熔体过热度对定向凝固藕状多孔金属结构均匀性的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第3期
论文作者:刘 源 张华伟 李言祥
文章页码:1004 - 1010
关键词:定向凝固;多孔金属;熔体过热度;结构均匀性
Key words:unidirectional solidification; porous metals; melt superheat; structural uniformity
摘 要:结构均匀性是影响藕状多孔金属的物理和力学性能的重要参数。系统研究熔体过热度对金属-气体共晶定向凝固(Gasar)制备藕状多孔金属的多孔结构均匀性以及气孔率、气孔形貌的影响规律。实验结果表明,凝固过程中存在一临界过热度(?Tc),超过该临界值时,凝固界面前沿熔体中会发生气泡的形核和上浮溢出(“冒泡”或“沸腾”)现象,结果造成气孔率的下降。另外,过高的过热度会导致相邻气孔的合并粗化,形成大尺寸气泡,最终获得不均匀的气孔结构。在实验结果基础上,建立气泡溢出的临界过热度(DTc)理论模型和氢气溢出系数计算模型。在考虑氢气溢出时,理论预测的气孔率与实验结果吻合较好。
Abstract: Structural uniformity is an important parameter influencing physical and mechanical properties of lotus-type porous metals prepared by directional solidification of metal-gas eutectic (Gasar). The effect of superheat on structural uniformity as well as average porosity, pore morphology of porous metals was studied. The experimental results show that, when the superheat is higher than a critical value (DTc), the bubbling or boiling phenomenon will occur and the gas bubbles will form in the melt and float out of the melt. As a result, the final porosity will decrease. In addition, a higher superheat will simultaneously cause a non-uniform porous structure due to the pores coalescence and bubbling phenomenon. Finally, a theoretical model was developed to predict the critical superheat for the hydrogen to escape from the melt and the corresponding escapement ratio of hydrogen content. Considering the escapement of hydrogen, the predicted porosities are in good agreement with the experimental results.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1004-1010
Yuan LIU1,2, Hua-wei ZHANG1,2, Yan-xiang LI1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Received 11 April 2014; accepted 20 June 2014
Abstract: Structural uniformity is an important parameter influencing physical and mechanical properties of lotus-type porous metals prepared by directional solidification of metal-gas eutectic (Gasar). The effect of superheat on structural uniformity as well as average porosity, pore morphology of porous metals was studied. The experimental results show that, when the superheat is higher than a critical value (DTc), the bubbling or boiling phenomenon will occur and the gas bubbles will form in the melt and float out of the melt. As a result, the final porosity will decrease. In addition, a higher superheat will simultaneously cause a non-uniform porous structure due to the pores coalescence and bubbling phenomenon. Finally, a theoretical model was developed to predict the critical superheat for the hydrogen to escape from the melt and the corresponding escapement ratio of hydrogen content. Considering the escapement of hydrogen, the predicted porosities are in good agreement with the experimental results.
Key words: unidirectional solidification; porous metals; melt superheat; structural uniformity
1 Introduction
Porous metallic materials are a kind of attractive engineering materials owing to their unusual combinations of physical and mechanical properties, such as low density, sound absorption, impact energy absorption capacity, heat dissipation and heat insulation ability. Various fabrication methods for porous materials were developed including powder metallurgy, casting, metal depositing, melt foaming with gas bubbling and so on [1,2]. However, the pores are usually random and it is hard to control the spatial distribution and structure parameters of pores fabricated by these methods.
A new type of porous metals with ordered and aligned long cylindrical pores was fabricated by metal/gas unidirectional solidification (also called “Gasar”) in a pressurized hydrogen and/or nitrogen [3,4]. This processing technique utilizes an invariant reaction of the so-called “metal/gas eutectic reaction” in which the melt is solidified into a solid solution and a gas phase. When the melt is solidified directionally, the supersaturated gas separates from the solid metal due to its solubility difference in the solid and liquid metal, then forms as gas bubbles growing simultaneously with the solid phase, as shown in Fig. 1. Lotus-type porous metals have some unique performances due to their regular porous structure. In particular, lotus-type porous metals have superior mechanical properties compared to the conventional porous metals [5], and superior heat dissipating capacity for micro-channel heat sink application [6-9].
