文章编号:1004-0609(2010)10-2038-07
盐酸强化还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀动力学
郭宇峰,刘水石,马晓雯,姜 涛,邱冠周
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:研究盐酸对攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀反应速率和锈蚀法铁钛分离效果的影响,并对还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应动力学进行分析。结果表明:盐酸显著提高还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应速率及锈蚀法钛铁分离的效果;当盐酸用量由0增加到4%时,还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀率由43%提高到90%以上,锈蚀法钛铁分离后富钛料中TiO2的品位由64.92%提高到81.21%,总铁含量(FeT)由18.25%降到5.06%;还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应受内扩散控制,添加4%的盐酸,锈蚀反应的表观活化能由59.26 kJ/mol 降低到38.65 kJ/mol,其作用机理是盐酸促进金属铁锈蚀过程的阴极反应,从而加快Fe2+的生成和扩散速率。
关键词:还原钛铁矿;钛铁分离;富钛料;还原锈蚀;动力学
中图分类号:TF823 文献标志码:A
Rusting kinetics of metallic iron in reduced ilmenite strengthened by hydrochloride
GUO Yu-feng, LIU Shui-shi, MA Xiao-wen, JIANG Tao, QIU Guan-zhou
(School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effect of hydrochloride on the rusting rate of metallic iron in Panzhihua reduced ilmenite and separation efficiency of titanium and iron by rusting process were studied. The rusting kinetic of the metallic iron in reduced ilmenite was analyzed. The results show that hydrochloride can significantly increase the reaction rate and separation efficiency of titanium and iron. As the dosage of hydrochloride increases from 0 to 4%, the rusting rate of the metallic iron in the reduced ilmenite increases from 43% to more than 90%, TiO2 grade of Ti-rich material increases from 64.92% to 81.21%, while total Fe grade decreases from 18.25% to 5.06%. The rusting reaction is controlled by internal diffusion. Adding 4% hydrochloride, the rusting apparent activation energy of the rusting reaction decreases from 59.26 kJ/mol to 38.65kJ/mol. The mechanism is that hydrochloride promotes the cathodic reaction of the rusting reaction , thus speeding up the formation and the diffusion rate of Fe2+.
Key words: reduced ilmenite; titanium-iron separation; Ti-rich material; reduction-rusting; kinetic
