铜铬触头材料的摩擦磨损性能
郭绍义1, 叶秉良1, 陶应啟2, 居 毅1
(1. 浙江理工大学 机械工程系, 杭州 310018;
2. 浙江省冶金研究院, 杭州 310013)
摘 要: 分别采用熔渗法和混粉压烧法制备技术生产出2种铜铬触头材料, 其含铜量均为48%~52%, 余量为铬。 利用销盘式摩擦磨损实验机对这2种技术制备的铜铬材料的摩擦磨损性能进行了比较研究。 结果表明: 在本实验条件下, 同一载荷稳定状态时2种铜铬触头材料的摩擦系数基本相当, 约在0.32~0.36之间; 随着载荷的增加其摩擦系数略有增加; 磨损质量损失随载荷的增加而增大, 低载荷时, 混粉法制备的铜铬合金具有较低的磨损率, 高载荷时熔渗法具有较低的磨损率; 低载荷时2种铜铬合金的磨损破坏机制都以粘着和微切削机理为主, 高载荷时以磨损表面的片状或颗粒簇剥落为主。
关键词: 铜铬触头材料; 摩擦; 磨损; 熔渗法; 混粉压烧法 中图分类号: TG146.1; TH117.1
文献标识码: A
Tribological behavior of CuCr contact materials
GUO Shao-yi1, YE Bing-liang1, TAO Ying-qi2, JU Yi1
(1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China;
2. Zhejiang Metallurgical Research Institute, Hangzhou 310013, China )
Abstract: Two kinds of CuCr contact materials have been made by powder metallurgy sintering process and infiltration process with 48%-52% copper. Their friction and wear properties were studied with help of a pin-disc type wear apparatus. The experiment results showed that their friction coefficients in stable were almost same at the same load, approximately between 0.32 and 0.36. Their friction coefficients slightly increase with wear load up. The load adding will augment their wear mass loss. The mass loss of the CuCr alloy made by powder metallurgy process is relatively low at 20N load and the loss of that made by infiltration process is relatively low at 40N load. SEM analysis also shows that the adhesive and microcutting wear are the dominant mechanisms in low loads and the thin feet or particle cluster spalling is the dominant mechanism in high loads.
Key words: CuCr contact material; friction; wear; infiltration process; compacting process
铜铬合金由于具有良好的导电、 导热、 耐腐蚀和良好的加工性能, 目前被广泛用于电力、 电子、 机械、 原子能等工业领域。 高铜含量的铜铬合金主要用作真空开关管和高压电器开关中的触头材料、 集成电路引线框架、 电力机车架导线、 电动机集电环、 电工插头和开关等。 此外, 该类合金还被用于制作散热元件如连铸机结晶器内衬以及耐磨材料在轴承、 螺栓等中的使用[1-4]。
