LiFSI电解液高温下的铝箔腐蚀机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第5期
论文作者:李春雷 曾双威 王鹏 李昭娟 杨莉 赵东妮 王洁 刘海宁 李世友
文章页码:1439 - 1451
关键词:锂离子电池;LiFSI基电解液;双草酸硼酸锂(LiBOB);腐蚀抑制;高温;界面膜
Key words:lithium-ion batteries; LiFSI-based electrolyte; lithium bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB); corrosion inhibition; elevated temperatures; interfacial film
摘 要:双氟磺酰亚胺锂(LiFSI)因其优异的性能有望取代六氟磷酸锂。利用LiFSI解决铝(Al)集流体在高温下的腐蚀问题至关重要。结合密度泛函理论计算和光谱学研究45 °C下LiFSI电解液中铝的腐蚀机理。研究发现,随着温度的升高,由Al(FSI)3溶解形成的不规则的、疏松的、对铝箔不具保护作用的AlF3加剧高温下铝的腐蚀。双草酸硼酸锂(LiBOB)对铝的腐蚀有较好的抑制作用。LiBOB 的加入改变铝箔和电解液之间的界面反应,使铝箔表面形成一层坚固、具有保护作用的固体界面膜,含硼化合物促进AlF3向LiF的变化,从而进一步加强固体界面膜的牢固性。本研究为LiFSI在锂离子电池中的应用提供合理设计铝箔界面的途径。
Abstract: Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) is a promising replacement for lithium hexafluorosphate due to its excellent properties. A solution to the corrosion of aluminum (Al) current collectors by LiFSI at elevated temperatures is essential. The mechanisms of Al corrosion in LiFSI-based electrolyte at 45 °C were studied with density functional theory calculations and spectroscopic investigations. It is found that the irregular, loose and unprotected AlF3 materials caused by the dissolution of co-generated Al(FSI)3 can exacerbate Al corrosion with the increase of temperature. Lithium bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB) can effectively inhibit the Al corrosion with a robust and protective interphase; this can be attributed to the interfacial interactions between the Al foil and electrolyte. Boron-containing compounds promote the change from AlF3 to LiF, which further reinforces interfacial stability. This work allows the design of an interface to Al foil using LiFSI salt in lithium-ion batteries.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 1439-1451
Chun-lei LI1, Shuang-wei ZENG1, Peng WANG1, Zhao-juan LI1, Li YANG1, Dong-ni ZHAO1, Jie WANG1, Hai-ning LIU2, Shi-you LI1
1. College of Petrochemical Technology, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China;
2. CAS Key Laboratory of Comprehensive and Highly Efficient Utilization of Salt Lake Resources, Qinghai Institute of Salt Lake, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining 810008, China
Received 2 May 2020; accepted 4 January 2021
Abstract: Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) is a promising replacement for lithium hexafluorosphate due to its excellent properties. A solution to the corrosion of aluminum (Al) current collectors by LiFSI at elevated temperatures is essential. The mechanisms of Al corrosion in LiFSI-based electrolyte at 45 °C were studied with density functional theory calculations and spectroscopic investigations. It is found that the irregular, loose and unprotected AlF3 materials caused by the dissolution of co-generated Al(FSI)3 can exacerbate Al corrosion with the increase of temperature. Lithium bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB) can effectively inhibit the Al corrosion with a robust and protective interphase; this can be attributed to the interfacial interactions between the Al foil and electrolyte. Boron-containing compounds promote the change from AlF3 to LiF, which further reinforces interfacial stability. This work allows the design of an interface to Al foil using LiFSI salt in lithium-ion batteries.
Key words: lithium-ion batteries; LiFSI-based electrolyte; lithium bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB); corrosion inhibition; elevated temperatures; interfacial film
1 Introduction
With the wide application of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, electric vehicles, and energy storage devices in various areas, improvements for LIBs are in demand [1,2]. As a significant part of electrolyte for LIBs, lithium hexafluorosphate (LiPF6) undergoes decomposition and releases corrosive gas at elevated temperatures [3,4]. To solve this problem, numerous efforts have been made to find a substitute for LiPF6 [5,6]. Among many salts synthesized so far, lithium bis(trifluoromethyl sulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) promises to replace LiPF6 because of its excellent properties such as high thermal stability, easy ionization, and good film formation on negative electrodes [7,8]. However, the problem of Al current conductor corrosion at low potentials (around 3.7 V (vs Li/Li+)) has limited its application [9]. Fortunately, in studying the corrosion of Al in LiTFSI-based electrolyte, it has been found that adding small amounts of other lithium electrolyte salts such as LiPF6, lithium difluoro(oxalate)borate (LiDFOB), or lithium bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB) into the electrolyte can effectively solve this problem [10-13].
In recent years, as another fluorosulfonyl- based lithium salt, LiFSI has attracted more and more attention of researchers [14,15]. Compared with LiTFSI, LiFSI displays good anticorrosive properties for Al, especially when used in a high concentration [16,17]. Unfortunately, impurities have constantly plagued this new salt [6,11]. This is why Al foil is severely corroded at the potential of 3.6 V in a LiFSI-based electrolyte. Some studies have even reported that the corrosion of Al foil appears around 3.3 V [18]; the difference in potential may correlate with the purity of lithium salt employed in tests and the definition for corrosion. Since the corrosion of Al in LiTFSI- based electrolyte can be suppressed effectively by adding other lithium salts that can form a passivating layer on the Al foil surface, it is reasonable to add them to LiFSI-based electrolyte. SHANGGUAN et al [19] confirmed that Al foil was stable in an electrolyte based on mixed salts of LiFSI and LiDFOB. YAN et al [20] reported that Al corrosion can be effectively suppressed by adding just 2% LiDFOB into LiFSI-based electrolyte.
Most of the above studies on the inhibition of Al corrosion were completed at room temperature, and there is a lack of analysis at elevated temperatures. However, LIBs are normally required to work at high temperatures, which makes it important to study the corrosion of Al foil at elevated temperatures. To fill this gap, we systematically studied the electrochemical behaviors of Al foil in electrolytes using a single salt of LiFSI and dual-salts of LiBOB+LiFSI at 45 °C. We intended to reveal whether Al corrosion becomes worse at high temperature in LiFSI-based electrolyte and whether LiBOB salt added remains effective at high temperature. As far as we know, LiBOB is a salt with excellent film-forming properties and provides good passivation for Al foil. Research reports on the electrochemical behavior of Al in LiBOB-based electrolyte have shown that Al maintains stability at potentials beyond 5 V [21]. However, Al metal can be completely oxidized to a trivalent Al-oxide around 1.4 V (vs Li/Li+) from a thermodynamic standpoint, which means that LiBOB can passivate Al [22].
