
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.01.029
基于EMD降噪的燃烧器火焰静电信号能量熵分析
李珊1,闫勇2,吴佳丽1,钱相臣1
(1. 华北电力大学 控制与计算机工程学院,北京,102206;
2. 肯特大学 工程与数字艺术学院,坎特伯雷,肯特CT2 7NT,英国)
摘要:采用灵敏度高、结构简单、环境适应性强的非侵入式静电传感器阵列测量甲烷及生物质火焰的能量变化特性。基于经验模态分解的降噪方法对测量信号进行去噪处理,以获得信号的能量熵用于表征火焰中带电颗粒运动复杂度。实验中对甲烷-空气预混和扩散火焰以及甲烷助燃生物质火焰进行测量。研究结果表明:甲烷扩散火焰带电颗粒运动复杂度随燃料流量的增大而增大,相同甲烷流量下,空气流量越大预混火焰颗粒运动复杂度越高,生物质火焰中带电颗粒运动复杂度比气态甲烷火焰的高,火焰中部带电颗粒运动复杂度最高。
关键词:可再生低碳燃料;火焰检测;静电传感器阵列;经验模态分解;能量熵
中图分类号:TP212 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)01-0285-09
Energy entropy analysis of flame signals obtained by an electrostatic sensor array based on EMD denoising method
LI Shan1, YAN Yong2, WU Jiali1, QIAN Xiangchen1
(1. School of Control and Computer Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China;
2. School of Engineering and Digital Arts, University of Kent, Kent CT2 7NT, U.K.)
Abstract: A non-invasive electrostatic sensor array with high sensitivity, simple structure and good environmental adaptability was used to measure the energy characteristics of burner flames in different combustion tests. A denoising method based on empirical mode decomposition(EMD) was adopted to denoise the original sensor signals before calculating the EMD energy entropy of the flame, which was used to evaluate the motion complexity of charged particles in a flame. Experimental tests were conducted under various flame conditions, such as methane-air diffusion flames, methane-air premixed flames and methane-assisted biomass flames. The results show that the motion complexity of charged particles in diffusion and premixed flames increases with the flow rate of methane. The motion complexity of charged particles in biomass flames is higher than that of methane flames. The motion complexity of charged particles in the middle region of a flame is the highest.
Key words: renewable low carbon fuel; flame monitoring; electrostatic sensor arrays; empirical mode decomposition; energy entropy
