网络首发时间: 2016-09-22 14:10
稀有金属 2017,41(10),1087-1092 DOI:10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy16040801
高压热处理对TC6钛合金α→β相变动力学的影响
赵军 谌岩 文全兴 张晗 李鑫 孙欢迎
北华航天工业学院材料工程学院
燕山大学亚稳材料制备技术与科学国家重点实验室
燕山大学环境与化学工程学院
摘 要:
针对高压热处理能改善 (α+β) 钛合金组织的问题, 对TC6钛合金进行5 GPa压力, 1000℃保温20 min的高压热处理, 利用差示扫描量热仪 (DSC) 测试了高压热处理前后TC6钛合金在不同升温速率下的α→β相变温度和转变时间, 根据Deloy方程和Ozawa方程分别计算其相变激活能和Avrami指数, 并利用光学显微镜 (OM) 和透射电镜 (TEM) 对高压热处理前后TC6钛合金的组织进行观察, 探讨了高压热处理对TC6钛合金中α→β相变动力学的影响。结果表明:5 GPa压力热处理能降低TC6钛合金的α→β相变温度, 缩短相变时间, 增大相变激活能。当合金以20℃·min-1升温时, 5 GPa压力热处理能使α→β相变起始温度和相变结束温度较5 GPa压力处理前分别降低了4.88和8.71℃, 相变时间也减少了0.2 min。当相变体积分数为50%时, 5 GPa压力处理后合金的α→β相变激活能较5 GPa压力处理前增大了155.29k J·mol-1, 但高压热处理对α→β相变机制影响不大。其原因主要是高压热处理能增大TC6钛合金组织中的晶界密度和位错密度。
关键词:
TC6钛合金;高压热处理;相变动力学;
中图分类号: TG146.23;TG166.5
作者简介:赵军 (1975-) , 男, 河北秦皇岛人, 博士, 副教授, 研究方向:高性能金属材料制备研究及成形控制, 电话:0316-2085740, E-mail:zjqhd@163.com;
收稿日期:2016-04-08
基金:河北省自然科学基金项目 (E2013409002, E2014203135);河北省教育厅科研基金项目 (Z2015178);河北省普通高等学校青年拔尖人才计划项目 (BJ2014001);燕山大学青年教师自主研究计划课题项目 (14LGA015);廊坊市科技支撑计划项目 (2014011047, 2016011081);北华航天工业学院科研基金重点项目 (ZD-2016-03) 资助;
Phase Transformation Kinetics of α→β in TC6 Titanium Alloy with High Pressure Heat Treatment
Zhao Jun Chen Yan Wen Quanxing Zhang Han Li Xin Sun Huanying
School of Materials and Engineering, North China Institute of Aerospace Engineering
State Key Laboratory of Metastable Materials Science and Technology, Yanshan University
College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Yanshan University
Abstract:
As high pressure heat treatment could improve the microstructure of ( α + β) titanium alloy, TC6 titanium alloy was heat treated at 5 GPa and 1000 ℃ for 20 min. The α→β phase transformation temperature and time in TC6 titanium alloy before and after high pressure treatment at different heating rates were measured by differential scanning calorimeter ( DSC) , the phase transition activation energy and Avrami exponent were calculated according to Deloy and Ozawa equation, respectively. The microstructure was observed by optical microscope ( OM) and transmission electronic microscope ( TEM) , and the effect of high pressure heat treatment on phase transformation kinetics of α→β in TC6 titanium alloy was studied. The results showed that 5 GPa pressure treatment could reduce the temperature and time for α→β phase transformation, and enhance the phase transformation activation energy. When the sample was heated at 20 ℃·min-1, initial temperature, ending temperature and time of α→β phase transformation in TC6 titanium alloy after high pressure treatment were decreased by 4. 88, 8. 71 ℃ and 0. 2 min, respectively. When the phase transformation volume fraction was 50%, the phase transformation activation energy was increased by 155. 29 k J·mol-1, compared with that without high pressure treatment, but high pressure heat treatment had little effect on its phase transition mechanism. The main reason was that the high pressure heat treatment could increase grain boundary density and dislocation density in titanium alloy.
