文章编号:1004-0609(2011)02-0411-07
钢芯铝绞导线大气腐蚀产物层的结构及腐蚀机理
张建堃1,陈国宏2,王家庆2,张 涛2,王 煦1,汤文明1
(1. 合肥工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,合肥 230009;
2. 安徽省电力科学研究院 材料所,合肥 230601)
摘 要:在模拟大气腐蚀环境中,采用干/湿NaHSO3+NaCl水溶液盐雾试验研究钢芯铝绞(ACSR)导线腐蚀产物的相组成及腐蚀层结构,讨论其腐蚀机理。结果表明:ACSR导线中单股铝线或镀锌钢芯线的腐蚀主要表现为点蚀,腐蚀产物组成复杂,主要为锌和铝的氢氧化物、硫酸盐与氯化物的复式盐;在腐蚀初期,内外层铝股线及钢芯线表面镀锌层开始形成点蚀坑,逐步形成连续的腐蚀层;由于镀锌层和内层铝股线之间构成原电池,因为牺牲阳极效应,镀锌层腐蚀速率最大;而内层铝股线受到保护,腐蚀速率最小,外层铝股线腐蚀速率居中。
关键词:钢芯铝绞导线;大气腐蚀;显微结构;腐蚀机理
中图分类号:TM752, TG17 文献标志码:A
Microstructures of corrosion layer of ACSR conductor in atmospheric corrosion and corrosion mechanism
ZHANG Jian-kun1, CHEN Guo-hong2, WANG Jia-qing2, ZHANG Tao2, WANG Xu1, TANG Wen-ming1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China;
2. Materials Department, Anhui Institute of Electric Power Science, Hefei 230601, China)
Abstract: The dry/wet NaCl+NaHSO3 atmosphere-salt spraying experiment of the aluminum conductor steel reinforced (ACSR) conductor was carried out to study the phases and microstructures of corrosion products and the corrosion mechanism in simulated air corrosion condition. The results show that the ACSR conductor is mainly corroded by pitting corrosion. The corrosion layer mainly consists of hydroxides, sulfates and sulfate-chloride double salts and their hydrates of Zn and Al. At the initial corroding stage, the corrosion pits form on the Al strands and the galvanizing Zn layer, which are gradually replaced by the continuous corrosion layers as prolonging the spraying time. In the ACSR conductor, a primary cell is generated between the galvanizing Zn layer and the internal Al layer in the electrolyte. In the cell, as an anode, the galvanizing Zn layer is violently etched, contrarily, as a cathode, the internal Al layer is protected. In the ACSR conductor, the sequence of the corrosion rate from high to low is the galvanizing Zn layer, the external Al layer and the internal Al layer.