目前,世界钛资源中可用于钛工业生产的主要是天然金红石和钛铁矿[1]。天然金红石精矿的TiO2品位可达95%~96%(质量分数),是钛工业的优质原料,但储量较少。随着天然金红石资源的逐渐枯竭和价格上涨以及钛工业的发展,储量丰富的钛铁矿已经成为钛工业的主要生产原料。但钛铁矿的TiO2品位较低,为适应钛工业的发展,必须将钛铁矿富集成高品位的富钛料[2-3]。因此,有关钛铁矿制取富钛料方法的研究,一直都是钛工业领域最为活跃的研究课题之一。已研究和提出的制取富钛料的方法主要有电炉熔炼法、选择氯化法、酸浸法、还原锈蚀法和还原磁选法等[4-8],但目前在工业上获得应用的方法主要是电炉熔炼法、酸浸法和还原锈蚀法等。还原锈蚀法是一种选择性除铁的方法,是澳大利亚国立化学研究所开发的,亦称Becher法、亚钛法和水相氧化法。其基本过程是先将钛铁矿其中的铁氧化物还原为金属铁,钛以氧化物形态存在,然后再将还原产品于NH4Cl溶液介质中鼓入空气使其中的金属铁锈蚀,利用锈蚀后生成的水合铁氧化物和富钛料因其粒度和密度的不同,采用物理分选的方法实现铁钛分离,得到富钛料和副产品水合铁氧化物(赤泥)。还原锈蚀法具有环境友好、投资少且生产成本低等优点而得到世界的普遍认可[9]。然而,还原锈蚀法的锈蚀反应速率很低,在某些情况下,工业上锈蚀反应需要22h才能完成[10]。为加快锈蚀反应速率、提高生产效率,国内外学者开展了大量研究。最初的研究表明[11],还原钛铁矿在锈蚀过程中添加一定数量的无机酸能加快锈蚀反应速率。近年来的研究表明,还原钛铁矿在锈蚀过程中添加一定数量的有机酸或有机物也能加快锈蚀反应速率,如KUMARI和MOHAN[12]的研究表明,加入丙酮+甲酸和甲醇+甲酸后,还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应基本在3 h内完成,甲醇+甲酸可以使锈蚀率提高到86%,丙酮+甲酸则可以将锈蚀率提高到90%。MARINOVICH等[13-14]的研究表明,加入1.5%铵盐反应8h仅能除去54%的金属铁,加入2%乙二醛反应8 h可除去80%的铁,蔗糖、葡萄糖的效果略低于乙二醛的,该研究证明乙二醛、蔗糖、葡萄糖在锈蚀反应过程中由于氧化反应生成相应的羧酸。由此可见,酸具有加快还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应速率的作用。
本文作者通过研究盐酸对还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应速率的影响,证实盐酸具有加快还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应速率过程的作用,在此基础上,为揭示盐酸在还原钛铁矿锈蚀过程中加快锈蚀反应速率过程的动力学机理,对盐酸强化还原钛铁矿的锈蚀动力学进行研究。
1 实验
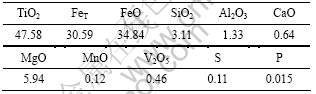
试验用还原钛铁矿采用攀枝花钛精矿(主要化学成分见表1)经固态还原制备的,所制备的还原钛铁矿金属化率为93.65%,金属铁含量为31.98%,总铁含量为 34.12%, TiO2含量为51.18%。将还原钛铁矿破碎至粒径小于0.1 mm,作为锈蚀试验研究的原料。
锈蚀反应选用1 L烧杯作为锈蚀反应器,采用恒温水浴锅控制体系温度。每次试验先将水加热到一定温度并恒温15 min后,根据试验要求,加入氯化铵或氯化铵和盐酸,随后再加入还原钛铁矿,按照试验要求对矿浆通气、搅拌。每次试验加入20 g的还原钛铁矿,每30 min向溶液中添加20 mL蒸馏水,补充因加
表1 钛铁矿精矿的主要化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of ilmenite concentrate (mass fraction, %)
热和通气蒸发损失的水。试验完成后,采用摇床重选将铁红和富钛料分离。
用锈蚀率γ和富钛料中铁品位、TiO2的品位来衡量锈蚀反应进程及铁钛分离效果,即
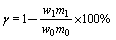 (1)
(1)
式中:w0为还原钛铁矿中金属铁的含量,%;w1为锈蚀所得产物中金属铁的含量,%;m0为反应前加入的还原钛铁矿的质量,g;m1为反应后得到的产物的质量,g;γ为锈蚀率,%。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 盐酸对锈蚀反应速率的影响
在70 ℃、原料粒度小于0.1 mm、氯化铵添加量为1.6%、搅拌速率为600 r/min、通气速率为5×103 L?min-1?m-3、液固质量比为10:1的条件下,研究盐酸对还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀反应速率的影响,试验结果如图1和2所示。
由图1可知:锈蚀反应速率随着盐酸浓度的提高而增加;当盐酸量由0%增加到4%,还原钛铁矿的锈