Keyword:
TC6 titanium alloy; high pressure heat treatment; phase transformation kinetics;
Received: 2016-04-08
TC6钛合金具有密度低、比强度高、耐蚀性能及耐热性能好等特性, 已在航空航天等领域得到广泛地应用[1,2]。随着现代技术的迅速发展, 对TC6钛合金的需求量越来越大, 同时对TC6钛合金的性能也提出更高的要求。由于TC6钛合金是可热处理合金[3,4,5,6], 通常采用适当的热处理可以改善其组织与性能。高压具有促进形核、减小原子扩散系数及抑制晶粒长大等特点, 因而在采用高压力来改善金属材料组织与性能方面进行了大量的研究工作, 但这方面研究主要集中在压力应用在金属材料的凝固过程[7,8]。由于金属材料的固态相变影响其最终组织与性能, 近几年, 在金属材料固态相变过程中施加高压力来改善其组织与性能引起材料研究者的关注[9,10,11]。近期研究表明[12,13], 高压热处理能改善钛合金的组织和性能, 为此, 本文从TC6钛合金在升温过程中固体相变的角度, 探讨了5 GPa压力热处理对TC6钛合金在升温过程中固体相变的影响, 所得结果对弄清高压热处理对TC6钛合金固体相变及制订高压热处理后TC6钛合金合适的热加工工艺提供一定的参考数据, 同时也丰富了高压在钛合金领域的研究。
1 实验
实验中所用的材料为退火态TC6钛合金棒料, 其化学成分 (%, 质量分数) 为6.27Al, 2.71Mo, 1.48Cr, 0.42Fe, 0.26Si, 其余为Ti。将退火TC6钛合金棒料加工成尺寸为Φ6 mm×10 mm的实验样品, 在CS-IB型六面顶压机上进行高压热处理实验, 采用边升温边升压的升温方式, 最大压力为5 GPa, 加热温度为1000℃, 保温20 min, 然后断电保压冷却至室温。