In Gasar process, the gas pressure and the melt temperature (superheat) as well as the solidifying velocity are the dominant processing parameters influencing the structural uniformity as well as the final porosity and pore size of the porous structure. Unsuitable processing parameters can cause the secondary nucleation, growth interruption, coalescence, even bubble floating and escaping phenomenon of gas pores, finally cause non-uniform porous structure and inferior mechanical and heat dissipating performance. In the past, most researches were concentrated on the effects of the gas pressure and the solidifying velocity [10-16]. But few researches have been made on the effect of the melt superheat. Only APPRILL et al [11] made experimental study on Gasar solidification of Ni and Inconel 718 alloy under a higher superheat condition and observed the bubble floating phenomenon. Systematic work, especially on the theoretical analysis of the effect of the superheat on the porous structural parameters was scarce.
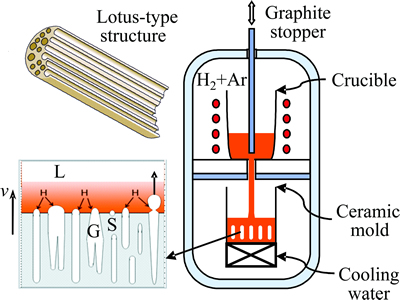
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of fabrication apparatus for louts- type porous metals
In order to prepare lotus-type porous metals with uniform structure, magnesium was selected as the representative system to study the influence of the melt temperature on the pore nucleation, growth, coalescence and the final pore morphology and porosity, especially the floating and escaping phenomenon of hydrogen bubbles through combination of experimental and theoretical analysis.
2 Experimental
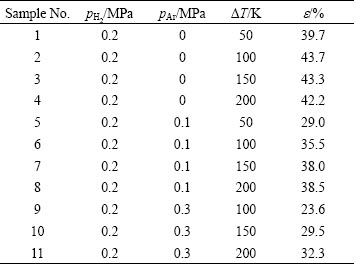
A schematic diagram of the apparatus for preparing louts-type porous metals is shown in Fig. 1. It consists of a graphite crucible (100 mm in inside diameter and 200 mm in height) surrounded by a heating coil and a ceramic mold with a water-cooled copper bottom. These are installed in a high-pressure chamber. High-purity magnesium is melted in the crucible in vacuum, and then high-pressure hydrogen or gas mixture of hydrogen and argon is introduced into the chamber. The melt is held for 1 h at a given superheat (or melt temperature) to ensure that the hydrogen dissolved into the magnesium melt. Then the graphite rod is lifted up to let the melt flow into the adiabatic ceramic mold with a water cooling copper chiller to solidify directionally. The ingot weighted 450 g is a cylinder with 60 mm in diameter and its porosity is evaluated through Archimedes’ principle. Table 1 shows the selected processing parameters together with the measured porosities of the prepared magnesium ingots. The aim is to study the influence of the superheat (ΔT) and the partial pressure of argon (pAr). It should be noted that the porosity is the average value of three samples prepared at the same processing parameters.
Table 1 Processing parameters together with porosity (e) of porous magnesium ingots
The cylindrical ingot is firstly sectioned into two equal parts along the central axis by the spark erosion wire cutting, then one part is sliced into several pieces at different heights (20, 40, 60 mm) for pore size and pore distribution observation on the cross sections. The samples are firstly polished with 800 grit to 2000 grit SiC papers, then degreased with acetone and cleaned with dilute HCl by ultrasonic cleaning. Then, the samples are observed with optical microscope and the images of the cross-sections are taken for porosity and average pore diameter evaluation by the image analysis software.
3 Experimental results
Figure 2 shows the experimental porosities (scattered symbols) and the predicted results (curves) of the porous magnesium ingots prepared at different superheats (ΔT) and gas pressures. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that, when the gas pressure (hydrogen and argon partial pressure) keeps constant, the porosity firstly increases linearly, then approaches flat even descends slightly with increasing superheat. In other words, the inflection point of the porosity corresponds to a critical superheat (DTc) above which the porosity will not increase anymore. In addition, it can also be found that the inflection point of the porosity moves right and the corresponding critical superheat increases with increasing partial pressure of argon (pAr) when the partial pressure of hydrogen (pH2) keeps as constant.