能源的低碳化和可再生化是全球能源结构转型的发展趋势。由于沼气、生物质等资源在碳排放和可再生性方面的优势以及相关技术突破和升级,它们替代高污染的煤炭等传统化石能源已经成为不可逆转的趋势[1]。甲烷是沼气的主要成分和生物质裂解的重要产物,相对于煤炭和石油,直接燃烧甲烷可以大大降低烟气和焦油等杂质的排放。然而,清洁能源的高效燃烧利用在技术和应用层面仍存在诸多问题亟待解决,需要研究甲烷及生物质的燃烧过程,以优化燃烧系统设计,达到提高燃料燃烧效率和降低污染物排放的目的。火焰是燃烧过程最直观的表现形式,针对火焰的不同特性可以使用相应类型的火焰检测方法来进行测量。目前,工业上广泛使用的红外、紫外和可见光检测装置利用了火焰的辐射特性[2-3],主要用于检测火焰的有无,而且容易被恶劣的使用环境污染,所以无法长期、实时监测火焰参数的动态变化。图像火检技术通过高速相机等成像设备实时采集火焰图像并通过图像处理得到特征参数反映燃烧状况[4-5]。这类方法实时性强准确度高,但是运行维护成本高和可视范围小等缺点仍阻碍了该方法的大规模应用。此外,利用光谱仪进行火焰的燃烧状态检测主要在实验室规模下进行[6],并不适用于工业条件下的长期在线监测。燃烧过程包含一系列复杂的化学反应,期间会产生大量带电粒子,包括阴阳离子、自由电子以及碳烟颗粒,因此火焰具有微弱的带电特性[7]。非侵入式静电传感技术通过对火焰的电学特性进行分析从而对火焰燃烧状态进行检测,具有灵敏度高、环境适应性强、成本低等优势[8-9]。而获取的火焰静电信号通常较为微弱,其时域频域包含大量有用信息,但容易受到环境背景噪声的干扰。经验模态分解(empirical mode decomposition,EMD)法是HUANG等[10]于1998年提出的一种自适应的信号分析方法。该方法能根据信号自身时间尺度特征(不需要任何先决条件)自适应的将复杂信号分解为有限个频率由高到低顺序排列的本征模函数(intrinsic mode function,IMF)和残余分量,各IMF分量包含了原信号在不同时间尺度的局部特征信号[10]。EMD避免了小波变换等方法中基函数选择的问题,常被应用于非平稳随机信号的分析,具有很高的信噪比[10]。火焰中静电信号为类随机信号,其具体特征目前还在探索阶段,额外引入基函数可能对信号本身造成干扰,因此,EMD分解是一种较好的适用于静电信号的去噪方法。信息熵是信息论中用于描述信息不确定度的重要概念,近年来被广泛应用于机械轴承、电力电缆的故障诊断等领域[11]。将静电信号作为信息载体同时结合EMD分解与信息熵得到火焰静电信号的能量熵,实现对火焰静电信号频率和能量分布的深入了解。火焰的特征提取是研究火焰燃烧状态和稳定性的基础,本文作者利用非侵入式静电传感器阵列实现对甲烷及生物质火焰静电信号的检测,然后结合经验模态分解和信息熵理论提取火焰静电信号的能量熵等特征参数,分析火焰静电信号能量熵与燃料燃烧状态间的联系,提供了一种适用于沼气和生物质燃烧状态分析、特征提取和稳定性检测的新方法。
1 静电法火焰检测原理
1.1 火焰的带电特性
燃料燃烧过程中与离子相关的反应包括火焰的热电离、化学电离以及电离之后的离子交换和离子重组。在化学电离中,基本放热化学反应的能量使产物之一处于电离状态,一旦通过化学电离产生1个离子,更多离子的产生可以通过电荷交换实现[12-13],比如烃类火焰由化学电离产生初始离子CHO+:
 (1)
(1)
火焰中常见的H3O+则可以通过由化学电离产生的初始离子由下列过程生成:
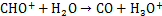 (2)
(2)
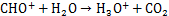 (3)
(3)
进而在含有过量烃基的富火焰中,烃类离子的形成很容易通过诸如此类的反应进行:
 (4)
(4)
由于燃料的不完全燃烧,火焰中存在着大量的碳烟颗粒。SUGDEN等[14]首次展示了碳烟颗粒荷电的实验结果,随后被证明火焰中每个颗粒最多荷有1~2个电子的电量[15]。较早的研究指出火焰中荷正负电的碳烟颗粒各占其总数的30%左右,并且随着火焰高度的变化,碳烟颗粒的荷电情况也有所改变[16]。但是,王宇等[17]则通过正负电场不对称实验证明火焰中有大于50%的碳烟颗粒荷正电,进一步明确了火焰的带电特性。
1.2 火焰静电信号测量
目前,静电检测技术已被成熟应用于气固两相流参数检测领域,实现气力输送管道中固体颗粒的速度、浓度、质量流量等参数的测量[8, 18-19]。类似的,火焰中存在复杂的气、固和等离子多相运动,燃料燃烧及颗粒碰撞摩擦产生的静电电荷能够反映火焰中颗粒的流动特性。由于火焰的波动带电颗粒接触到裸露静电电极后在电极表面产生传导电荷,从而产生静电信号,因此可以在火焰周围布置静电传感装置进行燃料燃烧状态检测。
