文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)12-1881-07
单晶高温合金的中温Ⅰ阶蠕变
——涡轮叶片伸长的重要因素
郑运荣, 杨素玲, 阮中慈
(北京航空材料研究院, 北京 100095)
摘 要: 单晶镍基高温合金已广泛用于制造先进燃气涡轮叶片, 但这种合金至今仍被忽视的薄弱环节是它的中温Ⅰ阶蠕变伸长量远高于高温蠕变, 而且与高温蠕变相比, 中温Ⅰ阶蠕变对取向偏离、 合金成分和热处理组织的变化更为敏感。 虽然预蠕变引进较高的位错密度能有效抑制中温蠕变, 但在实用上仍有困难。 在选用单晶合金作为涡轮叶片时, 应考虑到先进的二代和三代单晶在中温下的抗变形能力不如一代单晶, 同时中温大应力状态下的叶片根部可能过度伸长。
关键词: 单晶高温合金; 中温蠕变; 合金化; 显微组织; 应变; 涡轮叶片 中图分类号: TG113.25; TG132.3
文献标识码: A
Primary creep of single crystal superalloys at intermediate temperature
—An important factor of turbine blade extension
ZHENG Yun-rong, YANG Su-ling, RUAN Zhong-ci
(Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 10095, China)
Abstract: The single crystal Ni-base superalloys were widely used for manufacturing advance gas turbine blades, but the ignored weakness of these alloys to date is that the extent of primary creep at intermediate temperature is much higher than that at high temperature. Moreover, compared with high temperature creep, the primary creep strain at intermediate temperature is extraordinary sensitive to changes in the orientated deviation, composition and the heat-treated microstructure. Although the high-density dislocations introduced by pre-creep treatment can restrict the intermediate temperature creep, it is difficult for application in practice. As single crystal alloys are selected as manufacturing turbine blades, it is considered that the resistance to deformation of the second or the third generation single crystal superalloys at intermediate temperature is inferior to first generation alloys and the excessive extension of blade root could take place at the service environment of intermediate temperature and high stress.
Key words: single crystal superalloys; intermediate temperature creep; alloying; microstructure; strain; turbine blades
当前, 单晶高温合金已广泛用于制造燃气涡轮叶片[1-3], 特别是当用于地面大型燃气涡轮的单晶叶片, 其长度大于300mm带内冷通道, 而且单晶的[001]取向应平行于叶片主应力轴方向, 技术难度很高[4-6]。 这种地面涡轮的进口温度达1500℃, 而且要求有106 h的长寿命, 在叶片使用期内, 叶片的总伸长量被限制在规定范围内, 以保证高速转动的涡轮与外环之间有合适的间隙。 间隙过大, 发动机的效率得不到保证, 间隙过小会由于叶片与外环相碰造成事故[7]。 因此, 在一些材料手册中给出了叶片材料蠕变到一定变形量所需的时间[8]。
