J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 2767-2772
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3690-7
Precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels
WU Si-wei(吴思炜), LIU Zhen-yu(刘振宇), ZHOU Xiao-guang(周晓光),
YANG Hao(杨浩), WANG Guo-dong(王国栋)
State Key Laboratory of Rolling Technology and Automation, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany,part of Springer Nature 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany,part of Springer Nature 2017
Abstract: Precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels was investigated by means of the equilibrium solid solubility theory. The contributions of Ti content to yield strength were calculated. The calculated results were verified by the hot rolling experiment for C–Mn steel and C–Mn–Ti micro alloyed steel, respectively. The research results show that the precipitates are mainly TiN at the higher temperature. With the decreasing temperature, the proportion of TiC in precipitates increases gradually. When the temperature drops to 800 °C, TiC will become predominant for the precipitation of Ti. When Ti content is less than 0.014% (mass fraction), Ti has little influence on the yield strength. When Ti content is in the range of 0.014%–0.03% (mass fraction), the yield strength of Ti micro alloyed steel is greatly increased, which leads to instability of the mechanical properties of the steel. Therefore, the design of Ti content in high strength steels should avoid this Ti content range. When Ti content is higher than 0.03%, the yield strength increases stably. In this experiment, when added Ti content was controlled in the range of 0.03%–0.05%, the contribution to the yield strength of Ti micro alloyed steel can reach about 92.44 MPa.
Key words: precipitation strengthening; solid solubility; Ti(C, N); yield strength; high strength steel
1 Introduction
Micro alloying elements such as Nb, V and Ti, can generate fine grain strengthening and precipitation strengthening for the steels [1–5]. Among these micro alloying elements, Ti micro alloying technology should have broad application prospects in China because China has the largest Ti resources in the world. Additionally, the utilization of Ti is more economical than Nb or V [6].
Ti is easy to react with O, N and S to form large size compounds. Thus, the fluctuations of chemical composition in steels, such as N, S and O elements, can lead to the instability of mechanical properties [7]. Therefore, it is extremely important to study the precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels. Previous research focused on calculating the solid solubility of Ti micro alloyed steels [8]. However, the investigation on the calculation of precipitation behavior at different temperatures is still rare and the contribution of Ti content to strength of high strength steels is not yet clear.
Based on the above analysis, this work focused on the precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels. Besides, the influence of Ti micro alloying on the yield strength (YS) was also explored in this work.
2 Theory calculation of precipitation behavior in high strength steels
2.1 Mathematical method
The solid solubility of Ti in steels is quite small, so that it can generate solid solution strengthening effect. The main strengthening mechanisms are fine grain strengthening and precipitation strengthening. Precipitation behaviors containing various Ti contents at different temperatures were calculated in the precipitation equilibrium condition according to the Ti solid solubility formula. The sulfide and oxide elements were not considered since their contents were small. Therefore, one hypothesis was given that the precipitates only included TiC and TiN. Owing to the fact that TiC or TiN has the same crystal structure and the similar lattice constant as sodium chloride, which are usually completely miscible and form Ti(C, N). Another hypothesis was given that there were no C or N atom vacancies in micro alloyed steels, so the Ti(C, N) could be written in chemical formula as TiCxN1-x, where x was the mole fraction of TiC in the Ti(C, N), 0≤x≤ 1.For the binary system, the solubility products of TiC and TiN in austenite have been determined as following:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
where [Ti], [C] and [N] are the amount of solid solution of Ti, C and N in austenite, respectively. Ti, C and N contents are still needed to meet the following two conditions: 1) Ti, C and N contents in solid solution must comply with the solubility products; 2) Contents of Ti, C and N in TiCxN1-x phase must be maintained the ideal proportion of chemical composition [9]. Therefore, the relationship among them can be expressed as following:
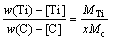 (3)
(3)
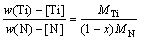 (4)
(4)
where MTi, MC and MN are relative atomic mass for Ti, C and N elements. Mass percents of Ti, C and N elements in steels are expressed as the symbols of w(Ti), w(C) and w(N), respectively. The constant in Eqs. (1) to (4) should be replaced by definition value, thus the following expression may be obtained as Eqs. (5) to (8):
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
From Eqs. (5) to (8), [Ti], [C], [N] and x can be determined. The x in TiCxN1–x is not constant and can change within a large range, which is related to the Ti, C and N contents in steels and the temperature.