2 Experimental
2.1 Electrolyte preparation
Battery-grade ethylene carbonate (EC), ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC), and diethyl carbonate (DEC) were provided by Chaoyang Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. (China). Battery-grade LiFSI and LiBOB were purchased from Huizhou Avenue New Materials Co., Ltd. (China). An electrolyte containing 1 mol/L LiFSI (abbreviated as LiFSI) was prepared by dissolving LiFSI into a mixture of EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1, in volume ratio, the same below). The novel dual-salts electrolyte containing 0.6 mol/L LiFSI and 0.4 mol/L LiBOB (abbreviated as LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4) was prepared by dissolving certain amounts of LiFSI and LiBOB into the mixture of EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1). All preparations were conducted in a glove box under Ar atmosphere, and the contents of water and oxygen were each less than 0.1×10-6.
2.2 Electrode and cell preparation
The battery-grade Al foils (20 μm in thickness and >99.45% in purity) were provided by Alnan Aluminium Co., Ltd. (China). Coin cell cases (EQ-CR2025-CASE button cells case, made of 304 stainless steel with a sealing O-ring) and battery-grade lithium foil were kindly offered by Shenzhen Kejing Star Technology Ltd. (China). The LiFePO4 (Hunan Shanshan Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., China) electrodes were prepared by mixing 80 wt.% cathode materials, 10 wt.% acetylene, and 10 wt.% polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF); the material was coated on Al foil. The mass loading of the cathode electrodes was about 2.0 mg/cm2. Assembly of a Li/LiFePO4 half-cell was conducted in a glove box in an Ar atmosphere with water and oxygen content each less than 0.1×10-6.
2.3 Measurements
Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) and cycle voltammetry tests were conducted in a three-electrode system that employed Al foil as a working electrode and lithium foil as counter and reference electrodes, with a sweep rate of 5 mV/s from open circuit potential to 5 V (vs Li/Li+). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was performed over frequencies from 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz at 5 mV. For chronoamperometry measurements, the three-electrode systems were polarized to 4.2 V and held at this potential for 12 h while monitoring the current variation. All the above-mentioned electrochemical experiments were carried out on an electrochemical workstation (CHI660E, Chenhua, China). After that, the three-electrode system was stripped down and the Al foils were taken out carefully in the glove box and were rinsed repeatedly with DEC to remove residual electrolyte. After rinsing, the foils were immersed in centrifugal tubes containing 2 mL EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1) and held at room temperature (around 25 °C) or 45 °C for one week. The concentration of Al3+ ions dissolved in the solvent was determined with inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES, Leeman, USA). The surface morphologies of Al foils were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-6510, Japan). The elemental analysis of the Al foil surface film was carried out with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Kratos AXIS ULTRADLD, UK). Electrochemical charge-discharge tests of the 2025-type coin cells were carried out on a LAND battery tester at a 0.5C rate. In this work, all potentials mentioned are referenced to the Li/Li+ redox couple unless otherwise specified.
2.4 Density functional theory (DFT) calculation
All calculations were performed with the Gaussian 09 program package. The geometry optimizations were carried out with the DFT models and the B3LYP method with the 631G (d,p) basis set. Frequency calculation was employed for an optimized structure in vacuum; no imaginary frequency was observed indicating that the structures are stable minima on the potential energy surface. The total energies and frontier molecular orbital energies of organic molecules were calculated at a 6311G (2df,3dp) level base on a polarizable conductor calculation model (PCM) with a dielectric constant of 33.67; this characterizes the effect of solvents containing EC/DEC/EMC with a volume ratio of 1:1:1 [23].
3 Results and discussion
Figure 1(a) presents the high-temperature cycling performance of Li/LiFePO4 half-cells with electrolytes based on single-salt LiFSI and dual salts LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4. With LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 electrolyte, the LiFePO4 cathode cycles fairly well. After 100 charge-discharge cycles, the LiFePO4 electrode retains a reversible capacity of 134.3 mA·h/g with a capacity loss of 8.4%. Moreover, the charge capacity and discharge capacity in every cycle are almost equal, indicating that coulombic efficiency for most of the electrochemical cycles is close to 100% and that very weak side reactions occur during the long-term cycling test. The improvement of electrochemical performance is believed to be due to the effective suppression of Al corrosion by the LiBOB salt. However, the cell with LiFSI electrolyte fails after only 20 charge-discharge cycles, after which the charge capacity far exceeds the theoretical capacity of 170 mA·h/g, even as high as 217 mA·h/g, as can be seen clearly from Fig. 1(a). This phenomenon of super-high charge capacity is caused by some disadvantageous side electrochemical reactions inside the cell. By comparing previous studies with the room-temperature cycling performance presented in Fig. 1(b), we believe that Al corrosion becomes worse with increased temperature in LiFSI-based electrolyte [6,11]. The side reactions are mainly correlated to the corrosion of Al current collector by LiFSI salt at elevate temperature. That is to say, the serious Al corrosion makes active materials peel off from conduct collector and reduces the utilization rate of active materials. As a result, the specific discharge capacity drops sharply.