在实际使用中发现, 涡轮叶片有时由于严重变形或过度伸长而报废, 通常都认为是材料高温承温能力不足、 蠕变变形过大引起的。 然而近期对某些单晶高温合金做中温蠕变试验时发现, 在不到20h内, 蠕变伸长量高达5%, 个别三代单晶合金甚至超过20%[9]。 因此, 单晶合金过度的中温蠕变伸长引起了工程界人士的广泛关注。 在该领域的研究工作一改以往大量工作侧重于蠕变机理方面的研究[10-13], 而是重点研究了几种已广泛应用的单晶合金Ⅰ阶蠕变变形量过大及数据分散的原因, 进而提出了某些应对措施[9, 14]。 现已确认, [001]取向单晶高温合金在中温下的Ⅰ阶蠕变伸长与温度、 应力、 取向偏离度、 热处理引起的显微组织变化以及合金成分等因素有着密切的联系。 本文作者就上述的影响因素作了综合评述。
1 单晶中温Ⅰ阶蠕变的重要性
单晶高温合金的蠕变过程通常分为3个阶段: Ⅰ阶蠕变为蠕变的减速阶段, 其蠕变速率随时间增加而逐渐降低; Ⅱ阶蠕变是恒速阶段, 此时蠕变速率基本保持不变; Ⅲ阶蠕变是加速阶段, 蠕变速率随时间增加而急剧增大, 最终导致断裂。 图1所示为一代单晶合金DD3于760℃, 736MPa和1000℃, 177MPa以及二代单晶合金CMSX-4于750℃, 750MPa条件下的蠕变曲线, 图中标出了蠕变的各阶段, 所列的这些实验条件反映了叶身高温区和榫头中温区的工作温度和应力。 由于材料Ⅲ阶蠕变速率急剧升高, 所以涡轮叶片的使用寿命都限在Ⅱ阶蠕变以内, 但Ⅱ阶蠕变的应变速率往往比Ⅰ阶蠕变速率低1~2个数量级, 所以会出现在Ⅰ阶蠕变期间短短数十小时的蠕变伸长占了全寿命伸长的近一半, 特别是第二代以上的单晶合金, 其中温Ⅰ阶蠕变伸长更为明显, 可见中温Ⅰ阶蠕变对单晶合金特别重要, 它明显影响涡轮叶片的整体寿命。
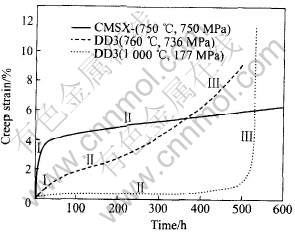
图1 [001]取向单晶合金的蠕变曲线[8, 9]
Fig.1 Creep curves of single crystal alloys with [001] orientation[8, 9]
2 [001]取向偏离度的影响
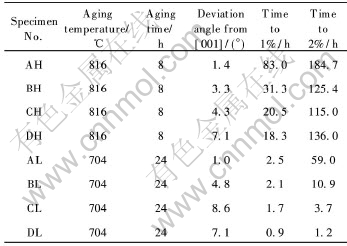
以往大量研究工作放在研究[001]、 [011]和[111]取向单晶性能各向异性上[15-18]。 近年来发现[001]取向单晶在中温下蠕变性能远比高温时分散, 即使由一块已测定取向的单晶机加工出来的试样, 其中温蠕变行为仍有明显的差异。 由于[001]取向是涡轮叶片使用的主应力方向, 因此研究重点放在取向偏离[001]产生的影响, 通常是对取自同一单晶加工好的试棒分别测其取向, 再测其蠕变性能。 图2示出了取向偏离对PWA1484单晶合金于732℃, 758MPa条件下Ⅰ阶蠕变行为的影响。 可以看出, 取偏离[001]取向7.8°的HT11试样蠕变2.8h后变形量达2%, 而且不到5h变形量就高达10%。 进一步的研究表明, 中温蠕变性能的分散极为明显, 由两根偏离[001]为4.8°和5.9°单晶棒机加工出来的3组试样的Ⅰ阶蠕变量和蠕变断裂寿命波动达8倍, 结果列于表1中。
从表1数据可知, 无论采用哪一种时效制度, 随着偏离[001]取向增大, 蠕变速率加快。 CMSX-4单晶取向偏离对Ⅰ阶蠕变的影响也有类似的情况[1, 19]。 中温蠕变性能对取向偏离极为敏感可能由下列因素引起, 首先是高温合金单晶并非完整晶体, 通常单晶试棒由横截面尺寸约200~300μm的一束枝晶组成, 这些枝晶通常彼此之间错向大约为2°, X射线劳厄法测取向的误差约2°, 因而试样轴向偏离在2°~4°范围存在不确定性, 即通常认为是一个“模糊”区。 当一个取向偏离[001]取向5°以内的单晶, 很难真正确定取向是更接近取向三角形的[001]-[011]边还是接近[001]-[011]边。 而现已确定, 取向接近[001]-[011]边的试样具有较低的Ⅰ阶蠕变量和高的断裂寿命。 因此, 当取向更加接近[001]时, 要确定数据分散性与测得的取向之间的关系时, 实验方法本身就存在困难。 一种补救的办法是通过测量蠕变断裂试样横切面的椭圆度(大径与小径之比)能很好地表征取向对变形各向异性的影响。 文献[14]系统地确定了椭圆度与Ⅰ阶变形度和断裂寿命之间的关系。 通常认为椭圆度大的试样, 试样变形更不均匀, 故而Ⅰ阶蠕变量更大, 寿命更短。
