文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0590-05
Ti40合金热加工保温过程中的组织演化
辛社伟1,李 倩1,李 笑1, 2,赵永庆1,洪 权1,毛小南1,杨海瑛1,葛 鹏1
(1. 西北有色金属研究院 钛合金研究所, 西安 710016;
2. 宝钛集团有限责任公司, 宝鸡 721014)
摘 要:针对Ti40合金大规格棒材锻造过程中的组织演化行为,在棒材锻造的不同阶段取样,对样品进行不同温度和不同时间的加热和保温,通过光学显微镜和EBSD测试对合金组织演化行为和再结晶机制进行分析。结果表明:Ti40合金棒材在加热保温过程中主要以晶界小晶粒长大为主,这些晶界小晶粒主要产生于锻造过程中,是依靠晶界变形从原始母晶粒上脱落产生的,这些晶粒在此后的棒材加热保温过程中长大,引起合金的组织均匀化和细化。从组织均匀性和晶粒平均尺寸考虑,合金最佳的加热工艺为1 000 ℃、4 h。
关键词:Ti40合金;热加工;组织;再结晶
中图分类号:TG146.3 文献标志码:A
Microstructure evolution of Ti40 alloy during hot working process
XIN She-wei1, LI Qian1, LI Xiao1, 2, ZHAO Yong-qing1, HONG Quan1, MAO Xiao-nan1, YANG Hai-ying1, GE Peng1
(1. Titanium Alloy Research Center, Northwest Institute for Non-ferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China;
2. BaoTi Group Co., Ltd., Baoji 721014, China)
Abstract: Aiming at the microstructure evolution of Ti40 big bar, the samples cut from bar blanks with different deformation were heated at different temperatures for different times. Optical microscope and EBSD were used to analyze the microstructure evolution and recrystallization behavior. The results indicate that the microstructure evolution of Ti40 bar during heated process mainly shows the growing behavior of small grains along grain boundaries. These small grains mainly results from forging process, which mainly come from original parent grains because of the grain boundaries deformation. After forging process, these small grains grow during heating process and which cause the uniform microstructure and the decrease of the average grain size. In view of the average grain size and microstructure uniformity, the best heating process is (1 000 ℃, 4 h).
Key words: Ti40 alloy; hot working; microstructure; recrystallization
Ti40(Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si)合金是西北有色金属研究院在美国Alloy C[1-2](Ti-35V-15Cr)合金的基础上研制的一种Ti-V-Cr系阻燃钛合金,对于该类合金,已有的研究工作中强调合金的使用性能和使用条件下的组织演化[3-7]。但是,作为我国现有使用合金中β稳定系数最高的合金,Ti40合金的难加工性一直是该合金使用的又一难题,Ti40合金属于典型的难变形合金,针对合金的热加工特性,现有的文献大都应用热模拟实验,从热压缩角度出发,研究合金在热压缩过程中的组织演变,得出一些关于合金热加工的结论[8-10]。但是实践证明,热模拟实验所得到的结论和实际大规格铸锭的开坯锻造还是有一定的偏差,得出的结论往往对合金实际锻造工艺指导有限。本文作者从Ti40合金实际大规格棒材不同锻造阶段取样,模拟合金锻造过程中的加热和冷却方式,研究在不同加热温度和保温时间下合金的组织演化特点,为揭示Ti40合金实际热加工过程中的晶粒细化机制和制定合理的热加工工艺提供参考。
1 实验
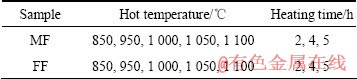
实验所用的材料来自西北有色金属研究院制备的Ti40合金吨级铸锭,采用“预应力包套+约束锻造”的锻造方法进行开坯锻造,经过多火次,累积变形量约250%后锻造成d 280 mm合金成品棒材,在锻造过程中,当累积变形量为110%时进行中间过程取样,该样品在本研究中标识为中间态试样(MF)。从直径 280 mm的成品棒材上取样所得的样品在本研究中的标识为终锻态(FF)。样品尺寸为12 mm×12 mm×12 mm,对样品进行加热保温,加热温度和保温时间工艺参数如表1所列。样品加热保温后采取在200 ℃的沙子里埋沙冷却,该冷却工艺是模拟大规格棒材锻造后的冷却工艺。实验样品的选择是对Ti40合金不同加工阶段进行取样,反映不同阶段样品在热加工阶段组织随加热保温时间变化规律。加热温度的选择主要依据Ti40合金热处理的固溶温度和Ti40合金锻造的实际热加工温度,目前,Ti40合金推荐的固溶温度为850 ℃,热加工温度范围为950~1 100 ℃。保温时间依据不同尺寸合金实际锻造过程中的保温时间进行选择。