人们对铜铬合金的研究主要集中在该类合金的制备方法, 合金的微观组织及性能的强化等方面[5-9]。 对该类合金的摩擦磨损性能特别是高铜含量触头材料的研究却鲜见报道[10-11]。 熔渗法和混粉压烧法是这类合金最常用的两种制备方法[1, 7]。 目前一般认为这两种工艺生产的铜铬触头材料技术性能差别不大, 但由于固结方式不同其微观结构存在一定的差异[12]。 本文作者拟对这2种工艺制备的铜铬触头材料的摩擦磨损性能进行实验研究, 考察其微观结构的差异对其摩擦磨损性能的影响规律, 同时也为更合理地选用该类材料提供相关的实验数据和参考依据。
1 实验
分别采用熔渗法和混粉压烧法制备实验用的铜铬触头材料, 粉料和烧结工艺参数均由浙江省冶金研究院有限公司提供。 烧结后实验样品的成分Cu含量为48%~52%, 其余为Cr, 导电率大于16MS/m。 采用数字式智能显微硬度计测得的平均硬度为: 熔渗法合金HV125, 混粉法合金HV94。 采用DWT-100电子万能实验机测得的两种铜铬触头材料的强度: 熔渗法合金为890MPa和混粉法合金为780MPa。
摩擦磨损实验在MMW-1型销-盘式摩擦磨损实验机上进行。 上试样为销, 采用熔渗法制造的铜铬合金, 尺寸为d4mm×15mm, 为保证实验的统一性, 销的端部加工成半径为4mm的球形; 下试样为盘, 为实验材料, 直径为30mm。 测试过程中盘试样固定不动, 销试样作圆周运动, 销的转速在本实验过程中固定为180r/min, 磨损半径为4mm(约75mm/s)。 摩擦系数和磨损载荷等参数直接由计算机采集记录。 实验载荷分别为20N和40N。 实验前所有样品表面均抛光至镜面。 实验样品每磨损5min称量其磨损质量损失。 在精度为0.01μg分析天平上称量试样的磨损质量损失, 取3次平均值。 磨损条件为室温大气环境。 采用日本电子公司生产的JSM-5610LV型扫描电镜观察磨损试样的表面形貌。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 摩擦系数
图1和图2所示为2种铜铬触头材料在不同载荷条件下其摩擦系数随位移变化的关系。 从图可见, 2种铜铬触头材料的摩擦系数在磨损起始阶段随位移的增加单调上升, 其后其摩擦系数渐趋稳定。 载荷较大时其初始阶段的摩擦系数上升较快。 2种合金的摩擦系数总体相差不大, 其平均摩擦系数在0.32~0.36之间。 随着载荷的增加其摩擦系
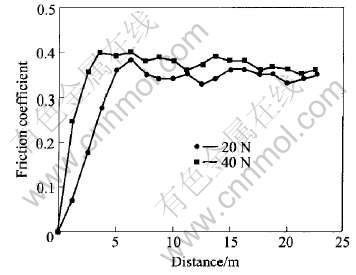
图1 混粉压烧法制备的铜铬合金材料在不同载荷下的摩擦系数
Fig.1 Relations of friction coefficients vs wear distance in different loads of CuCr materials by powder metallurgy process
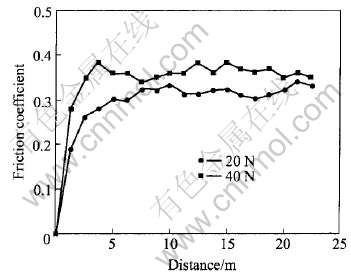
图2 熔渗法制备的铜铬合金材料在不同载荷下的摩擦系数
Fig.2 Relations of friction coefficients vs wear distance in different loads of CuCr materials by infiltration process
数上升, 但增加的幅度不大。 磨损的初始阶段, 材料表面由于存在各种污染物如氧化物等, 同时由于接触面较光滑等原因使其摩擦系数较低, 这与文献[13-14]所观察到的现象相似。 随着磨损的进行, 其摩擦系数逐渐上升, 同时由于接触表面加工硬化使接触表面的硬度逐渐增加并趋于稳定[15], 最终结果将导致摩擦系数趋于稳定。 在本研究中由于2种铜铬合金的铜含量较高(约50%), 硬度比较低, 低载荷条件下, 材料的磨损机制主要为粘着和微切削磨损。 随着载荷的增加, 在剪切应力反复作用下磨损表面层发生硬化、 破裂、 剥落, 材料的磨损机制转变为磨粒脱落及块状剥落磨损为主, 导致材料的摩擦系数增加。 即便是载荷不变, 随着磨损圈数的增加, 材料的磨损表面在销子的反复碾压下其加工硬化程度也将逐渐增加[15-16], 同时, 在磨损表面也会出现因接触点温度升高形成氧化现象, 两者的共同作用使得材料的摩擦系数呈现出总体下降趋势。