Key words: ACSR conductor; atmospheric corrosion; microstructure; corrosion mechanism
架空导线是高压输电线路的主体,目前,国内外高压输配电网架空导线仍主要是钢芯铝绞导线(Aluminum conductor steel reinforced,ACSR)。ACSR导线在工业污染区、沿海地区及沿海工业污染区等强腐蚀性环境下的腐蚀破坏给输电线路的安全运行带来相当大的威胁,因此,受到世界各国输电行业的高度重视[1]。美国电力科学研究院(EPRI)和加拿大电力技术研究机构如 Power Tech Lab等把输电网的腐蚀评估、控制与防护等列为输电网管理的重要研究课题,我国也在输电线路的腐蚀评估和防护等方面展开相当多的研究。
ACSR导线是由内、外层铝线及镀锌钢芯线绞合在一起的一种复合结构。经大气腐蚀后,ACSR导线的力学性能和电气性能均降低,且可能导致线路断股、断线、甚至停电事故的发生。国内外已就铝及其合金及锌等在不同大气腐蚀介质下的腐蚀行为开展了较多的基础研究[2-5],但由于ACSR导线组成与结构复杂,其腐蚀行为及腐蚀产物的组成、结构更加复杂。LYON等[6]首次在实验室条件下通过在周期性干/湿中性盐雾环境下的加速腐蚀试验研究了铝、钢及镀锌钢的腐蚀行为,基于导线的质量损失来评价导线的大气腐蚀程度,开始了实验室研究输电导线腐蚀行为的先河。随着我国工业化进程加快,大气污染日益严重,金属材料的大气腐蚀研究已受到人们的高度正视。WANG等[7]和王振尧等[8]采用NaHSO3+NaCl的去离子水溶液开展锌及LY12铝合金的大气腐蚀过程研究,主要研究结果与野外暴露实验结果相吻合。但迄今为止,ACSR导线大气腐蚀的实验研究成果尚未见报道。本文作者通过大气腐蚀介质下的周期性干/湿盐雾试验,首次研究ACSR导线大气腐蚀产物类型和腐蚀层结构等,并就ACSR导线的大气腐蚀机理进行了探讨。
1 实验
实验采用未服役的LGJ150/25钢芯铝绞线(ACSR),该绞线含直径为2.7 mm的铝线26股,分内外两层:内层10股,外层16股;镀锌钢芯线7股,单股直径2.1 mm[9]。截取约30 cm长的ACSR导线若干根,进行周期性干/湿模拟大气腐蚀的盐雾腐蚀试验。在试验前,导线先进行清洗、干燥。盐雾试验按GB 10125—1997的要求在YWX/F-250E型盐雾试验箱进行,喷雾介质为0.1 mol/L NaHSO3+0.01 mol/L NaCl的去离子水溶液,试验箱温度为(35±2) ℃,沉降量1/80~2/80 mL/(cm2·h)[10]。每连续喷雾8 h后停机,将试样从盐雾箱中取出,在实验室内自然干燥16 h,完成一个干/湿腐蚀试验周期(24 h)。腐蚀试验时间最高达1 440 h (60个周期),达到设定的腐蚀时间后,将试样取出、晾干,再用流动的自来水清洗6~8 h,然后取出,自然干燥。
将腐蚀后的ACSR导线拆开,从内外层铝股线及镀锌钢芯线上剥下腐蚀产物,采用D/MAX2500VL/PC型X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行腐蚀产物的物相分析。采用Olympus光学显微镜(OM)及JSM-6490LV型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)及INCA能谱仪(EDS)进行内外层铝股线及镀锌钢芯线腐蚀层的表面及截面形貌观察,并进行元素成分分析。为观察腐蚀后单根铝线及镀锌钢线的截面形貌,先在这些导线上取样后,沿轴向或径向用环氧树脂镶嵌,再进行研磨、抛光,最后铝股线使用10%NaOH溶液,镀锌钢丝用4%硝酸酒精腐蚀。在进行SEM分析前,镶嵌试样表面需进行喷金处理。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 ASCR导线腐蚀状态和腐蚀物相成分分析