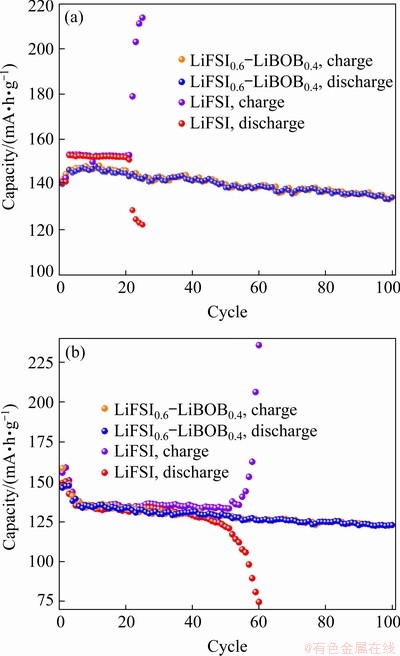
Fig. 1 Cycling performance of Li/LiFePO4 half-cells with 0.5C charge–discharge rates using electrolytes based on LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 and LiFSI at 45 °C (a) and at room temperature (b)
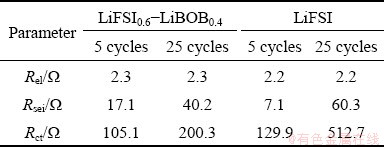
EIS was used to investigate the charge transport behavior at the cathode. Figures 2(a, b) show the electrochemical impedance spectra of Li/LiFePO4 half-cells with LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 and LiFSI after cycles at 0.5C, respectively. The high frequency range can be ascribed to the solid electrolyte interphase film resistance (Rsei), the middle frequency range corresponds to the charge transfer resistance (Rct), and the low frequency region represents the lithium ions diffusion (Wdif) [24-26]. Rsei comes from the resistance to lithium ion migration in SEI, while Rct mainly refers to the desolvation resistance of solvated lithium ions on the surface of electrode materials. The EIS spectra were fitted using an equivalent circuit (insert) where Rel is the ohmic resistance. It can be seen that the cell’s impedance spectra using LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4- and LiFSI-based electrolytes show two inconspicuous semicircles in the high- and middle-frequency regions and an inclined line at the low-frequency end. Fitted parameter values of the impedance spectra are given in Table 1. The gap between the Rel values of the two types of cells is not very large. Obviously, after the initial five cycles, the cell using LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte shows higher Rsei than the other. This is because Rsei is determined by the SEI characteristics on the working electrode surface that reflect how the Li+ ions have difficulty in penetrating the SEI film. The larger the Rsei is, the greater the resistance of the SEI film to the passage of Li+ ions is. Also, the thicker the SEI is and the worse the lithium conductivity is, the greater the Rsei is. Therefore, under the same conditions, the SEI formed on the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte is thicker than that on the LiFSI-based electrolyte, so the Rsei in LiFSI-based electrolyte is smaller than that in LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte after the first five cycles. With the increase of cycle number, the SEI film on the LiFSI-based electrode surface is gradually improved and Rsei increases slowly, and the Al collector on the electrode is seriously corroded. Therefore, after 25 charge-discharge cycles, the cell using LiFSI-based electrolyte shows higher Rsei and Rct than the other cell. The corrosion behavior deteriorates the interface between the electrode material and Al current collector as reflected in the increase of Rsei and Rct in the EIS. As a result, the capacity of the cell fades fast. In contrast, the cell using LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte shows lower Rsei and Rct than the other cell. This is consistent with its good capacity retention.
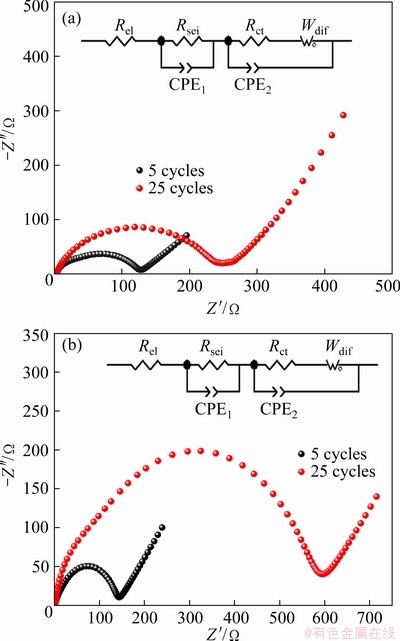
Fig. 2 EIS of cycled Li/LiFePO4 half-cells using LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based (a), and LiFSI-based (b) electrolytes
Table 1 Fitted parameters of impedance spectra of half- cells after specific cycles
To study LiBOB inhibition of the corrosion of Al foil at elevated temperatures, we ran LSV in a three-electrode system with Al foil as the working electrode. As shown in Fig. 3(a), the current density is around 0 mA/cm2 when the poling potential is below 3.3 V. When the poling potential reaches 3.3 V, the current density begins to increase with rising poling voltage, indicating the presence of corrosion. In the potential range from 3.6 to 4.3 V, the current density maintains a constant value, indicating a maximum corroding reaction. The current density starts rising again near 4.3 V which corresponds to the decomposition of the electrolyte [27,28]. Figure 3(b) reinforces this conclusion. It is well known that solid electrolyte interphase is composed of electrolyte decomposition products that play a significant role in protecting the electrode surface and inhibit the further decomposition of the electrolyte. To investigate whether decomposition products of the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte passivate the Al foil, further LSV experiments were conducted under the same conditions. As shown in Fig. 3(c), the rising current density at around 3.3 V disappears; given this, combined with Fig. 3(a), we can safely conclude that LiBOB can prevent the corrosion of Al foil in LiFSI-based electrolyte at elevated temperature. On the contrary, as shown in Fig. 3(a), although the current density at 3.3 V in the second test is smaller than that in the first test, the rising current density in the LiFSI-based electrolyte still exists, indicating that Al foil corrosion is persistent. These results confirm that LiBOB can effectively prevent the corrosion of Al foil in LiFSI-based electrolyte even at elevated temperature. The protective film formed on the surface of Al foil during the first poling process of LSV hinders direct contact between the electrolyte and the Al foil because of the excellent LiBOB film-forming performance. As a result, the corrosion of Al foil is remarkably inhibited. Three consecutive cyclic voltammograms were recorded to demonstrate the passivation mechanism of LiBOB for Al foil at elevated temperatures. As shown in Fig. 3(d), the oxidation rate of Al foil in LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4- based electrolyte is very low and is independent of the potential between 2 and 3.3 V. The low oxidation rate is attributed to the protection provided by an air-formed Al oxide film [29]. The current density abruptly increases at 3.5 V and reaches a maximum at 3.7 V. As the sweeping direction of poling potential reverses, the anode current decreases rapidly. As a result, a noticeable hysteresis is present in the first cyclic polarization curve, which indicates that the Al foil corrosion extent decreases during the reverse scanning process [30]. During the second and third polarization cycles, the current densities do not rise at 3.5 V. Besides, the current density is much lower and there is only a very small hysteresis on the second cyclic polarization curve and virtually no hysteresis on the third cyclic polarization curve. This can be attributed to the formation of a passivation film on the Al foil surface by the decomposition of LiBOB. However, the electrochemical behavior of Al foil in LiFSI-based electrolyte differs completely from that of LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte. Here, as soon as the initial oxidation of electrolyte occurs at the current collector surface, the electrolyte becomes a pool of different decomposition species which can contribute to further deterioration of the current collector. In this case, Al foil exhibits interesting electrochemical behaviors in the LiFSI-based electrolyte: corrosion and passivation. As revealed in Fig. 3(e), with the increase of scanning times, the hysteresis of CV curves gradually lessens, and the potential at which the current density begins to rise gradually shifts to the right, showing a slight passivation behavior. This may be related to diffusion control steps in the metal corrosion process. We speculated that there might be some substances on the Al interface that hardly diffuse to the electrolyte. Since the diffusion rate of these substances is lower than that of the electrochemical oxidation of Al metal, the diffusion process is the control step of the dissolution of Al foil. As a result, slight passivation occurs. Nevertheless, in subsequent cycles, the peak at about 3.7 V is still visible, showing severe corrosion behavior [31]. This can be due to two reasons: (1) the interface is not robust enough and the contact between Al and electrolyte cannot be effectively isolated, and (2) in combination with this galvanic corrosion of Al, the high-temperature corrosion (that is, the electrolyte solvent damage to the deposited layer on the Al foil surface) occurs. This can be well-proven by the dissolution experiments with Al foil surface film in mixed organic solvents.