2.2 磨损率与载荷的关系
根据经典的粘着磨损理论和Kato[16]的研究表明, 金属材料的磨损率与材料的硬度成反比, 与载荷成正比, 同时与材料的磨损破坏机理相关。 图3和4所示为混粉法和熔渗法制备的铜铬触头材料磨损质量损失与磨损距离之间的关系。 实验条件为:
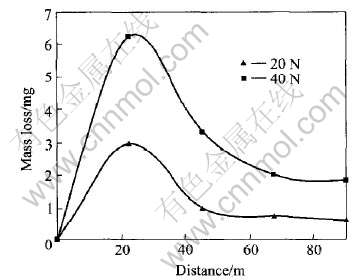
图3 混粉法制备的铜铬触头材料在不同载荷时的磨损质量损失
Fig.3 Relations of mass loss vs wear distance in different loads for CuCr materials by powder metallurgy process

图4 熔渗法制备的铜铬触头材料在不同载荷时的磨损质量损失
Fig.4 Relations of mass loss vs wear distance in different loads for CuCr materials by infiltration process
磨损半径4mm, 销的转速180r/min, 每磨损5min称量一次质量损失(即每滑动900圈的质量损失)。 从图中可见, 随着载荷的增加其磨损质量损失增加。 在起始阶段, 其磨损质量损失较大, 随着磨损距离的增加其磨损质量损失逐步减少并趋于稳定。 在起始阶段, 销与盘的接触面积比较小, 磨损接触区域承受较大的压力, 此时的磨损机理主要以微切削和粘着磨损为主, 在磨损表面形成明显的沟槽, 使得材料的磨损质量损失较多。 Kato等[16]认为磨销嵌入基体越深其材料的磨损率越大。 本实验从一个侧面征实了这一结果。 随着滑移距离的增加和销子对磨损表面的反复碾压使得磨损表面出现加工硬化并伴随着磨粒的形成, 使得销子侵入基体的深度减少, 导致其磨损率降低并趋于稳定。 图5和6所

图5 在20N载荷下2种铜铬合金的磨损质量损失与磨损距离的关系
Fig.5 Relations of mass loss vs wear distance at 20N loads for two kinds of CuCr materials
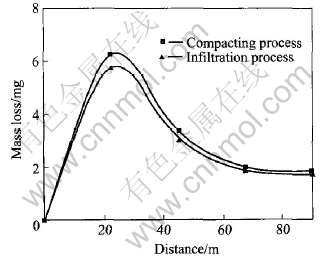
图6 在40N载荷下2种铜铬合金的磨损质量损失与磨损距离的关系
Fig.6 Relations of mass loss vs wear distance at 40N loads for two kinds of CuCr materials
示为2种方法制备的铜铬合金在载荷分别为20、 40N时的磨损质量损失与磨损距离的关系。 载荷为20N时, 熔渗法磨损质量损失最大, 混粉法最小; 载荷为40N时, 结果则相反。 文献[13-14, 16]显示基体组织、 第二相、 晶粒及内部缺陷是影响合金耐磨性的重要因素。 室温下铜铬合金是一种伪合金, 混粉法制备的铜铬合金中铜是连续相, 铬为分散相。 熔渗法制备的铜铬合金中铬呈网状连续分布, 铜渗入其中。 由于2种合金的铜含量较多, 低载荷时, 其磨损失效机制都表现为塑性的微切削和粘着磨损机制。 对于熔渗法制备的铜铬合金, 当脆性的连续相在犁耕的作用下受到破坏时易从表面脱落, 同时脱落的颗粒会形成三体磨粒磨损, 使材料的磨损进一步加重; 对于混合粉法制备的铜铬合金而言, 虽然磨损变形严重但由于在磨沟两侧形成隆起且不易脱落, 同时, 脱落的硬质磨屑个头较小, 结果导致其磨损质量损失反而较低。 高载荷时, 2种铜铬合金的磨损失效主要表现为表面硬化层的剥落或颗粒簇的剥落。 对于混粉法制备的铜铬材料而言, 在磨销的反复碾压作用下, 磨沟底部由于加工硬化导致层状的剥落[13]。 对于熔渗法制备的合金, 一方面由于其具有较高的硬度, 可以承受较高的载荷; 另一方面其磨损失效主要表现为颗粒簇的剥落, 与层片状的剥落相比块头较小, 同时脱落的碎片在高载荷作用下易焊接在磨损表面导致其磨损质量损失较低, 但总体上与混粉法相差不大。
