对含铅及高铁固体废物还原造锍熔炼炉渣和铁锍的环境评价
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第10期
论文作者:柴立元 吴见珣 吴延婧 唐朝波 杨卫春
文章页码:3429 - 3435
Key words:reducing-matting smelting; lead-bearing waste; heavy metal; environmental risk
摘 要:还原造锍熔炼技术是可综合回收利用高铁、含铅固体废物的一种新技术。其主要副产物是炉渣和铁锍。采用浸出毒性实验、BCR三步连续浸提以及Hakanson潜在生态风险评价等方法系统地对还原造锍主要副产物和进炉炉料中重金属(Cd、Zn、Pb和As)的环境风险进行评价。结果表明,经过还原造锍熔炼后,水淬渣和铁锍中重金属潜在的环境生态风险明显比进炉炉料的低。
Abstract: A new process for utilization of hazardous lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes by reducing-matting smelting has been developed. The slag (SG) and the iron-rich matte (IRM) are the main by-products from reducing-matting smelting of lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes. The environmental risk of heavy metals (Cd, Zn, Pb and As) in the main by-products versus the charging material for reducing-matting smelting (CM) has been systematically assessed using leaching toxicity test, the three-stage sequential extraction procedure of European Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) and Hakanson Potential Ecological Risk Index Method (PERI). The results demonstrate that the ecological risk level of heavy metals for SG and IRM is significantly reduced after the reducing-matting smelting process compared with that for CM.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3429-3435
Li-yuan CHAI1,2, Jian-xun WU1, Yan-jing WU1, Chao-bo TANG1,2, Wei-chun YANG1,2
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control and Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 17 November 2014; accepted 10 March 2015
Abstract: A new process for utilization of hazardous lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes by reducing-matting smelting has been developed. The slag (SG) and the iron-rich matte (IRM) are the main by-products from reducing-matting smelting of lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes. The environmental risk of heavy metals (Cd, Zn, Pb and As) in the main by-products versus the charging material for reducing-matting smelting (CM) has been systematically assessed using leaching toxicity test, the three-stage sequential extraction procedure of European Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) and Hakanson Potential Ecological Risk Index Method (PERI). The results demonstrate that the ecological risk level of heavy metals for SG and IRM is significantly reduced after the reducing-matting smelting process compared with that for CM.
Key words: reducing-matting smelting; lead-bearing waste; heavy metal; environmental risk
1 Introduction
Each year, significant amounts of iron-rich wastes and lead-bearing wastes are generated. For example, over 1×107 t of pyrite cinders are generated annually in China [1]. In 2012, 5.47×105 t of various lead-bearing wastes (such as lead soot, lead mud, lead sulfate slag and smelting slag of waste batteries) were produced from non-ferrous metal smelting and rolling processing industry in China [2]. These wastes contain high levels of iron oxides or lead and a bit of rare expensive elements (Au, Ag), but their compositions are very complicated and include considerable various harmful elements such as As, Cd and Zn, which limit their usage in pig iron industry and lead smelting industry. At present, almost all of these wastes are dumping as solid wastes, causing resource waste and serious environmental pollution [3].
In recent decades, many techniques have been developed to recover lead from lead-bearing wastes, including flotation [4], leaching [5,6], and reduction smelting [7,8]. However, application of these techniques has been limited by factors such as high costs, technical difficulty, relatively low recovery ratio and serious secondary pollution. For example, the widely used reduction smelting process has the problems such as excessive emission of SO2 and lead dust, and high energy consumption [7].
A new process for utilization of these hazardous lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes by reducing-matting smelting has been developed. In this process, using iron oxides in the wastes (such as pyrite cinder) as sulfur-fixed agent, the reducing-matting smelting of the lead-bearing wastes can be used for the recovery of lead and precious metals without SO2 emission, while the sulfur in the wastes could be stabilized in the form of matte [9,10]. Due to its advantages such as process simplicity, high efficiency, low pollution, this technology has a promising application prospect in the utilization of lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes and has been selected in the “advanced and applicable technologies catalog for industrial solid waste utilization” released by Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China (MIIT) in 2013 [11].