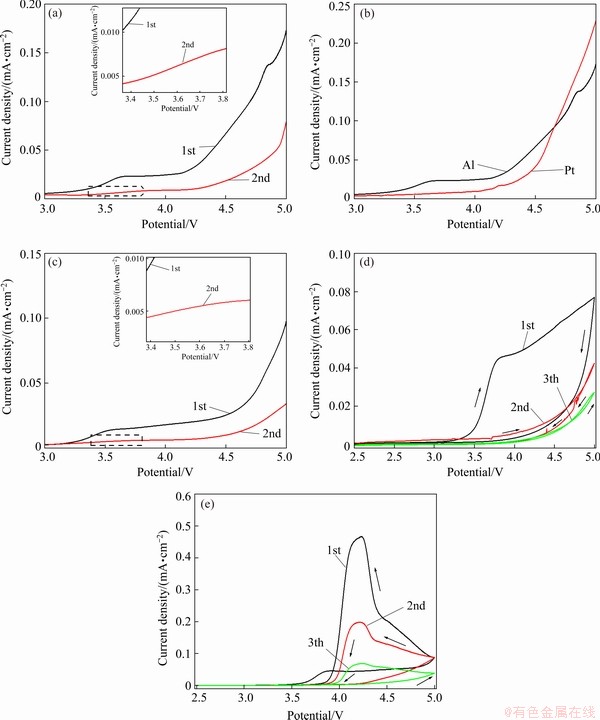
Fig. 3 LSV curves of LiFSI-based (a) and LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based (c) electrolyte in electrochemical cell employing Al foil as working electrodes from open circuit potential to 5 V at sweep rate of 5 mV/s; LSV curves of LiFSI-based electrolyte in electrochemical cell employing Al foil and Pt foil electrodes (b); CV curves of LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based (d) and LiFSI-based (e) electrolytes in electrochemical cell employing Al foil as working electrodes from open circuit potential to 5 V at sweep rate of 5 mV/s
As shown in Fig. 4(a), at room temperature and elevated temperature, the concentrations of Al3+ ions dissolved in mixed organic solvents are 9.06 and 10.76 mg/L, respectively. This indicates that on one hand, these films are unstable and can be dissolved in organic solvents, and on the other hand, increased temperature will increase the physical destruction (dissolution) of organic solvents on the surface film. Based on the analysis of CV experiments, it seems safe to say that, similar to the development of an SEI layer, the formation of a passivation film on Al foil surface is also a gradual improvement process. The ideal passivation film should be formed and stable in the first few cycles and no longer grow in subsequent cycles. Otherwise, the continuous growth of the film will continuously thicken it and will increase battery internal resistance. On the other hand, the continuous thickening of passivation film will also continuously consume electrolyte, resulting in the reduced lithium stock. This raises the question of how to evaluate the passivation film stability. It is feasible to measure static leakage at the interface between electrodes and electrolytes. Static leakage current is a quantitative indicator of the rate of parasitic reactions in an electrochemical measurement system with controlled potentials [32]. The main purpose of a leakage current test is to evaluate the stability of a working electrode in an electrolyte by measuring its current density. After three consecutive cyclic voltammogram experiments and the formation of a passivation film on the surface of the Al foil, the static leakage current of the foil in the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based and LiFSI-based electrolyte systems was measured using chronoamperometry. Chronoamperometry was achieved by polarizing the electrode up to 4.2 V. During the test, changes of current were monitored by holding the working Al electrode at 4.2 V for 12 h. The potentiostatic holding began immediately after applying the terminal potential, and the multiple phenomena involved contributed to the measured current and gave rise to a complex curve (Fig. 4(b)). Three separate processes can be assigned as P1, P2, and P3 on the curve detailed in Fig. 4(b). A strong current decay (P1) occurs while reaching 4.2 V, which is associated with the polarization of the Al foil electrode. The oxidative decomposition current dominates the signal immediately after this process has finished.
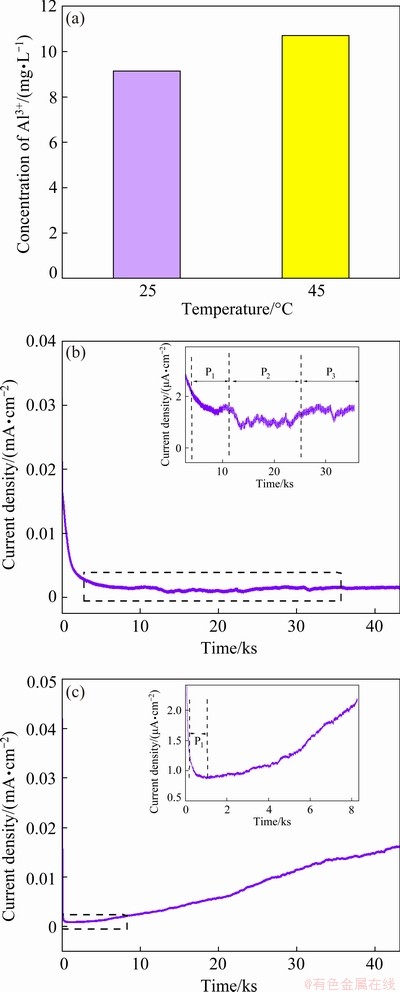
Fig. 4 Concentrations of Al3+ ions dissolved from surface film of Al foils stored in 2 mL mixed solvent of EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1) for one week at 25 °C and 45 °C, respectively (a) and chronoamperometry curves with constant potential of 4.2 V for 12 h in LiFSI0.6- LiBOB0.4-based (b) and LiFSI-based (c) electrochemical cells employing Al as working electrodes at 45 °C
It is important to note that the constant decrease of measured current in P2 can be attributed to a series of processes including depletion of reacting species, the deposition on the surface of Al electrode, and the diffusion of the reaction products in the electrolyte body. Once the processes above reached equilibrium, the third process (P3) begins. It can be seen that in the final stage the leakage current stabilizes at about 0.001 mA/cm2, which indicates that the electrochemical reaction occurring on the Al electrode is very poor. However, the response current characteristics measured in the LiFSI-based electrolyte are completely different from those of the former. The initial stages (P1) are similar, but there are different trends in the current subsequently (Fig. 4(c)). The leakage current increases steadily in P2 and there is no trend to stabilize at a certain point. The source of varying behavior in P2 is the absence of passivation film on the surface of the Al electrode.