用STA449C差示扫描量热分析仪 (DSC) 对5 GPa压力热处理前后的样品进行热分析, 样品分别以5, 10和20℃·min-1的速度加热到1200℃, 保温1 min后, 冷却至室温。由DSC曲线可获得TC6钛合金在不同升温过程中的固体相变温度和相变时间。用Deloy小泽大夫方程[14]计算TC6钛合金的固体相变激活能:

式中, E为相变激活能, B为升温速度, F (x) 为相变函数, T为温度, R为气体常数, A为频率因子, x为相变分数, 当x为常数时, lg AE[RF (x) ]-1为常数。对于某一温度, 由Ozawa方程[15]可获得Avrami指数n:
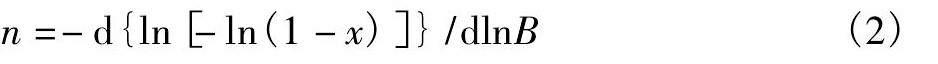
借助Axiovert200MAT金相显微镜 (OM) 和JEM-2010透射电镜 (TEM) 对实验试样的组织进行观察分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 相变温度及时间
图1为不同升温速率下5 GPa压力热处理前后TC6钛合金的DSC曲线。可看出, 两种状态的TC6钛合金分别以5, 10和20℃·min-1升温时, 在DSC曲线上均出现一个放热峰。由文献[16]可知, 该放热峰是钛合金在升温过程中由α→β相变所引起的。由DSC曲线可得出, 5 GPa压力热处理前后钛合金中α→β相变的起始温度、峰值温度、结束温度以及相变时间, 见表1。可看出, 升温速率越大, 两种状态的TC6钛合金中α→β相变的起始温度、峰值温度及结束温度越低, 相变时间也越短。5 GPa压力处理能降低α→β相变温度, 缩短其相变时间。以20℃·min-1速率升温时, 5 GPa压力处理能使α→β相变起始温度、峰值温度及结束温度较5 GPa压力处理前的分别降低4.880, 6.238和8.710℃, 相变时间也减少了0.2 min。