2.3 磨损形貌与磨损机理
根据疲劳磨损理论和剥层磨损理论[13], 在循环应力的反复作用下磨损接触区材料发生塑性变形, 当其积累到一定程度时将导致开裂现象并形成磨屑。 同时由于工况条件、 材料的组织性能差异以及磨损的不同时段, 材料的失效表现为不同的形式如粘着、 微切削、 剥层、 犁耕等。 对于金属材料而言, 滑动磨损首先引起基体材料的流失, 使内部的增强相或夹杂物暴露于磨损表面。 其次, 连续的塑性变形、 应变硬化以及磨损表面或亚表面的孔洞、 位错的集中形成裂纹的共同作用使增强相或夹杂物与基体分开, 并最终影响到其具体的磨损破坏形式。
图7和8所示为2种合金磨损的SEM表面形貌。 从图7(a)中可以观察到对于混粉法制备的铜铬合金在载荷为20N时其磨损的主要特点有: 磨损表面有明显的浅犁沟、 微裂纹以及由于塑性变形产生的滑移舌和薄片状的磨屑黏附在磨痕表面上。 随着载荷和磨损滑动距离的增加磨损表面层的加工硬化现象加重(图7(b)), 表现为滑移轨迹上有更多的微裂纹, 塑性变形更严重, 层片状磨屑增多, 使其磨损机理逐渐由粘着和微切削磨损转变为以薄片状的剥落为主, 这些现象与文献[14]的研究结果相似。 浅的犁沟主要为铬颗粒的脱落变为磨粒形成的。
图8所示为熔渗法制备的铜铬合金的摩擦磨损形貌。 在20N载荷时(图8(a))其磨损形貌与同样条件下混粉法制备的合金相似, 但磨痕上的犁沟更深更宽, 表层的剥落更严重, 导致其磨损率更大。 从图8(b)中可以观察到40N载荷时磨痕表面较光滑, 磨痕底部出现了颗粒簇的脆性剥落现象, 基本为球形, 尺寸明显小于图7(b)中剥落片。 电镜观察表明这种较大面积的颗粒簇剥落并不是一个普遍现象, 使得高载条件下熔渗法合金的磨损率略小于混粉法合金的磨损率。 总之, 在本实验条件下, 熔渗法与混粉法2种工艺制备的合金其磨损破坏的形式基本一致。

图7 混粉法制备铜铬合金的表面磨损形貌
Fig.7 Worn surface morphologies of CuCr materials by powder metallurgy process

图8 熔渗法制备铜铬合金的表面磨损形貌
Fig.8 Worn surface morphologies of CuCr materials by infiltration process at different loads
上述的观察分析表明: 虽然2种合金的化学成分基本相同, 但由于其制备工艺的不同导致其微观组织的差异, 致使其磨损破坏的细节产生差异。 低载荷时, 混粉法合金表现为更为明显得塑性变形; 高载时熔渗法表现为较多的脆性剥落。 混粉法合金中铬为颗粒状的分散相, 熔渗法合金中铬为网状的连续相。 磨损过程中剥落的铬颗粒在混粉法中较小且大小均匀形成浅而均匀的沟槽; 在熔渗法合金中剥落的铬颗粒大小不均形成深浅不一宽窄不同的磨沟并在高载荷出现较大区域的脆性剥落。 同时随着磨损滑移距离的增加以及载荷的不同使其磨损破坏的形式和机理产生一定的差异并最终影响到其磨损率。
3 结论
在本实验条件下, 同一载荷稳定磨损阶段时2种铜铬触头材料的摩擦系数基本相当, 约在0.32~0.36之间。 随着载荷的增加其摩擦系数略有增加, 但幅度有限。 磨损质量损失随着载荷的上升而增大。 低载荷时, 混粉法制备的铜铬合金具有较低的磨损率, 高载荷时熔渗法具有较低的磨损率。 低载荷时2种铜铬合金的磨损破坏机制都以粘着和微切削机理为主, 高载荷时以磨损表面的片状或颗粒簇剥落为主; 表明材料微观结构的差异及磨损工况的差异对材料的磨损性能产生明显的影响。
REFERENCES
[1]张瑞丰, 沈宁福. 快速凝固高强高导铜合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 材料科学与工程, 2001, 19(1): 143-147.