ACSR导线在模拟大气腐蚀条件下,经过96~ 1 440 h的腐蚀后,将导线拆开,肉眼观察各层线股的表面状态:经过96 h腐蚀后,外层铝股线表面发白,无金属光泽;经过240 h腐蚀后,外层铝股线已经被腐蚀层完全覆盖,而内层铝股线仍有金属光泽,未见明显的腐蚀;随着腐蚀时间的延长,ACSR导线不仅外层包裹着白色的腐蚀产物层,且线股之间也基本上被腐蚀产物填满;经过720 h腐蚀后,内层铝股线表面也形成了连续的腐蚀层;经过1 440 h腐蚀后,内、外层铝股线表面腐蚀层增厚,腐蚀产物甚至堵塞了线股的间隙,形成一个致密的壳层,镀锌钢芯线表面有黄褐色的铁锈斑,镀锌层可能因腐蚀已消耗殆尽,失去了对钢芯线的保护,使钢芯线遭受明显的腐蚀。
图1所示为ACSR腐蚀1 440 h后腐蚀产物的XRD谱。由图1可知,ACSR导线腐蚀产物的成分复杂。铝股线表面的腐蚀产物主要有Al3(SO4)2(OH)5?9H2O、Na2Al22O34、Al10(SO4)3(OH)24·20H2O,可能还有从镀锌钢线表面渗出的腐蚀产物Na2Zn(SO4)2·4H2O(其衍射峰较弱);而镀锌钢芯线表面的腐蚀产物主要有Zn(OH)2·0.5H2O、ZnSO4·6H2O、NaZn4(SO4)Cl(OH)6·
6H2O及从铝股线表面渗入的腐蚀产物Al2(SO4)3·18H2O和Na2Al22O34·6H2O等。值得注意的是,铝股线表面的腐蚀产物未见Al的氯化物,这是因为Al的氯化物一般为水溶性,在导线腐蚀后的洗涤过程中可能溶于水而消失。
2.2 ASCR导线腐蚀层的显微组织结构
2.2.1 初期腐蚀状态
图2所示为腐蚀96 h后外层铝股线的表面与截面形貌。由图2可看出,在ACSR导线初期腐蚀阶段(96 h),外层铝股线表面腐蚀现象不明显,没有形成腐蚀层,铝股线表面形成局部的腐蚀产物堆积(见图2(a)中箭头所示)。在铝股线截面上出现深约1~2 μm的腐蚀坑,产生点蚀[11](见图2(b)中箭头所示)。
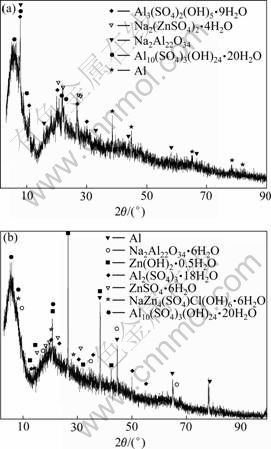
图1 ACSR腐蚀1 440 h后腐蚀产物的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of corrosion products after ACSR conductor being etched for 1 440 h: (a) Corrosion product around external Al strand; (b) Corrosion product around galvanized steel core strand
图3所示为腐蚀96 h后镀锌钢芯股线的截面SEM像。由图3可看出,经96 h腐蚀后,镀锌钢芯线表面的镀锌层比内、外层铝股腐蚀剧烈得多,其原因将在后面讨论。尽管从图3中仍可见厚度约15 μm的镀锌层,但在镀锌层外侧形成了约50 μm厚的腐蚀产物层。腐蚀层分为内外两层,外层结构疏松,主要成分(摩尔分数)为60.41% O、3.54% Al、1.03% Cl、1.10% Fe和33.92% Zn(见图3中点1的成分),主要由Zn、Al的氢氧化物及氯化物组成;内层的腐蚀产物结构致密,与镀锌层结合紧密,主要成分(摩尔分数)为39.95% O、0.79% Cl、0.47% Fe和56.37% Zn (见图3中点2的成分),主要由Zn的氢氧化物构成。镀锌钢芯线表面内层腐蚀产物结构致密,具有延缓镀锌层腐蚀的作用。
2.2.2 中期腐蚀状态
图4和5所示分别为腐蚀720 h后外层和内层铝股线的表面与截面形貌。由图4可看出,在ACSR导线中期腐蚀阶段,如该导线腐蚀720 h后,在外层铝股线表面不仅形成了约20~30 μm厚的腐蚀产物层(见图4(a))。腐蚀层因为干燥、脱水,产生龟裂,部分从铝股线基体上剥落。EDS分析表明,未剥落腐蚀层表层的主要成分为74.73% O、19.23% Al和6.04% S(见图4(a)中区域1),而表层剥落后内层的成分为42.01% O、56.43% Al和1.56% S(见图4(a)中区域2)。可见,外层铝线表面腐蚀层的成分并不均匀,表层含有更高的S成分,形成更多的硫酸盐类反应产物。