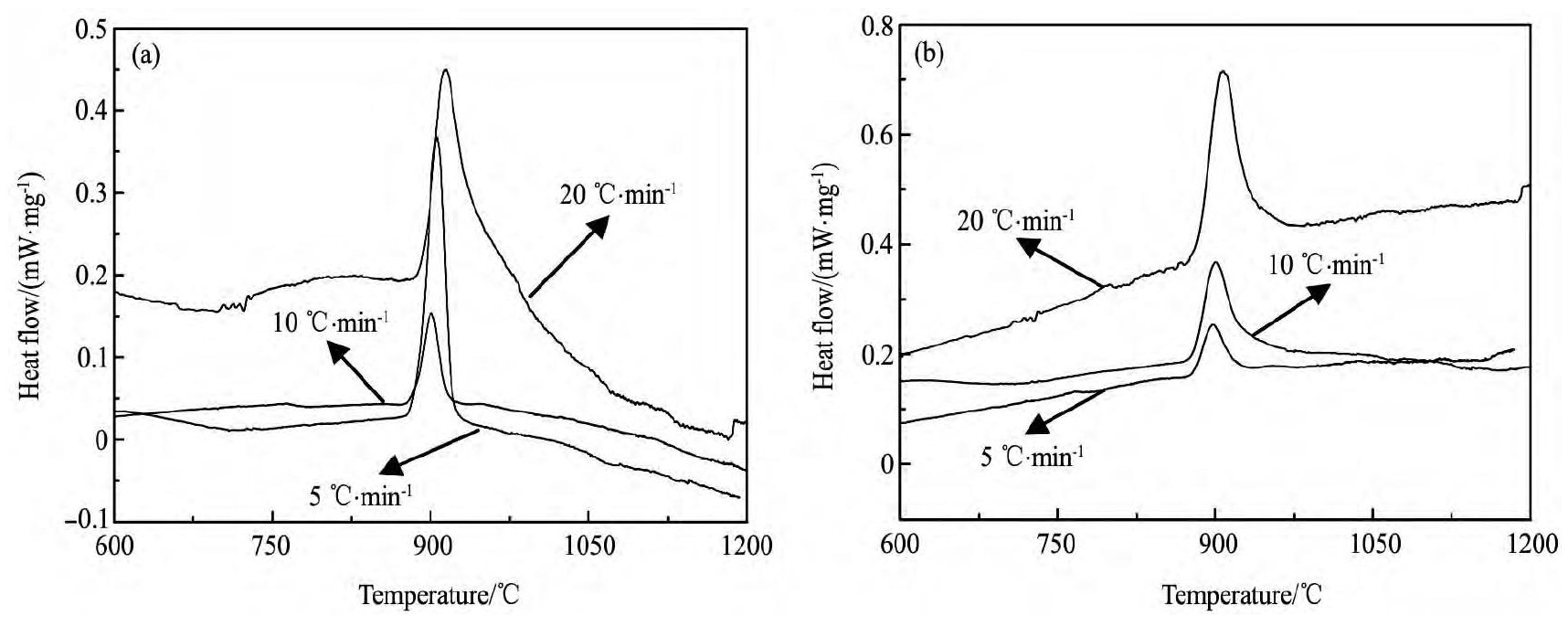
图1 不同状态下TC6钛合金的DSC曲线Fig.1 DSC curves of TC6 alloy at different conditions (a) As-annealed; (b) 5 GPa treatment
表1 不同升温速率下的TC6钛合金中α→β相变温度和相变时间Table 1 Temperature and time ofα→βphase transformation in TC6 alloy at different heating rates 下载原图
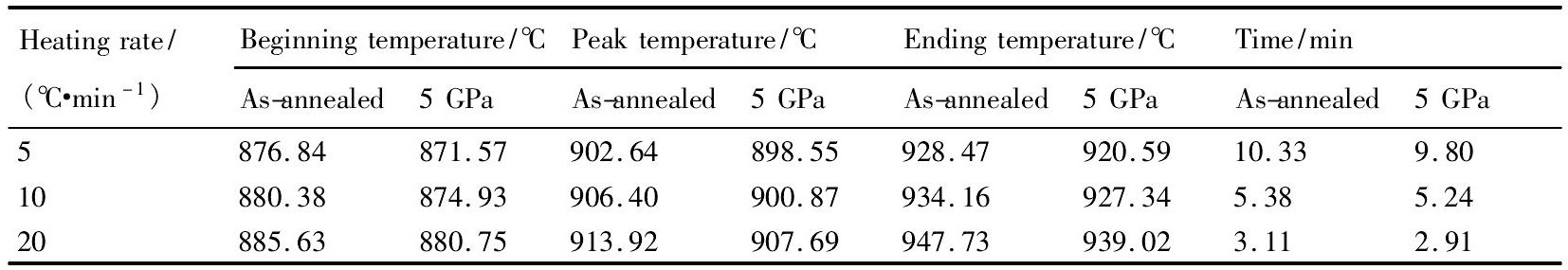
表1 不同升温速率下的TC6钛合金中α→β相变温度和相变时间Table 1 Temperature and time ofα→βphase transformation in TC6 alloy at different heating rates
图2为高压热处理前后TC6钛合金后的显微组织。可以看出, 高压热处理前后TC6钛合金后的组织均为条状α+β, 仅是高压热处理后钛合金的组织明显细化。由TEM照片 (图3) 可见, 高压热处理后钛合金的组织破碎, 且位错数量明显增多。这主要是由于5 GPa压力处理能细化TC6钛合金组织, 使组织中晶界密度和位错密度增大, 这为α→β相变新晶核的形核及长大提供了更多的部位和扩散通道, 使得α→β相变更为容易, 从而降低相变温度, 缩短了相变时间。

图2 TC6钛合金后的显微组织Fig.2 Microstructure of TC6 titanium alloy (a) As-annealed; (b) 5 GPa treatment
