
Effect of metallic ions on dispersibility of fine diaspore
ZHOU Yu-lin, HU Yue-hua, WANG Yu-hua
School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 24 May 2010; accepted 30 August 20a10
Abstract: Dispersion experiments were conducted to study the influence of metallic cations on the dispersibility of diaspore. The reaction mechanisms were investigated based on the analysis of zeta (ζ) potential and calculations of solution chemistry and DLVO theory. The results show that the valence of cations, instead of the cation type, plays an important role in the dispersibility of diaspore. The impact of multivalent metallic cations is greater than that of monovalent cations. In the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, the dispersion of diaspore doesn’t change in the range of pH value below 10. However, Ca2+ and Mg2+ may induce strong coagulation of particles when pH value is higher than 10. The adsorption of species of calcium and magnesium ions on diaspore can cause the compression of electric double layer, the decrease of the absolute value of zeta potential and the repulsion force between diaspore particles. The new IEP (isoelectric point) appeared at pH value of 11 may attribute to the adsorption of Mg(OH)2(s).
Key words: diaspore; metallic ions; dispersibility; zeta potential; DLVO theory
1 Introduction
The influences of metal ions on mineral processing have aroused attention from many mineral processing researchers[1-5]. Metal ions affect the surface properties, dispersion-flocculation and flotation characteristics of minerals[6]. FANG[7] found that Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions could induce the coagulation of fine quartz and hematite without selectivity, and with the increasing concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, the gradually increased destruction to dispersion stability of suspending fine particles may be attributed to the formation of “static bridge” because of the hydroxide precipitation of Ca2+ and Mg2+. LI et al[8] thought that the addition of Ca2+ lowered the negative value of zeta(ζ) potential of minerals, due to the electrostatic adsorption of Ca2+ onto the particle surface, and the trivalent cations, such as Fe3+, could strongly change the zeta potential of minerals, and even reverse the negatively charged surface to be positive. The positive shifts in zeta potentials of talc take place partly due to the strong adsorption of hydroxo complexes of Al(III) and Cr(III)[9]. It was reported that as Ca2+ may consume CO32- and Na4P6O182- in the pulp system, therewith the electric double layer of the particles can be compressed and the absolute value of zeta potential of minerals can be reduced, therefore, the electrostatic repulsion among mineral particles can be weakened and the dispersibility of aluminum silicate minerals can be disrupted. The Al3+ hydroxyl compound produced from the hydrolization of Al3+ adsorbed on the particle surface, which may reduce the absolute value of zeta potential of minerals and decrease the electrostatic repulsion among mineral particles, thus, the dispersibility of aluminum silicate minerals was decreased[10-12].
Based on the previous study, the effect of a series of metallic ions on the dispersion of diaspore and some possible reaction mechanisms are investigated in this work.
2 Experimental
2.1 Material
Pure mineral sample of diaspore was obtained from Jiaxian in Henan Province, China. The bulk ore was hand-picked and ground by a porcelain mill with agate balls, and was screened to obtain powder with a particle size less than 10 μm for further investigation. To measure zeta potential, the as-prepared sample was ground using agate mortar to less than 5 μm. A Brookhaven Zeta Plus instrument (New York, USA) was used to measure the particle size of the samples. The chemical composition of this ore is listed in Table 1.
In the study, metal ions were generated using analytical reagents, including NaCl, KCl, CaCl2 and MgCl2. Analytical grade NaOH and HCl were used to adjust the pulp pH value. Double distilled water was used for all experiments.
Table 1 Chemical composition of diaspore mineral (mass fraction, %)
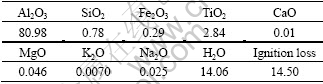
2.2 Method
2.2.1 Dispersion test
For dispersion state evaluation, 5 g pure mineral samples were added into a plastic beaker containing 30 mL water, and the suspension was agitated for 5 min using magnetic stirrer and then transferred to a glass sedimentation cylinder. The cylinder was turned up and down 20 times, and then rested for 7 min. The upper part, which takes 88% of the total volume of the suspension, was siphoned out. The sediment and upper fractions were collected, dried and weighed.