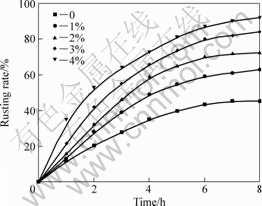
图1 盐酸对还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应速率的影响
Fig.1 Effect of hydrochloric acid content on rusting rate of reduced ilmenite
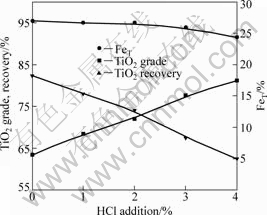
图2 盐酸添加量对锈蚀产品(8 h)指标影响
Fig.2 Effect of hydrochloric acid addition on rusted product
蚀率可由43%提高到90%以上,显著提高金属铁的锈蚀率。对锈蚀8 h产品的分析也证明了盐酸能有效提高钛铁的分离效果,不加盐酸时,锈蚀产品中FeT为18.25%,而加入2%HCl可使FeT含量降为12.82%,盐酸用量增至4%后,还原钛铁矿中FeT降为5.06%,并且随着盐酸用量的增加,TiO2品位由63.43%提高到81.21%。
为进一步验证盐酸对还原钛铁矿铁钛分离的强化效果,采用JSM-56600LV型扫描电镜分析仪,对还原钛铁矿添加4%盐酸和不加盐酸两种条件下锈蚀8 h所得富钛料的微观结构进行分析。图3所示为添加4%盐酸处理得到的富钛料的SEM像,图4所示为不加盐酸处理所得富钛料的SEM像。由图3和4可知,加盐酸处理后的富钛料金属铁的残余量远小于不加盐酸处理的富钛料。可见,盐酸能显著提高金属铁锈蚀反应速率和钛铁分离效率锈蚀产品的品位。
为查明盐酸中H+和Cl-在锈蚀反应中的作用,进行了以下对比实验,试验方案及结果如表 2所列。其
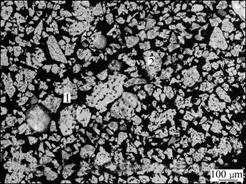
图3 添加4%盐酸处理所得富钛料的SEM像
Fig.3 SEM image of Ti-rich material with hydrochloride treatment: 1—Metal iron (white zone); 2—Ilmenite (gray zone)
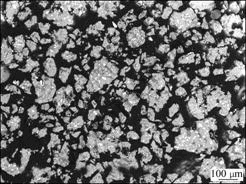
图4 不加盐酸处理所得富钛料的SEM像
Fig.4 SEM image of Ti-rich material without hydrochloride treatment: 1—Metal iron (white zone); 2—Ilmenite (grey zone)
表2 不同实验条件下TiO2的品位和总铁含量
Table 2 Grade of TiO2 and FeT under different experimental conditions
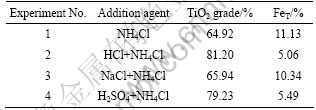
中盐酸和氯化钠的氯离子摩尔浓度相同;硫酸和盐酸的氢离子摩尔浓度相同。各试验条件如下:原料粒径小于0.1 mm、氯化铵添加量为1.6%、搅拌速率为600 r/min、温度为70 ℃、通气速率为5×103 L?min-1?m-3,反应为6 h。由表 2中实验3与实验1、实验2的对比可知,NaCl对锈蚀中钛铁的分离效果远低于盐酸,这说明盐酸中的Cl-对还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应没有明显的促进作用。实验4与实验1、实验2对比可知,相同H+浓度的H2SO4代替HCl后,锈蚀反应钛铁分离效果相差不大。由此可以推断,盐酸对锈蚀反应的促进作用应主要是源于其中的H+。
2.2 盐酸对锈蚀过程动力学的影响
2.2.1 不加盐酸时的锈蚀动力学
图5所示为在1.6%的NH4Cl溶液中、搅拌速率600 r/min、通气速率5×103 L·min-1·m-3、液固质量比10:1、粒度小于0.1 mm、盐酸添加量为0条件下,攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁等温锈蚀试验结果。
应用未反应核模型[8]对还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀反应的等温试验结果进行分析[15-19]。对图5中锈蚀率γ(浸出分数x)与时间t的关系分别以1-(1-x1/3)对时间t、1-3(1-x)2/3+2(1-x)对时间t作图。在试验温度范围内,1-3(1-x)2/3+2(1-x)对时间t的线性关系最好,结果如图6所示,这表明在试验温度范围内,该反应过程受内扩散控制。由图6中各直线的斜率可得出各温度下的速率常数k值。采用Arrhenius方程可求出还原钛铁矿中铁锈蚀反应的活化能,即
 (2)
(2)
对式(2)两边取对数,可得
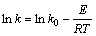 (3)
(3)