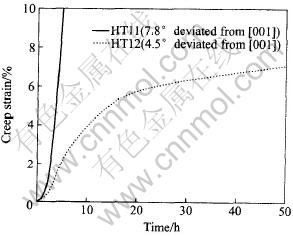
图2 PWA1484单晶合金取向偏离[001]对732℃, 758MPa条件下Ⅰ阶蠕变的影响[14]
Fig.2 Effects of deviation from [001] orientation on primary creep at 732℃,758MPa for single crystal PWA 1484 alloy[14]
表1 PWA1484单晶取向对816℃, 621MPa条件下蠕变行为的影响[14]
Table 1 Effects of [001] orientation on creep behavior of PWA 1484 single crystal alloy at 816℃, 621MPa[14]
3 显微组织的影响
单晶的显微组织是铸造高温合金中最简单的。 主要由γ和γ′两相组成。 γ′的大小、 形状和体积百分数都强烈影响单晶的蠕变行为。 由于一代至四代单晶合金的γ′的体积百分数都在65%左右, 且都热处理成立方形状, 因此本文仅讨论γ′尺寸的影响。 法国宇航院的Caron等[20]通过不同热处理对CMSX-2单晶合金获得了0.23, 0.30和0.45mm大小的γ′相, 结果证明具有0.45μm粗γ′相[001]取向单晶的Ⅰ阶蠕变量最低, 蠕变断裂寿命最长, 如图3所示。
γ′相尺寸对二代单晶PWA1484 816℃, 621MPa蠕变行为同样有类似的作用, 相同取向的试样, 在816℃温度时效得到比704℃时效更粗的γ′相时, 可降低Ⅰ阶蠕变的变形度(比较图4中AH与AL, DH与DL试样)。 从图4还可以看出, 在相同γ′相尺寸下, 取向偏角越大, Ⅰ阶蠕变量越大。
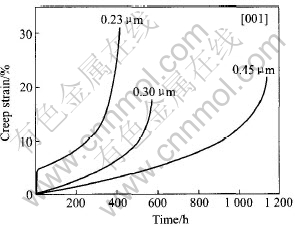
图3 γ′相尺寸对[001]取向CMSX-2单晶合金于760℃, 750MPa条件下蠕变性能的影响[20]
Fig.3 Effects of γ′precipitate size on creep properties at 760℃, 750MPa for CMSX-2 single crystal alloy with [001] orientation[20]
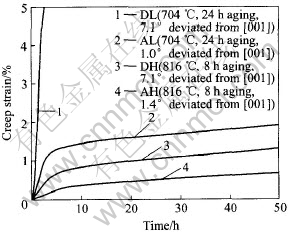
图4 时效处理和取向偏离对PWA1484单晶于816℃, 621MPa条件下Ⅰ阶蠕变行为与时效处理和取向的影响[14]
Fig.4 Effects of aging treatment and orientated deviation on primary creep behavior at 816℃, 621MPa for PWA1484 single crystal alloy[14]
4 合金成分的影响
最近对比研究了二代和三代单晶合金的中温Ⅰ阶蠕变行为, 结果表明不同合金Ⅰ阶蠕变变形量变化很大[9]。 表2比较了几种单晶合金于750℃, 750MPa条件下的Ⅰ阶蠕变应变量。 这些试样的取向基本相同, 但三代单晶TMS75的Ⅰ阶蠕变量明显高于其它单晶合金。 图5的蠕变曲线进一步说明这种情况。 Shah等在816℃, 621MPa条件下比较了经充分热处理后不同柱晶和单晶合金的Ⅰ阶蠕变性能, 结果表明在蠕变5h内一代柱晶PWA1422和一代单晶PWA1480的蠕变应变小于0.5%; 二代柱晶PWA1426和单晶大于2%; 而三代单晶合金则超过5%。 林栋梁等[21]系统地比较了6种[001]取向一代柱晶合金在760℃, 689MPa条件下的蠕变行为, 发现不同合金的Ⅰ阶蠕变应变相差1个数量级, 例如DSK403合金和DSK409合金分别为0.38%和4.30%。 而且Ⅰ阶蠕变应变越大的合金, 其蠕变寿命越短。 合金成分对Ⅰ阶蠕变行为影响原因很复杂。 目前公认一种看法是合金中的Co和Re是增加Ⅰ阶蠕变应变的元素[22], 三代单晶TMS75含有高达12%(质量分数)的Co和6%(质量分数)Re都降低了γ相的层错能, 促进了Ⅰ阶蠕变。 看来DSK403合金低的Ⅰ阶蠕变应变与该合金Co量低(5%Co)有关。 上述情况表明, 许多高温强度很高的三代单晶合金, 其中温蠕变应变和寿命方面并无优势, 这就要求在合金成分设计方面要兼顾中温蠕变性能, 以便提高涡轮叶片的整体寿命。
表2 单晶合金750℃, 750MPa蠕变性能[9]