The dispersion degree (D) was calculated as:
D=msusp./(msusp.+msed.)×100% (1)
where msusp. is the mass of suspension and msed. is the mass of sediment. The diameter, height and volume of the sedimentation glass tube are 3.5 cm, 17 cm and 100 mL, respectively.
2.2.2 Zeta potentials measurement
Zeta potential of diaspore was measured using Brookhaven Zeta Plus instrument (USA). Before the measurement, the samples were ground to less than 5 μm with an agate mortar. Each sample for zeta potential measurement contains 0.03% (mass fraction) solids, and it was conditioned in a beaker for 15 min. And the pH value was measured at room temperature (25 °C).
2.2.3 Calculation of interfacial energy between fine particles
Based on the classical DLVO theory, static electricity action energy and Van der Waals action energy were calculated, and the interfacial energy between fine particles was defined as the combined effect of these two energies. Static electricity action energy was calculated as:
Vε=2πεaRΨ02ln[1+exp(-кH)] (2)
where surface potential Ψ0 is approximatively replaced by ζ potential, the double-layers (1/к) is described by the classical Possion-Boltzmann (PB) equation and εa, R and H are constants.
Meanwhile, the Van der Waals action energy was calculated as:
Vw=-A131R/(12H) (3)
where A131 is the Hammack constant and H is the distance of interfacial force between particles.
Therefore, the total action energy VT can be calculated as:
VT=Vε+Vw (4)
Based on Eq.(4), the DLVO energy can be calculated and the curves of DLVO energy versus the distance between particles (H) can be depicted.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Dispersion-coagulation behavior of pure minerals
The dispersion of diaspore in distilled water without and with metal ions, such as Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+, was investigated at different pH values. The results are shown in Figs.1 and 2.
It can be seen from Figs.1 and 2 that in absence of metal ions, the dispersibility of diaspore particles declines with the increase of pH value within a range from 2 to 6, and the yield of suspension keeps around 15% in a wide pH range from 6 to10, and then an improved dispersion behavior of diaspore can be observed when the pH value is above 10.
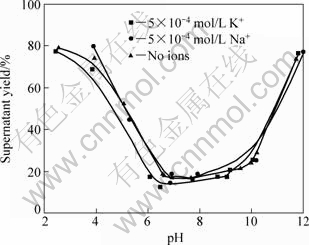
Fig.1 Effect of pH value on dispersion of mineral particles in presence of Na+ and K+
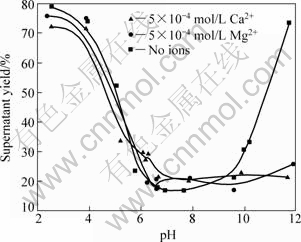
Fig.2 Effect of pH value on dispersion of mineral particles in presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+
The variation of dispersion properties of diaspore vs pH value in the presence of 5×10-4 mol/L monovalent cations , such as Na+ and K+, is also shown in Fig.1. The three curves are almost superposed, which indicates that monovalent cations Na+ and K+ have little effect on the dispersion of diaspore particles under this condition.
Comparatively, in the presence of 5×10-4 mol/L divalent cations of Ca2+ and Mg2+, the dispersion of diaspore particles along with the solution pH value was studied and the results are shown in Fig.2. The dispersion behavior of diaspore is not affected by Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions when the pH value of the solution is lower than 10. However, the suspension yield in solutions with Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions is significantly lower than that of the solution with no ions when pH value is above 10, which means that these two kinds of divalent cations can cause the coagulation of diaspore particles in alkaline pulp.