由于火焰中静电信号通常较为微弱,并且原始静电信号中包含了其工作环境中的背景噪声,为提高特征提取的准确性需要通过信号处理电路对原始信号进行电流/电压转换、电压放大和基础滤波,随后通过程序对传输至计算机的电压信号进行降噪和特征提取。火焰中带电颗粒浓度、运动状态的变化都会导致静电信号的变化,因此可以对获取的静电信号进行分析进一步了解燃料的燃烧状态。
火焰中带电颗粒的浓度可以通过静电传感器电极所获静电信号的强度体现。均方根(root mean square,RMS)是指一组数据的有效值,常用于表征采样系统信号的平均水平。气固两相流测量领域使用静电信号的RMS表征管道内固体颗粒相对体积浓度的高低[18-19],本文同样利用静电信号的RMS评估静电电极对应区域火焰中带电颗粒的相对体积浓度[20],静电信号的RMS计算公式如下:
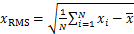 (5)
(5)
式中:N为采样点数;xi为第i个采样点值;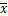 为采样信号的均值。
为采样信号的均值。
2 基于EMD分解的静电信号能量熵
2.1 基于EMD分解的静电信号去噪方法
火焰静电信号x(t)的EMD分解流程如图1所示,其中SD为h(t)的标准偏差,计算公式为
 (6)
(6)
SDT为筛分门限值,一般取值0.2~0.3[10]。原始信号x(t)与所有符合条件的h(t)之和相减即为余项r(t)。

图1 EMD分解流程图
Fig. 1 Flowchart of EMD decomposition
火焰静电信号经过EMD分解后得到的IMF分量,随着分解阶数的增加,其频率逐渐减小。而静电信号包含的噪声通常集中在相对高频的区域,因此可以将高频IMF去除后将剩余分量进行重构达到去噪目的,但这样有可能丢失高频信号中的有用信号。为避免直接剔除高频分量造成的信息损失,本文将对IMF进行如下处理[21]:
1) 对静电信号所有的IMF分量进行自相关计算,由于随机噪声具有较弱的时间相关性,因此其自相关函数曲线通常接近冲击函数,即在零点处取得最大值后,在零点两旁迅速衰减至0。具有此类特征的IMF分量,即为噪声主导的IMF分量;
2) 采用固定阈值规则和软阈值函数对噪声主导的IMF分量进行小波降噪处理;
3) 将经过小波阈值降噪处理的IMF分量和信号主导的IMF分量与余项r(t)进行信号重构,从而得到去噪后的信号。
这种方法克服了传统的降噪算法无法确定噪声成分所处频段的缺陷。为验证本方法的降噪效果,使用降噪后甲烷体积流量为0.8 L/min扩散燃烧火焰静电信号模拟纯火焰静电信号,加入信噪比为8 dB的高斯白噪声,随后使用上述方法进行降噪,处理后信号的信噪比为16.986 dB,得到了明显提升。
2.2 火焰静电信号的信息熵和能量熵
SHANNON[22]于1948年提出信息熵的概念,用于量化随机变量的不确定程度,作为系统有序化程度的度量,可以理解为某种特定信息的出现概率。假设某系统X可能处于n种不同的状态x1,x2,…,xn,P(xi)代表状态xi(i=1,2,…,n)出现的概率,则该系统的信息熵H(X)定义为

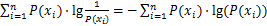 (7)
(7)
由于信息熵的非负性和可加性,0≤P(xi)≤1且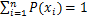 ,当P(xi)=0时规定0lg0=0。
,当P(xi)=0时规定0lg0=0。
根据EMD分解,可以提取出信号各个频段的成分,假设一个火焰的静电信号可以被分解为n个IMF分量,则可以计算出各分量的能量E1,E2,…,En:
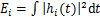 (8)
(8)
由于EMD分解具有正交性,因此这n个IMF分量的能量之和E0与原静电信号总能量相等:
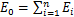 (9)
(9)
根据信息熵理论,EMD分解的能量熵表示为
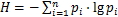 (10)
(10)
其中:pi表示第i个IMF分量的能量占全部能量的比例,即pi=Ei/E0。
EMD分解中能量熵表征的是信号能量与频率的变化关系,能够反映频率分布和能量分布的等细节信息[11]。根据能量熵的极值性和最大熵定理,当各个频段能量分布出现的概率相等时,能量熵最大。因此,能量熵越小,代表静电信号的能量集中在个别的IMF分量当中,火焰中带电颗粒波动频率单一,燃烧较为稳定。反之,则意味着静电信号能量分散在各IMF分量中,带电颗粒波动频率范围宽,颗粒运动复杂燃烧稳定性差。实验中对重构后的火焰静电信号进行EMD分解并计算各IMF分量的能量,从而得到各电极信号的能量熵。
