DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.11.021
四川拉拉IOCG矿床方解石REE与C,O同位素地球化学特征及意义
黄从俊,李泽琴
(成都理工大学 地球科学学院,四川 成都,610059)
摘要:对拉拉铁氧化物-铜-金(IOCG)矿床中与铜矿化密切相关的变质期方解石(Ⅰ)和热液期方解石(Ⅱ)的稀土元素(REE)及C,O同位素地球化学特征进行研究,以探讨方解石成因及沉淀影响因素、成矿流体来源及性质。研究结果表明:方解石(Ⅰ)具有极低的REE总质量分数(wREE平均75.98×10-6),方解石(Ⅱ)的REE总质量分数相对较高(平均313.85×10-6);方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(13CPDB)为-3.84‰~0‰,方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(13CPDB)为-3.98‰~-1.40‰,二者大小接近且相对变化较小;方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(18OSMOW)为9.45‰~12.2‰,方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(18OSMOW)为8.1‰~11.6‰,后者相对低于前者。分析认为:方解石(Ⅰ)不是变质成矿期的主要REE载体,其成矿流体中REE含量很低;方解石(Ⅱ)为热液期REE的主要载体,其成矿流体中REE含量较高。两期方解石均为热液成因,但二者成矿流体不同源;水岩反应及降温作用耦合影响本矿床两期方解石的沉淀。方解石(Ⅰ)的REE配分曲线为平坦型,既有正Eu异常也有负Eu异常,无Ce异常,配分模式受流体中REE络合物稳定性控制,其成矿流体为大量LREE沉淀后的残余高温变质成矿流体,继承了海相喷发的火山围岩部分特征;方解石(Ⅱ)的REE配分曲线为左倾型,显著正Eu异常,无Ce异常,配分模式受方解石晶体化学因素控制,其成矿流体为大气降水与围岩反应形成的低温高氧逸度热卤水。方解石(Ⅰ)的成矿流体中的C由深源C和海水C共同提供;方解石(Ⅱ)的成矿流体中的C来自地幔柱成因的基性辉长岩浆分异释放的CO2,O同位素受大气降水影响发生明显负漂移。
关键词:方解石;稀土元素;同位素;IOCG矿床;四川拉拉
中图分类号:P595;P597 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)11-3765-10
REE and carbon-oxygen isotope geochemistry of calcite from Lala IOCG deposit, Sichuan and its significance
HUANG Congjun, LI Zeqin
(School of Earth Science, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China)
Abstract: Calcite (Ⅰ) from metamorphic mineralization stage (MMS) and calcite (Ⅱ) from hydrothermal mineralization stage (HMS) have close relationship with copper mineralization in the Lala IOCG deposit. Factors controlling the genesis of calcite, and the features and source of ore-forming fluids were discussed through systematic investigation of REE and C-O isotope geochemistry of calcites. The results show that the average 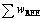 , δ(13CPDB) and δ(18OSMOW) of calcite (Ⅰ) are 75.98×10-6, -3.84‰-0‰ and 9.45‰-12.2‰, respectively, while the calcite (Ⅱ) are 313.85×10-6, -3.98‰~-1.40‰ and 8.1‰~11.6‰, respectively. The results show that calcite (Ⅰ) is not the main carrier of REE in the MMS, and its ore-forming fluid has very low
, δ(13CPDB) and δ(18OSMOW) of calcite (Ⅰ) are 75.98×10-6, -3.84‰-0‰ and 9.45‰-12.2‰, respectively, while the calcite (Ⅱ) are 313.85×10-6, -3.98‰~-1.40‰ and 8.1‰~11.6‰, respectively. The results show that calcite (Ⅰ) is not the main carrier of REE in the MMS, and its ore-forming fluid has very low 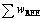 . Calcite (Ⅱ) is the dominate REE carrier of HMS, and its ore-forming fluid has higher
. Calcite (Ⅱ) is the dominate REE carrier of HMS, and its ore-forming fluid has higher 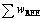 than calcite (Ⅰ). Both calcite (Ⅰ) and calcite (Ⅱ) are hydrothermal origin,water-rock interaction and cooling effect the precipitation of calcite, but their ore-forming fluids have different sources. REE distribution pattern of calcite (Ⅰ) is flat type. There are both positive and negative Eu anomalies, and no Ce anomaly, which is controlled by the stability of REE complexes in the fluid. The ore-forming fluid of calcite(Ⅰ) is a kind of high temperature residual fluid after the precipitation of a large number of LREE, and has inherited characteristics of the surrounding marine eruption volcanic rock. REE distribution pattern of calcite (Ⅱ) is leftist type, with significant positive Eu anomaly and no Ce anomaly, which is controlled by crystal chemical factors. The ore-forming fluid of calcite (Ⅱ) is a kind of hot brine originated from the reaction between meteoric water and surrounding rocks, which has a feature of low temperature and high oxygen fugacity. C of calcite (Ⅰ) is derived from mantle fluids and marine carbonates, while C of calcite (Ⅱ) is sourced from CO2 which is released by gabbro magma. O isotope obviously has negative drift being affected by meteoric water.
than calcite (Ⅰ). Both calcite (Ⅰ) and calcite (Ⅱ) are hydrothermal origin,water-rock interaction and cooling effect the precipitation of calcite, but their ore-forming fluids have different sources. REE distribution pattern of calcite (Ⅰ) is flat type. There are both positive and negative Eu anomalies, and no Ce anomaly, which is controlled by the stability of REE complexes in the fluid. The ore-forming fluid of calcite(Ⅰ) is a kind of high temperature residual fluid after the precipitation of a large number of LREE, and has inherited characteristics of the surrounding marine eruption volcanic rock. REE distribution pattern of calcite (Ⅱ) is leftist type, with significant positive Eu anomaly and no Ce anomaly, which is controlled by crystal chemical factors. The ore-forming fluid of calcite (Ⅱ) is a kind of hot brine originated from the reaction between meteoric water and surrounding rocks, which has a feature of low temperature and high oxygen fugacity. C of calcite (Ⅰ) is derived from mantle fluids and marine carbonates, while C of calcite (Ⅱ) is sourced from CO2 which is released by gabbro magma. O isotope obviously has negative drift being affected by meteoric water.