ZHANG Rui-feng, SHENG Ning-fu. Review and prospect of researches on rapidly solidified high-strength high-conductivity copper alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2001, 19(1): 143-147.
[2]Alexander D J, Zinkle S J, Rowcliffe A F. Fracture toughness of copper-base alloys for fusion energy applications[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1999, 271-272: 429-434.
[3]马凤仓, 倪锋, 杨涤心. 铜铬合金制备方法研究现状[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2002, 17(3): 35-38.
MA Feng-cang, NI Feng, YANG Di-xin. The present situation of preparation methods of CuCr alloy materials[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2002, 17(3): 35-38.
[4]HU Jian-sheng, LI Jian-gang, ZHANG Xiao-dong, et al. Design of actively cooled flat toroidal limiter with CuCr heat sink for the HT-7 superconducting tokamak[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2005, 72(4): 377-390.
[5]PENG Li-ming, MAO Xie-min, XU Kuang-di, et al. Property and thermal stability of in situ composite Cu-Cr alloy contact cable[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, (166): 193-198.
[6]FAN Zhi-kang, YANG Hong-wang, LIANG Shu-hua, et al. Effects of extrusion on chromium precipitation in Cu-Cr alloy[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2003, 13(2): 267-270.
[7]王强, 梁淑华, 范志康. CuCr系合金材料制造工艺的新进展[J]. 材料导报, 2000, 14(8): 22-24.
WANG Qiang, LIANG Shu-hua, FAN Zhi-kang. New developments in production technology of CuCr ally materials[J]. Materials Review, 2000, 14(8): 22-24.
[8]ZHANG Cheng-yu, WANG Ya-ping, YANG Zhi-mao, et al. Microstructure and properties of vacuum induction melted CuCr25 alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 366(1-2): 289-292.
[9]Haugsrud R, Lee K L. On the oxidation behaviour of a Cu-10% Cr in situ composite[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, A396(1-2): 87-91.
[10]Chen Z, Liu P, Verhoeven J D, et al. Electrotri-bological behavior of Cu-15% Cr in situ composites under dry sliding[J]. Wear, 1997, 203-204: 28-35.
[11]Chen Z, Liu P, Verhoeven J D, et al. Sliding wear behavior of deformation-processed Cu-15%Cr in situ composites [J]. Wear, 1996, 195(1-2): 214-222.
[12]傅肃嘉. 烧结法与熔渗法铜铬触头微观组织差异及对电性能的影响[J]. 高压电器, 2003, 39(4): 52-55.
FU Su-jia. Microstructures and interrupting behaviors of CuCr contacts made by P/M manufacture process[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2003, 39(4): 52-55.
[13]Suh N P. The delamination theory of wear[J]. Wear, 1973, 25: 111-124.
[14]徐建林, 陈超, 喇培清, 等. 新型铸造铝青铜的润滑摩擦性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004 , 14(6): 917-921.
XU Jian-lin, CHEN Chao, LA Pei-qing, et al. Lubrication friction performance of new as-cast aluminum bronze[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004 , 14(6): 917-921.
[15]Misra R D K, Satya Prasad V , Rama-Rao P . Dynamic embrittlement in an age hardenable copper chromium alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1996, 35(1): 129-133.
[16]Kato K. Micro-mechanisms of wear-wear mode[J]. Wear, 1992, 152: 277-295.
(编辑陈爱华)
基金项目: 浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(ZC0203,Y404277); 浙江省科技厅资助项目(2003F13013)
收稿日期: 2006-05-10; 修订日期: 2006-09-28
通讯作者: 郭绍义, 教授; 电话: 0571-86843343; E-mail: syiguo@163.com