3.2 Zeta potential analysis
Adjusting the pH value of the system can influence the surface properties[13]. Zeta potentials of diaspore as a function of pH value in double distilled water is presented in Figs.3 and 4. It can be seen that diaspore has a point of zero charge (PZC) at pH=7.2 in absence of metal ions. This result is in accordance with the results reported in other literatures[14-17] which listed PZC values of diaspore as 5.2-7.7. The zeta potential of diaspore decreases as the pH value increases. The results in Fig.3 show that the zeta potential of diaspore doesn’t change in the presence of 5×10-4 mol/L Na+.
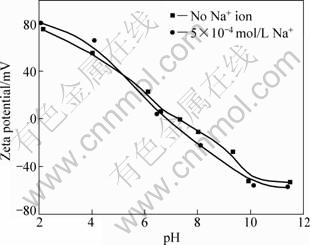
Fig.3 Effect of pH value on zeta potentials of diaspore particles in presence of Na+
Figure 4 shows that the values of zeta potential decrease as pH value increases in the presence of 5×10-4 mol/L Ca2+ or Mg2+. The PZC of diaspore shifts slightly from 7.2 to 6.5. Abnormally, for high alkaline solution containing Mg2+, namely, when the pH value amounted from 10 to 12, the negatively charged surface can even be positively charged again and a second new PZC appears at pH value of 11.

Fig.4 Effect of pH value on zeta potentials of diaspore particles in presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+
3.3 Calculation of solution chemistry for metallic ions
At different pH values, the composition and content of the species in the presence of 5×10-4 mol/L Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions were analyzed and calculated using the stability constants for hydroxide formation and the results are shown in Figs.5 and 6, respectively. At pH value of 9.8, Ca(OH)+ appears, and its concentration keeps increasing along with the increase of pH value until it reaches a maximum value at pH value of 12.5. The specy Ca(OH)2 appears at pH value of 11.3, and its concentration increases as well with the increase of pH value. When pH value is lower than 12.5, Ca2+ is the predominant species in the system. Figure 6 shows that Mg(OH)+ appears at pH value of 7.8, and its concentration increases with the increase of pH value, until it reaches the maximum point around pH value of 10, and Mg(OH)2 appears at this pH value. Mg2+ and Mg(OH)+ are the predominant ingredients in the system within a pH range lower than 12.
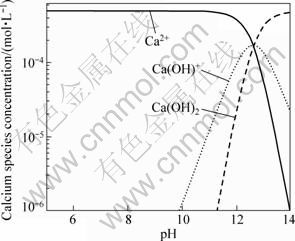
Fig.5 Calculated concentration of calcium species in solution with calcium concentration of 5×10-4 mol/L
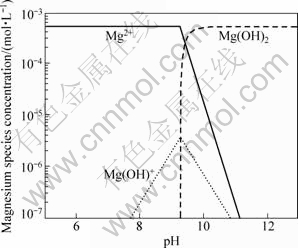
Fig.6 Calculated concentration of magnesium species in solution with magnesium concentration of 5×10-4 mol/L
3.4 Calculation of surface energy of particles using classic DLVO theory
Combining the results of zeta potential measurement and the solution chemistry calculation, the interaction energy values of particles in absence or presence of metal ions were calculated according to classical DLVO theory, and the results are shown in Figs.7-10.
The results in Fig.7 show that the total interaction energies are positive at pH values of 3 and 11, but the total energies are negative at pH value of 7. These results testified that the diaspore particles are dispersive both in alkali and acid media, and coagulative in the middle pH range. These results are in good accordance with the results of dispersion experiments.
After the addition of Na+, an obvious decline of the total interaction energies at pH values of 3 and 11 can be observed, yet the total energies remain positive, and the total interaction energies at pH value of 7 remains negative. These calculations verify the results of the dispersion tests, showing that diaspore may exhibit similar dispersion behaviors in the presence of Na+ and in distilled water without metal ions.