SEM images of the corroded Al foil in chronoamperometric experiments are shown in Fig. 5. It can be seen from Fig. 5(b) that after being polarized in LiFSI-based electrolyte, the original oxide film on the Al foil surface is destroyed and covered with a large area of corrosion products. In the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte, the original oxide film as shown in Fig. 5(c) can hardly be seen on the surface of the Al foil after the chronoamperometric experiments, but a new uniform passivation film is present, as shown in Fig. 5(a) which is attributed to the excellent film-forming performance of LiBOB.
To get further insights into the surface composition of fresh Al after chronoamperometric experiments, the XPS data were recorded. In Fig. 6(b), the peak at 193.1 eV in B 1s spectra can be attributed to the B—O peak, which originates from boron oxides produced by the decomposition of LiBOB salt on the surface of Al foil [9,33,34]. It has been reported that B—O peak may originate from compounds AlBO3 or B2O3 [30,33,35]. The core-level XPS spectrum of Al 2p (Fig. 6(a)) demonstrates that the existence of B—O bonds corresponding to the binding energy of 192.90 eV is attributed to the compound B2O3 because there is no Al element detected on the surface of Al foil; the peak corresponding to the binding energy of 685.01 eV in the core-level XPS spectrum of F 1s originates from LiF, which comes from the decomposition of LiFSI salt on the surface of the Al foil [36-38], and the peak intensity of Li-F bond in LiFSI sample is much weaker than that in LiFSI0.6- LiBOB0.4 sample. The F—S peak at 687.4 eV can be attributed to the corrosion product Al(FSI)3 on the surface of Al foil [20,39]. Also, the lowered peak intensity derived from F—S bonds in the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 sample indicates that Al corrosion is suppressed significantly. The Al—F peak at 686.3 eV is attributed to another corrosion product of AlF3 on the surface of Al foil [4,40], while the intensity of the peak in the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 sample is much weaker than that in the LiFSI sample. These results show that there is more than one corrosion reaction occurring in the Al foil. Besides the well-known corrosion mechanism of Al(FSI)3 formation, there is another electrochemical reaction that forms AlF3 in which the F- anion comes from the decomposition of FSI- anion on the surface of the Al foil electrode. Because the F- anion produced by the decomposition of the FSI- anion is much closer to Al3+ cation produced by the electrochemical oxidation of the Al foil than the Li+ cation in the electrolyte, a large amount of AlF3 and a small amount of LiF form on the surface of Al foil. Although compacted AlF3 is protective for Al corrosion, irregular and loose AlF3 materials that result from the dissolution of co-generated Al(FSI)3 have little effect on prevention. Also, the formation of unprotected AlF3 aggravates the corrosion of the Al foil.
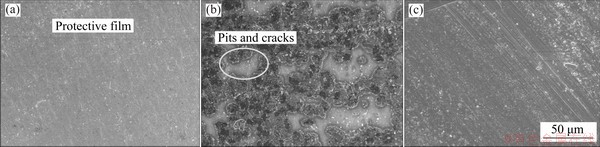
Fig. 5 SEM images of Al foils after chronoamperometric experiments in LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based (a) and LiFSI-based (b) electrolytes, and fresh Al (c)
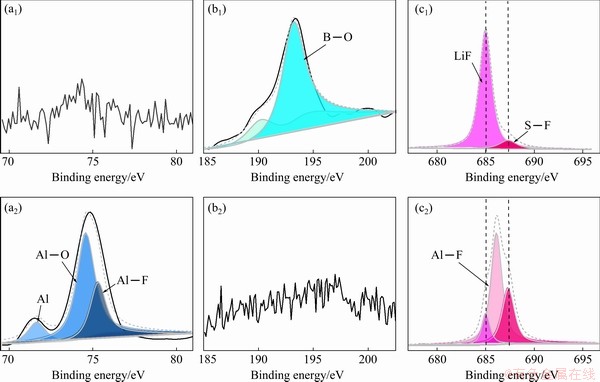
Fig. 6 Al 2p (a1, a2), B 1s (b1, b2) and F 1s (c1, c2) XPS patterns of Al foil after chronoamperometric experiments with LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based (a1, b1, c1) and LiFSI-based (a2, b2, c2) electrolytes
The process of AlF3 formation can be well-proven by the results of quantum chemistry calculation. As shown in Fig. 7(a), the N—S bond and S—F bond in the FSI- anion are both broken, and a new Al—F bond appears after providing an oxidizing environment (losing an electron) for the FSI- anion in the presence of the Al3+ cation; this differs from the case of substituting Al3+ with the Li+ cation. In the latter case, the S—F bond close to the Li+ cation is longer than that of the other, and its bond order is only 0.51. It is thought that the S—F bond is broken and the oxidation of FSI- anion shows difficulties. That is to say, between the two competing reactions of AlF3 generation and LiF generation, the former has more competitive advantages. This is in good agreement with the results of the XPS analysis. It is noteworthy that the oxidative decomposition of the FSI- cation becomes difficult without adding the Li+ or Al3+ cation. As shown in Fig. 7(b), after giving FSI- anion an oxidative environment, the FSI- anion bond length changes little, the N—S bond length increases slightly, and the S—F bond has nearly no change.