Besides lead bullion, there are three other products, iron-rich matte, slag and soot, from the reducing-matting smelting of lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes. These by-products contain residual metals such as As and Cd, and probably pose potential risks to the environment. However, so far, no systematic environmental risk assessment has been conducted for this new process. To obtain a more comprehensive understanding of this new technology, it is necessary to systematically quantify the heavy metal hazards in the by-products from the reducing-matting smelting.
In this work, the chemical speciation analyses of heavy metals and two typical assessment models, the potential ecological risk index (PERI) [12] and the risk assessment code (RAC) [13], were used to assess the degree of heavy metal pollution in the by-products from the reducing-matting smelting of lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes. Because the amount of the soot generated is small, only accounting for about 5% of the by-products, and the soot can be used as auxiliary material returning to the smelting furnace, only the iron-rich matte (IRM) and slag (SG) were evaluated. Moreover, the same analyses were performed on the charging material of reducing-matting smelting (CM) (which is mainly composed of the lead-bearing solid wastes and iron-rich wastes) for comparison.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
The samples (IRM, SG and CM) used for testing were obtained from a reducing-matting smelting plant for the lead-bearing waste in Hunan Province, China. The smelting plant has handled 90 t lead-bearing and iron-rich wastes in reverberatory furnace a day, and 40-50 t slag, 15 t IRM, 4-5 t soot would be produced in normal smelting conditions. The technological process is developed by RAO et al [14]. Rude lead can be obtained from the bottom of furnace, matte can be separated from slag due to the different density, the soots are collected from dust collection system of reverberatory furnace, and then all soots which contain a large amount of lead (40%) would be sent to mix with lead-bearing and iron-rich wastes and return to furnace again. Only the IRM and SG were investigated in this work because they were the by-products directly disposed into the environment after smelting.
The samples were collected every day in smelting cycle (4 d) for three smelting cycles when the lead- bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes were processed under normal production conditions. All solid samples were taken at the outlet except the soot which would be returned to furnance. All samples were air-dried, then sieved to less than 2 mm, and stored. All chemicals used were of analytical reagent grade.
2.2 Analyses
The total content of heavy metals could be obtained by the digestion developed by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA, Method 3052) [15], and elemental compositions were analyzed for Cd, Zn, Pb, Fe, S and As using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, IRIS Intrepid II XSP, Thermo Electron Corporation). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained using Rigaku D/Max-RB diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ=0.15406 nm, 35 kV, 40 mA). The pH was measured in sample extracts (solid/distilled water ratio 1:20, ratio of mass to volume) using a pH meter (FE20) [16]. The pH values were 6.21, 8.04 and 5.77 for SG, IRM and CM, respectively.
2.3 Contamination assessment methodology
Leaching procedure: The toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) developed by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) was used to simulate the leaching of contaminated materials by organic acid leachates [17]. The purpose of this analysis was to predict the long-term behavior of heavy metals. As the pH was found to be higher than 5.0 for all samples, the TCLP leaching was carried out by extraction fluid of sodium acetate solution (liquid-to- solid ratio, 20:1) in a plastic container. Moreover, the H2SO4-HNO3 leaching was used to simulate leaching characteristics of contaminated materials under specified conditions of acid rain. It was carried out by extraction fluid of mixed solution (mass ratio of H2SO4 to HNO3, 2:1) at pH 3.20±0.05 with liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 [18]. All the tests were conducted in a standard tumbler and operated at 163 r/min for 18 h. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate to ensure the reproducibility, and the concentrations of heavy metals were determined by ICP-OES.
Sequential extraction procedure: The adopted sequential extraction test was improved over the sequential extraction procedure proposed by the European Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) based on the Tessier analysis method [19]. Besides soils and sediments, the three-stage BCR has also been applied to evaluating the environmental availability of heavy metals in sewage sludge [20], mine tailings [21] and smelting slag [22,23]. Details of the experiment protocol were introduced by DAVIDSON et al [24].
Potential ecological risk index (IPER): The IPER is also introduced to assess the contamination degree of heavy metals in the products from the reducing-matting smelting.