3 实验结果分析
3.1 实验装置与实验条件
本研究使用非侵入式静电传感技术通过测量甲烷及生物质火焰燃烧时的电荷波动实现燃料燃烧过程的特征提取。图2所示为火焰检测系统示意图,该系统主要包括燃烧器、非侵入式静电传感器阵列、信号调理电路和信号接收及处理单元。实验时,配气系统按设定流量向燃烧器提供甲烷和空气,生物质则通过给料机以一定的质量流量送至管道后由给料空气吹至燃烧器。实验所使用的静电传感器参数如图3所示,该传感器包含10个静电电极,其高度和宽度能够覆盖实验中燃料火焰,测量火焰各个区域带电颗粒的动态特性,每个电极配有相同参数的独立信号处理电路[8-9]。信号调理电路包含电流-电压转换和信号放大及滤波预处理的功能。传感器通过底部支撑柱固定于圆盘状支撑架的卡槽内,通过移动支撑柱在卡槽中的位置调整传感器与火焰间的距离。采集到的静电信号由数据采集卡(DAQ)接收后传至计算机进行处理,提取火焰静电信号的特征参数。

图2 火焰检测系统示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of flame monitoring system

图3 静电传感器结构及几何参数
Fig. 3 Structure and dimensions of electrostatic sensor
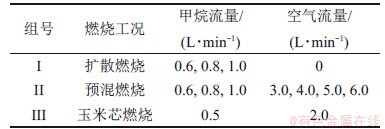
表1所示为非侵入式静电传感器阵列测量不同燃料火焰实验工况设置,I组为甲烷扩散燃烧工况,共进行3组实验。II组为甲烷与空气预混燃烧工况,在3种甲烷体积流量下按照表1所示分别改变空气流量,共进行12组实验。III组为生物质预混燃烧实验,燃料选择粒径范围为210~230 μm的玉米芯颗粒,除表1所示的助燃空气外,给料空气流量为6 L/min。实验时综合考虑信号的幅值,将静电传感器阵列距离燃烧器中心水平距离固定为25 mm,静电信号采样频率为250 Hz,每组实验采样时间均大于20 s。
表1 甲烷及生物质燃烧条件
Table 1 Test Matrix of methane and biomass combustion
3.2 火焰静电信号的EMD去噪
本研究采用基于EMD的降噪方法对纯甲烷扩散燃烧、甲烷与空气预混燃烧和甲烷助燃的生物质燃烧火焰典型工况下的静电信号进行去噪处理。对甲烷空气体积流量比为1.0:3.0(燃空当量比为3.18)的预混火焰静电信号进行EMD分解,共获得7个IMF分量及余项,图4(a)所示为分量IMF1~IMF4,图4(b)所示为这4个分量自相关运算结果,IMF5~IMF7直接参与重构故不再列出。根据前文所述原则IMF1和IMF2为噪声主导的分量,其余分量不具备零点衰减特性,可见噪声主要分布在信号的高频段,为最大程度保留有用信号,对此部分分量进行小波阈值处理后,与剩余的IMF分量一同进行重构完成降噪,结果如图5(b)所示。由图5可以看出:甲烷扩散火焰静电信号幅值比预混火焰和生物质火焰信号幅值小。此外,由于给料机给料不均匀,玉米芯燃烧颗粒成簇的喷出燃烧口,并且火焰中时常喷溅出火星,导致传导电荷在某个瞬间突然增大,因此,甲烷助燃的玉米芯火焰静电信号具有规律的类尖峰信号。

图4 静电信号IMF分量及自相关函数
Fig. 4 IMF components and autocorrelation function of senior signals

图5 不同工况下火焰静电信号去噪前后对比
Fig. 5 Comparison of denoising effect of flame signals under different combustion conditions
3.3 火焰静电信号能量分析
由于实验中火焰高度最多到达第10个电极,因此将10个电极计算各自能量熵后取平均值作为各工况下整体燃料燃烧静电信号能量熵,实验结果如图6所示,其中橙色圆圈标注的为甲烷在不同体积流量下扩散燃烧的结果,其余为甲烷体积流量分别为0.6,0.8和1.0 L/min时改变空气量从而形成的预混火焰的计算结果。此外,甲烷助燃的玉米芯火焰静电信号能量熵为1.518。由图6可以看出:纯甲烷扩散火焰静电信号的能量熵普遍低于相同甲烷流量下预混火焰静电信号的能量熵,并且在甲烷流量相同的情况下,随着空气量增大,相应静电信号的能量熵呈增大趋势。与气态燃料相比,玉米芯火焰静电信号的能量熵明显较大。