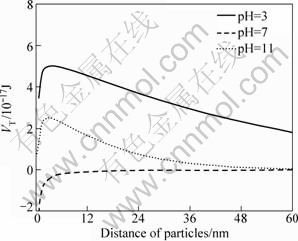
Fig.7 Total interaction energy of particles at different pH values without ions
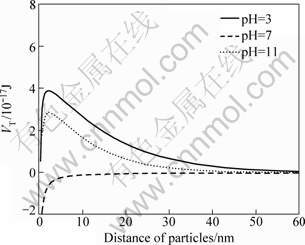
Fig.8 Total interaction energy of particles at different pH values in presence of Na+ (5×10-4 mol/L)
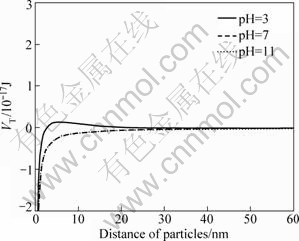
Fig.9 Total interaction energy of particles at different pH values in presence of Ca2+ (5×10-4 mol/L)

Fig.10 Total interaction energy of particles at different pH values in presence of Mg2+ (5×10-4 mol/L)
It can be seen from Figs.9 and 10 that in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, a sharp decrease of total interaction energy occurs at pH=3, but the values are still positive for a distance between particles longer than 3 nm, which shows that there are still repulsive forces between particles. However, the total interaction energy becomes negative at pH=11, which is superposed with that at pH=7. The aforementioned analysis shows that in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, there are attractive forces between diaspore particles when the pH values are 7 and 11, which testifies the phenomenon of dispersion experiments.
According to the results of dispersion experiments and mechanism study, the dispersion of diaspore is identical to its zeta potential in aqueous media without ions. The bigger the absolute value of zeta potentials, the better the diaspore particles disperse. The addition of monovalent Na+ makes no change to the zeta potential of diaspore which has good parallelism of dispersion (see Figs.1, 3 and 8). Under the condition of pH<12, dissociative Ca2+ and Ca(OH)+ are the key species in the solution (see Fig.5). The adsorption of Ca2+ and Ca(OH)+ on diaspore lowers the absolute value of zeta potential and induces a compression of double electric layer (see Figs.4 and 9). Mg2+ and Mg(OH)+ are the key species at pH<10. The adsorption of Mg2+ and Mg(OH)+ on diaspore has similar effect as Ca2+ (see Figs.4, 6 and 10). However, Mg(OH)2(s) is the main species under the condition of pH value higher than 12, and a new isoelectric point (IEP) caused by Mg2+ ions at pH value of 11 may attribute to the adsorption of Mg(OH)2(s) on diaspore, and this phenomenon agrees with the results researched by KRISHNAN and IWASAKI[18], which reported that Mg(OH)2(s) was electronegative below pH value of 12.5.
4 Conclusions
1) In absence of metal ions, diaspore is dispersed in pH range from 2 to 6 and from 10 to 12, but it is coagulated in pH range from 6 to 10.
2) The addition of Na+ and K+ doesn’t show the influence on the dispersion of diaspore in the whole pH range. In the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+,the dispersion of diaspore doesn’t change in the range of pH<10. However, Ca2+ and Mg2+ cause the strong coagulation of diaspore in the range pH>10.
3) The adsorption of species of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on diaspore causes the compression of electric double layer, the decrease of the absolute value of zeta potential and the repulsion force between diaspore particles. In the presence of magnesium ions, the new IEP at pH value of 11 maybe caused by the adsorption of Mg(OH)2(s).
References
[1] HAZENMANN J L, MANCEAU A, SAINCTAVIT P H. Structure of the α-FexAl1-xOOH solid solution [J]. Phys Chem Minerals, 1992, 19: 25-38.
[2] FORNASIERO D, RALSTON J. Cu(Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ) activation in the flotation of quartz, lizardite and chlorte [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76: 75-81.