表1 晶粒生长行为研究方案
Table 1 Experiment program of grain growth behavior
本研究光学组织和EBSD测试分别时在OLMPUS PMG光学显微镜和配备EBSD探头的FEINova400场发射扫描电镜下进行的,电解抛光的电解液为93%乙酸+7%高氯酸(体积分数)。
2 结果与分析
2.1 合金锻态原始组织
图1所示为合金棒材中间态和终锻态的金相组织。由图1可以看出,经过110%的变形量后的中间态组织显示粗大的β晶粒,而且晶粒大小不均匀。相对而言,终锻态组织晶粒较为均匀,平均晶粒尺寸约为500 μm。证明250%变形量基本满足合金棒材锻造的需求,可以得到相对均匀的组织。

图1 合金锻态金相组织
Fig. 1 OM microstructures for as-forged samples
2.2 合金组织随加热保温时间变化
合金中间态和终锻态样品经过表1工艺处理后的显微组织如图2所示。根据图2显示的典型组织基本可以判断,合金中间态和终锻态样品在保温过程中的组织演化规律。对于中间态样品,可以看到,在加热温度为850 ℃时,组织形貌和锻态相差不大,随着保温时间的延长,晶界的一些小晶粒开始长大,整体组织仍然保持粗大不均匀。随着加热温度的升高,晶界的小晶粒继续长大,其向原始晶粒延伸,这反而导致晶粒趋向均匀化。特别是当加热温度温度为1 000 ℃时,组织相对均匀化程度最好。当加热温度升高为1 100 ℃时,在晶粒均匀化的基础上,组织粗化,主要还是由于加热温度过高,晶粒异常长大所致。对于终锻态样品,加热温度和保温时间对合金组织整体影响趋势和中间态相似,只是由于终锻态原始组织均匀,且沿晶界形成的再结晶小晶粒连续、充分,所以得到的结果更有规律性。在晶粒长大均匀化的同时,还可以在850 ℃保温后的组织中看到原始晶界痕迹,以点状析出物形成存在,这主要是由于在锻造后冷却速度较低,冷却过程中,析出物主要在晶界形核并长大,这些沿晶界分布的析出物和晶界再结晶晶粒混和在一起,在锻态光学组织中观察不到。当锻态组织在850 ℃保温后,晶界再结晶晶粒长大,但析出物不能溶解,所以形成了如图2所示的晶粒内部显示原始晶界痕迹。当加热温度升高到1 000 ℃时,原始晶界痕迹完全消失,证明锻造过程中沿晶界分布的析出物完全溶解。当加热温度超过1 000 ℃,整体晶粒明显粗化,并且在个别位置发生晶粒异常长大,导致组织不均匀。

图2 合金中间态和终锻态样品在不同温度保温不同时间后的显微组织
Fig. 2 Microstructures of MF and FF samples held at different temperatures for different times
图3所示为合金中间锻态和终锻态样品在不同温度下晶粒平均尺寸随温度的变化。从图3可以看出,中间锻态样品平均晶粒尺寸变化起伏较大,终锻态样品变化较为平缓,这主要是由于中间锻态在取样时原始组织变形不充分,且取样集中在棒材的端头处,本身变形不是很均匀,导致原始组织不均匀,在随后的加热过程其中,晶粒长大也不均匀,为统计带来一定的困难和误差。但从总体晶粒度变化趋势可以看出,随着加热温度的进一步升高,晶粒平均尺寸反而有减小的趋势,这主要是由于随着加热温度的提高,晶界处的小晶粒逐渐长大,吞并原始的大晶粒,使得合金晶粒度趋向于均匀化,最终反而导致平均晶粒尺寸减小;当温度到达1 000 ℃时,组织的均匀化程度最好,当温度继续升高时,由于二次再结晶的关系,晶粒的平均尺寸又逐渐变大。因此,根据以上合金在不同温度不同保温时间下的晶粒度的统计,认为Ti40合金的锻造加热保温温度适宜选在1 000 ℃,保温时间选择 4 h左右为宜。

图3 中间态和终锻态样品平均晶粒尺寸随温度和保温时间的变化
Fig. 3 Change of average grain size of MF (a) and FF (b) with temperature and time
2.4 合金锻造的再结晶机制分析
根据以上组织分析可以看出,Ti40合金不同锻造状态试样在保温过程中组织变化主要以晶界小晶粒长大为主,而这些晶界小晶粒来源可能有两个过程:第一,小晶粒是产生于锻造过程中,随后的加热保温只是这些晶粒的长大过程;第二,这些小晶粒是加热保温过程中通过静态再结晶形核长大。对于这个问题的研究,可以参考图4分析。图4所示为合金终锻态试样的三叉晶界放大图,并示出其对应的EBSD取向成像图和不同晶粒取向差图。根据晶界放大图可以清楚的看到,在锻造后,合金的晶界已经存在大量小晶粒,基本可以证明加热保温过程中沿晶界长大的晶粒是原始锻态组织中已经存在的,主要产生于锻造过程。由横跨原始晶粒Ⅱ、小晶粒1、小晶粒2和原始晶粒Ⅲ的AB线的位向差分析图可以看到,晶粒1、晶粒2和原始晶粒3的位向接近。同时,根据CD线的取向差分析,看到经过区域3处,从晶粒Ⅲ到晶粒Ⅰ的取向有一个渐变过程,而不是传统晶界的取向突变。横跨晶粒Ⅱ和晶粒Ⅲ的晶界的位向差也存在一个渐变过程。这些位向差的渐变说明锻态组织中沿晶界分部的小晶粒是从母晶粒上脱落产生的。在Ti40合金锻造锻造过程中,合金承受应力,为协调变形,晶界发生转动或滑动,使比邻晶界部位变形,形成亚晶。随着变形量的增加,亚晶转动,当亚晶取向和原始晶粒取向差超过一定程度时,在晶界形成稳定的再结晶晶粒。所以图4所示的晶粒1、2就是通过以上再结晶方式从母晶粒Ⅲ上脱落而来的,而区域3则是承受了一定变形的亚晶。图4中区域3和母晶粒Ⅲ的最大位向差约为13°,在光学组织中完全看不出和母晶粒有差别;而小晶粒2和母晶粒Ⅲ取向差为17.8°,可以看到明显的晶界。证明形成稳定的从母晶粒上脱落的再结晶小晶粒的位向差应该大于13°,小于17.8°,这个范围也接近传统意义上的小角度晶界与大角度晶界的分界值15°。
从以上分析可以看出,Ti40合金锻造过程中再结晶机制是依靠晶界处的变形,在晶界形成亚晶,随着变形程度的增加,当亚晶与母晶粒的位向差超过一定的度,产生从母晶粒上脱落的再结晶晶粒,这些小晶粒在此后的棒材加热保温过程中长大,使得合金的组织细化和均匀化,这是Ti40合金大规格棒材锻造过程中晶粒细化的主要机制。

图4 终锻态样品晶粒取向差分析
Fig. 4 Misorientation analysis of grains for FF samples
3 结论
1) Ti40合金棒材在加热保温过程中主要以晶界小晶粒长大为主,从组织均匀性和晶粒平均尺寸考虑,最佳的加热温度为1 000 ℃,最佳的保温时间约为4 h。