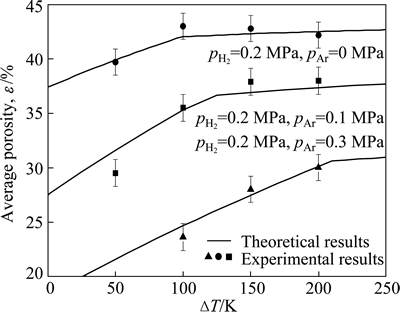
Fig. 2 Experimental porosities together with corresponding theoretical results of porous magnesium ingots prepared at different superheats and gas pressures
For magnesium melt [17], the solubility equation (C0=exp(-2532.75/TL+6.55)·(pH2)1/2) of hydrogen describes that a higher temperature or superheat leads to a higher hydrogen solubility, then should lead to a higher theoretical porosity according to the ideal gas law. But the experimental results do not completely respond to the theoretical evolution trend. The experimental porosity will not increase anymore when the superheat exceeds a critical value. APPRILL et al [11] observed the bubble floating (“bubbling” or “boiling”) phenomenon during the preparing process of Gasar Ni under a higher superheat condition. So here we have reason to believe that part of the dissolved hydrogen escapes from the melt due to the bubbling or boiling phenomenon if the superheat exceeds a critical value.
Figure 3 shows the pore morphology and distribution on the cross sections at different heights of some selected porous magnesium ingots. It can be seen from Figs. 3(a)-(d) that, in the pure hydrogen atmosphere (pH2=0.2 MPa, pAr=0 MPa), when the superheat exceeds 150 K, many big pores appear at the bottom and the top of the ingot. In this case, the porous structure becomes non-uniform. When the superheat further is raised up to 200 K, more and more extraordinary big pores form and the structural non-uniformity further aggravates. This kind of structural evolution corresponds directly to the porosity evolution displayed in Fig. 2. In other words, there exists a same critical superheat (DTc), above which some extraordinary big pores appear and non-uniform porous structure forms, simultaneously, and the porosity does not increase further. At the same time, it can be seen from Figs. 3(c)-(d) that most of the big pores are formed owing to the coalescence of several gas pores. This kind of coalescence phenomenon is very noticeable especially when the superheat is 200 K, as shown in Fig. 3(d). Actually, the coalescence of gas pores and the formation of non-uniform porous structure are all related to the bubbling or boiling phenomenon during Gasar solidification at a higher superheat. We will make a detailed theoretical analysis on this problem in the following section.
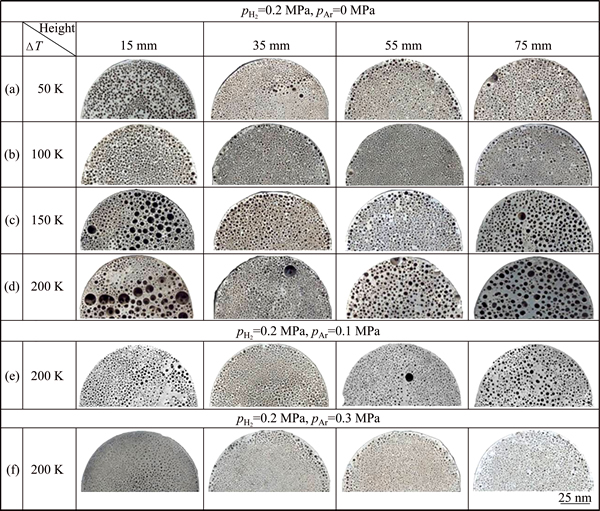

Fig. 3 Pore morphologies and distribution on cross sections at different heights of porous magnesium ingots prepared at different superheats and gas pressures
Figures 3(d)-(f) show the porous structures prepared at different partial pressures of argon when the superheats are all kept as 200 K. It is obvious that the number of the extraordinary big pores decreases (pAr= 0.1 MPa), even disappears (pAr=0.3 MPa) with increasing partial pressure of argon. In other words, the addition of argon can suppress occurrence of the bubbling or boiling phenomenon and the formation of extraordinary big pores. As a result, the structural uniformity improves. This phenomenon also replies that, when the partial pressure of hydrogen keeps as constant, the addition of argon can enhance the critical superheat for the extraordinary big pores and non-uniform porous structure.