Table 2 Creep properties of single crystal alloys at 750℃, 750MPa
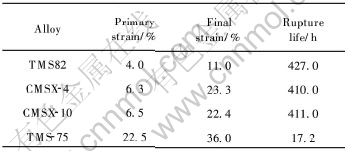
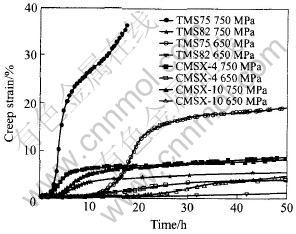
图5 几种单晶合金的中温蠕变曲线[9]
Fig.5 Creep curves of several alloys at 750℃, 750MPa[9]
5 温度和应力的影响
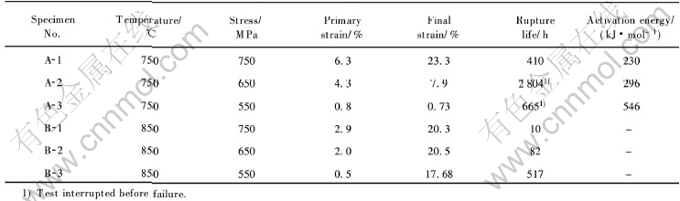
700~850℃和650~750MPa是Ⅰ阶蠕变最受关注的温度和应力范围。 750℃时对Ⅰ阶蠕变影响最大, 在此温度下, Ⅰ阶蠕变应变最大, 而在此温度下当应力超过600MPa时, Ⅰ阶蠕变应变急剧升高, 应力达750MPa时影响最为强烈, 相应地其蠕变激活能显著降低。 表3列出了相同[001]取向的CMSX-4单晶试样在700~850℃, 550~750MPa条件下的蠕变数据[9]。 证实了在750℃, 750MPa条件下单晶合金Ⅰ阶蠕变应变量最高, 蠕变激活能最低。
6 预应变的影响
对单晶合金的中温蠕变变形的各向异性机理作了大量研究工作[23-26]。 得到的结论是, 含高体积分数γ′相的[001]取向单晶镍基合金, 其Ⅰ阶蠕变是在{111}滑移面上由a/2〈110〉位错滑移通过γ相开始的。 由于单晶消除了晶界, 这类位错主要来源于枝晶间的低角界, 且初始位错密度远低于多晶高温合金。 a/2〈110〉位错剪切通过γ′颗粒需要很高的能量, 在中温下切割通过γ′颗粒较为困难。 然而当γ中a/2〈110〉位错的密度在变形过程中不断增加, 促使a〈112〉型位错在γ/γ′界面上成核, 这类位错较易切割γ′, 最终在γ′中产生层错。 a〈112〉位错滑移剪切γ′一旦开动, 就会大距离滑动而不会离开它们的滑移面, 造成了大的Ⅰ阶蠕变应变和短的蠕变寿命, 所以需要改变这种不均匀的变形方式。 其方法是激活{111}〈112〉滑移系的各个滑移, 由于多重滑移产生大量交割而使位错滑动的距离被限制在一个或几个γ′颗粒的尺度范围, 使蠕变尽快向Ⅱ阶过渡, 降低蠕变速率。 采用预应变的方法达到了上述效果。 早期一个有益的实验是在室温下用强度为100MPa的冲击波对Mar-M200单晶加载, 在位错亚结构中立刻引进了大量a〈112〉位错, 结果使760℃, 690MPa下的Ⅰ阶蠕变应变量由3.3%降到0.33%[10, 27]。
表3 温度和应力对[001]取向CMSX-4单晶蠕变性能的影响[9]
Table 3 Effects of temperature and stress on creep properties of
CMSX-4 single crystal alloy with [001] orientation
CMSX-4单晶合金先经950℃, 485MPa蠕变至应变为0.4%, 然后预先蠕变和未预先蠕变试样同时在750℃, 750MPa条件下做蠕变实验, 结果表明Ⅰ阶蠕变应变量由未经预蠕变处理的4.5%降到预应变处理后的2%。 其蠕变曲线如图6所示[9]。 该图表明, 预应变处理不仅使Ⅰ阶蠕变的应变量至少降低一半, 而且也大大降低了Ⅰ阶蠕变速率, 但对Ⅱ阶蠕变速率无明显影响。
预蠕变处理明显改变了单晶合金内部的位错结构。 预蠕变和非预蠕变试样在750℃, 750MPa下蠕变到1%后中断实验, 取样对比分析两种试样的位错结构, 结果表明预蠕变试样在γ′相上的堆垛层错段较短而分散, 在γ/γ′界面上的位错密度远高于未经预蠕变处理的试样(图7)。
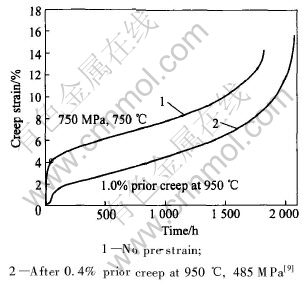
图6 预处理对CMSX-4单晶高温合金于750℃, 750MPa条件下蠕变的影响
Fig.6 Effects of pre-strain treatment on creep at 750℃, 750MPa of
CMSX-4 single crystal superalloys
7 截面尺寸的影响
不同截面尺寸铸造高温合金涡轮零件的性能有明显差别, 当截面尺寸小于2mm时, 力学性能降低, 因此把截面尺寸对高温合金铸件的蠕变变形和断裂性能的影响纳入涡轮叶片设计与寿命评价[28, 29]。 美国普惠公司最近系统研究了不同温度下第二代单晶PWA1484的蠕变性能[30], 他们从一块[001]取向单晶板块切取厚度为0.38~3.18mm的板状试样, 这样可消除取向、 显微组织、 偏析度以及疏松等因素的影响, 从而更精确考察截面尺寸的作用。 每种蠕变实验做3根试样, 取其平均结果, 结果如图8所示。 可知, 试样厚度对PWA1484单晶在760℃, 758MPa下Ⅰ阶蠕变应变量影响甚微: Ⅰ阶应变量都在6%左右, 且应变速率也无明显差异, 然而薄截面试样的蠕变断裂寿命明显降低。 厚度为0.38mm的试样寿命大约只有厚度为3.18mm试样寿命的40%左右。