In this work, only the acid soluble and reducible fractions were used to assess the contamination degree of heavy metals in the by-products from the reducing- matting smelting [25]. The formulas of the IPER were listed below:
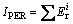 (1)
(1)
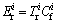 (2)
(2)
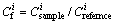 (3)
(3)
where IPER is calculated as the sum of all risk indices for heavy metals in the samples, 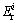 is the monomial potential ecological risk index,
is the monomial potential ecological risk index,  is the toxic response-factor for a given heavy metal,
is the toxic response-factor for a given heavy metal, 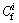 is the single heavy metal pollution index,
is the single heavy metal pollution index, 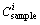 is the concentration of heavy metal in the samples (mg/kg), and
is the concentration of heavy metal in the samples (mg/kg), and 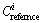 is the reference value for metals (mg/kg).
is the reference value for metals (mg/kg).
The values of 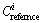 for Pb, As, Cd and Zn are 500, 40, 1.0, 500 mg/kg, respectively, which come from the Grade III standard of the environmental quality standard for soil [26]. The values of toxic response-factor
for Pb, As, Cd and Zn are 500, 40, 1.0, 500 mg/kg, respectively, which come from the Grade III standard of the environmental quality standard for soil [26]. The values of toxic response-factor 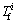 for Pb, As, Cd and Zn are 5, 10, 30 and 1, respectively, which come from HAKANSON [12]. Five categories of
for Pb, As, Cd and Zn are 5, 10, 30 and 1, respectively, which come from HAKANSON [12]. Five categories of 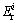 and four classes of the IPER were defined as shown in Table 1 [12].
and four classes of the IPER were defined as shown in Table 1 [12].
Table 1 Classification criteria of 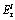 and IPER
and IPER

Risk assessment code (RAC): The RAC was used to estimate the environment risk of heavy metal pollution in SG, IRM and CM. The RAC assesses the availability of heavy metals by applying a scale to the percentage of heavy metals in acid soluble fractions (F1) [18,27]. The classification of risk has been assorted in terms of RAC. When the RAC value is less than 1%, the sample does not represent a risk for the aquatic environment, while values between 1% and 10% reflect a low risk, values between 11% and 30% reflect a moderate risk, and values between 31% and 50% reflect high risk. Values higher than 50% imply a very high risk.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Chemical composition
The chemical compositions for SG, IRM and CM are listed in Table 2. The total content of Pb in SG and IRM was significantly less than that in CM. This can be attributed to the high recovery of Pb in the reducing- matting smelting [9,10]. Moreover, the total contents of Cd in SG and IRM were low with only 0.01% and 0.02%, respectively, while that in CM was relatively high, being 0.83%. It can be explained that Cd was volatile, and could become gaseous at high temperature, causing it to condense into the soot. It was also found that As was enriched in IRM, and its content reached 5.63%. It may be due to the high content of Fe in IRM (48.81%). However, the total metal concentrations cannot afford accurate information for their mobility, biological availability and potential toxicity, which are primarily determined by their specific chemical forms or ways of binding. Therefore, further research is necessary.
Table 2 Chemical compositions of CM, SG and IRM

3.2 Leachable metal concentrations
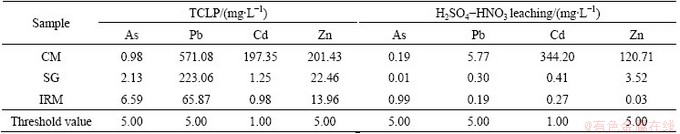
Leachable metal concentrations for SG, IRM and CM as determined by TCLP test and H2SO4-HNO3 leaching test are listed in Table 3. For CM, the concentrations of Pb, Cd and Zn in TCLP extract exceeded the respective threshold values [16]. The concentrations of Cd, Pb and Zn extractable by TCLP declined both in SG and IRM. In particular, leachable Cd concentration was reduced from 197.35 mg/L in CM to 1.25 mg/L in SG and 0.98 mg/L in IRM. Leachable Zn concentration was reduced from 201.43 mg/L in CM to 22.46 mg/L in SG and 13.96 mg/L in IRM. According to the H2SO4-HNO3 leaching test, the leachable concentrations for all these metals in SG and IRM decreased significantly compared to those in CM, and were under the acceptable threshold values [16]. The lower leachable concentrations of Pb, Cd and Zn in IRM and SG compared to CM may be due to the following reasons: 1) because of the high recovery of Pb, the total content of Pb is low in SG and IRM; 2) the high content of Fe which is alkali metal has a strong buffering for acid solution to deduce the leaching of heavy metals; 3) on the other hand, As would be absorbed by the iron of the solution so that the ability of As dissolving into solution decreases, however, the concentration of As in IRM is higher than the limited value, because of large amount of As contained in IRM. This indicates that the leaching toxicity of the lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes decreases sharply after the reducing-matting smelting treatment.