Key words: calcite; REE; isotope; IOCG deposit; Sichuan Lala
拉拉Fe-Cu-REE多金属矿床是我国西南地区典型的铁氧化物-铜-金(IOCG)矿床[1-3],前人对其成因机 制[4-5]、成矿流体特征[3, 5-7]、成矿年龄[3, 8]及成矿物质来源[3, 8]进行了大量的研究探讨工作,但其中有争议且研究最薄弱的是成矿流体特征。孙燕等[5]对矿床进行了H-O同位素研究,并认为成矿流体早期为岩浆水、中期为变质水、晚期有大气降水参与。黄从俊等[7]通过萤石的REE元素地球化学特征研究认为:变质期成矿流体为海相喷发火山岩变质脱水形成的高温含矿流体;热液期成矿流体为大气水参与的低温高氧逸度含矿流体。成矿流体作为迁移成矿元素的介质,是研究矿床成因的关键。稀土元素(REE)在地质作用过程中,通常作为一个整体进行运移,其地球化学行为具有一定的可预见性,在探讨矿床成矿流体来源与演化过程中已得到广泛应用。流体在方解石沉淀以后对其中的微量元素影响很小,除非方解石溶解,否则不可能破坏其记录沉淀流体REE信息的地质密码,因此,方解石的REE地球化学特征可以很好地反映其沉淀流体的地球化学特征。由于C和O同位素常在不同地球化学单元之间存在明显的同位素分馏,因此,C和O同位素可以有效地示踪成矿流体的来源与演化。目前,方解石的 C和O同位素体系已经广泛用于示踪各类热液矿床成矿流体的来源及演化[9]。拉拉矿床有与铜矿化关系密切的方解石产出,可以为研究该矿床成矿流体来源及演化提供重要的信息,但迄今为止,尚未有人对矿床中方解石进行系统的REE及C和O同位素研究。鉴于以往研究中对成矿流体的争论以及方解石研究的重要性,本文作者试图通过分析该矿床与成矿相关的两期方解石的REE及 C和O同位素地球化学特征,探讨其成矿流体的来源及演化,为深入认识该矿床的成因提供必要的元素及同位素地球化学证据。
1 矿床地质特征
图1所示为拉拉矿区构造纲要图。拉拉IOCG矿床位于扬子地块西缘,康滇地区中部;康滇地区在早—中元古代处于大陆裂谷环境。矿区出露地层主要有下元古界河口群、会理群通安组、上三叠统白果湾组和第四系。河口群(Pt1hk)地层为一套变质火山-沉积岩,包括长冲组、落凼组、大营山组,其中拉拉IOCG矿床赋存于落凼组中(图1),落凼组地层主要为(石榴 石)黑云母片岩、结晶大理岩、(磁铁矿±石英)钠长变粒岩及钠长石角砾岩。
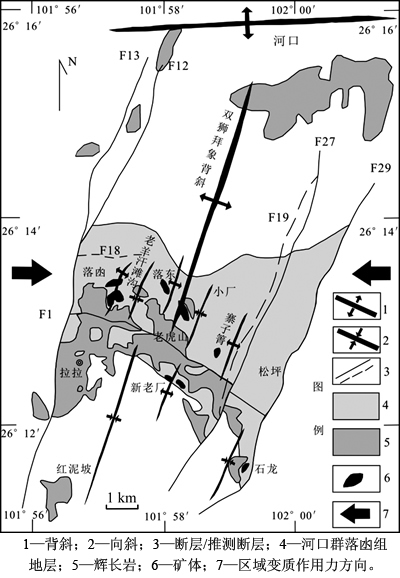
图1 拉拉矿区构造纲要图(底图据文献[6])
Fig. 1 Sketch map of Lala IOCG deposit(modified after[6])
矿区的构造主要为EW向和SN向。EW向的F1断层切错落东矿体,西端北西侧为落凼矿体,东端南东侧为石龙矿体,SN向的F29和F13断层限制了F1断层的延伸,分别构成了矿区的东西边界。层间破碎带发育,破碎带中发育构造角砾岩和假玄武玻璃。矿区北部有河口复式背斜南翼的轴向约NE20°的双狮拜象背斜,其南部由一系列小型背斜和向斜组成(图1)。
拉拉铜矿自西向东分为落凼、落东和石龙3个矿区。矿体呈层状、似层状、透镜状产出。已探明铜矿石量200 Mt以上,其中铁质量分数为15.48%,铜质量分数为0.95%,金为0.16 g/t,银为1.88 g/t,钼质量分数为0.03%,钴质量分数为0.02%,稀土质量分数为0.14%[2]。铜的赋存矿物以黄铜矿为主,其次为斑铜矿,少量铜蓝、辉铜矿、孔雀石等。铁以磁铁矿、黄铁矿、赤铁矿等形式存在。钴的赋存状态有2种:其一为单矿物,如辉钴矿、辉砷钴矿、硫镍钴矿;其二为以类质同象方式存在于硫铁镍矿和黄铁矿中。钼主要以独立矿物辉钼矿的形式存在。金以包体金、粒间金、裂隙金及类质同象状态赋存,以包体金为主;主要的载金矿物有黄铁矿、黄铜矿、叶碲铋矿等。稀土有2种赋存状态:其一为独立矿物,有独居石、磷钇矿、褐帘石、氟碳铈矿、氟碳钙铈矿等;其二呈类质同象赋存于磷灰石等矿物中[3]。矿石类型主要为黑云母片岩型矿石和钠长石变粒岩型矿石。矿石构造主要为条痕状、条带状、层纹状、网脉状及角砾状构造。围岩蚀变主要有钠长石化、黑云母化、碳酸盐化和萤化石等。
拉拉矿床Fe-Cu矿化被划分为3个时期[10],第1期为1 712~1 680 Ma,发生海相火山喷发—沉积成矿作用,形成早阶段的磁铁矿+富稀土磷灰石+黄铁矿+少量黄铜矿;第2期,大约1 000 Ma,该期发生变质热液成矿作用,形成黄铜矿+黄铁矿+辉钼矿+紫色萤石和方解石的脉状或浸染状矿石;第3期为850 Ma左右,该期发生热液改造成矿作用,形成众多规模不大的富集脉体或贫化脉体,如黄铜矿+黑云母+方解石脉、黄铜矿+方解石+石英脉等,矿物生成顺序及矿物共生组合见表1。
表1 拉拉IOCG矿床矿物生成顺序表(据文献[1]补充修改)