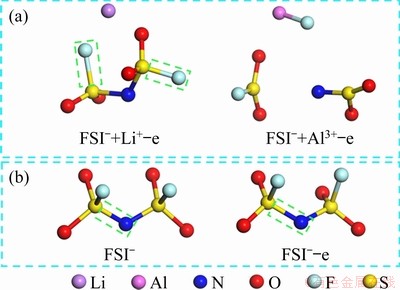
Fig. 7 Schematic diagrams of calculation results of FSI- anion being oxidized under different conditions, calculated by DFT
This indicates that the environment has an important influence on the oxidative decomposition of FSI- anions. Once LiBOB is added to the LiFSI-based electrolyte, B2O3 produced by the decomposition of LiBOB is deposited on the Al foil surface, thus forming a stable and protective interphase that inhibits electrochemical oxidation. As a result, the reaction that generates LiF dominates, and a relatively large amount of LiF instead of AlF3 appears in LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4 samples. In return, LiF reinforces the interphase further. The Al—O bond at 74.2 eV may originate from two oxidation products of Al. One is Al2O3 produced during the process of XPS testing [7,15] since the inner Al metal is exposed after the Al foil is corroded and oxidized after encountering oxygen in the air. The other is Al(FSI)3, one of the corrosion products produced during electrochemical testing. To summarize the XPS results, the surface film of the Al foil formed in the LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte mainly consists of B2O3 and LiF; both are products of the decomposition of lithium salts. The main components of the Al foil surface film formed in the LiFSI electrolyte system are AlF3 and Al(FSI)3, both of which are the corrosion products of Al foil. This situation is quite different from that of room temperature. YAMADA et al [15] thought that the main product of Al corrosion at room temperature is Al(FSI)3. This means that the corrosion process of Al at elevated temperature may differ from that at room temperature. As for the role AlF3 plays in passivating Al, it seems controversial and needs further study. ZHANG and DEVINE [41] demonstrated that AlF3 formed on the surface of Al foil can effectively inhibit the corrosion by isolating the foil from the electrolyte body. Nevertheless, MATSUMOTO et al [4] argued that the formation of AlF3 is the result of Al foil corrosion. Our experiment results also show that film enriched in AlF3 is not an effective passivation film because there is some Al. However, Al is stable because it can form AlF3 in LiPF6-based electrolyte. These contradictory results show that the formation of AlF3 on an Al surface is not a necessary condition for its stability in an electrolyte. This may be related to the firmness of binding between AlF3 and other decomposition products. If the combination of AlF3 and other decomposition products is strong enough, the film will play a protective role; otherwise, it will not passivate the Al foil. As shown in Fig. 5(b), despite the formation of large amounts of AlF3 on the surface of Al, the Al foil is still severely damaged. This is because Al(FSI)3 produced simultaneously with AlF3 dissolves in the electrolyte, resulting in the loss of adhesion between AlF3 and other decomposition products, and the appearance of defects or cracks on the interphase of Al foil. This kind of defect or crack worsens under the constant impact of electrochemical action and eventually leads to the corrosion of the Al foil.
Therefore, we conclude that the film-forming process on the Al surface when potential is applied at elevated temperatures occurs as follows: In LiFSI-based electrolyte, the lithium salt is mostly separated into Li+ cations and FSI- anions which remain separated in the electrolyte. Once potential is applied, a new surface of electric double layer (mainly composed of anions and solvent molecules) rapidly forms on the surface of Al foil. Afterward, the FSI- anion is oxidized on the Al and the F- anion is generated. Then, the F- anion easily connects with Al3+ cation instead of Li+ cation since the Li+ cation is far away from the F- anion. Meanwhile, many FSI- anions also compete to participate in the binding of Al3+ cation. Al(FSI)3 steadily dissolves into the electrolyte body so the Al foil is corroded. The corrosion mechanism is shown in Fig. 8(a). In LiFSI0.6-LiBOB0.4-based electrolyte, as shown in Fig. 8(b), a passivation layer enriched in B2O3 produced by the decomposition of BOB- anions forms on the surface of the Al foil; this layer is stable and insoluble in this electrolyte and thus inhibits the electrochemical oxidation of the Al foil. As a result, the reaction that generates LiF prevails over its competitor (the reaction to form AlF3) so a large amount of LiF forms. The LiF formation further enhances the stability of the passivation layer, and Al foil corrosion is effectively inhibited.
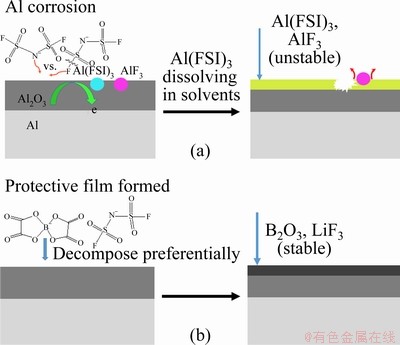
Fig. 8 Proposed corrosion mechanism of Al caused by LiFSI salt (a) and mechanism of LiBOB suppressing Al corrosion caused by LiFSI salt at elevated temperature by reinforcing interphase (b)
4 Conclusions
(1) Studies on the corrosion mechanism of Al in LiFSI-based electrolyte at elevated temperatures reveal that Al corrosion is aggravated with increasing temperature in LiFSI-based electrolyte owing to the formation of irregular, loose and unprotected AlF3 materials.
(2) Electrolyte properties can be retained at elevated temperatures by introducing LiBOB salt. The interphase interactions between the Al foil and electrolyte change and a robust and protective interphase forms. In this case, the decomposition products (B2O3) of LiBOB play a key role in reinforcing the Al interphase. The boron-containing compounds promote the change from AlF3 to LiF, which further reinforces interphase stability. A robust interphase can prevent Al from being corroded and hence support excellent Li/LiFePO4 cell performance at a high temperature.
(3) This work provides a reference for the design of a stable electrode/electrolyte interface by using LiFSI or LiBOB salts. In subsequent work, we will further study the influence and mechanisms of LiBOB salt in LiFSI-based electrolyte on the interface reactions between Al current conductors and electrolyte at elevated temperatures.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21766017, 51962019), the Major Science and Technology Projects of Gansu Province, China (No. 18ZD2FA012), the Chinese Academy of Sciences “Western Light” Young Scholars Project, and Lanzhou University of Technology Hongliu First-class Discipline Construction Program, China.
References
[1] KERNER M, PLYLAHAN N, SCHEERS J, JOHANSSON P. Thermal stability and decomposition of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) salts [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(28): 23327–23334.
[2] BERHAUT C L, DEDRYVERE R, TIMPERMAN L, SCHMIDT G, LEMORDANT D, ANOUTI M. A new solvent mixture for use of LiTDI as electrolyte salt in Li-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 305: 534–546.
[3] AHMED F, MAHBUBUR R M, SUTRADHAR S C, LOPA N S, RYU T, YOON S, CHOI I, LEE Y, KIM W. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of an imidazolium based Li salt as electrolyte with Li fluorinated sulfonylimides as additives for Li-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 302: 161-168.