[3] JIA Mu-xin, SUN Chuan-yao. Study on adsorption behavior of metal ions on some silicalte minerals [J]. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, 2001, 10(3): 25-30. (in Chinese)
[4] LIU Gu-shan, FENG Qi-ming, OU Le-ming, LU Yi-ping, ZHANG Guo-fan. Influence and mechanism of copper ions and nickel ions on flotation of talc [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2005, 33(8): 1019-1022. (in Chinese)
[5] FENG Qi-ming, LIU Gu-shan, YU Zheng-jun, OU Le-ming, ZHANG Guo-fan. Influence and mechanism of ferric and ferrous ions on flotation of talc [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(3): 476-480. (in Chinese)
[6] WANG Dian-zuo, HU Yue-hua. Solution chemistry of flotation [M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1998: 132-156. (in Chinese)
[7] FANG Qi-xue. Study on stability of dispersion and mechanism of calcium and magnesium on fine mineral particles [J]. Metallic Ore Dressing Abroad, 1998(6): 42-45. (in Chinese)
[8] LI Yu-kang, ZHANG Zhong-han, SUN Ji. About of flotation activation law and mechanism of calcium and iron ions on beryl and spodumene [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1982, 1(2): 31-411. (in Chinese)
[9] KUSAKA E, AMANO N, NAKAHIRO Y. Effect of hydrolysed aluminum(III) and chromium(III) cations on the lipophilicity of talc [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1997, 50: 243-253.
[10] ZHU Jian-guang, ZHU Yu-shuang. Chemical principle of flotation reagent [M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Press, 1996: 228-236. (in Chinese)
[11] SUN Chuan-rao, YIN Wan-zhong. Principle of silicate flotation [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 196-241. (in Chinese)
[12] WANG Yu-hua, CHEN Xing-hua, ZHOU Yu-lin. Effect of metal ions on dispersibility of fine aluminum silicate minerals [J]. Metal Mine, 2007, 5: 38-43. (in Chinese)
[13] FUERSTENAU D W, PRADIP. Zeta potentials in the flotation of oxide and silicate minerals [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2005: 9-26
[14] YOON R H, SALMAN T, DONNAY G. Predicting point of zero charge of oxides and hydroxides [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1979, 70(3): 483-493.
[15] PARKS G A. The isoelectric point of solids, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems [J]. Chemical Review, 1965, 65: 177-198.
[16] OU Yang-jian. Study on mechanism and application of the dispersion and aggregation of fine particles [D]. Changsha: School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University of Technology, 1995: 65-81. (in Chinese)
[17] ZHANG Jan-feng. Studies on preparation of new flotation reagents and structure-activity relationship [D]. Changsha: School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, 2001: 58-89. (in Chinese)
[18] KRISHNAN S V, IWASAKI I. Floc formation in quartz-Mg(OH)2 system [J]. Colloid and Surfaces, 1985, 15: 89-100.
金属离子对微细粒一水硬铝石分散性的影响
周瑜林,胡岳华,王毓华
中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过分散实验研究金属阳离子对一水硬铝石分散性的影响,以Zeta电位测试、溶液化学计算和DLVO理论计算分析金属离子对一水硬铝石分散性影响的作用机理。结果表明:金属离子的价态对一水硬铝石分散性的影响大于金属离子的种类,且多价金属离子对一水硬铝石分散性的影响比一价金属离子大。钙、镁离子存在时,当pH小于10,一水硬铝石的分散性不发生改变,但是当pH大于10后,钙、镁离子促使一水硬铝石发生强烈聚沉。钙、镁离子在一水硬铝石上的吸附使双电层厚度减小,从而降低Zeta电位绝对值并导致一水硬铝石颗粒间排斥力减小。当pH为11时,由于颗粒吸附Mg(OH)2(s),在一水硬铝石表面产生一个新的零电点。
关键词:一水硬铝石;金属离子;分散性;动电位;DLVO理论
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project (2005CB623701) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: HU Yue-hua; Tel: +86-731-88871804; E-mail: HYH@mail.csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60838-8