Table 3 Leachable metal concentrations based on TCLP test and H2SO4-HNO3 leaching test
3.3 Speciation of heavy metals
The bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals mainly depend on their speciation [22,28]. The acid soluble fraction (F1) is a loosely bound phase and is liable to change with environmental conditions such as pH changes. Meanwhile, the reducible fraction (F2) is thermodynamically unstable and available under anoxic conditions. Two fractions (F1 and F2) are defined as direct effect phases which are more harmful to the environment. The oxidizable fraction (F3) containing metals binding to organic matter and metals in the sulfide combination state can be mobilized and transformed to F1 or F2 in oxidizing condition. Thus, it is identified as a potential effect fraction. The residual fraction (F4) is a stable fraction in which the metals are not expected to be released in solution under environmental conditions. The speciation of Pb, As, Cd and Zn represented as percent of total concentrations is shown in Fig. 1. In general, there was a good agreement between the sums of the fractions and the total metal contents, with recovery ratios in the range of 90%-105%.
Pb is one of the most important metals in this work because of its significant presence in all samples. It would be found that the proportion of Pb in F3 fraction increased, and less Pb existed in the form of F2 because of strong reducing atmosphere in the smelting. Pb mainly existed in F4 fraction in CM, accounting for 89.95% of its total content. The proportion of Pb in F4 fraction was 39.95% in SG and 62.90% in IRM. This may be because most of Pb in CM existed in the form of PbSO4 according to the XRD pattern (Fig. 1(a)), which was transformed into metallic Pb after the reducing-matting smelting treatment [14].
PbSO4+FeO+C=Pb+FeS+CO (4)
PbSO4+FeO+CO=Pb+FeS+CO2 (5)
It is shown by XRD (Fig. 1(b)) that Pb in IRM is in the form of metallic Pb and PbO. PbSO4 is more stable in acid environment than metallic Pb or PbO [29]. The XRD pattern for SG is not shown as SG existed in amorphous form.
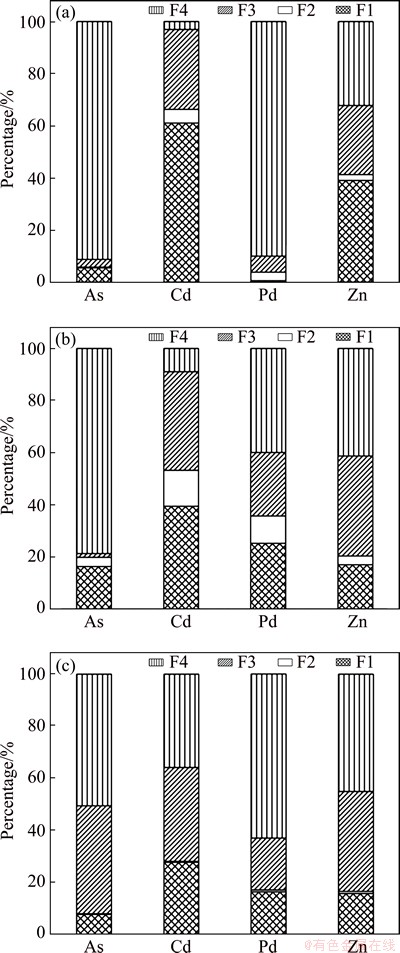
Fig. 1 Speciation of heavy metals in CM (a), SG (b) and IRM (c)
Cd is mainly associated to the two fractions with direct toxicity to the environment (F1 and F2) in CM (66.33%). Only 3.06% of total Cd in CM was associated with F4 fraction. Meanwhile, the proportions of Cd in F1 and F2 fractions were 53.28% in SG and 28.16% in IRM. The proportions of Cd in F4 fraction were 8.98% in SG and 35.82% in IRM. According to these results, it may be concluded that the Cd in SG and IRM was more stable than that in CM.