式中:E为活化能,kJ/mol; k0为系数,h·L-1 ;k为速率常数,h·L-1;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314×10-3 kJ·mol-1·K-1;T为温度,K。
在30 ℃~70 ℃范围内,以lnk对T-1作图,如图7所示。lnk与T -1成线性关系,该直线的斜率为-E/R。
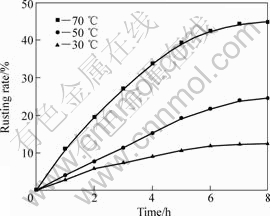
图5 攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀等温曲线
Fig.5 Isothermal rusting curves of metallic iron in reduced ilmenite
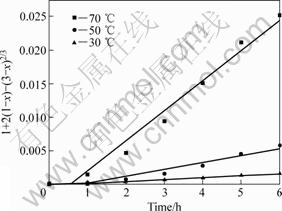
图6 不加盐酸时 t与1+2(1-x)-3(1-x)2/3 的关系
Fig.6 Relationship between t and 1+2(1-x)-3(1-x)2/3 without hydrochloric acid
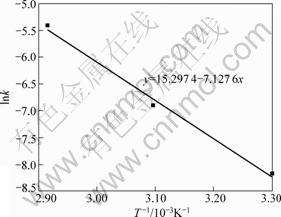
图7 不加盐酸时的Arrhenius图
Fig.7 Plot of Arrhenius without hydrochloric acid
由图7直线的斜率可求出还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀反应表观活化能为59.26 kJ/mol。
2.2.2 加盐酸时的锈蚀动力学
图8所示为在1.6%的NH4Cl溶液,搅拌速率为600 r/min、通气速率为5×103 L·min-1·m-3、液固质量比为10:1、粒度小于0.1 mm的条件下,盐酸添加量为4%的条件下,攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁的等温锈蚀试验结果。
采用未反应核模型对图8进行分析,对锈蚀率γ(浸出分数x)与时间t的关系分别以1-(1-x1/3)对时间t、1-3(1-x)2/3+2(1-x)对时间t作图。在试验温度范围内,1-3(1-x)2/3+2(1-x)对时间t的线性关系最好,所得结果如图9所示。这表明攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁在盐酸-氯化铵体系中锈蚀反应过程受内扩散控制。由图9中各直线的斜率可得出各温度下的速率常
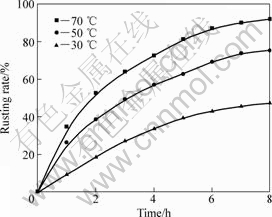
图8 加盐酸时攀枝花还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀等温曲线
Fig.8 Isothermal rusting curves of metallic iron in reduced ilmenite adding hydrochloric
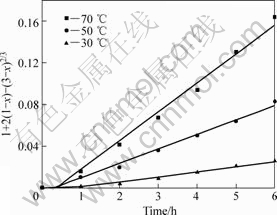
图9 加盐酸时t与1+2(1-x)-3(1-x)2/3 的关系
Fig.9 Relationship between of t and 1+2(1-x)-3(1-x)2/3 adding hydrochloric acid
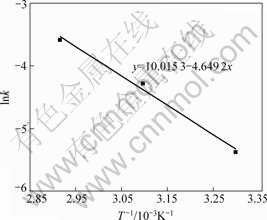
图10 加盐酸时的Arrhenius图
Fig.10 Plot of Arrhenius with hydrochloric acid
数k值。利用Arrhenius图(见图10),可求出盐酸强化还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应的表观活化能为38.65 kJ/mol。
通过对比氯化铵锈蚀反应体系中有、无盐酸两种条件下锈蚀反应活化能可知,添加4%的盐酸使得金属铁锈蚀反应的表观活化能由59.26 kJ/mol降低到38.65 kJ/mol。
2.3 盐酸强化锈蚀过程动力学的微观机理
还原钛铁矿在锈蚀过程中,颗粒内的金属铁微晶相当于原电池的阳极,颗粒外表面相当于阴极,在阳极,Fe失去电子转换为Fe2+进入溶液[8]:
2Fe(s)→2Fe2+(aq)+4e (4)
在阴极区,溶液中的氧接受电子生成OH-离子:
O2+2H2O+4e→4OH- (5)
颗粒内溶解下来的Fe2+沿着微孔扩散到颗粒外表面的电解质溶液中,在溶液中进一步氧化生成水合氧化物铁细粒沉淀:
2Fe2++2OH-+1/2O2=Fe2O3·H2O↓+H2O (6)