4 Theoretical analysis
4.1 Porosity evolution
The formation of regular lotus-type porous structure depends on the coupled and cooperative growth between the gas pores and the solid phase. In other words, the gas pore should have a steady and moderate growth velocity matching the growth of solid metal phase. But the steady growth will be broken under a higher superheat condition. As shown in Fig. 4, on the one side, the liquid ahead the solidifying front will become supersaturated with hydrogen due to the hydrogen released from the solidified solid. On the other side, during the unidirectional solidifying process, there exists a temperature gradient in the melt ahead the solidifying front. The melt temperature quickly changes from Tm at the solidifying front to Tp (the original melt temperature, Tp=Tm+△T) at a certain distance above the solidifying front. Correspondingly, this region will become supersaturated with hydrogen due to the drop of the melt temperature. Here, this region is defined as supersaturation zone. When the hydrogen content in this supersaturation zone exceeds the minimal value for bubble nucleation (Cn(min)), as shown in Fig. 4, the hydrogen bubbles will nucleate and grow up.
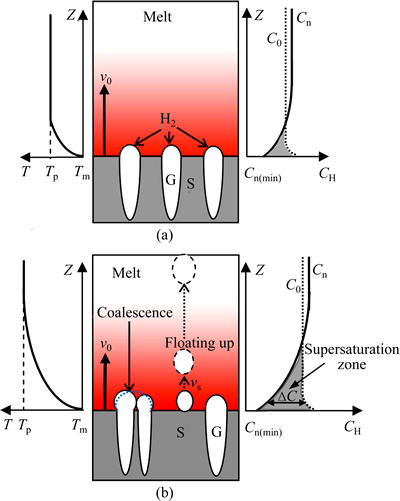
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of nucleation, growth, coalescence and floating up phenomenon of gas bubbles in melt ahead solidifying front under low superheat (a) and high superheat (b)
In the supersaturation zone, the supersaturation degree (DC) in the melt ahead the solidifying front can be approximately described as
DC≈C0-Cn(min) (1)
According to Sieverts’ law, the original hydrogen content (C0) in the liquid metal can be expressed by the melt temperature (Tp) and the partial pressure of hydrogen (pH2):
 (2)
(2)
where x(T)=exp(-A/T+B) is a coefficient term, A and B are solubility constants, and Tm is the melting point of the metal.
The hydrogen content needed for the bubble embryo to nucleate (Cn) in the supersaturation zone must satisfy the following Sieverts’ law:
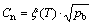 (3)
(3)
where pb is the total gas pressure in the nucleated bubble. It is obvious that Cn in the melt also has the same evolution trend as that of the melt temperature distribution. Correspondingly, the minimum of Cn locates at the solidifying front and can be described as [18]
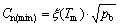 (4)
(4)
where for a new nucleated bubble with a radius of r, pb can be calculated from the equilibrium relationship between internal and external pressures acting on the gas bubble:
 (5)
(5)
the static pressure of the melt is ps=rLgh, rL is the density of the melt, g is the gravity acceleration, g= 9.8 m/s2, h is the depth of melt above the bubble (h≈120 mm), approximating to the average height of the melt. The capillary pressure caused by the surface tension is pc=2sLG/r, sLG is the surface tension at the liquid/gas interface, and r is the radius of the bubble.
If C0≥Cn(min), the gas bubbles will nucleate at the solidifying interface. After that, the nucleated gas bubble has the potency to float up due to the buoyancy. If the Stokes floating rate (vs) of the bubble is faster than the solidifying velocity (v0), it cannot be captured by the solidifying front and will float out of the melt. This is the typical bubbling or boiling phenomenon. The final result is the decrease of the effective hydrogen content for the formation of gas pores. So, the critical conditions for the gas bubble floating can be expressed as
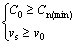 (6)
(6)
According to C0≥Cn(min), the superheat condition for a bubble to nucleate in the melt can be obtained:


 (7)
(7)
If the fluid flow is laminar (Reynolds number below 2000), the floating speed (vs) of a spherical bubble can be calculated by Stokes’ law:
 (8)
(8)
where h is the viscosity of the melt, rG is the density of the gas. Compared with rL, rG is much small and can be ignored.