图6 甲烷在不同流量条件下火焰静电信号能量熵分布
Fig. 6 Energy entropy distribution of the sensor signals under different methane flow rate conditions
根据能量熵的性质,熵值越小能量分布越集中,反之则能量分布较为分散。如图7所示,对比火焰中部同一电极在3种典型燃烧工况下静电信号各IMF分量间的能量分布,扩散火焰能量集中在较低频段的IMF分量中,与其能量熵最小的结论相符。预混火焰和生物质火焰的能量则分散分布在高频IMF分量中,生物质火焰能量分布更为分散,各IMF能量占比均在0.5以下,对应相对较大的能量熵。结合3种燃烧工况下火焰静电信号IMF能量分布图和能量熵计算结果,由于颗粒微观运动复杂度和颗粒运动的能量间存在相关关系[23],因此静电信号能量熵能够反映静电传感器电极敏感区域内颗粒运动的复杂程度,熵值越大带电颗粒运动复杂度越高。
图8所示为各工况下火焰静电信号RMS分布。扩散燃烧没有额外助燃空气参与,随着甲烷在环境中的扩散,逐渐与氧气混合,由于燃料的不完全燃烧而产生的碳烟颗粒致使火焰带有微弱电量。扩散燃烧过程缓慢,火焰较为无力容易发生几何波动[5],带电颗粒随火焰的波动而运动,从而造成静电信号能量在IMF低频段的集中。扩散燃烧下带电颗粒的低浓度和气流的缓慢波动造成较小的静电信号能量熵,带电颗粒运动相对简单规律,燃烧稳定。预混燃烧条件下,由于甲烷和空气充分混合后再点燃,其火焰面(燃烧产物与预混气体的分界面)附近的燃烧化学反应复杂而剧烈。同时伴随着光能和热能等能量的释放,产生大量的阴阳离子、自由电子以及部分燃料的不完全燃烧产生的碳烟颗粒,因此带电颗粒浓度大于扩散火焰。这个过程中火焰中间自由基间的能量转换和反应物能量释放速率的转变是造成能量集中在IMF高频段的主要原因。此外,由于预混火焰中的带电颗粒浓度较大,而且甲烷气体和空气流速之间的差异引起火焰面附近强烈的热量和质量交换,所以带电颗粒在较为复杂的气流条件下发生摩擦碰撞的概率增大使得带电颗粒运动复杂度增大,这就降低了燃烧的稳定性,严重时过大的空气流量会引发火焰剧烈抖动甚至脱火。

图7 甲烷扩散燃烧、预混燃烧及生物质颗粒燃烧火焰静电信号IMF能量分布
Fig. 7 IMF energy distribution of sensor signals of methane and methane-biomass co-firing flames
甲烷助燃的生物质火焰中同时存在固体和气体燃料,颗粒在高温气体的裹挟下进行挥发分和固定碳的逐级燃烧。由于生物质固体颗粒形状不规则,燃烧过程中颗粒间较为分散,难以完全氧化,并且固定碳完全燃烧需要较长的燃烧时间和较高的反应温度,因此生物质火焰中长时间存在未完全燃烧的固体碳颗粒。除燃烧产生的带电颗粒外,生物质颗粒和未完全燃烧的碳颗粒随气流发生不规则运动,从而发生碰撞摩擦而荷电[16],造成较大的带电颗粒浓度。期间火焰中进行的气体间以及气固间热质交换造成能量在IMF高频段的集中分布。此外,生物质燃烧过程中给料空气与燃料间流速差异更大气流条件更为复杂,造成相对较大的能量熵值,整体火焰中的带电颗粒反映出更大的运动复杂程度,对应较为复杂且不稳定的燃烧状况。

图8 甲烷扩散燃烧、预混燃烧及生物质颗粒燃烧火焰静电信号RMS分布
Fig. 8 RMS distribution of sensor signals of methane and methane-biomass co-firing flames
图9所示为3种典型燃烧工况下不同电极的能量熵,电极自下向上进行编号分别对应火焰自根部至顶部的燃烧区域。甲烷扩散火焰和预混火焰能量熵呈现根部、顶部小,中上部大的分布,预混火焰分布得更为规律。这是因为气态火焰不同区域呈现不同的燃烧状态[16],火焰自底部逐渐与空气混合后在火焰中部进行剧烈、复杂的化学反应导致这一区域气流紊乱。大量的阴阳离子和碳烟颗粒在气流的影响下剧烈运动,因而火焰中部带电颗粒的运动复杂度较大,相比较下,火焰根部燃烧则更加稳定。扩散火焰整体气流平稳,带电颗粒容易聚集在化学反应剧烈的火焰中部,缺少空气气流的影响而向两边扩散较慢。中部较大的带电颗粒浓度使得颗粒间碰撞摩擦概率增大,火焰根部虽有电荷聚集但较难发生明显波动呈稳定燃烧状态,因此,扩散火焰中部能量熵明显大于火焰根部和顶部能量熵。

图9 甲烷扩散燃烧、预混燃烧及生物质颗粒燃烧火焰不同区域静电信号能量熵分布
Fig. 9 Energy entropy distribution in different regions of methane and methane-biomass co-firing flames
