[J]. Gold, 2009, 30(8): 41-43.
[10] 杨洪英, 杨 立, 魏绪钧. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌(SH-T)氧化毒砂的机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2001, 11(2): 323-327.
YANG Hong-ying, YANG Li, WEI Xu-jun. Mechanism on biooxidation of arsenopyrite with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans strain SH-T[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 21(2): 323-327.
[11] 杨洪英, 巩恩普, 訾建威, 杨 立. 嗜热菌对高砷金精矿氧化-氰化提金试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 27(4): 426-429.
YANG Hong-ying, GONG En-pu, ZI Jian-wei, YANG Li. Experimental investigation on gold recovery from high-As concentration through bio-oxidation/cyanidation with thermophilic bacteria[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2006, 27(4): 426-429.
[12] 罗志雄, 张广积, 方兆珩. 采用中温菌和常温菌浸出含砷金精矿[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(8): 1342-1347.
LUO Zhi-xiong, ZHANG Guang-ji, FANG Zhao-heng. Bioleaching arsenic-containing gold concentrates with MLY and At.f[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1342-1347.
[13] 戴红光. 湖北某难处理金精矿中温菌预氧化-氰化浸出试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2009, 28(2): 81-83.
DAI Hong-guang. Experiment research on pre-oxidation by moderate bacteria and leaching by cyanide for a refractory gold concentrate[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2009, 28(2): 81-83.
[14] 柳建设, 王铧泰, 闫 颖, 王秀美, 贺治国, 邱冠周. 气升式反应器中细菌氧化预处理难浸金精矿的浸出参数优化[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(5): 35-39.
LIU Jian-she, WANG Hua-tai, YAN Ying, WANG Xiu-mei, HE Zhi-guo, QIU Guan-zhou. Optimum parameters for bacterial pre-oxidation of refractory gold concentrate in an airlift reactor[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2008, 28(5): 35-39.
[15] 崔日成, 杨洪英, 张谷平, 范 金. pH值对浸矿细菌的活化以及金精矿脱砷的影响[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 29(11): 1597-1600.
CUI Ri-cheng, YANG Hong-ying, ZHANG Gu-ping, FAN Jin. Effect of pH value on activation of bioleaching bacteria and dearsenification of gold ore concentrates[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2008, 29(11): 1597-1600.
[16] 佟琳琳, 姜茂发, 杨洪英, 殷书岩. 湖南某高砷难处理金精矿的细菌氧化-氰化提金实验研究[J]. 贵金属, 2008, 29(1): 15-18.
TONG Lin-lin, JIANG Mao-fa, YANG Hong-ying, YIN Shu-yan. Experimental investigation on gold extraction from high-as concentrate in Hunan province through bio-oxidation/ cyanidation[J]. Precious Metals, 2008, 29(1): 15-18.
[17] 李万全, 张永奎, 陈 宁, 梁 颖, 黄亚洁. 某高硫砷难浸金精矿的细菌氧化预处理[J]. 金属矿山, 2007(2): 42-44.
LI Wan-quan, ZHANG Yong-kui, CHEN Ning, LIANG Ying, HUANG Ya-jie. Bio-oxidation pretreatment of high arsenic high sulfur refractory gold concentrate [J]. Metal Mine, 2007(2): 42-44.
[18] 李育林, 伍赠玲, 吴在玖, 张永奎. 高硫高砷金精矿细菌氧 化-氰化浸金试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2005, 24(2): 73-76.
LI Yu-lin, WU Zeng-ling, WU Zai-jiu, ZHANG Yong-kui. Bacterial oxidation and cyanide leaching process of gold concentrate containing arsenic and sulphur[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2005, 24(2): 73-76.
[19] BALLESTER A, AMILS R. Biohydronetallurgy and the environment toward the mining of 21st century[M]. Netherlands: Elsevier Scicence B V, 1999: 431-441.
[20] LANGHANS D, LORD A, LAMPSHIRE D. Biooxidation of an arsenic-bearing refractory gold ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1995, 8(2): 147-158.
[21] 崔日成, 杨洪英, 张谷平, 马玉蕊, 范 金, 李科峰. 毒砂型高砷金精矿的细菌氧化[J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(12): 3090-3094.
CUI Ri-cheng, YANG Hong-ying, ZHANG Gu-ping, MA Yu-rui,FAN Jin, LI Ke-feng. Biooxidation of high arsenic gold concentrate with arsenopyrite type[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2008, 59(12): 3090-3094.
[22] 杨松荣, 邱冠周, 胡岳华, 谢纪元. 含砷难处理金矿石生物氧化工艺及其应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 93.
YANG Song-rong, QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, XIE Ji-yuan. The biological oxidation technology and application of refractory gold ores containing arsenic[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 93.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2010CB630905)
收稿日期:2010-08-25;修订日期:2010-11-22
通信作者:杨玮,高级工程师,博士;电话:13507710579;E-mail:ywmsco@126.com