8 结语
单晶镍基高温合金是现代燃气涡轮的关键材料。 高达1150℃的承温能力使它广泛用于制造先进的燃气涡轮叶片。 以往使用中的涡轮叶片过度伸长通常被认为是高温强度不足, 因而在合金研发过程中过分追求高温强度指标而对中温蠕变不够重视。 考虑涡轮叶片不同部位具有不同的工作环境, 大应力中温使用的叶片榫根及延伸段的蠕变伸长是不容忽视的因素。 本文评述表明, 单晶高温合金在中温下的蠕变变形量以及蠕变寿命受取向的偏离度、 合金化和显微组织的影响十分明显。 在以中温蠕变伸长为主要考虑因素时, 昂贵的二、 三代单晶合金并无优势。 因此在选材和合金研发过程中, 要根据完整的使用条件, 综合平衡各种因素的作用, 最终做出正确的选择。
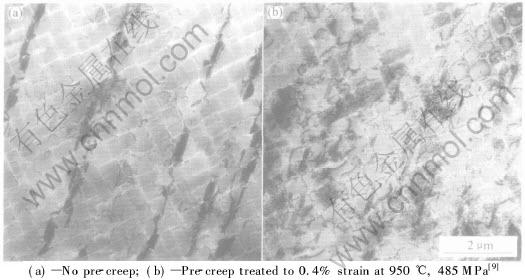
图7 预蠕变处理对CMSX-4单晶于750℃, 750MPa条件下蠕变至1%后位错结构的影响
Fig.7 Effects of pre-creep treatment on dislocation structures after
1% creep at 750℃, 750MPa
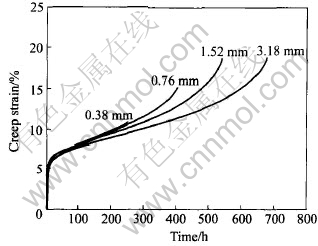
图8 不同厚度PWA1484单晶试样在760℃,
758MPa下的典型蠕变曲线比较[30]
Fig.8 Comparison of typical creep curves for PWA 1484 single crystal specimens with different thicknesses at 760℃, 758MPa[30]
REFERENCES
[1]Getel A D, Duhl D N. Second-generation nickel-base single crystal superalloy[A]. Reichman S, Duhl D N, Maure G, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1988[C]. Warrendale: AIME, 1988. 235-244.
[2]Walston W S, Ohara K S, Ross E. ReneN6: third generation single crystal superalloy[A]. Kissinger R D, Deye D J, Anton D A, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1996[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 1996. 15-24.
[3]Walston S, Getel A, Mackay R, et al. Joint development of a fourth generation single crystal superalloy[A]. Green K A, Pollock T M, Harada H, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 2004[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 1996. 15-24.
[4]Seth B B, Freyer P D, Hebbar M A, et al. Cost-effective manufacturing of high performance power generation combustion turbine components using the fabricated component method[A]. Strang A, Banks W M, Conrog R D, et al. Proceedings of the 4th Charles Parsons Turbine Conference[C]. London: The Institute of Materials, 1997. 129-147.