预混火焰中部火焰面附近燃烧剧烈,火焰面外侧燃烧产物聚集,使得带电颗粒在火焰中上部浓度较大,带电颗粒在空气气流和重力的共同影响下造成火焰中部较大的能量熵和复杂的燃烧状况。由于复杂的气固运动和气流影响,生物质火焰静电信号能量熵在整个火焰高度范围内差别不大。生物质燃烧火焰根部未燃烧颗粒在给料空气的气流中剧烈运动,碰撞摩擦而带电使得静电信号能量熵增大,火焰中部与气态火焰相似同样为剧烈燃烧区,燃烧产生的大量带电颗粒与生物质颗粒一同在复杂的气流下剧烈运动。由于空气流速较大,火焰根部和中部的部分带电粒子运动到火焰顶部,火焰顶部发生剧烈抖动。此外,生物质火焰尖端还会有未完全燃烧的碳颗粒造成的火星飞溅与静电电极进行接触,因此,生物质燃烧火焰内带电粒子整体都呈现较大的运动复杂度,各部位能量熵差别不大,燃烧稳定性较差。
4 结论
1) 分析了非侵入式静电传感器阵列测得的纯甲烷扩散火焰、甲烷空气预混火焰和甲烷助燃的生物质火焰静电信号,并针对火焰静电信号的类随机特征采用基于EMD分解的降噪方法进行降噪处理去除了高频随机噪声,达到了良好的去噪效果。
2) 扩散火焰静电信号的平均能量熵随燃料流量的增大而增大,且相同甲烷流量下空气流量越大预混火焰能量熵越高,甲烷助燃的生物质火焰能量熵较甲烷气态燃烧火焰大。扩散火焰和预混火焰静电信号能量熵均呈现火焰中部大,根部和顶部小的趋势,生物质火焰各部位能量熵差别较小。
3) 火焰静电信号能量熵越大带电颗粒运动复杂度越高,燃料燃烧的稳定性越差。从能量熵出发联系火焰带电颗粒运动情况与燃烧状态,为火焰燃烧状态分析、特征提取和稳定性检测提供一种新途径,为可再生低碳排放燃料的高效利用提供新思路。
参考文献:
[1] 吕建燚, 石晓斌. 生物质燃烧碳烟的物化特性及生成机理研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(10): 1184-1190.
LU Jianyi, SHI Xiaobin. Physicochemical properties and formation mechanism of soot during biomass burning[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2013, 41(10): 1184-1190.
[2] 石发强. 基于紫红外线检测原理的火焰传感器的设计[J]. 煤炭与化工, 2015, 38(9): 101-104, 107.
SHI Faqiang. Design of flame sensor based on the detection principle of UV and IR[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry, 2015, 38(9): 101-104, 107.
[3] 曹向宇, 夏智勋, 黄利亚. 基于辐射成像的固体燃料燃烧温度测量技术综述[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2018, 41(5): 650-657.
CAO Xiangyu, XIA Zhixun, HUANG Liya. Review of solid fuel combustion temperature measurements based on radiation imaging[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2018, 41(5): 650-657.
[4] SUN Duo, LU Gang, ZHOU Hao, et al. Condition monitoring of combustion processes through flame imaging and kernel principal component analysis[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2013, 185(9): 1400-1413.
[5] LU G, YAN Y, COLECHIN M, et al. Monitoring of oscillatory characteristics of pulverized coal flames through image processing and spectral analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2006, 55(1): 226-231.