Precipitates of Ti(C, N) are complete solid solution when the conditions ([Ti]=w(Ti), [C]=w(C), [N]=w(N)) are all satisfied. By calculating Eqs. (5) to (8), expression can be obtained as Eq. (9):
 (9)
(9)
The complete solid solution temperature, TCS, of Ti(C, N) can be calculated by Eq. (9). At the complete solid solution temperature, x in the TiCxN1-x can be derived from Eq. (10):
 (10)
(10)
2.2 Results and discussions
The x, [Ti], [C] and [N] in the TiCxN1–x were calculated for different Ti contents from 800 °C to TCS, which were calculated through the Newton descent method. The iteration calculation results of precipitation behavior in Ti micro alloyed steels are shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1(a) shows the influence of Ti content on x at different temperatures. It is suggested that a decrease of temperature leads to an increase in x. It shows that the proportion of TiC increases in Ti(C, N). The proportion of TiN increases with the increase of Ti content at a certain temperature. When Ti content is less than 0.014%, the composition of precipitates is almost TiN. As Fig. 1(b) shows, the solid solution C content increases with the rising temperature. However, while the Ti content increases, the C content in austenite hardly changes at a high temperature for the reason of complete solid solution. With the temperature dropping, the steels with high Ti content can dissolve more C in austenite and less C in the precipitates. The N content of solid solution increases with the temperature rising. With the increase of Ti content in steels, N in austenite has a small amount of residue. Most of N and Ti combine into Ti(C, N) precipitates as Fig. 1(c) shown. Figures 1(d) and (e) indicate that Ti addition can lead to a complete solid solution temperature rising. Figure 1(f) shows the curves of x, [Ti], [C] and [N] versus temperature. The precipitation rate of Ti(C, N) can be fast when Ti content in steels is 0.112% and the temperature is in the range of 1000–1300 °C. The same time the N element is basically all out. As the curve of [C] shows that the precipitation of TiN is stopped at a high temperature and the precipitates are almost all TiC.
2.3 Influence of Ti content on yield strength of high strength steels
Dispersed fine particles of carbonitride usually form during the transformation of austenite to ferrite [10]. Because those particles are very hard, the moving dislocations are almost impossible to cut through particles. The dispersion strengthening mechanism for micro alloyed steels is that the dislocation leaves the Orowan dislocation loop when it comes around the particles and becomes bent, and it can add stress to the matrix [11]. The strengthening mechanism of the dislocation loop is negatively correlated with the particle size. Ashby-Orowan model can be used to calculate the yield strength increment by the particle diameter and the volume fraction of precipitates in high strength steels. Considering G=80300 MPa, and b=2.5×10–4 μm, yield strength increment can be expressed as following:
 (11)
(11)
where Rp is yield strength increment generated by the second phase particles, MPa; f is the volume fraction of precipitates, %; dp can be identified as the average diameter of the precipitation particles, μm.
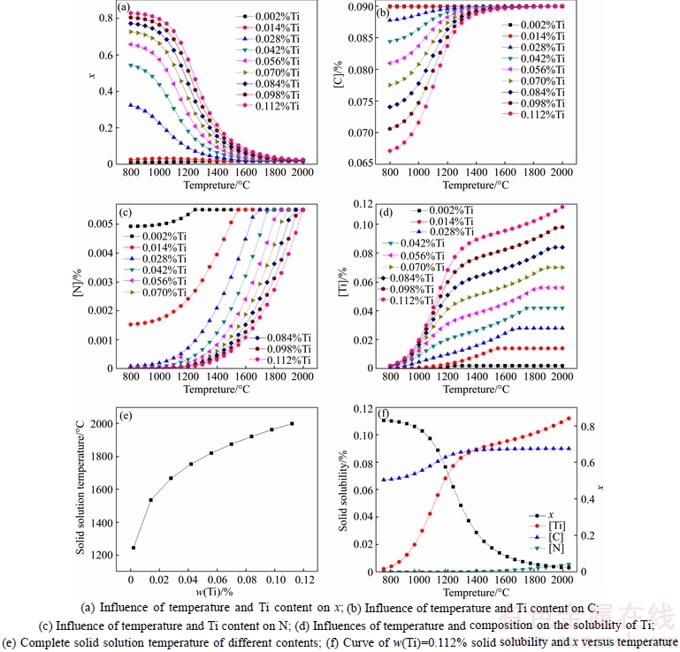
Fig. 1 Calculation results of precipitation behavior in Ti micro alloyed steels:
Assuming that there is no phase transition at 800 °C, the precipitation behavior at 800 °C is investigated. Due to the large size of the TiN particles, it has been considered that the precipitation strengthening is mainly derived from the TiC. The average diameter of the precipitates can be assumed to be 0.005 μm. In addition to TiC, the other compositions are in free state. The results of volume fraction of precipitates can be obtained through the density and mass fraction of each composition:
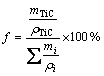 (12)
(12)
where i is main composition (C, Si, Mn, P, S, Ti, Al, Fe) in steels and m is the mass; ρ can be identified as density.