由于还原钛铁矿由离析的铁晶粒和富钛相组成,铁晶粒通过复杂网状微孔连通到还原钛铁矿颗粒外部,因此,在锈蚀反应中还原钛铁矿中的金属铁氧化后可以以Fe2+形式会从还原钛铁矿颗粒中扩散分离出来[20]。研究发现[21]:如果还原钛铁矿中的金属铁在还原钛铁矿颗粒内部被氧化为氢氧化亚铁(Ⅱ)并在矿物颗粒内部沉淀,沉淀后的铁氧化物或氢氧化物很难再从钛铁矿颗粒内部分离出来,锈蚀过程中出现的这种现象称为“原位锈蚀”。“原位锈蚀”会直接影响钛铁分离效果。
根据前面的实验结果可知,还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀过程符合未反应核模型,且受内扩散控制,由此可以推测其模型可用图11来表示。金属铁失去电子转化为Fe2+,溶液中的氧接受电子生成OH-,生成的Fe2+从金属铁颗粒内部扩散出来被氧化生成铁红,金属铁和富钛层分离,金属铁固体颗粒转化为铁红。
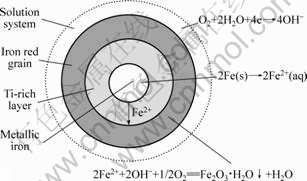
图11 锈蚀反应的未反应核模型
Fig.11 Unreacted core model of rusting reaction
在本实验中,添加盐酸后,体系值降低,有利于反应(5)向正方向进行,使其得到电子速度加快,从而促进了反应(4),加快Fe2+的生成,使金属铁颗粒表面Fe2+浓度增加,而还原钛铁矿颗粒外部Fe2+因反应(6)的消耗使其浓度降低,导致还原钛铁矿颗粒内外Fe2+的浓度梯度增大,其结果是加快了Fe2+的扩散速率。由此可见,还原钛铁矿锈蚀体系中添加盐酸使Fe2+的生成及其扩散速率加快是降低锈蚀反应表观活化能的根本原因。
3 结论
1) 盐酸能显著加快还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀反应速率,提高钛铁分离效果。在原料粒度小于0.1 mm、温度为70 ℃、氯化铵添加量为1.6%、盐酸为4%、搅拌速率为600 r/min、通空气速率为5×103 L?min-1?m-3、液固质量比为10:1、锈蚀反应时间8 h的条件下,盐酸用量由0提高到4%,还原钛铁矿中金属铁的锈蚀率可由43%提高到90%以上,富钛料中TiO2品位由64.92%提高到81.21%,锈蚀产品中总铁含量由18.25%降到5.06%。
2) 锈蚀反应的动力学研究表明,有、无盐酸条件下,锈蚀反应都受内扩散控制。无盐酸体系下锈蚀反应的表观活化能为59.26 kJ/mol,加盐酸后锈蚀反应的表观活化能降低到38.65 kJ/mol。
3) 在还原钛铁矿锈蚀反应过程中,盐酸促进还原钛铁矿中金属铁锈蚀过程的阴极反应,使Fe2+的生成和其扩散速率加快是降低锈蚀反应表观活化能的根本原因。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘椒清, 彭 毅. 钛原料的供需趋势分析及前景展望[J]. 钛工业进展, 2000, 4(1): 6-11.
LIU Jiao-qing, PENG Yi. Analysis of titanium raw material supply and demand trends and prospects[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2000, 4(1): 6-11.
[2] 韩明堂. 如何发展我国的富钛料生产[J]. 钛工业进展, 2001, 11(1): 4-7.
HAN Ming-tang. How to develop China's production of Ti-rich material[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2001, 11(1): 4-7.
[3] 孙朝晖. 攀枝花钛铁矿精矿制备高品质富钛料的比较[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2007(6): 32-36.
SUN Zhao-hui. Preparation of high quality titanium material for boiling chlorination from Panzhihua ilmenite[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2007(6): 32-36.
[4] 胡克俊, 锡 淦, 姚 娟, 席 歆. 还原-锈蚀法生产人造金红石技术现状及攀钢采用该工艺可行性分析[J]. 钛工业进展, 2006, 23(9): 17-22.
HU Ke-jun, XI Gan, YAO Juan, XI Xin. The feasibility analysis of Becher process used in Panzhihua[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2006, 23(9): 17-22.