[5]Seth B B. Superalloys-the utility gas turbine perspective[A]. Pollock T M, Kissinger R D, Bowman R R, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 2000[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 2000. 3-15.
[6]Hashizume R, Yoshinari A, Kiyono T, et al. Development of Ni-base single crystal superalloys for power-generation gas turbines[A]. Green K A, Pollock T M, Harada H, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 2004[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 2004. 53-62.
[7]美国金属学会主编. 金属手册(第8卷)[M]. 第9版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1994. 377-380.
American Society For Metals. Metalls Handbook(Vol.8)[M]. 9th ed. Beijing: Mechincal Industry Press, 1994. 377-380.
[8]《中国航空材料手册》编辑委员会. 中国航空材料手册(第2卷)[M].第2版. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002. 792-828.
The Editional Committee of China Aeronautical Materials Handbook. China Aeronautical Materials Handbook(Vol.2)[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2002. 792-828.
[9]Drew G L, Reed R C, Kakehi K, et al. Single crystal superalloy: The transition from primary to secondary creep[A]. Green K A, Pollock T M, Harada H, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 2004[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 2004. 127-136.
[10]Leverant G R, Kear B H. The mechanism of creep in gamma prime precipitation-hardened nickel-base alloys at intermediate temperature[J] Metall Trans, 1970, 1: 491-498.
[11]Feller-Kniepmeier M, Hemmersmeier U, Kuttner T, et al. Analysis of interfacial dislocations in a single crystal nickel-base superalloy after[001] creep at 1033K[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1994, 30: 1275-1280.
[12]Mueller L, Glatzel U, Feller-Kniepmeier M. Calculation of the internal stresses and strains in the microstructure of a single crystal nickel-base superalloy during creep[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1993, 41: 3401-3411.