The calculation results of yield strength increments of different Ti contents micro alloyed steels are shown in Table 1.
Figure 2 shows that when Ti content is less than 0.014%, the influence of Ti content on yield strength is extremely weak. As Ti content is in the range of 0.014%–0.03%, it has a great influence on the yield strength, and the yield strength is highly sensitive to Ti content. Therefore, the design of Ti content in high strength steels should avoid this Ti content range. To keep stable mechanical properties it should ensure that Ti content lower limit is higher than 0.03%. After Ti content is higher than 0.03%, the yield strength increases with the addition of Ti element.
3 Experimental procedures
3.1 Experimental method
The calculated results were verified by the hot rolling experiment for C–Mn steel (1# sample) and C–Mn–Ti micro alloyed steel (2# sample), respectively. The experimental steels were taken from hot rolling plate, whose mass fraction compositions are controlled in the range of w(C)=0.08%–0.1%, w(Mn)=1.0%–1.2% and w(N)=0.0055%. For the 2# sample, the addition of Ti content is in the range of 0.03%–0.05 %.
Samples were mechanically ground and polished by with SiC papers, followed by corroded with the reagent of 4% nitric acid and 96% alcohol. The morphology of the two kinds of experimental steels was observed with LEICA-DMIRM multi-function microscope. Precipitation behavior of Ti element was observed with Tecnai G2F20 FEI field emission transmission electron microscope, working into 0.5 mm thick, followed by mechanically ground at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. Samples for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were cut and polished into 50 μm thick. Thin foils for TEM were processed by double-jet electrolytic thinning.The electrolyte was 6%–9% (volume fraction) perchloric acid alcohol solution, maintained at 38 mV, and current of 108 nA.
3.2 Results and discussion
As shown in Fig. 3, the microstructure of 1# experimental steel mainly consists of quasi-polygonal ferrite and a small amount of pearlite. The average grain size is 10 μm. While the microstructure of 2# experimental steel is predominantly composed of quasi- polygonal ferrite, needle ferrite and pearlite, with an average grain size of 7 μm. Figure 4 shows the TEM of 2# experimental steel; there are a large number of nano- scale precipitates, and the size of the precipitates is about 5 nm.
The main strengthening mechanism of hot rolling plate is solid solution strengthening, fine grain strengthening and dispersion strengthening. The solid solution elements can increase the lattice distortion and the resistance of dislocation migration. Assume that there is a linear relationship between the solid solution strengthening and the composition of the steels. Additionally, considering the influence of grain size, the yield strength through Hall-Petch formula can be expressed as following [12]:
 (13)
(13)
where σy is the yield strength of C–Mn steel, MPa; σi the ferrite friction stress, N; ki is the strengthening coefficient, which is related to the composition; Ci is identified as the percent of solid solution elements, mass %; ky is the strengthening coefficient which is related to grain size and d is the grain size, mm.