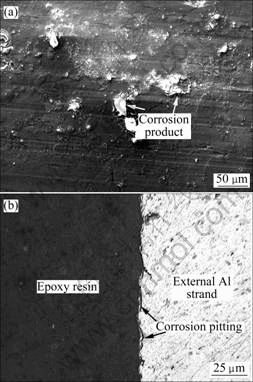
图2 腐蚀96 h后外层铝股线的表面与截面形貌
Fig.2 Superficial (a) and cross-sectional (b) morphologies of external Al strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 96 h
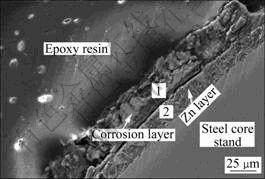
图3 腐蚀96 h后镀锌钢芯股线的截面SEM像
Fig.3 Cross-sectional SEM image of galvanized steel core strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 96 h
由图5可看出,经720 h腐蚀后,ACSR导线内层铝股线的表面形成了连续的腐蚀产物壳层,但腐蚀层干燥、龟裂、部分脱落(见图5(a))。同样地,从图5(b)的腐蚀层截面形貌像中同样可见腐蚀层的开裂。从图5(a)可见,腐蚀层结构不同,表层以下紧贴铝股线的有一个腐蚀产物的薄层,龟裂细密。它们连同未腐蚀的铝股线表面的成分如表1所列。由表1可知,从铝股线表面向外腐蚀层中的S的含量逐渐增加,腐蚀层中Al的硫酸盐腐蚀产物逐渐增多。腐蚀720 h后,ACSR导线内层铝股线的腐蚀程度小于外层铝股线的,但局部也形成了20 μm厚的反应层(见图5(b))。
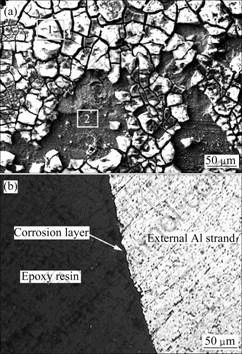
图4 腐蚀720 h后外层铝股线的表面与截面形貌
Fig.4 Superficial (a) and cross-sectional (b) morphologies of external Al strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 720 h

图5 腐蚀720 h后内层铝股线的表面和截面形貌
Fig.5 Superficial (a) and cross-sectional (b) morphologies of internal Al strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 720 h
图6所示为腐蚀720 h后钢芯线的表面和截面SEM像。由图6可见,经过720 h腐蚀的钢芯线镀锌层厚度比经过96 h腐蚀的小,约为10~12 μm,腐蚀层的结构与96 h腐蚀的相同,也分为内外两个部分,腐蚀层的总厚度约100 μm。
表1 图5中各微区的EDS成分分析
Table 1 EDS analyzing results of micro-zones in Fig.5
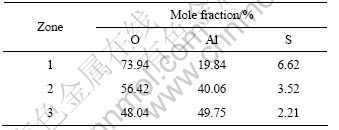

图6 腐蚀720 h后钢芯线的表面和截面SEM像
Fig.6 Cross-sectional SEM image of galvanized steel core strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 720 h
2.2.3 末期腐蚀状态
在ACSR导线末期腐蚀阶段,如该导线腐蚀1 440 h后的外层铝股线表面有约40~50 μm的连续腐蚀产物层(见图7);同样地,外层铝股线表面的腐蚀产物部分剥落。EDS成分分析表明,腐蚀产物的表层的成分(摩尔分数)为75.86% O、19.73% Al、4.32% S和0.09% Zn,外层铝股线表面的腐蚀产物层主要是铝的氢氧化物和硫酸盐,表层中含有少量的锌成分,说明有少量的镀锌层表面腐蚀产物从内、外层铝股线的狭缝中向外渗出,沉积在外层铝股线的表面。而内层铝股线腐蚀程度相对外层铝股线较轻,腐蚀层厚度约为30 μm。

图7 腐蚀1 440 h后外层铝股线的表面和截面SEM形貌
Fig.7 Superficial (a) and cross-sectional (b) SEM images of external Al strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 1 440 h