[4] MATSUMOTO K, INOUE K, NAKAHARA K, YUGE R, NOGUCHI T, UTSUGI K. Suppression of aluminum corrosion by using high concentration LiTFSI electrolyte [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 231: 234-238.
[5] ZHAO Dong-ni, WANG Jie, WANG Peng, LIU Hai-ning, LI Shi-you. Regulating the composition distribution of layered SEI film on Li-ion battery anode by LiDFBOP [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 337: 135745.
[6] HAN Hong-bo, GUO Jun, ZHANG Dai-jun, FENG Shao-wei, FENG Wen-fang, NIE Jin, ZHOU Zhi-bin. Lithium (fluorosulfonyl) (nonafluorobutanesulfonyl) imide (LiFNFSI) as conducting salt to improve the high- temperature resilience of lithium-ion cells [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2011, 13(3): 265-268.
[7] MA Tian-yuan, XU Gui-Liang, LI Yan, WANG Li, HE Xiang-ming, ZHENG Jian-ming, LIU Jun, ENGELHARD M H, ZAPOL P, CURTISS L, JORNE J, AMINE K, CHEN Zong-hai. Revisiting the corrosion of the aluminum current collector in lithium-ion batteries [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2017, 8(5): 1072-1077.
[8] MAUGER A, JULIEN C M, PAOLELLA A, ARMAND M, ZAGHIB K. A comprehensive review of lithium salts and beyond for rechargeable batteries: Progress and perspectives [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2018, 134: 1–21.
[9] PETER L, ARAI J. Anodic dissolution of aluminium in organic electrolytes containing perfluoroalkylsulfonyl imides [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29(9): 1053–1061.
[10] LI Fa-qiang, SHANGGUAN Xue-hui, JIA Guo-feng, WANG Qing-lei, GONG Yan, BAI Bin, FAN Wei. Dual-salts of LiTFSI and LiODFB for high voltage cathode LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2016, 20(12): 3491-3498.
[11] LIU Ai-min, GUO Meng-xia, LU Zi-yang, ZHANG Bao-guo, LIU Feng-guo, TAO Wen-ju, YANG You-jian, HU Xian-wei, WANG Zhao-wen, LIU Yu-bao, SHI Zhong-ning. Electrochemical behavior of tantalum in ethylene carbonate and aluminum chloride solvate ionic liquid [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(8): 2283-2292.
[12] WANG Zheng-qi, HOFMANN A, HANEMANN T. Low-flammable electrolytes with fluoroethylene carbonate based solvent mixtures and lithium bis(trifluoro- methanesulfonyl)imide for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 298: 960-972.
[13] DAHBI M, GHAMOUSS F, FRANCOIS T V, LEMORDANT D, ANOUTI M. Comparative study of EC/DMC LiTFSI and LiPF6 electrolytes for electrochemical storage [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(22): 9743-9750.
[14] NEUHAUS J, HARBOU E V, HASSE H. Physico-chemical properties of solutions of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) in dimethyl carbonate, ethylene carbonate, and propylene carbonate [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 394: 148–159.
[15] YAMADA Y, CHIANG C H, SODEYAMA K, WANG J, TATEYAMA Y, YAMADA A. Corrosion prevention mechanism of aluminium metal in superconcentrated electrolytes [J]. ChemElectroChem, 2015, 2: 1687-1694.
[16] SCHWEIKERT N, HOFMANN A, SCHULZ M, SCHEUERMANN M, BOLES S T, HANEMANN T, HAHN H, INDRIS S. Suppressed lithium dendrite growth in lithium batteries using ionic liquid electrolytes: Investigation by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and in situ Li nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 228: 237-243.
[17] SHKROB I A, MARIN T W, ZHU Y, ABRAHAM D P. Why bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide is a “Magic Anion” for electrochemistry? [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(34): 19661-19671.
[18] ABOUIMRANE A, DING J, DAVIDSON I J. Liquid electrolyte based on lithium bis-fluorosulfonyl-imide salt: Aluminum corrosion studies and lithium ion battery investigations [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189: 693-696.
[19] SHANGGUAN Xue-hui, JIA Guo-feng, LI Fa-qiang, WANG Qing-lei, BAI Bin. Mixed salts of LiFSI and LiODFB for stable LiCoO2-based batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society A, 2016, 163(13): 2797-2802.
[20] YAN Guo-chun, LI Xin-hai, WANG Zhi-xing, GUO Hua-jun, PENG Wen-jie, HU Qi-yang. Lithium difluoro(oxalato)- borate as an additive to suppress the aluminum corrosion in lithium bis(fluorosulfony)imide-based nonaqueous carbonate electrolyte [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2016, 20(2): 507-516.
[21] XU Kang, ZHANG Sheng-shui, JOW T R, XU Wu, ANGELL C A. LiBOB as salt for lithium-ion batteries: A possible solution for high temperature operation [J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters A, 2002, 5(1): 26-29.
[22] MYUNG S T, NATSUI H, SUN Y K, YASHIRO H. Electrochemical behaviour of Al in a non-aqueous alkyl carbonate solution containing LiBOB salt [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(24): 8297-8301.
[23] FRISCH M, TRUCKS G, SCHLEGEL H, SCUSERIA G, ROBB M, CHEESEMAN J, SCALMANI G, BARONE V, MENNUCCI B, PETERSSON G, NAKATSUJI H, CARICATO M, LI X, HRATCHIAN HIZMAYLOV A, BLOINO J, ZHENG G, SONNENBERG J, HADA M, EHARA M, TOYOTA K, FUKUDA R, HASEGAWA J, ISHIDA MNAKAJIMA T, HONDA Y, KITAO O, NAKAI H, VREVEN T, MONTGOMERY J, PERALTA JOGLIARO F, BEARPARK M, HEYD JBROTHERS E, KUDIN K, STAROVEROV V, KOBAYASHI RNORMAND J, RAGHAVACHARI K, RENDELL ABURANT J, IYENGAR S, TOMASI J, COSSI MREGA N, MILLAM J, KLENE M, KNOX JCROSS J, BAKKEN V, ADAMO C, JARAMILLO JGOMPERTS R, STRATMANN R, YAZYEV OAUSTIN A, CAMMI R, POMELLI C, OCHTERSKI J, MARTIN R, MOROKUMA K, ZAKRZEWSKI V, VOTH G, SALVADOR PDANNENBERG J, DAPPRICH S, DANIELS AFARKAS O, FORESMAN J, ORTIZ J, CIOSLOWSKI J, FOX DMONTGOMERY Jr. J, GAUSSIAN I. Gaussian 09 [M]. Amsterdam: Wallingford C T, 2016: 226-310.