Table 1 Paragenetic sequence of mineralization and alteration in Lala IOCG deposit(modified after[1])

2 样品及分析方法
矿床中主要有2个世代的方解石产出。方解石(Ⅰ)产出于变质成矿期萤石+辉钼矿+碳酸盐阶段(Ⅲ)(表1),方解石(Ⅰ)呈脉状平行于石榴石+黑云母+黄铜矿阶段(Ⅱ)形成的片理产出(图2(a)),肉红色或白色,晶体三组解理发育,与黄铜矿(Ⅲ)和萤石(Ⅱ)共生,脉中黄铜矿富集程度高,团块状或云朵状,具锖色薄膜(图2(b))。方解石(Ⅱ)产出于热液成矿期(表1),淡黄色、白色或乳白色,晶体颗粒粗大,解理发育,与萤石±黑云母±黄铜矿形成切割早期片理的黄铜矿富集脉(图2(c))或者少黄铜矿的贫化脉(图2(d)),脉体众多但规模较小。
本次研究对不同世代的方解石进行了代表性采样分析。样品破碎后,用尼龙筛分选出粒度为550 μm和250 μm的粉末进行手工挑纯,纯度在99%左右;用超声波清洗挑纯后的方解石样品,自然晾干后再用玛瑙研钵研磨至75 μm。REE分析测试由澳实矿物分析检测(广州)有限公司承担完成,分析方法采用硼酸锂熔融-等离子质谱法定量,分析数据相对误差小于10%,绝大多数小于5%,分析测试结果见表2。C和O同位素分析测试在成都理工大学国家级地质学实验教学示范中心同位素实验室完成;分析采用100%磷酸法,在25 ℃时,样品与磷酸发生反应,将反应释放出来的CO2在Finnigan公司MAT-251型质谱仪上进行C和O同位素组成测试,分析精度为±0.2‰。所有分析结果δ(13C)以PDB为标准,δ(18O)以SMOW为标准,分析测试结果见表2。
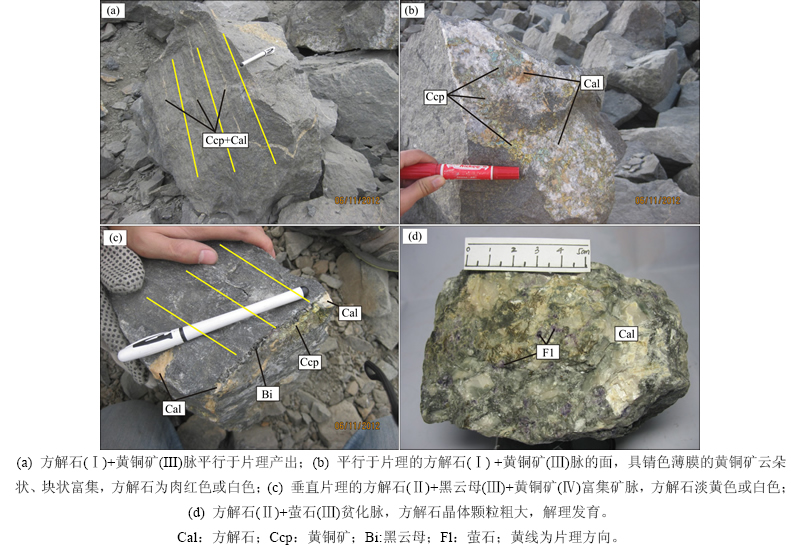

图2 拉拉IOCG矿床中代表性方解石照片
Fig 2 Representative photos of calcite in Lala IOCG deposit
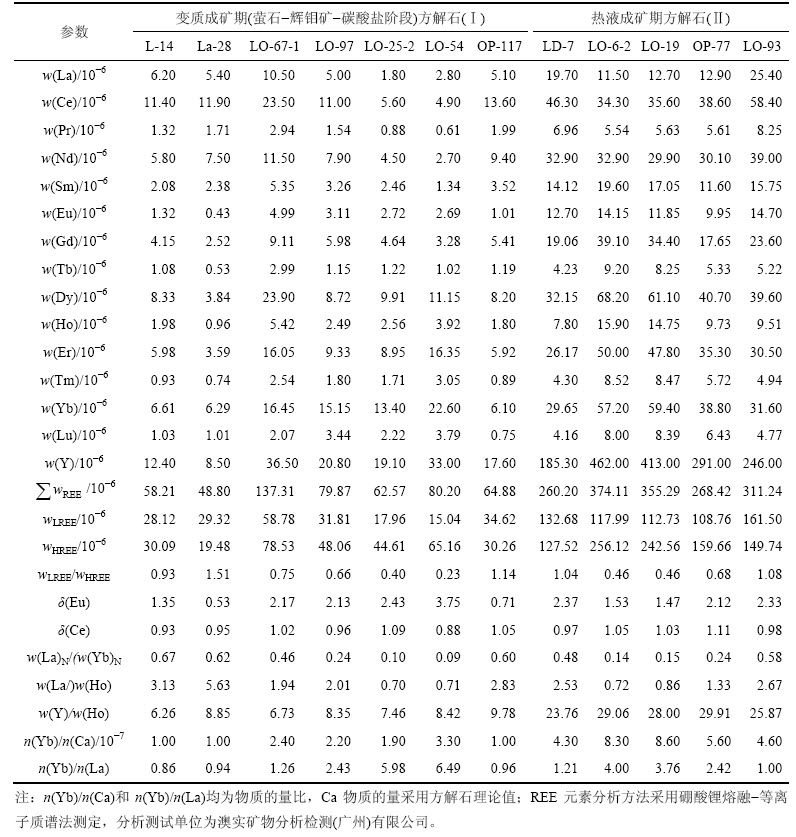
表2 拉拉IOCG矿床方解石稀土元素组成及特征参数
Table 2 Rare earth elements composition and parameters of calcite from Lala IOCG deposit
3 结果分析
3.1 方解石REE分析结果
由表2可知:矿床中两期方解石均具有较低的REE总量;其中,方解石(Ⅰ)稀土总量(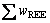 )为48.80×10-6~137.71×10-6,平均为75.98×10-6;方解石(Ⅱ)的
)为48.80×10-6~137.71×10-6,平均为75.98×10-6;方解石(Ⅱ)的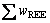 为260.20×10-6~374.11×10-6,平均为313.85×10-6,方解石(Ⅱ)的
为260.20×10-6~374.11×10-6,平均为313.85×10-6,方解石(Ⅱ)的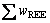 高于方解石(Ⅰ)。方解石(Ⅰ)的wLREE/wHREE为0.23~1.51,平均为0.80;w(La)N/w(Yb)N为0.09~0.67,平均为0.40,说明方解石(Ⅰ)轻重稀土分馏不明显。方解石(Ⅱ) 的w(LREE)/w(HREE)为0.46~1.08,平均为0.75;w(La)N/ w(Yb)N为0.14~0.58,平均为0.32,说明方解石(Ⅱ)轻重稀土分馏较方解石(Ⅰ)明显。方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(Eu)既有大于1也有小于1,大于1的为1.35~3.75,小于1的为0.53~0.71;方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(Eu)均大于1,为1.47~2.37。两期方解石δ(Ce)均在1.00附近。
高于方解石(Ⅰ)。方解石(Ⅰ)的wLREE/wHREE为0.23~1.51,平均为0.80;w(La)N/w(Yb)N为0.09~0.67,平均为0.40,说明方解石(Ⅰ)轻重稀土分馏不明显。方解石(Ⅱ) 的w(LREE)/w(HREE)为0.46~1.08,平均为0.75;w(La)N/ w(Yb)N为0.14~0.58,平均为0.32,说明方解石(Ⅱ)轻重稀土分馏较方解石(Ⅰ)明显。方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(Eu)既有大于1也有小于1,大于1的为1.35~3.75,小于1的为0.53~0.71;方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(Eu)均大于1,为1.47~2.37。两期方解石δ(Ce)均在1.00附近。