According to vs≥v0, we can get the following relationship:
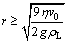 (9)
(9)
The solidifying velocity (v0) is 0.5-1.0 mm/s during unidirectional solidification of Mg-H system measured in our experiments. If we set v0=0.75 mm/s and substitute the melt viscosity h=1.25 mPa×s and the melt density rL=1.59 g/cm3 into Eq. (9), the minimal radius (rc) for the gas bubble to float up can be calculated as 15.1 mm. Thus, the capillary pressure is pc=2sLG/rc= 0.075 MPa. In our experiments, the average height (h) of the melt is 120 mm and the corresponding static pressure ps(ps=rLgh) is about 0.02 MPa. If substituting pc=0.075 MPa and ps=0.02 MPa into Eq. (7), the critical superheat condition (DTc) for a bubble to form and escape from the melt can be written as
 (10)
(10)
In other words, when the superheat exceeds DTc, the supersaturated hydrogen in the melt ahead the solidifying front will nucleate as bubbles, then float up and escape from the melt. This is called as bubbling or boiling phenomenon. So further increasing the superheat not only can not enhance the total porosity, but also cause the formation of extraordinary big pores and non-uniform porous structure due to the bubbling or boiling phenomenon.
If substituting A=253275 [17] and pH2=0.2 MPa into Eq. (10), Eq. (10) can be used to predict the critical superheat (DTc) for hydrogen escapement at different partial pressures of argon. As shown in Fig. 5, the predicted DTc increases with increasing pAr. When pAr=0, 0.1 and 0.3 MPa, the corresponding DTc is 61, 122 and 222 K, respectively. This is why many big pores exist (see Figs. 3(c)-(d)) on the cross sections of magnesium ingots prepared at △T=150 K and 200 K when pAr=0 MPa. A small amount of big pores still exist at △T=200 K when pAr=0.1 MPa. But the big pores will disappear at △T =200 K when pAr=0.3 MPa.
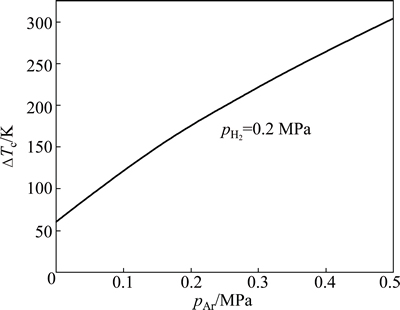
Fig. 5 Critical superheat degree for hydrogen to escape vs partial pressure of argon with constant hydrogen partial pressure
When the bubbling or boiling phenomenon takes place, a part of hydrogen will escape from the melt and not form as the final gas pores in the solid metal. Here, we define parameter a as the escapement ratio which represents the ratio of the hydrogen content escaping from the melt by the bubbling way to the original hydrogen content in the melt. According to the criterion conditions (Eq. (6)) for hydrogen bubble to nucleate and escape from the melt, the excess hydrogen will escape until the hydrogen concentration equals Cn(min), so the escapement ratio (a) can be expressed as
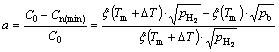
 (11)
(11)
Figure 6 shows the evolution of the escapement ratio against the superheat DT under a given pH2 and pAr condition. It is obvious that the hydrogen begins to escape from the melt by the bubbling way when the superheat exceeds a critical value. Once the hydrogen begins to escape, the ratio of the hydrogen content escaping from the melt quickly rises when the superheat increases further. In addition, the calculated result also reveals that, under the same superheat condition, the addition of argon can reduce the escapement ratio and suppress the escapement trend of hydrogen.