[13]Shah D M, Getel A. Creep anisotropy in nickel base g, gand g/g superalloy single crystals[A]. Kissinger R D, Deye D J, Anton D L, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1996[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 1996. 273-282.
[14]Shah D M, Vega S, Woodard S, et al. Primary creep in nickel-base superalloys[A]. green K A, Pollock T M, Harada H, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 2004[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 2004. 197-206.
[15]Sass V, Schneider W, Mughrabi H. On the orientation dependence of the intermediate temperature creep behavior of monocrystalline nickel-base superalloys[J]. Scripta Metall Mater, 1994, 31: 885-890.
[16]Feller-Kniepmeier M, Kuttner T.[011] creep in a single crystal nickel-base superalloy at 1033K[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1994, 42: 3167-3174.
[17]尹泽勇, 岳珠峰, 杨治国, 等. 各向异性单晶合金结构强度与寿命[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003. 76-132.
YIN Ze-yong, YUE Zhu-feng, YANG Zhi-guo, et al. Strength and Life of Anisotropic Single Crystal Alloy Structures[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2003. 76-132.
[18]Voelkl R, Glatzel U, Feller-Kniepmeier M. Analysis of matrix and interfacial dislocations in the nickel-base superalloy CMSX-4 after creep in [111] diretion[J]. Scripta Metall Trans, 1994, 31: 1481-1486.
[19]Rae C M F, Martan N, Cox D C. On the primary creep of CMSX-4 superalloy single crystals[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2000, 31A: 2219-2228.
[20]Caron P, Ohta Y, Nakagawa Y G, et al. Creep deformation anisotropy in single crystal superalloy[A]. Reichman S, Duhl D N, Maure G, et al. Superalloys 1988[C]. Warrendale: AIME, 1988. 215-224.
[21]LIN Dong-liang, YAO De-liang, SUN Chuan-qi. The effect of stress and temperature on the extent of primary creep in directionally solidified nickel-base superalloys[A]. Gell M, Kortovich C S, Brincknesll R H, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1984[C]. Warrendale: AIME, 1984. 199-210.
[22]Chen Q Z, Knowles D M. Mechanism of 〈112〉/3 slip initiation and anisotropy of gphase in CMSX-4 during creep at 750℃ and 750MPa[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, A356: 352-367.
[23]Mackay R A, Dreshfield R L, Maier R D. Anisotropy of nickel-base superalloy single crystals[A]. Tien J K, Wlodek S T, Morrow , et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1980[C]. Ohio: AMS, 1980. 385-394.
[24]Matan N, Cox D C, Carter P, et al. Creep of CMSX-4 superalloy single crystals: effects of microrientation and temperature[J]. Acta Matall Mater, 1999, 47: 1549-1563.
[25]Kakehi K. Effect of primary and secondary precipitates on creep strength of Ni-base superalloy single crystals[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, A278: 135-141.
[26]Pollock T M, Argon A S. Creep resistance of CMSX-3 nickle base superalloy single crystals[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40: 1-30.
[27]Leverant G R, Duhl D N. The effect of stress and temperature on the extent of primary creep in directionally solidified nickel base superalloys[J]. Metall Trans, 1971, 2: 907-908.
[28]Sims C T, Stoloff N S, Hagel W C. Superalloy(Ⅱ)[M]. New York: John Wiley, 1987. 189-214.
[29]Doner M, Heckler J A. Identification of mechanisms responsible for generation in thin-wall stress rupture properties[A]. Reichman S, Duhl D N, Maure G, et al. Proceedings of Superalloys 1988[C]. Warrendale: AIME, 1988. 653-662.
[30]Seetharaman V, Getel A D. Thickness debit in creep properties of PWA 1484[A]. Green K A, Pollock T M, Harada H. Proceedings of Superalloys 2004[C]. Warrendale: TMS, 2004. 207-214.
收稿日期: 2005-05-20; 修订日期: 2005-08-17
作者简介: 郑运荣(1941-), 男, 研究员
通讯作者: 郑运荣, 研究员; 电话: 010-62496148; E-mail: yunrong.zheng@biam.ac.cn
(编辑陈爱华)