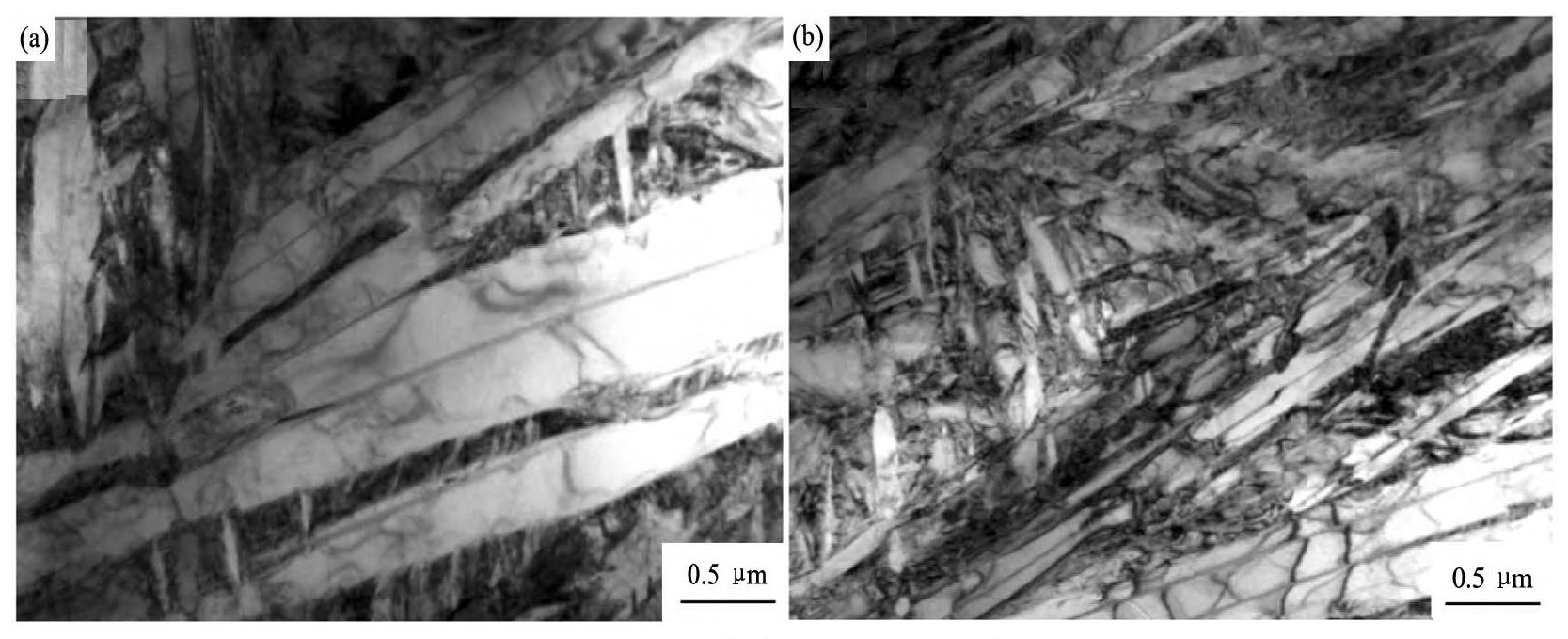
图3 TC6钛合金的TEM照片Fig.3 TEM images of TC6 titanium alloy (a) As-annealed; (b) 5 GPa treatment
2.2 相变激活能
根据DSC曲线可得出, 5 GPa压力处理前后TC6钛合金的α→β相变体积分数与所对应温度的关系曲线, 见图4, 由图4数据作出, 相变体积分数为50%时, lg B~T-1关系曲线, 如图5所示。可见两种状态TC6钛合金的lg B~T-1基本呈线性关系。由最小二乘法可获得直线的斜率, 根据Deloy小泽大夫公式, 通过其斜率可计算出α→β相变激活能, 示于图6。可以看出, 两种样品的α→β相变激活能均随相变体积分数的增加而减小, 5 GPa压力处理未改变相变激活能随相变体积分数变化的趋势, 但5 GPa压力处理能增大TC6钛合金α→β相变激活能, 当相变体积分数为50%时, 5 GPa压力处理后合金的α→β相激活能为1582.70 k J·mol-1, 较5 GPa压力处理前的提高155.29 k J·mol-1。其原因可能是β相是体心立方晶体结构, 而α相是密排六方晶体结构, β相的致密度较α相的差[17]。由于高压处理能增大金属材料的致密度, 这可能导致经5 GPa压力处理后的TC6钛合金在加热过程中α→β相阻力增大, 即其相变激活能增大。
2.3 Avrami指数
根据DSC曲线, 可获得5 GPa压力处理前后TC6钛合金在915℃时的-ln[-ln (1-x) ]~ln B的关系曲线 (图7) , 可看出, -ln[-ln (1-x) ]~ln B基本呈线性关系。由ln[-ln (1-x) ]~ln B直线斜率, 可获得两种状态下TC6钛合金在不同温度下的Avrami指数 (n) , 示于图8。