2) Ti40合金加热保温过程中的晶界小晶粒主要产生于锻造过程,锻造过程中依靠晶界处的变形,在晶界形成亚晶,当亚晶与母晶粒的位向差超过一定 值,产生从母晶粒上脱落的再结晶晶粒,这是Ti40合金大规格棒材锻造过程中再结晶的主要机制。
REFERENCES
[1] WARD C H, SPANOS G, BRODERICK T F, RESHAD J. Isothermal transformation of precipitates in alloy C+ [C]// Ti’95 Science and Technology. UK: The Institute of Materials, 1995: 2377-2384.
[2] HANSEN J O, NOVOTNAK D, WELTER M F, WOOD J R. Properties and processing of high strength beta titanium alloy [C]// Ti’95 Science and Technology. UK: The Institute of Materials, 1995: 675-682.
[3] LI Y A, BLENKINSOP P A, LORETTO M H, RUGG D, VOICE W. Effect of carbon and oxygen on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al(wt%) alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(10): 2889-2905.
[4] LI Y G, LORETTO M H, RUGG D, VOICE W. Effect of heat treatment and exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C(wt%) [J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 3011-3017.
[5] ZHAO Y Q, QU H L, ZHU K Y, WU H, ZHOU L. The second phases in a burn resistant stable beta titanium alloy-Ti40 [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38: 1579-1584.
[6] XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong. Effect of heat treatment on thermal stability of Ti40 alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(s1): s526- s531.
[7] 辛社伟, 赵永庆, 曾卫东. 钒和铬对Ti40阻燃钛合金力学性能的影响机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(7): 1216-1222.
XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong. Mechanism of V and Cr on mechanical properties of Ti40 burn-resistant titanium alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(7): 1216-1222.
[8] 赵永庆, 周 廉, 邓 炬. β型Ti40阻燃钛合金铸态组织高温变形的微观组织[J]. 机械工程材料, 2000, 24(1): 14-16.
ZHAO Yong-qing, ZHOU Lian, DENG Ju. Microstructures after high temperature deformation of β Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy as-casting [J]. Materials of Mechanical Engineering, 2000, 24(1): 14-16.
[9] SHU Ying, ZENG Wei-dong, ZHANG Xue-min, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZHOU Yi-gang, ZHOU Lian. Fracture predicting of Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy in hot forming [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006, 35(12): 1900-1903.
[10] 曾卫东, 周义刚, 舒 滢, 赵永庆, 杨 锦, 张学敏. 基于加工图的Ti40阻燃钛合金热变形机理研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(1): 1-6.
ZENG Wei-dong, ZHOU Yi-gang, SHU Ying, ZHAO Yong-qing, YANG Jin, ZHANG Xue-min. A study of hot deformation mechanism in Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy using processing map [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(1): 1-6.
(编辑 李艳红)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:辛社伟,高级工程师,博士;电话:029-86231078;E-mail: nwpu_xsw@126.com