3.2 方解石C和O同位素分析结果
本次拉拉IOCG矿床方解石C和O同位素测定结果(表3)表明,方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(13CPDB)为-3.84‰~0,方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(13CPDB)为-3.98‰~-1.40‰,二者大小接近且相对变化较小。方解石(Ⅰ)的δ(18OSMOW)为9.45‰~12.2‰,方解石(Ⅱ)的δ(18OSMOW)为8.1‰~ 11.6‰,后者相对低于前者。
4 讨论
4.1 方解石成因及沉淀影响因素
矿床中两期方解石均具有较低的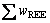 ,与大多数热液方解石是一致的[11];方解石C和O同位素组成亦与许多热液矿床中形成的碳酸盐类似[12],说明本矿床中的方解石具有热液成因特征。M
,与大多数热液方解石是一致的[11];方解石C和O同位素组成亦与许多热液矿床中形成的碳酸盐类似[12],说明本矿床中的方解石具有热液成因特征。M LLER等[13]研究认为,岩浆成因方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)一般大于100,热液成因方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)则常小于100;本矿床中两期方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)比值均小于1,也说明矿床中方解石具有热液成因特征。M
LLER等[13]研究认为,岩浆成因方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)一般大于100,热液成因方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)则常小于100;本矿床中两期方解石的w(La)/w(Yb)比值均小于1,也说明矿床中方解石具有热液成因特征。M LLER等[14]对不同成因碳酸岩的稀土元素研究发现:火成碳酸岩、热液碳酸岩(方解石)和沉积碳酸岩(灰岩)中的n(Yb)/ n(Ca)和n(Yb)/n(La)区别明显,n(Yb)/n(Ca)-n(Yb)/n(La)变化图能有效地判别方解石的形成及演化,本矿床两期方解石投点均落在热液成因区域内(图3)。综上认为,本矿床中两期方解石均为热液成因。
LLER等[14]对不同成因碳酸岩的稀土元素研究发现:火成碳酸岩、热液碳酸岩(方解石)和沉积碳酸岩(灰岩)中的n(Yb)/ n(Ca)和n(Yb)/n(La)区别明显,n(Yb)/n(Ca)-n(Yb)/n(La)变化图能有效地判别方解石的形成及演化,本矿床两期方解石投点均落在热液成因区域内(图3)。综上认为,本矿床中两期方解石均为热液成因。
热液方解石发生沉淀的影响因素主要有:1) 流体混合作用;2) CO2脱气作用;3) 流体与围岩之间的水—岩反应;4) 温压条件的变化。本矿床中两期方解石的δ(13CPDB)和δ(18CSMOW)变化范围均很窄,表明流体混合作用不是影响本矿床方解石沉淀的主要因素。若方解石沉淀是由CO2脱气作用所致,则因热液流体一般以 H2O 为主,CO2 的去气对流体O同位素组成的影响并不明显,而对C同位素组成的影响是显著的[15],从而形成的方解石C同位素组成变化也应显著;同时方解石中流体包裹体有流体沸腾迹象。在本矿床中,两期方解石的成矿流体C同位素变化不大,经流体包裹体研究未发现流体沸腾现象,所以,CO2脱气作用不是影响本矿床方解石沉淀的主要因素。在热液流体中,方解石的溶解度随温度的降低而升高、随压力的降低而降低[16],在封闭体系中的单纯冷却不能使方解石从热液流体中沉淀,故本矿床中方解石的沉淀应主要是由水-岩反应和温度降低耦合作用所致。
4.2 REE配分模式及其控制因素
热液矿物的REE配分模式一般受其晶体结构和热液体系中REE络合物稳定性的控制[23]。然而,近年来,越来越多的学者认为,热液矿物中REE配分模式并非受晶体化学因素的控制,而是与热液体系中REE络合物的稳定性密切相关[11, 18-19]。研究表明,方解石成矿热液中的REE主要是以络合物的形式存在的,且REE与CO32-和HCO3- 等形式的络合物的稳定性随着REE原子序数的增大而增加[19];REE进入热液方解石主要是通过REE3+与Ca2+之间的置换,由于LREE3+的离子半径比HREE3+的离子半径更接近于Ca2+的离子半径,从而使LREE比HREE更容易置换晶格中的Ca2+而进入方解石,REE在方解石—流体中的分配系数随其原子序数增加而减小[20]。因此,从热液体系中沉淀出的方解石应该是富LREE的。在许多热液矿床中,热液成因的方解石往往也表现出LREE 相对富集、HREE 相对亏损的右倾配分曲线特征。