According to a large number of experimental data, empirical formula has been summarized for yield strength in steels as following:
 (14)
(14)
Table 1 Calculation results of yield strength increments of different Ti contents micro alloyed steels
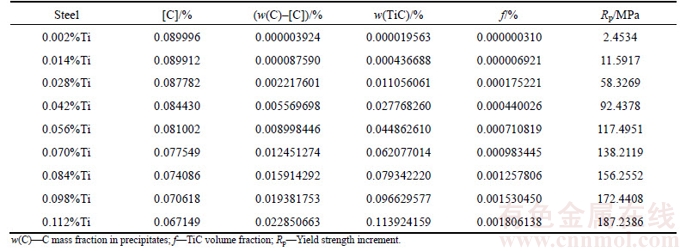
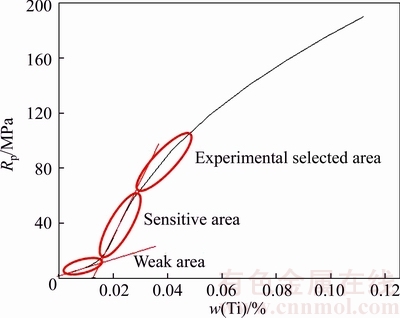
Fig. 2 Yield strength increment of different Ti contents micro alloyed steels
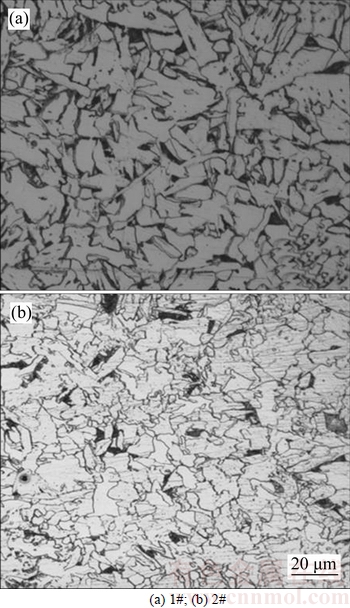
Fig. 3 Microstructures of experimental steels:
where [Mn] and [Si] are mass percent for manganese and silicon elements; [Nf] is free N in a solid solution state, mass fraction, %, and d is the average ferrite grain size measured through the line transect method, mm.
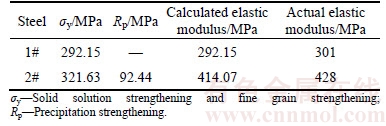
N element in steels is divided into two parts. One part is in the form of nitride precipitation and another part dissolves in austenite. N solid solution in austenite transforms into N solid solution in ferrite with the γ–a phase transition. The N in austenite is calculated in Table 1, from which the free N in ferrite can be obtained Therefore, it is possible to calculate the contribution to the yield strength of solid solution strengthening and fine grain strengthening. For 1# experimental steel,[Nf1]=0.0055%, d1=0.010 mm. For 2# experimental steel, [Nf2]=0.000030902%, d2=0.007 mm. Hence, σy can be calculated through Eq. (14): σy1=292.15 MPa, σy2= 321.63 MPa; σy1 and σy2 are strength increment of fine strengthening and solid solution strengthening in steels, respectively.
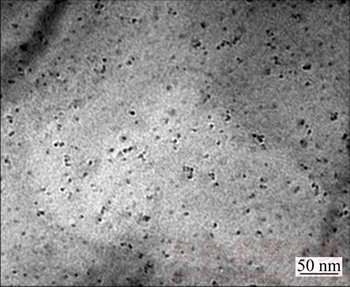
Fig. 4 Precipitates in 2# experimental steel
On account of the added Ti, precipitation strengthening can be generated in Ti micro alloyed steel, too. Through calculating Eqs. (11) and (12), the precipitates’ contribution to the yield strength in high strength steels can be obtained from Table 1, Rp=92.44 MPa.
Table 2 shows that the calculated results agree with measured yield strength. The calculated values are slightly different from the measured values, but they are similar. The reason is that the calculation takes no account of the pearlite influence. The reinforcement of the small amount of pearlite is neglected, which leads to the difference between the calculated values and the measured values [13]. The addition of Ti element mainly plays a role of precipitation strengthening [14]. After Ti content is higher than 0.03%, the influence on yield strength increment is obvious. The results are in agreement with the consequences in Ref. [15]. The calculated results proves that the strengthening mechanism for 0.03%–0.05% Ti content in high strength steels is mainly based on fine grain strengthening and precipitation dispersion strengthening. Among them, Ti addition makes contribution for precipitation strengthening.
Table 2 Calculation results of strength of two experimental steels
4 Conclusions
1) Precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels was investigated by means of the equilibrium solid solubility theory. The contributions of Ti content to yield strength of high strength steels were calculated. The calculated results showed that the precipitation at a higher temperature is mainly TiN. With the drop of temperature, the proportion of TiC in precipitates increases gradually. When the temperature drops to 800 °C, the precipitation of Ti is almost in the form of TiC. The solid solution temperature rises with the increase of Ti content.
2) A method design of Ti content in high strength steels was proposed. When Ti content addition is less than 0.014%, Ti has a little influence on the yield strength. When Ti content addition is in the range of 0.014%–0.03%, the yield strength of Ti micro alloyed steels is greatly increased, which leads to instability of the mechanical properties of the steels. Therefore, the design of Ti content in high strength steels should avoid this Ti content range and keep the lower limit of Ti content addition higher than 0.03%. After Ti content is higher than 0.03%, the yield strength increases stably.