ACSR绞线经过1 440 h腐蚀后,腐蚀层与钢芯线基体结合紧密,没有明显的腐蚀层脱落现象,但腐蚀层也因为干燥过程中所产生的应力等因素的作用,形成细密的微裂纹。钢芯线表面镀锌层已经基本上腐蚀殆尽,原来镀锌钢芯线表面的腐蚀产物双层结构已经不明显,腐蚀层结构较为疏松(见图8(b))。钢芯线边缘处点1的成分(摩尔分数)为52.34% O、7.64% Al、2.29% S、31.61% Zn、3.08% Fe和3.04% Cl,形成了Zn的氢氧化物、硫酸盐及氯化物的腐蚀产物层,钢芯线表面的镀锌层消失。钢芯线失去镀锌层的保护,在随后的腐蚀过程中将加剧腐蚀,直至钢芯线断股。由于ACSR导线中的钢芯线是载荷的主要承受体,钢芯线的加剧腐蚀必然导致导线的承载能力下降,在恶劣的气候条件下(如覆冰和舞动),易导致断股、断线,造成供电事故。
2.3 ASCR导线大气腐蚀产物的形成及腐蚀机理分析
2.3.1 铝股线的腐蚀机理
当ACSR导线的铝股线暴露在大气环境中时,在其表面形成连续、致密的水合氧化铝膜(Al(OH)3),与基体结合性紧密。该氧化膜不溶于水,除了强酸和强碱,在pH为4~9的水溶液中一般都是稳定的。但在一定浓度的Cl-溶液(如NaCl溶液)中,将加速氧化膜的破坏,最终导致铝的浸蚀[11-14]。当腐蚀介质中HSO3-和Cl-同时存在时,铝股线表现为局部腐蚀,主要为点蚀,其中Cl-较易形成点蚀源。
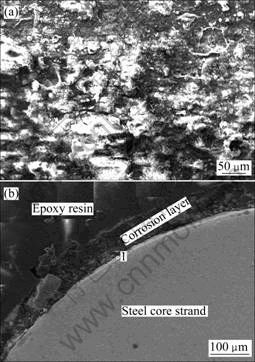
图8 腐蚀1 440 h后钢芯线的表面和截面SEM形貌
Fig.8 Superficial (a) and cross-sectional (b) SEM images of galvanized steel core strand after ACSR conductor being etched for 1 440 h
首先,腐蚀介质中的Cl-吸附在氧化膜表面,加速氧化膜水解,并与水解产物反应,形成系列碱式氯化物盐。
Al(OH)3+Cl-→Al(OH)2Cl+OH- (1)
Al(OH)2Cl+Cl-→Al(OH)Cl2+OH- (2)
Al(OH)Cl2+Cl-→AlCl3+OH- (3)
同时,HSO3-水解,形成SO32-,SO32-被氧化形成SO42-,反应过程如下:
HSO3-→ SO32-+H+ (4)
2SO32-+ O2→2SO42- (5)
而后,铝的氯化物中的Cl-被SO42-所取代,形成铝的硫酸盐和碱式硫酸盐及其水合物:
2Al3++3SO42-→Al2(SO4)3 (6)
xAl3++ySO42-+zOH-+nH2O→Alx(SO4)y(OH)z·nH2O (7)
其中,Alx(SO4)y(OH)z·nH2O中的z=3x-2y。在本研究中,Alx(SO4)y(OH)z·nH2O主要为Al3(SO4)2(OH)5·9H2O和Al10(SO4)3(OH)24·20H2O。由于模拟大气腐蚀介质中Cl-含量太少,加上某些氯化物反应产物(如AlCl3)还易溶于水,在腐蚀后导线的漂洗过程中溶解消失。所以,在图1的腐蚀产物物相分析中并没有检测到Al的氯化物产物,而主要是Al的硫酸盐和碱式硫酸盐及其水合物。
上述反应常在氧化膜薄弱处产生点蚀坑并向四周和深处扩展,直到腐蚀介质穿透氧化层直接作用于铝股线。铝股线在溶液中离子的作用下发生电化学腐 蚀,产生大量的点蚀坑,点蚀坑沿铝线股圆周方向扩展,形成连续的腐蚀产物层,同时点蚀坑不断沿线股径向向里扩展,导致腐蚀层厚度逐渐增加。
2.3.2 钢芯线表面镀锌层的腐蚀机理
ACSR导线中镀锌钢芯的腐蚀主要表现为镀锌层的腐蚀。由镀锌钢芯线表面腐蚀层结构分析可知,镀锌层的腐蚀首先在镀锌层形成点蚀,然后腐蚀坑向四周和深度方向扩展,主要腐蚀机理为电化学腐蚀。反应过程如下:
阳极反应:Zn→Zn2++2e (8)
阴极反应:1/2O2+H2O+2e→2OH- (9)
总反应:Zn+1/2O2+H2O→Zn(OH)2 (10)
Zn(OH)2为白色沉淀。随着腐蚀反应的进行,Cl-向阳极区迁移,并在阳极区发生如下反应:
5Zn2++2Cl-+8H2O→Zn5(OH)8Cl2+8H+ (11)