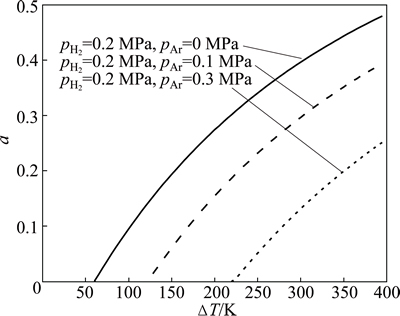
Fig. 6 Predicted escapement ratio of hydrogen against superheat
According to the ideal gas law as well as the mass conservation law, considering the escapement of the hydrogen, the average porosity of the ingot prepared by Gasar process can be described as [15]
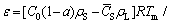
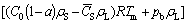 (12)
(12)
where C0 and`CS are average hydrogen contents in the liquid and solid metal separately, ρS is the solid metal density, Tm is the melting point of the metal, a is the escapement ratio,pb is the pressure inside the bubble during solidification. The average hydrogen concentration in the solid metal can be calculated using the model developed in Ref. [15]. Substituting the corresponding escapement ratio into Eq. (13), the porosity at different superheats and gas pressures can be calculated. As shown in Fig. 2, the predicted porosities are in good agreement with the experimental results.
4.2 Formation of non-uniform porous structure
For a gas bubble in a liquid supersaturated with gas, its growth rate (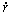 ) has a proportional relationship with the supersaturation degree (DC) [19].
) has a proportional relationship with the supersaturation degree (DC) [19].
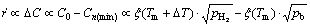 (13)
(13)
It is obvious that the growth rate is just directly proportional to the superheat (△T) under the given pH2 and pAr conditions. But it is inversely proportional to the total gas pressure when the superheat is constant. So, under a higher superheat condition, two kinds of phenomena may occur:
1) Coalescence phenomenon: A higher supersaturation degree leads to a higher growth rate, finally causes a bigger gas bubble at the solidifying interface. Simultaneously, these adjacent bubbles grow up quickly and approach with each other (coalescence phenomenon). As a result, many extraordinary big pores form and a non-uniform porous structure is obtained, as that observed in Figs. 3(c)-(d).
2) Bubbling or boiling phenomenon: The bubbles may nucleate in the supersaturation zone and rapidly grow up to a larger size due to the higher supersaturation degree. These large bubbles will float up with a certain velocity (vs) due to buoyancy action. If vs>v0 (the moving velocity of the solidifying front), these large bubbles will float up to the top of the melt and escape from the melt, finally result in a lower porosity. Whereas, if vs
When △T and pH2 all keep as constants, a higher pAr will lead to a higher Pb and a lower supersaturation degree, then reduce the growth rate of the gas bubbles. In this case, these two kinds of phenomena mentioned above will weaken even disappear. As a result, as that observed in Figs. 3(e)-(f), the big pores cannot form and a uniform porous structure can be obtained because the argon suppresses the nucleation and growth rate of the hydrogen bubble ahead the solidifying front.
5 Conclusions
1) The experimental results demonstrate that there exists a critical superheat DTc, above which the porosity approaches flat even descends slightly with increasing superheat. Simultaneously, many big pores form at the bottom and the top of the ingot and the pore distribution uniformity becomes worse.
2) The theoretical analysis reveals that the bubbling or boiling phenomenon will happen and a part of supersaturated hydrogen will escape from the melt when the superheat exceeds a the critical value (DTc). So further increasing the superheat will not enhance the total porosity. After considering the escapement ratio of hydrogen, the predicted porosities are in good agreement with the experimental results.
3) A theoretical model has been developed to predict the critical superheat for hydrogen to escape from the melt. The critical superheat increases with increasing partial pressure of argon at a given partial pressure of hydrogen.
4) A higher superheat can cause the pores coalescence and bubbling or boiling phenomenon during Gasar solidification process. As a result, many big pores arise at the bottom and the top of the ingot and a non-uniform porous structure forms.
5) The addition of argon can suppress the coalescence and bubbling or boiling phenomenon, then help prepare lotus-type porous metals with uniform structure.
References
[1] BANHART J. Manufacture, characterization and application of cellular metals and metal foams [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2001, 46: 559-632.
[2] Lefebvre L P, Banhart J, Dunand D. Porous metals and metallic foams: Current status and recent developments [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2008, 10(9): 775-787.
[3] SHAPOVALOV V I. Formation of ordered gas-solid structures via solidification in metal-hydrogen system [J]. Mat Res Soc Symp Proc, 1998, 521: 281-290.
[4] SHAPOVALOV V I, WITHERS J C. Hydrogen technology for porous metals (Gasars) production [M]//Carbon Nanomaterials in Clean Energy Hydrogen Systems. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series–C: Environmental Security. Berlin; Springer, 2008: 29-51.