[6] 李新利, 李一娇, 卢钢, 等. 基于火焰光谱和特征工程的生物质燃料识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(15): 4474-4481.
LI Xinli, LI Yijiao, LU Gang, et al. Biomass fuel identification based on flame spectroscopy and feature engineering[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(15): 4474-4481.
[7] LAWTON J, WEINBERG F. Electrical aspects of combustion[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1969: 5-6.
[8] HU Yonghui, YAN Yong, QIAN Xiangchen, et al. A comparative study of induced and transferred charges for mass flow rate measurement of pneumatically conveyed particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 356: 715-725.
[9] WU Jiali, YAN Yong, HU Yonghui, et al. Flame boundary measurement using an electrostatic sensor array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1-12.
[10] HUANG N E, SHEN Zheng, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995.
[11] 王伟, 李兴华, 陈作彬, 等. 基于小波包变换的爆破振动信号能量熵特征分析[J]. 爆破器材, 2019, 48(6): 19-23.
WANG Wei, LI Xinghua, CHEN Zuobin, et al. Characteristic analysis of energy entropy of blasting vibration signal based on wavelet packet transform[J]. Explosive Materials, 2019, 48(6): 19-23.
[12] HIRANO T, SUZUKI T, HASHIMOTO Y, et al. Basic characteristics of cylindrical, electrostatic probes for the measurements of fluctuating premixed flames[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1981, 24(187): 168-174.
[13] CALCOTE H F. Ion production and recombination in flames[J]. Symposium(International) on Combustion, 1961, 8(1): 184-199.
[14] SUGDEN T M, THRUSH B A. A cavity resonator method for electron concentration in flames[J]. Nature, 1951, 168(4277): 703-704.
[15] BALTHASAR M, MAUSS F, WANG H. A computational study of the thermal ionization of soot particles and its effect on their growth in laminar premixed flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2002, 129(1/2): 204-216.
[16] MARICQ M M. A comparison of soot size and charge distributions from ethane, ethylene, acetylene, and benzene/ethylene premixed flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 144(4): 730-743.
[17] 王宇, 姚强. 电场对火焰形状及碳烟沉积特性的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2007, 28(z2): 237-239.
WANG Yu, YAO Qiang. Variation of flame shape and soot deposits by applying electric fields[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2007, 28(z2): 237-239.
[18] QIAN Xiangchen, YAN Yong, HUANG Xiaobin, et al. Measurement of the mass flow and velocity distributions of pulverized fuel in primary air pipes using electrostatic sensing techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(5): 944-952.
[19] YAN Yong, HU Yonghui, WANG Lijuan, et al. Electrostatic sensors:their principles and applications[J]. Measurement, 2021, 169: 108506.
[20] WU J, HU Y, YAN Y, et al. Flicker measurement of burner flames through electrostatic sensing and spectral analysis[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2018, 1065(20): 202004.
[21] 李一博, 刘嘉玮, 芮小博, 等. 基于集合经验模态分解和小波阈值的真空泵振动信号降噪方法[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2019, 36(5): 450-457.
LI Yibo, LIU Jiawei, RUI Xiaobo, et al. De-noising based on EEMD and wavelet threshold for vacuum pump vibration signals[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2019, 36(5): 450-457.
[22] SHANNON C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(3): 379-423.
[23] 王超, 张靖宇, 张一顺, 等. 基于静电法的气力输送局部流动特性R/S分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(5): 1794-1798.
WANG Chao, ZHANG Jingyu, ZHANG Yishun, et al. R/S analysis for local flow characteristics of pneumatically conveyed particles using electrostatic method[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(5): 1794-1798.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期: 2020 -10 -12; 修回日期: 2020 -11 -13
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(61673170, 51827808);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2019MS023)(Projects(61673170, 51827808) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019MS023) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:钱相臣,博士,副教授,从事多相流与火焰检测技术、智能仪表与工业参数检测研究;E-mail: xqian@ncepu.edu.cn
引用格式: 李珊, 闫勇, 吴佳丽, 等. 基于EMD降噪的燃烧器火焰静电信号能量熵分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(1): 285-293.
Citation: LI Shan YAN Yong, WU Jiali. Energy entropy analysis of flame signals obtained by an electrostatic sensor array based on EMD denoising method[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(1): 285-293.