碱式氯化物Zn5(OH)8Cl2是Zn在Cl-腐蚀溶液中最主要的腐蚀产物[15-16]。在本实验的模拟大气腐蚀介质中,Cl-和SO42-的共同作用下,形成了Zn的硫酸盐及组成更加复杂的复合盐类化合物,总反应式如下:
Zn2++SO42-→ZnSO4 (12)
4Zn2++Na++Cl-+SO42-+12H2O→
NaZn4(SO4)Cl(OH)6·6H2O+6H+ (13)
因此,ACSR导线中镀锌钢芯线表面锌层的大气腐蚀产物主要是Zn(OH)2、ZnSO4和NaZn4(SO4)Cl(OH)6的水合物。
2.3.3 ACSR导线的腐蚀机理
与单一的铝股线及镀锌钢芯线相比,ACSR导线在模拟大气腐蚀介质中构成了一个复杂得多的腐蚀系统,ACSR导线的腐蚀是多种机理共同作用的结果[17]。最重要的是电化学腐蚀,包括单股线内的电化学腐蚀与不同层股线之间的电化学腐蚀。正如上文所述,单股线内的电化学腐蚀,表现为股线上的点蚀,并逐渐在线股表面形成连续的腐蚀产物层,最终导致断股。
至于导线线股间的电化学腐蚀,研究表明[17-18],在盐水溶液中金属的自然电极电位依次增大的次序排列是Zn、A1、Fe。对于ACSR导线,由于NaCl+NaHSO3溶液在线股间存留,钢芯线表面的镀锌层和内层铝股线之间构成原电池,发生电化学腐蚀,Zn为阳极,被腐蚀,而Al受到保护。这可能也是本实验中镀锌层的腐蚀速率明显高于内外层铝股线的,而外层铝股线的腐蚀程度大于内层铝股线的原因。当镀锌层被腐蚀后,将在内层铝股线和钢芯线之间再次形成新的微电池,此时,内层铝股线为阳极,加速腐蚀,而钢芯线受到保护。可以假设,如果ACSR导线在模拟大气腐蚀介质中的腐蚀时间超过1 440 h, 内层铝股线的腐蚀程度很可能会超过外层铝股线的。
3 结论
1) 在模拟大气腐蚀条件下,ACSR导线铝股线 表面的腐蚀产物主要有Al3(SO4)2(OH)5·9H2O、Na2Al22O34和Al10(SO4)3(OH)24·20H2O;而镀锌钢线表面的腐蚀产物主要有Zn(OH)2·0.5H2O、ZnSO4·6H2O和NaZn4(SO4)Cl(OH)6·6H2O。
2) 在ACSR导线腐蚀经96 h,外层铝股线表面只形成局部的腐蚀产物堆积,产生点蚀;而内层铝股线没有发生腐蚀。镀锌层表面形成了约50 μm腐蚀产物层,腐蚀层分为内外两层,外层结构疏松;内层结构致密,并与镀锌层结合紧密。
3) 在ACSR导线经720 h腐蚀,在内、外层铝股线表面均形成了约20~30 μm厚连续的腐蚀产物层,腐蚀层龟裂、部分剥落。镀锌层表面腐蚀层的厚度约100 μm,仍为两层结构。
4) 在ACSR导线经1 440 h腐蚀,外层铝股线表面腐蚀产物层厚约40~50 μm,而内层铝股线腐蚀层厚约为30 μm。钢芯线表面镀锌层已经基本上腐蚀殆尽,腐蚀层结构疏松。
5) ACSR导线的电化学腐蚀,包括单股线内的电化学腐蚀与不同层股线之间的电化学腐蚀。单股线内的电化学腐蚀,表现为各股线上的点蚀,并逐渐在股线表面形成连续的腐蚀产物层。由于Zn的电极电位比Al的高,在钢芯线表面镀锌层和内层铝股线之间构成原电池。因牺牲阳极效应,腐蚀层的腐蚀速率最高,而内层铝股线腐蚀速率最低,外层铝股线居中。
REFERENCES
[1] 王凤平, 张学元, 杜元龙. 大气腐蚀研究动态与进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2000, 12(2): 104-109.
WANG Feng-ping, ZHANG Xue-yuan, DU Yuan-long. The review of atmospheric corrosion research[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2000, 12(2): 104-109.
[2] FUENTE D D, OTERO-HUERTA E, MORCILLO M. Studies of long-term weathering of aluminum in the atmosphere[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 3134-3148.