[5] Nakajima H. Fabrication, properties, and applications of porous metals with directional pores [J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B-Physical and Biological Sciences, 2010, 86(9): 884-899.
[6] Chiba H, Ogushi T, Nakajima H. Heat transfer capacity of lotus-type porous copper heat sink for air cooling [J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2010, 5(2): 222-237.
[7] Muramatsu K, Ide T, Nakajima H. Heat transfer and pressure drop of lotus-type porous metals [J]. Journal of Heat Transfer- Transactions of the ASME, 2013, 135(7): 072601.
[8] Chen liu-tao, Zhang Hua-wei, Liu Yuan. Experimental research on heat transfer performance of porous copper heat sink [J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2012, 48(3): 329-333. (in Chinese)
[9] Zhang H W, Chen L T, Liu Y. Experimental study on heat transfer performance of lotus-type copper heat sink [J]. Int J Heat Mass Trans, 2013, 56(1-2): 172-180.
[10] Ide T, Iio Y, NAKAJIMA H. Fabrication of porous aluminum with directional pores through continuous casting technique [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2012, 43(13): 5140-5152.
[11] Apprill J M, Poirier D R, Maguire M C. Gasar porous metals process control [J]. Mat Res Soc Symp Proc, 1998, 521: 291-296.
[12] Li Zai-jiu, Jin Qing-ling, Yang Tian-wu. Fabrication of lotus-type porous Cu-Zn alloys with the Gasar continuous casting process [J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2013, 49(6): 757-762. (in Chinese)
[13] Jiang guang-rui, Li Yan-xiang, Liu Yuan. Influence of solidification mode on pore structure of directionally solidified porous Cu-Mn alloy [J]. Transactions Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(1): 88-95.
[14] Liu Yuan, Li Yan-xiang, wan jiang, Zhang Hua-wei. Metal-gas eutectic growth during unidirectional solidification [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2006, 37: 2871-2878.
[15] Liu Yuan, Li Yan-xiang, wan jiang. Evaluation of porosity in lotus-type porous magnesium fabricated by metal/gas eutectic unidirectional solidification [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 402: 47-54.
[16] Liu Yuan, Li Yan-xiang, Liu Run-fa. Theoretical analysis on effect of transference velocity on structure of porous metals fabricated by continuous casting Gasar process [J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2010, 46(2): 129-134. (in Chinese)
[17] Shapovalov V I, Semik A P, Timchenko A G. On the solubility of hydrogen in liquid magnesium [J]. Metally, 1993, 3: 25-28. (in Russian)
[18] Liu Yuan, Li Yan-xiang. Theoretical analysis of bubble nucleation in GASAR materials [J]. Transactions Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13: 830-834.
[19] Grinin A P, Kuni F M, Gor G Y. The rate of nonsteady gas bubble growth in liquid supersaturated with gas [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2009, 148: 32-34.
刘 源1,2,张华伟1,2,李言祥1,2
1. 清华大学 材料学院,北京 100084;2. 先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
摘 要:结构均匀性是影响藕状多孔金属的物理和力学性能的重要参数。系统研究熔体过热度对金属-气体共晶定向凝固(Gasar)制备藕状多孔金属的多孔结构均匀性以及气孔率、气孔形貌的影响规律。实验结果表明,凝固过程中存在一临界过热度(△Tc),超过该临界值时,凝固界面前沿熔体中会发生气泡的形核和上浮溢出(“冒泡”或“沸腾”)现象,结果造成气孔率的下降。另外,过高的过热度会导致相邻气孔的合并粗化,形成大尺寸气泡,最终获得不均匀的气孔结构。在实验结果基础上,建立气泡溢出的临界过热度(DTc)理论模型和氢气溢出系数计算模型。在考虑氢气溢出时,理论预测的气孔率与实验结果吻合较好。
关键词:定向凝固;多孔金属;熔体过热度;结构均匀性
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51271096) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (NCET-12-0310) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, Ministry of Education, China
Corresponding author: Yuan LIU; Tel: +86-10-62789328; E-mail: yuanliu@tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63691-3