表3 拉拉IOCG矿床方解石C-O同位素组成特征
Table 3 C-O isotopic composition of calcite from Lala IOCG deposit
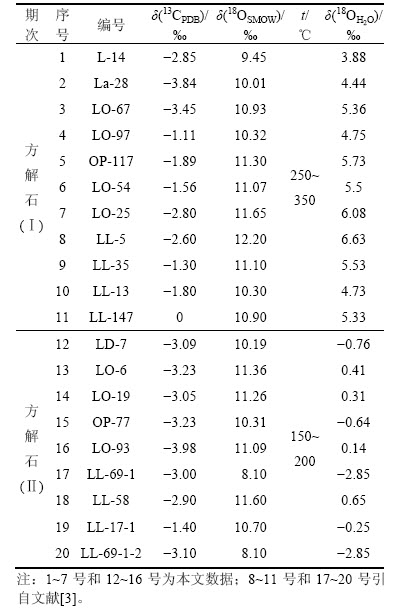
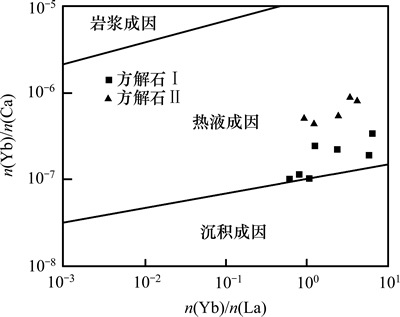
图3 拉拉IOCG矿床中方解石n(Yb)/n(Ca)与n(Yb)/n(La)的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between n(Yb)/n(Ca) and n(Yb)/n(La) of calcite from the Lala IOCG deposit
在本矿床中,方解石(Ⅰ)的球粒陨石标准化配分曲线为轻重稀土分异不明显的平坦型(球粒陨石值据文献[21]),即有正Eu异常,也有负Eu异常,基本无Ce异常(图4(a));方解石(Ⅱ)为HREE富集的左倾型,均为正Eu异常,基本无Ce异常(图4(b))。本矿床两期热液方解石配分模式不一致,且与一般热液方解石LREE明显富集的右倾配分曲线特征不符。虽然两期方解石的均一温度存在差异(表2),但成矿流体的温度并不改变热液矿物中REE配分系数的内部关系[22],因此,本矿床热液方解石的REE差异可能是由成矿流体本身性质引起的。
萤石的REE地球化学特征及矿相学研究表明,变质成矿期萤石+辉钼矿+碳酸盐阶段(Ⅲ),存在与方解石(Ⅰ)共生的高度富集LREE的萤石(Ⅱ)和独居石(Ⅲ)等矿物[7];在大量REE(特别是LREE)随萤石和独居石结晶沉淀后,残余的变质期成矿流体中LREE含量及REE总量已经很低,致使从中沉淀析出的方解石(Ⅰ)中LREE含量及REE总量很低、REE配分模式呈现 平坦型。所以,方解石(Ⅰ)的平坦型REE配分模式代表变质成矿期成矿过程中有大量LREE带出后的残余变质热液REE特征,其REE含量受残余流体中REE浓度影响,REE配分模式受流体中络合物稳定性控制。
然而在矿床热液成矿期,没有与方解石(Ⅱ)共生的LREE大量富集矿物,萤石(Ⅲ)虽为LREE富集型矿物,但其含量(平均51.07×10-6)比方解石(Ⅱ)(平均 313.85×10-6)低1个数量级,LREE随萤石沉淀对残余成矿流体REE配分模式影响权重较小,即流体中REE络合物的稳定性对方解石(Ⅱ)的REE配分模式影响程度很低,因此,推测方解石(Ⅱ)的左倾REE配分模式可能是受其晶体化学因素控制。彭建堂等[11]对锡矿山锑矿床中方解石晶体化学因素研究表明,HREE和MREE离子半径与方解石晶格中Ca2+半径(0.100 nm)相差较大,但与晶格中最佳位置的离子半径((0.091±0.001) nm)相似,该位置容纳能力较强,故MREE和HREE优先富集,分配系数高,致使配分模式为左倾型。所以方解石(Ⅱ)的REE特征可以反映热液期成矿流体REE特征,其REE配分模式受晶体化学因素控制。

图4 拉拉IOCG矿床方解石REE球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(球粒陨石值据文献[21])
Fig. 4 REE chondrite standardized distribution patterns of calcite from Lala IOCG deposit(value of chondrite after[21])
4.3 成矿流体来源及性质
4.3.1 REE指示意义
方解石(Ⅰ)的稀土平均总质量分数为75.98×10-6,远低于与其共生萤石(II)平均稀土总质量分数1 272.26×10-6[7],说明方解石(Ⅰ)不是该阶段REE的主要载体;方解石(Ⅱ) 稀土平均总质量分数为313.85×10-6,明显高于其共生萤石(Ⅲ)平均稀土总质量分数51.07×10-6[7],说明方解石(Ⅱ)为热液成矿期主要的REE载体之一。彭建堂等[23]研究表明,方解石的REE总量受成矿流体中REE浓度控制。本矿床中方解石(Ⅰ)的REE总质量分数很低,方解石(Ⅱ)则相对较高,据此推测沉淀方解石(Ⅰ)的流体中REE含量比较低,而沉淀方解石(Ⅱ)的流体中REE质量分数较高。
方解石(Ⅰ)即有正Eu异常也有负Eu异常,基本无Ce异常,其Ce和Eu异常特征与围岩和萤石(II)一致[7],加之其REE配分模式代表有LREE大量沉淀后的残余变质成矿流体,说明方解石(Ⅰ)应当继承了变质海相喷发火山岩的REE特征;方解石(Ⅰ)流体包裹体测温显示其具有较高的均一温度(250~350 ℃)(表2)。