[3] VERA R, DELGADO D, ROSALES B M. Effect of atmospheric pollutants on the corrosion of high power electrical conductors: Part 1. aluminum and AA6201 alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48: 2882-2900.
[4] 屈 庆, 严川伟, 白 玮, 曹楚南. SO2存在下NaCl沉积量对Zn大气腐蚀的影响[J]. 金属学报,2001,37(1):72-76.
QU Qing, YAN Chuan-wei, BAI Wei, CAO Chu-nan. Influence of NaCl deposition on atmospheric corrosion of zinc in the presence of SO2[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica, 2001, 37(1): 72-76.
[5] 王凤平, 陈 华, 李晓刚. 盐粒沉降对Zn大气腐蚀的影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2002, 24(4): 445-448.
WANG Feng-ping, CHEN Hua, LI Xiao-gang. Effect of deposition of electrolytes on atmospheric corrosion of Zn under thin liquid film[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2002, 24(4): 445-448.
[6] LYON S B, THOMPSON G E, JOHNSON J B. Accelerated atmospheric corrosion testing using a cyclic wet/dry exposure test: aluminum, galvanized steel and steel[J]. Corrosion, 1987, 43: 719-726.
[7] WANG Zhen-yao, MA Teng, HAN Wei, YU Guo-cai. Corrosion behavior on aluminum LY12 in simulated atmospheric corrosion process[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 326-334.
[8] 王振尧, 于国才, 郑逸苹, 贾斌平. 锌的加速腐蚀与大气暴露腐蚀的相关性研究[J]. 环境技术, 2001(4): 18-22.
WANG Zhen-yao, YU Guo-cai, ZHENG Yi-ping, JIA Bin-ping. Investigation on interrelation of accelerated corrosion testing and atmospheric exposure of zinc[J]. Environment Technology, 2001(4): 18-22.
[9] GB/T 1179—2008. 圆线同心绞架空导线[S].
GB/T 1179—2008. Round wire concentric lay overhead electrical stranded conductors[S].
[10] GB/T 10125—1997. 人造气氛腐蚀试验—盐雾试验[S].
GB/T 10125—1997. Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres- salt spray tests[S].
[11] BOXLEY C J, WATKINS J J, WHITE H S. Al2O3 film dissolution in aqueous chloride solutions[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2003, 38/41: 6-10.
[12] SZKLARSKA-SMIALOWSKA Z. Pitting corrosion of aluminum[J]. Corrosion Science, 1999, 41: 1743-1767.
[13] FRANKEL G S. Pitting corrosion of metals[J]. J Electrochemical Soc, 1998, 145(6): 2186-2198.
[14] BHATTAMISHRA A K, LA K, NAIR G G, KUMAR R. Corrosion behavior of overhead aluminum/alloy conductors in industrial and coastal environments[J]. NML Technical Journal, 2002, 29(1/4): 20-24.
[15] YADAV A P, NISHIKATA A, TSURU T. Degradation mechanism of galvanized steel in wet-dry cyclic environment containing chloride ions[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46: 361-376.
[16] 屈 庆, 严川伟, 张 蕾, 阎一功, 万 晔, 曹楚南. Zn 初期大气腐蚀中NaCl 和SO2 的协同效应[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(6): 1272-1276.
QU Qing, YAN Chuan-wei, ZHANG Lei , YAN Yi-gong, WAN Ye, CAO Chu-nan. Synergism of NaCl and SO2 in initial atmospheric corrosion of Zn[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(6): 1272-1276.
[17] CALITZ J. Overhead conductor corrosion study[D]. South Africa, Tshwane: Tshwane University of Technology, 2004: 11-14.
[18] 符圣旭, 靳武刚, 王福恒. 不同环境介质中热喷涂Al 和Zn 的腐蚀行为[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2007, 28(1): 6-12.
FU Sheng-xu, JIN Wu-gang, WANG Fu-heng. Corrosion performance of thermal sprayed aluminum and zinc coatings in various environmental media[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2007, 28(1): 6-12.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家电网科技攻关项目(2009144)
收稿日期:2010-04-06;修订日期:2010-07-19
通信作者:汤文明,教授,博士;电话:0551-2901373;E-mail: wmtang69@126.com