可以看出, 5GPa压力处理能略增大Avrami指数, 但5 GPa压力处理前后TC6钛合金的Avrami指数值 (n) 均在1~2之间。由Avrami指数 (n) 数据 (1<n<2) [18], 可知两种状态下TC6钛合金中α→β相变过程是一个形核率随时间减少且晶粒生长为扩散控制的生长。由此可断定, 5 GPa压力处理对TC6钛合金中α→β相变机制影响不大。

图4 不同冷却速率下相变体积分数与温度的关系Fig.4 Relationship between transformation volume fraction and temperature under different cooling rates (a) As-annealed; (b) 5 GPa treatment
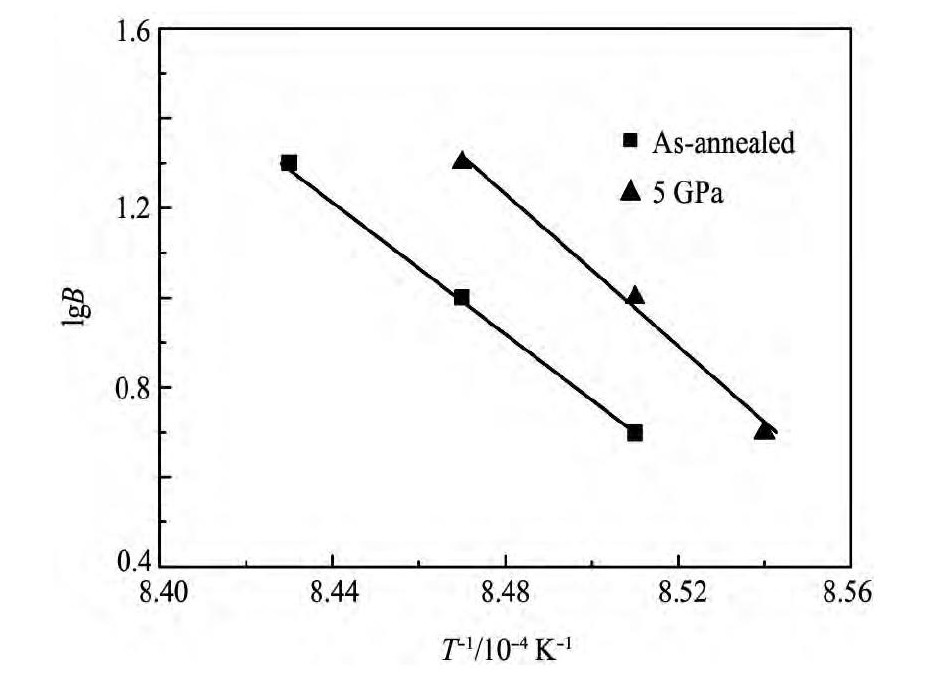
图5 50%相变体积分数所对应的lg B与T-1的关系Fig.5 Relationship between lg B and T-1at 50%phase trans-formation volume fraction

图6 相变激活能与相变体积分数的关系Fig.6Relationship between phase transformation activation energy and phase transformation volume fraction
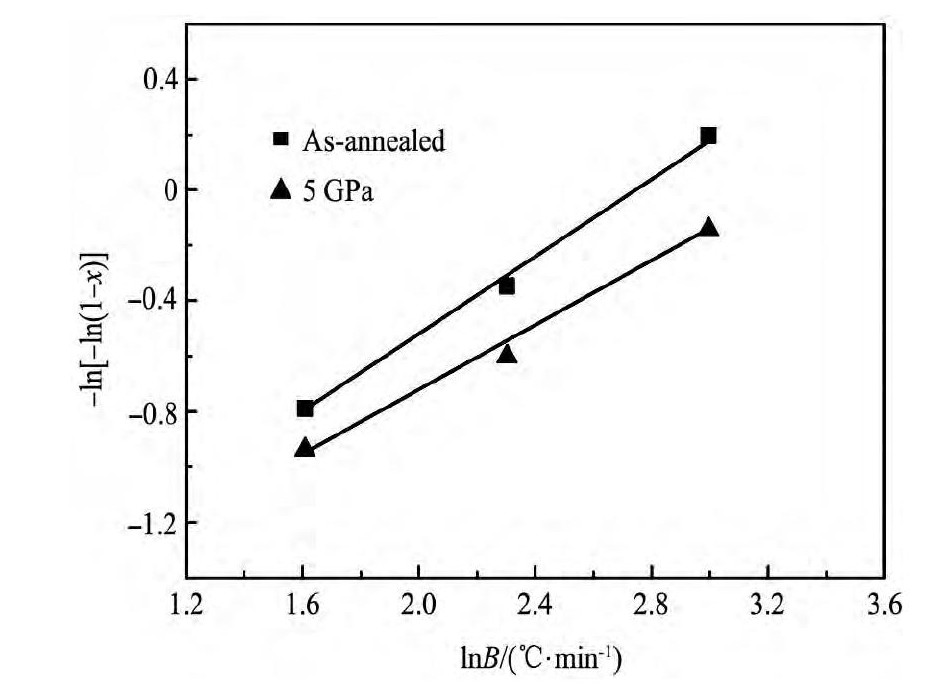
图7-ln[-ln (1-x) ]与ln B的关系Fig.7 Relationship between-ln[-ln (1-x) ]and ln B (915℃)
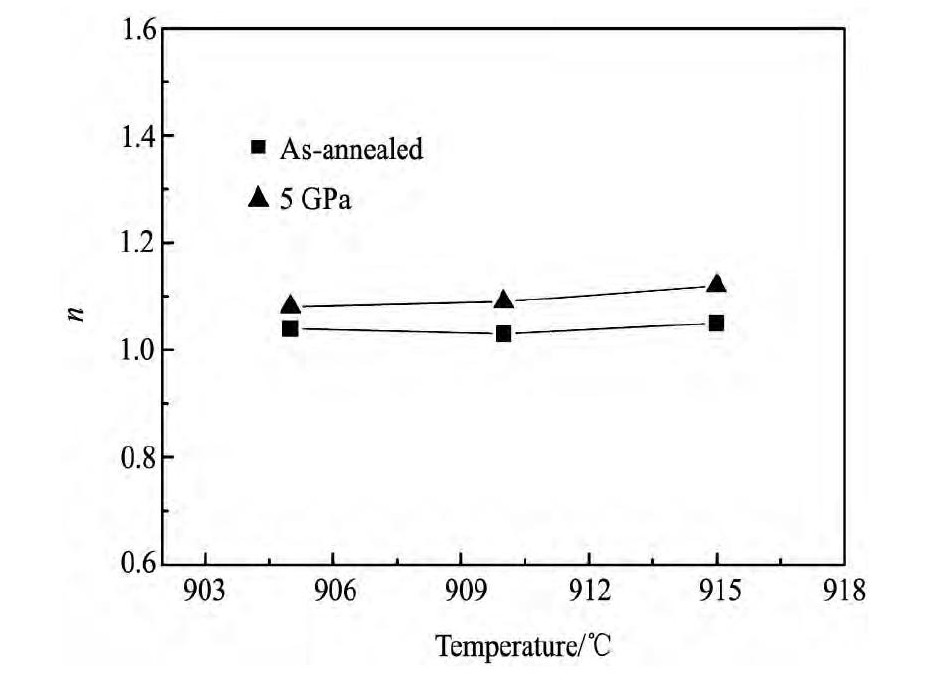
图8 Avrami指数 (n) 与所对应温度的关系Fig.8 Relationship between Avrami and temperature exponent (n) temperature
3 结论
1.5 GPa压力处理能降低TC6钛合金中α→β相变温度, 缩短相变时间, 增大相变激活能, 但对α→β相变机制影响不大。
2.经5 GPa压力下1000℃保温20 min高压处理后的TC6钛合金能使其在20℃·min-1升温过程中的α→β相变起始温度、峰值温度及结束温度分别降低4.880, 6.238和8.710℃, 相变时间也减少了0.2 min。
3.高压热处理能影响TC6钛合金中α→β相变温度和相变时间, 该研究对制订经高压热处理后TC6钛合金的热加工工艺提供一定的参考数据。
参考文献
[1] Nie X F, He W F, Zhou L C, Li Q P, Wang X D.Experiment investigation of laser shock peening on TC6titanium alloy to improve high cycle fatigue performance[J].Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 594:161.
[2] Pei C H, Fan Q B, Cai H N, Li J C.High temperature deformation behavior of the TC6 titanium alloy under the uniform DC electric field[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 489 (2) :401.