SVERJENSKY[24]研究认为:当流体温度大于250 ℃时,流体中Eu3+离子被还原成Eu2+,出现Eu2+和Eu3+共存的现象,所以,方解石(Ⅰ)的成矿流体性质为大量LREE沉淀后的高温残余变质成矿流体。方解石(Ⅱ)与其共生萤石(Ⅲ)具有一致的强烈正Eu异常、基本无Ce异常特征,由于流体包裹体测温显示其结晶温度比较低(150~200 ℃)(表2),因此,其正Eu异常特征可能反映成矿流体具有较高氧逸度特征,方解石(Ⅱ)成矿流体性质为低温高氧逸度成矿流体。
BAU等[25]研究认为:方解石的w(Y)/w(Ho)和w(La)/w(Ho)能有效的判别成矿流体是否同源;同源脉石矿物在w(Y)/w(Ho)-w(La)/w(Ho)图解上呈现出水平分布的特征。从图5可以看出:本矿床中变质成矿期方解石(Ⅰ)和热液成矿期方解石(Ⅱ)位于2条不同的水平线上,说明两期方解石为不同源成矿流体产物;本矿床中两期方解石具有不同的REE总量、相关参数及配分模式,加之其不同的成矿期次及矿物共生组合,说明二者确为不同源产物,亦即变质期成矿流体与热液期成矿流体不同源。
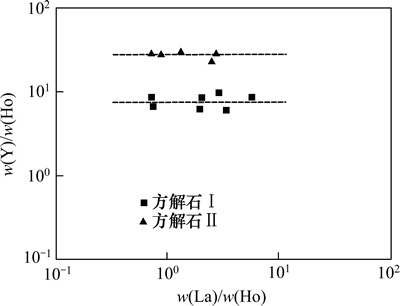
图5 方解石w(Y)/w(Ho)与w(La)/w(Ho)的关系
Fig. 5 Relationship between w(Y)/w(Ho) and w(La)/w(Ho) for calcite form Lala IOCG deposit
4.3.2 C-O同位素指示意义
研究表明,热液方解石的 C和O 同位素组成是示踪成矿流体来源的有效手段[9]。在通常情况下,成矿热液中的C主要有3种可能的来源:岩浆或地幔碳、沉积碳酸盐岩以及各类有机碳。OHMOTO[26]的研究认为:当矿床内热液脉中无石墨与方解石共生时,方解石(或包裹体热液中的CO2)的碳同位素组成(δ(13CPDB))可以近似作为成矿流体的总C同位素组成(δ(13CΣC))。由于本矿床中未发现与成矿有关的石墨等含碳物种,因此热液方解石的C同位素组成可以近似的看作成矿流体的总C同位素组成;两期方解石的δ(13CPDB)介于地幔C同位素值(-5‰±2‰)[27]和海水(沉积海相碳酸盐)δ(13CPDB)之间(-1‰~+2‰)[28],因而矿床中方解石的C可能是由深源C及海水C共同提供。对于O同位素,由于流体组分以H2O为主,故流体中水的氧同位素组成起主导作用。本次对矿床中两期方解石均一温度测定工作表明,方解石(Ⅰ)均一温度为250~350 ℃,方解石(Ⅱ)为150~200 ℃,分别取平均结晶温度为300 ℃和175 ℃,根据O’NEIL[29]建立的方解石与平衡流体之间在 0~700 ℃范围的O同位素分馏方程(1 000lnα方解石-水= 2.78×106/T2-2.89,T为热力学温度)计算得出:与变质成矿期方解石(Ⅰ)平衡的流体的δ(18OH2O)为 3.88 ‰~6.63‰(表3),与热液成矿期方解石(Ⅱ)平衡的流体的δ(18OH2O)为-2.85‰~0.65‰(表3),分别与孙燕等[5]测得的变质期和热液期流体的δ(18OH2O)变化范围一致,说明方解石(Ⅰ)的成矿流体为变质水、方解石(Ⅱ)的成矿流体可能有大气降水参与。
图6所示为与方解石平衡的流体的δ(13C)-δ(18O)图解。图6中,给出了地壳流体中CO2 的3大主要来源(有机质、海相碳酸盐岩和岩浆-地幔源)的C和O同位素值范围,用箭头标出了从这3个物源经8种主要过程产生CO2时,其同位素组成的变化趋势[30]。将本矿床两期方解石成矿流体的C和O同位素组成投在该图解中,可见方解石(Ⅰ)的C可能由火成碳酸岩和地幔包体等深源C提供,并受到海水渗透或混合作用影响;方解石(Ⅱ)的C则可能来源于基性-超基性岩浆分异释放的CO2,O同位素可能受大气降水影响发生明显负漂移。尽管这一结论未考虑到碳酸盐矿物沉淀时的各种同位素分馏过程,但总体趋势清楚。
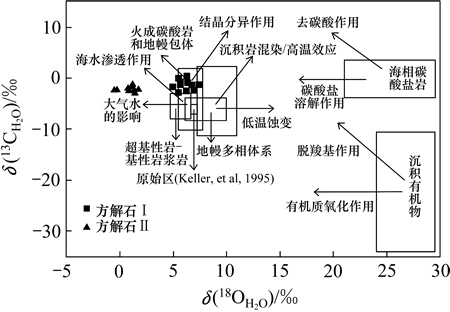
图6 与方解石平衡的流体的δ(13C)-δ(18O)图解 (底图据文献[30])
Fig. 6 Diagram of δ(13C) and δ(18O) for the fluids equilibrium with calcites from Lala IOCG deposit (modified after [30])
在古元古代末期,来自地幔深部的岩浆从海底喷 发-沉积形成本矿床原始的矿源层及围岩,在火山喷发-沉积过程中,受到海水流体的渗透和物质交换;中元古代末期,受全球尺度的Rodinia超大陆拼贴事件影响,扬子西南缘受挤压发生区域变质作用,变质作用过程中,各类围岩脱水形成高温变质成矿流体,流体演化至晚阶段,方解石(Ⅰ)受水岩交换反应和降温作用耦合与黄铜矿(Ⅲ)从LREE大量沉淀后的残余高温热液中顺围岩片理呈脉状晶出,所以,其C同位素具有深源C和海水C混合特征。在新元古代初期,地幔柱成因的基性辉长岩岩浆入侵到矿床地层中,致使地层中出现一系列的张性裂隙,由其分异演化出的CO2沿裂隙向上逃逸;大气降水和地下水下渗与围岩发生水岩交换反应形成热卤水,逃逸的CO2溶于热卤水中并发生O同位素交换反应,致使O同位素发生负漂移,同时加剧了流体渗透作用和水岩交换反应,在降温过程耦合作用下,方解石(Ⅱ)与黄铜矿(IV)沿裂隙呈脉状析出。