[5] 温旺光. 钛铁矿选择氯化法制取人造金红石的热力学与动力学[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2003, 24(1): 8-15.
WENF Wang-guang. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the ilmenite selective chlorination produce synthetic rutile[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2003, 24(1): 8-15.
[6] 王曾洁, 张利华, 王海北, 蒋训雄, 薛济来, 扈维明, 王 舰. 盐酸常压直接浸出攀西地区钛铁矿制备人造金红石[J]. 有色金属, 2007, 59(4): 108-111.
WANG Zeng-jie, ZHANG Li-hua, WANG Hai-bei, JIANG Xun-xiong, XUE Ji-lai, HU Wei-ming, WANG Jian. Ilmenite hydrochloric acid leaching for synthetic rutile preparation[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 59(4): 108-111.
[7] 杨绍利, 盛继孚. 钛铁矿熔炼钛渣与生铁技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 42-44.
YANG Shao-li, SHENG Ji-fu. Technology of titanium slag and iron metallurgy by ilmerite titanium slag and iron[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 42-44.
[8] 莫 畏, 邓国珠, 罗方承. 钛冶金[M]. 第二版. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007: 188-189.
MO Wei, DENG Guo-zhu, LUO Fang-cheng. Metallurgy of titanium[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007: 188-189.
[9] MAHMOUD M H, AFIFI A I, IBRAHIM I A, Reductive leaching of ilmenite ore in hydrochloric acid for preparation of synthetic rutile[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 73(4): 99-109.
[10] WARD C B, GIBBONS S L, RITCHIE I M. and MUIR D M, Transformations of iron oxide by-products during the Becher process[C]//Proc AuslMM Annu Conf, Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, 1989: 209-215.
[11] BENJAMIN S E, SYKES J M. Chloride-induced pitting corrosion of Swedish iron in ordinary Portland cement mortars and alkaline solutions: the effect of temperature[J]. Elsevier Applied Science, 1990, 5(2): 234-239.
[12] JAYA KUMARI, MOHAN P N. A structural model for the rusting of reduced ilmenite[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 43(9): 13-20.
[13] MARINOVICH Y, BAILEY S, AVRAAMIDES J, JAYASEKERA S. An electrochemical study of reduced ilmenite carbon paste electrodes[J]. Appl Electrochem, 1995, 23(11): 34-35.
[14] MARINOVICH Y, BAILEY S. A structural model for the rusting of reduced ilmenite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2002, 35(14): 13-20.
[15] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 第三版. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2005: 82-87.
HUANG Xi-hu. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005: 82-87.
[16] 刘玉民, 齐 涛, 张 懿. KOH亚熔盐法分解钛铁矿的动力学分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(6): 1142-1147.
LIU Yu-min, QI Tao, ZHANG Yi. Kinetics analysis of decomposition of ilmenite by KOH sub-molten salt method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(6): 1142-1147.
[17] FARROW J B, RITCHIE I M. The reaction between reduced ilmenite and oxygen in ammonium chloride solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 39(8): 21-39.
[18] LI Chun, LIANG Bin, GUO Ling-hong, WU Zi-bin. Effect of mechanical activation on the dissolution of Panzhihua ilmenite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(14): 1430-1438.
[19] LIU Xiao-hua, GAI Guo-sheng, YAN Yu-fen. Kinetics of the leaching of TiO2 from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2008, 18(6): 275-278.
[20] JAYASEKERA S, AVRAAMIDES J. Rotating disc electrode apparatus for aqueous electrochemical studies at elevated temperatures and pressures application to the Becher process[C]//Proceeding 6th AuslMM Extractive Metallurgy Conference, Brisbane: Aust Inst Min Metall Parkville, 1994: 123-126.
[21] JAYA KUMARI E, BERCKMAN E. An electrochemical investigation of the rusting reaction of ilmenite using cyclic voltammetry[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1987, 12(3): 217-221.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金委青年科学基金资助项目(50504018);国家基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613606)
收稿日期:2009-11-11;修订日期:2010-03-21
通信作者:郭宇峰,副教授;电话:13975894856;E-mail:guo.yf@126.com