[24] LIU Ya-dong, LIU Qi, LI Zhe-fei, REN Yang, XIE Jian, HE Hao, XU Fan. Failure study of commercial LiFePO4 cells in over-discharge conditions using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society A, 2014, 161(4): 620-632.
[25] ZHENG Jian-ming, KAN Wang-Hay, MANTHIRAM A. Role of Mn content on the electrochemical properties of nickel-rich layered LiNi(0.8-x)Co(0.1)Mn(0.1+x)O2 (0.0≤x≤0.08) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(12): 6926-6934.
[26] WU Bing, YANG Xiu-kang, JIANG Xia, ZHANG Yi, SHU Hong-bo, GAO Ping, LIU Li, WANG Xian-you. Synchronous tailoring surface structure and chemical composition of Li-rich-layered oxide for high-energy lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(37): 1803392.
[27] AN Seong-jin, LI Jian-lin, DANIEL C, MOHANTY D, NAGPURE S, WOOD D L. The state of understanding of the lithium-ion-battery graphite solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and its relationship to formation cycling [J]. Carbon, 2016, 105: 52-76.
[28] POHL B, HILLER M M, SEIDEL S M, GRüNEBAUM M, WIEMHOFER H D. Nitrile functionalized disiloxanes with dissolved LiTFSI as lithium ion electrolytes with high thermal and electrochemical stability [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 274: 629-635.
[29] WANG Xian-ming, YASUKAWA E, MORI S. Inhibition of anodic corrosion of aluminum cathode current collector on recharging in lithium imide electrolytes [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(17): 2677-2684.
[30] MYUNG S T, NATSUI H, SUN Y K, YASHIRO H. Electrochemical behavior of Al in a non-aqueous alkyl carbonate solution containing LiBOB salt [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(24): 8297-8301.
[31] SAYED F N, RODRIGUES M F, KALAGA K, GULLAPALLI H, AJAYAN P M. Curious case of positive current collectors: Corrosion and passivation at high temperature [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(50): 43623-43631.
[32] ZENG Xiao-qiao, XU Gui-Liang, LI Yan, LUO Xiang-yi, MAGLIA F, BAUER C, LUX S F, PASCHOS O, KIM S J, LAMP P, LU Jun, AMINE K, CHEN Zong-hai. Kinetic study of parasitic reactions in lithium-ion batteries: A case study on LiNi(0.6)Mn(0.2)Co(0.2)O2 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(5): 3446-3451.
[33] MARKOVSKY B, AMALRAJ F, GOTTLIEB H E, GOFER Y, MARTHA S K, AURBACH D. On the electrochemical behavior of aluminum electrodes in nonaqueous electrolyte solutions of lithium salts [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society A, 2010, 157(4): 423-429.
[34] LI Fa-qiang, GONG Yan, JIA Guo-feng, WANG Qing-lei, PENG Zheng-jun, FAN Wei, BAI Bing. A novel dual-salts of LiTFSI and LiODFB in LiFePO4-based batteries for suppressing aluminum corrosion and improving cycling stability [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 295: 47-54.
[35] ZHANG Xue-yuan, DEVINE T M. Passivation of aluminum in lithium-ion battery electrolytes with LiBOB [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society B, 2006, 153(9): 365-369.
[36] SUO Liu-min, XUE Wei-jiang, GOBET M, GREENBAUM S G, WANG Chao, CHEN Yu-ming, YANG Wan-lu, LI Yang-xing, LI Ju. Fluorine-donating electrolytes enable highly reversible 5-V-class Li metal batteries [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(6): 1156-1161.
[37] MARKEVICH E, SALITRA G, AURBACH D. Fluoroethylene carbonate as an important component for the formation of an effective solid electrolyte interphase on anodes and cathodes for advanced Li-ion batteries [J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(6): 1337-1345.
[38] ZHU Yun-min, LUO Xue-yi, XU Meng-qing, ZHANG Li-ping, LE Yu, FAN Wei-zhen, LI Wei-shan. Failure mechanism of layered lithium-rich oxide/graphite cell and its solution by using electrolyte additive [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 317: 65-73.
[39] PHILIPPE B, DEDRYVERE R, GORGOI M, RENSMO H, GONBEAU D, EDSTROM K. Improved performances of nanosilicon electrodes using the salt LiFSI: A photoelectron spectroscopy study [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(26): 9829-9842.
[40] XIE Jin, SENDEK A D, CUBUK E D, ZHANG Xiao-kun, LU Zhi-yi, GONG Yong-ji, WU Tong, SHI Fei-fei, LIU Wei, REED E J, CUI Yi. Atomic layer deposition of stable LiAlF4 lithium ion conductive interfacial layer for stable cathode cycling [J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(7): 7019-7027.
[41] ZHANG Xue-yuan, DEVINE T M. Identity of passive film formed on aluminum in Li-ion battery electrolytes with LiPF6 [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society B, 2006, 153(9): 344-351.
李春雷1,曾双威1,王 鹏1,李昭娟1,杨 莉1,赵东妮1,王 洁1,刘海宁2,李世友1
1. 兰州理工大学 石油化工学院,兰州 730050;
2. 中国科学院 青海盐湖所 盐湖资源综合高效利用重点实验室,西宁 810008
摘 要:双氟磺酰亚胺锂(LiFSI)因其优异的性能有望取代六氟磷酸锂。利用LiFSI解决铝(Al)集流体在高温下的腐蚀问题至关重要。结合密度泛函理论计算和光谱学研究45 °C下LiFSI电解液中铝的腐蚀机理。研究发现,随着温度的升高,由Al(FSI)3溶解形成的不规则的、疏松的、对铝箔不具保护作用的AlF3加剧高温下铝的腐蚀。双草酸硼酸锂(LiBOB)对铝的腐蚀有较好的抑制作用。LiBOB 的加入改变铝箔和电解液之间的界面反应,使铝箔表面形成一层坚固、具有保护作用的固体界面膜,含硼化合物促进AlF3向LiF的变化,从而进一步加强固体界面膜的牢固性。本研究为LiFSI在锂离子电池中的应用提供合理设计铝箔界面的途径。
关键词:锂离子电池;LiFSI基电解液;双草酸硼酸锂(LiBOB);腐蚀抑制;高温;界面膜
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Shi-you LI, E-mail: lishiyou@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65588-7
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