5 结论
1) 拉拉IOCG矿床中有方解石(Ⅰ)和方解石(Ⅱ)两期产出,方解石均为热液成因,结晶沉淀均受水—岩反应和温度降低耦合作用控制。
2) 方解石(Ⅰ)的REE配分模式为平坦型,受络合物稳定性控制;方解石(Ⅱ)的REE配分模式为左倾型,受晶体化学因素控制。
3) 方解石(Ⅰ)的C来自地幔深源C与海水中C的混合,其成矿流体为大量LREE分离沉淀后的高温残余变质成矿流体;方解石(Ⅱ)的C来自基性辉长岩演化分异释放的CO2,成矿流为大气降水与围岩反应形成的低温高氧逸度热卤水,O同位素发生负漂移。
参考文献:
[1] 李泽琴, 胡瑞忠, 王奖臻, 等. 中国首例铁氧化物-铜-金-铀-稀土型矿床的厘定及其成矿演化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2002, 21(4): 258-260.
LI Zeqin, HU Ruizhong, WANG Jiangzhen, et al. Lala Fe-Oxide-Cu-Au-U-REE ore deposit, Sichuan China-an example of superimposed mineralization[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2002, 21(4): 258-260.
[2] 朱志敏, 曾令熙, 周家云, 等. 四川拉拉铁氧化物铜金矿床(IOCG)形成的矿相学证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 2009, 15(4): 485-495.
ZHU Zhimin, ZENG Lingxi, ZHOU Jiayun, et al. Lala iron oxide-copper -gold deposit in Sichuan Province: evidence from mineralography[J]. Geological Journal of China University, 2009, 15(4): 485-495.
[3] CHEN Weiterry, ZHOU Meifu. Paragenesis, Stable Isotopes, and Molybdenite Re-Os Isotope Age of the Lala Iron- Copper Deposit, Southwest China[J]. Economic Geology, 2012, 107: 459-480.
[4] 陈根文, 夏斌. 四川拉拉铜矿床成因研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(1): 42-44.
CHEN Genwen, XIA Bin. Study on the genesis of Lala copper deposit, Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2001, 20(1): 42-44.
[5] 孙燕, 舒晓兰, 肖渊甫. 四川省拉拉铜矿床同位素地球化学特征及成矿意义[J]. 地球化学, 2006, 35(5): 553-559.
SUN Yan, SHU Xiaolan, XIAO Yuanfu. Isotopic geochemistry of the Lala copper deposit, Sichuan Province, China and its metallogenetic significance[J]. Geochimica, 2006, 35(5): 553-559.
[6] 陈好寿, 冉崇英. 康滇地轴铜矿床同位素地球化学[M].北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 29-84.
CHEN Haoshou, RAN Chongying. Isotope geochemistry of the Cu deposit in Kangdian basement[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992: 29-84.
[7] 黄从俊, 王奖臻, 李泽琴. 扬子西缘拉拉IOCG矿床萤石稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(1): 95-102.