3) The calculated results were verified by the hot rolling experiment for C–Mn steel and C–Mn–Ti micro alloyed steel. It shows that precipitation strengthening and fine grain strengthening are the main reason for yield strength increment in high strength steels. Precipitation strengthening is mainly attributed to the addition of Ti element. When added Ti content is controlled in the range of 0.03%–0.05%, the contribution to the yield strength of Ti micro alloyed steel can reach about 92.44 MPa.
References
[1] LIU Wei-jian, LI Jing, SHI Cheng-bin, WANG Chun-miao. Effect of micro-alloying element boron on the strengthening of high-strength steel Q690D [J]. Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis, 2015, 4(2): 102–108.
[2] YONG W K, SONG S W, SEO S J, HONG S G, CHONG S L. Development of Ti and Mo micro-alloyed hot-rolled high strength sheet steel by controlling thermomechanical controlled processing schedule [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 565(5): 430–438.
[3] YONG W K, KIM J H, HONG S G, CHONG S L. Effects of rolling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–Mo microalloyed hot-rolled high strength steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 605(27): 244–252.
[4] ANDRADE A R, BOLFARINI C, FERREIRA L A M, FILHO C D S, BONAZZI L H C. Titanium micro addition in a centrifugally cast HPNb alloy: High temperature mechanical properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 636(11): 48–52.
[5] CHAUDHURY J N. Effect of heat treatment, pre-stress and surface hardening on fracture toughness of micro-alloyed steel [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(1): 152–168.
[6] HAN Y, SHI J, XU L, CAO, W Q, DONG H. TiC precipitation induced effect on microstructure and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 530(15): 643–651.
[7] WANG Chang-jun, YONG Qi-long, SUN Xin-jun, MAO Xin-ping, LI Zhao-dong, YONG Xi. Effects of Ti and Mn contents on the precipitate characteristics and strengthening mechanism in Ti microalloyed steels produced by CSP [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2011, 47(12): 1541–1549. (in Chinese)
[8] YONG Qi-long. Second phase in steel materials [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[9] YONG Qi-long, LIU Zheng-dong, SUN Xin-jun, CAO Jian-chun, ZHAO Kun-yu, ZHANG Yong, CHA Xiao-qin. Theoretical calculation for equilibrium solubility and compositional coefficient of titanium carbonitrides in Ti-bearing microalloyed steel [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2005, 26(3): 12–16. (in Chinese)
[10] WANG Zhen-qiang, MAO Xin-ping, YANG Zhi-gang, SUN Xin-jun, YONG Qi-long, LI Zhao-dong, WENG Yu-qing. Strain-induced precipitation in a Ti micro-alloyed HSLA steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 529(1): 459–467.
[11] YUAN Xiao-hong, ZHENG Shan-ju, YANG MAO-sheng, ZHAO Kun-yu. Carbide precipitation and microstructure refinement of Cr-Co-Mo-Ni bearing steel during hot deformation [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(9): 3265–3274.
[12] LI De-qiang, YE Qi-bin, ZHOU Chen, YAN Lin. Precipitation of low carbon steel with Nb-Ti and study on the strengthening effect of fine grain [J]. AISC Techniques, 2012(4): 21–25. (in Chinese)
[13] CHEN C Y, CHEN C C, YANG J R. Dualism of precipitation morphology in high strength low alloy steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 626(25): 74–79.
[14] JAVAHERI V, SHAHRI F, MOHAMMADNEZHAD M, TAMIZIFAR M, NASERI M. The effect of Nb and Ti on structure and mechanical properties of 12Ni-25Cr-0.4C austenitic heat-resistant steel after aging at 900 °C for 1000 h [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(10): 3558–3566.
[15] XU Guang, GAN Xiao-long, MA Guo-jun, LUO Feng, ZOU Hang. The development of Ti-alloyed high strength microalloy steel [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(6): 2891–2896.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Cite this article as: WU Si-wei, LIU Zhen-yu, ZHOU Xiao-guang, YANG Hao, WANG Guo-dong. Precipitation behavior of Ti in high strength steels [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(12): 2767–2772. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3690-7.
Foundation item: Project(U1460204) supported by the Joint Funds of The Iron and Steel Key Project, China; Project(2015020180) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China; Project(N140704002) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Received date: 2016-03-07; Accepted date: 2016-12-28
Corresponding author: LIU Zhen-yu, PhD, Professor; E-mail: zyliu@mail.neu.edu.cn