[3] Bai X F, Wei Y P, Xin S W.Effect of heat treatment on sublayer microstructure and hardness of TC6 titanium alloy[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2010, 35 (1) :106. (白新房, 魏玉鹏, 辛社伟.热处理对TC6钛合金内表层组织及硬度的影响[J].金属热处理, 2010, 35 (1) :106.)
[4] Chen X, Fan Q B, Yang X W.Phase transformation in TC6 titanium alloy during heating and cooling[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41 (12) :2123. (陈勋, 范群波, 杨学文.TC6钛合金加热和冷却过程中的相转变研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41 (12) :2123.)
[5] Wang X D, Li Y H, Li Q P.Property and thermostablity study on TC6 titanium alloy nanostructure processed by LSP[J].Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012, 29 (1) :68.
[6] Li M Q, Xiong A M, Cheng S H.Effects of process parameters on the microstructure during the hot compression of a TC6 titanium alloy[J].Rare Metals, 2004, 23 (3) :263.
[7] Straumal B B, Baretzky B, Mazilkin A A, Phillipp F, Kogtenkova O A, Volkov M N, Valiev R Z.Formation of nanograined structure and decomposition of supersaturated solid solution during high pressure torsion of Al-Zn and Al-Mg alloys[J].Acta Materialia, 2004, 52 (15) :4469.
[8] Xu R, Zhao H, Li J, Liu R.Wang W K.Microstructures of the eutectic and hypereutectic Al-Ge alloys solidified under different pressures[J].Materials Letters, 2006, 60 (6) :783.
[9] Zhao J, Li J M, Zhao L M, Yin S, Chen J C, Wen Q X.Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity of Cu-37.67Zn-1.13 Al alloy with high pressure heat treatment[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2015, 39 (2) :97. (赵军, 李冀蒙, 赵陆民, 尹硕, 陈久川, 文全兴.高压热处理对Cu-37.67Zn-1.43Al合金导热及导电性能的影响[J].稀有金属, 2015, 39 (2) :97.)
[10] Wang Y H, Zhao J, Liu J H.Effect of high pressure heat treatment on microstructures and micro-mechanical properties of Cu Zn alloy[J].High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2014, 33 (4) :339.
[11] Ma Y Q.Effects of 4 GPa pressure heat treatment on mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of CuCr Ni Al alloy[J].Materials Transactions, 2013, 54 (5) :725.
[12] Xiao Y, Ma J, Li Z B, Zhang H Q, Chen Y.Effect of5 GPa pressure treatment on nanoindentation creep property of TC6 titanium alloy[J].Journal of Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 5 (1-2) :37.
[13] Cao D, Liu J Q, Feng L L.Effect of heat treatment under 3 GPa pressure on hardness and compressive strength of TC6 titanium alloy[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015, 40 (7) :25. (曹栋, 刘建强, 冯仑仑.3 GPa压力热处理对TC6钛合金的硬度和抗压强度的影响[J].金属热处理, 2015, 40 (7) :25.)
[14] Han Z L.Effects of high pressure treating on the phase transformation kinetics of austenite to pearlite in low carbon and low alloy steel[J].Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2007, 1 (1) :61.
[15] Ozawa T.Kinetics of non-isothermal crystallization[J].Polymer, 1971, 12 (8) :150.
[16] Zhang Z, Wang Q J, Mo W.Metallography and Heat Treatment of Titanium[M].Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009.13. (张翥, 王群骄, 莫畏.钛的金属学和热处理[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2009.13.)
[17] Zhao P, Xie F Z, Sun Z G.Materials Science Essentials[M].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2009.11. (赵品, 谢辅洲, 孙振国.材料科学基础教程[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2009.11.)
[18] Wang Y H, Liao B, Liu J H.Effects of deep cryogenic treatment on the solid-state phase transformation of Cu-Al alloy in cooling process[J].Phase Transitions, 2012, 85 (7) :650.