HUANG Congjun, WANG Jiangzhen, LI Zeqin. REE geoche-mistry of fluorite from the Lala IOCG deposit, SW of Yangtze Block[J]. ActaMineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(1): 95-102.
[8] 黄从俊, 李泽琴, 王奖臻, 等. 拉拉铁氧化物-铜-金-铀矿床成矿时代分析[J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版) , 2012, 40(6): 80-84.
HUANG Congjun, LI Zeqin, WANG Jiangzhen, et al. Metallogenic epoch analysis of Lala Fe-Oxide-Cu-Au-U deposit [J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(6): 80-84.
[9] 沈能平, 彭建堂, 袁顺达, 等. 湖北徐家山锑矿床方解石C、O、Sr同位素地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(5): 479-485.
SHEN Nengping, PENG Jiantang, YUAN Shunda, et al. Carbon, oxygen and strontium isotope geochemistry of calcites from Xujiahsan antimony deposit, Hubei Province[J]. Geochemica, 2007, 36(5): 479-485.
[10] 王奖臻, 李泽琴, 黄从俊. 康滇地轴元古代重大地质事件与拉拉IOCG矿床成矿响应[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(10): 1074-1079.
WANG Jiangzhen, LI Zeqin, HUANG Congjun. The main geological events of the kangdian Proterozoic eon and response from to the Lala IOCG deposit[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(10): 1074-1079.
[11] 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 漆亮, 等. 锡矿山热液方解石的REE分配模式及其制约因素[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(1): 25-32.
PENG Jiantang, HU Ruizhong, QI Liang, et al. REE distribution pattern for the hydrothermal calcites from the Xikuangshan antimony deposit and its constraining factors[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(1): 25-32.
[12] RYE R O, OHMOTO H. Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: A review [J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69: 826-842.
[13] M LLER P, MORTEANI G, SCHLEY F. The application of Tb/Ca-Tb/La abundance ratios t problems of fluorspar genesis[J]. Mineral Deposita, 1976, 11: 111-116.
LLER P, MORTEANI G, SCHLEY F. The application of Tb/Ca-Tb/La abundance ratios t problems of fluorspar genesis[J]. Mineral Deposita, 1976, 11: 111-116.
[14] M LLER P, MORTEANI G. On the geochemical fractionation of rare earth elements during the formation of Ca-minerals and its application to problems of the genesis of ore deposits[C]// AUGUSTHITIS S S, ed. The Significance of Trace Elements in Solving Petrogenetic Problems and Controversies. Theophrastus, Athens, 1983: 747-791.
LLER P, MORTEANI G. On the geochemical fractionation of rare earth elements during the formation of Ca-minerals and its application to problems of the genesis of ore deposits[C]// AUGUSTHITIS S S, ed. The Significance of Trace Elements in Solving Petrogenetic Problems and Controversies. Theophrastus, Athens, 1983: 747-791.
[15] 郑永飞, 陈江峰. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 289-296.
ZHENG Yongfei, CHEN Jiangfeng. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Publishing House, 2000, 289-296.
[16] BARNES H L. Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits[M]. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1997, 971-972.
[17] MORGAN J W, WANDLESS G A. Rare earth element distribution in some hydrothermal minerals: Evidence for crystallographic control[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44: 973-980.
[18] LOTTERMOSER B G. Rare earth elements and hydrothermal ore formation processes[J]. Ore Geology Review, 1992, 7: 25-41.
[19] HAAS J R, SHOCK E L, SASSANI D C. Rare earth elements in hydrothermal systems: estimates of standard partial molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous complexes of the rare earth elements at high pressures and temperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59: 4329-4350.
[20] RIMSTIDT J D, BALOG A, WEBB J. Distribution of trace elements between carbonate minerals and aqueous solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62: 1851-1863.
[21] SUN S S, MCDNOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implicaions for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[22] GRAF J L. Effects of Mississippi Valley-Type mineralization on REE patterns f carbonate rocks and minerals, Viburnum Trend, southeast Missouri[J]. Geology, 1984, 92(3): 307-324.
[23] 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 漆亮, 等. 晴隆锑矿床中萤石的稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(3): 277-287.
PENG Jiantang, HU Ruizhong, QI Liang, et al. REE geochemistry of fluorite from the Qinlong antimony deposit and its geological implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2002, 37(3): 277-287.
[24] SVERJENSKY D A. Europium equilibria in aqueous solution[J]. Earth Planet Science Letter, 1984, 67(1): 70-78.
[25] BAU M, DULSKI P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviors in fluorite-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 1995, 119: 213-223.
[26] OHMOTO H, RYE R O. Isotopes of sulphur and carbon[C]// BARNES HL, ed. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. New York: Wiley, 1979: 509-567.
[27] ZHENG Yongfei. Carbon and oxygen isotopic covariations in hydrothermal calcites[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1993, 28: 79-89.
[28] VEIZER J, HOLSER W T, WILGUS C K. Correlation of 13C/12C and 34S/32S secular variation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(4): 579-587.
[29] O’NEIL J R, CLAYTON R N, MAYEDA T K. Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1969, 51: 5547-5558.
[30] 刘家军, 何明勤, 李志明, 等. 云南白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区碳氧同位素组成及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(1): 1-10.
LIU Jiajun, HE Mingqin, LI Zhiming, et al. Oxygen and carbon isotopic geochemistry of Baiyangping sliver-copper-polymetallic ore concentration are in Lanping basin of Yunnan Province and its significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2004, 23(1): 1-10.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2016-01-12;修回日期:2016-03-27
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(41072065);教育部博士点基金资助项目(20105122110001);中国地质调查局项目(12120113095500) (Project(41072065) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20105122110001) supported by the Doctoral Program of the Ministry of Education of China; Project(12120113095500) supported by the China Geological Survey)
通信作者:李泽琴,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事矿床地球化学研究;E-mail: lzq@cdut.edu.cn