For As, high content in F4 fraction was found in all the samples, especially for CM, up to 91.21% of As existing in the F4 fraction. The proportions of As in the direct effect phases (F1 and F2) were 19.89% in SG and 8.17% in IRM, which suggested a high direct toxicity to the environment. In addition, the proportions of As in F3 fraction were 1.42% in SG and 41.31% in IRM. Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns for CM and IRM. XRD analysis of IRM indicated the presence of Fe2As, FeS as the predominant crystalline phases, and Fe, FeO and Pb were detected at the same time. Arsenic would be reduced to zero-valent arsenic and trivalent arsenic when it reacted with iron in the reducing atmosphere [30]. The arsenic would stay mainly in the form of arsenate for SG, it has been proved that As(V) binds more strongly with the metal oxides of Fe and Mn, as compared with the As(III) species. As(V) species are also less soluble and toxic as compared to the reduced form As(III). Hence, As in the by-products from the reducing-matting smelting, especially for IRM, presented a significant environmental risk due to their direct and potential eco-toxicity and bioavailability.
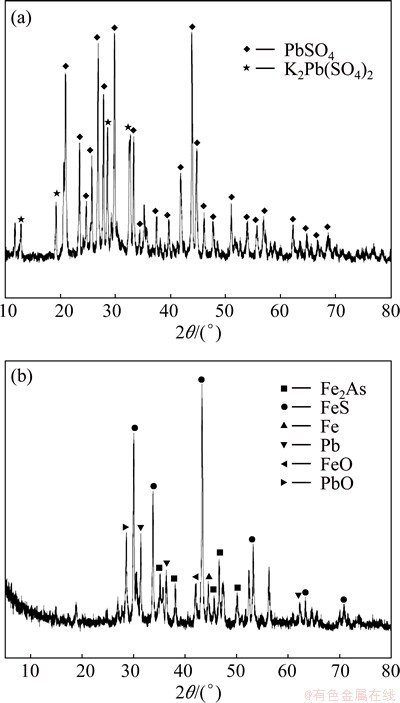
Fig. 2 X-ray diffraction patterns for CM (a) and IRM (b)
The percentages of Zn in CM distributed in F1 and F2 were 39.04% and 2.29%, respectively. The amounts bound to the direct effect phases (F1 and F2) in SG and IRM were greatly reduced compared with the amount in CM. These results indicated that the stability of Zn in SG and IRM was greater than that in CM.
3.4 Environment risk assessment based on RAC
The results of the environmental risk assessment according to RAC are shown in Fig. 3. The percentages of heavy metals in acid soluble fraction (F1) for CM ranged from the highest to the lowest in the order: Cd>Zn>As>Pb. Accordingly, Cd posed a very high risk to the ecosystem, Zn posed a high risk, As posed a low risk, and Pb posed no risk. Meanwhile, metals associated with the F1 fraction decreased in the order Cd>Pb> Zn>As for SG and IRM. The heavy metals of Pb, Zn and As in SG were all categorized as having moderate risk to the environment, and Cd presented a high risk. For IRM, Pb, Cd and Zn presented moderate risk, As presented a low risk. However, the classification of RAC only considered the percentages of F1, ignoring the proportions of the reducible fraction (F2), the oxidizable fraction (F3) and the toxicity of the metal.
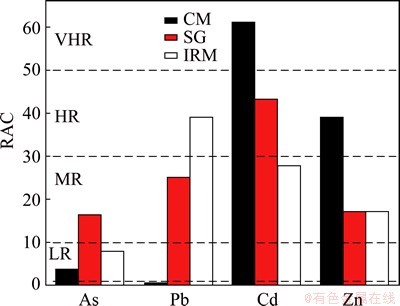
Fig. 3 Environmental risk assessment (RAC) for CM, SG and IRM
3.5 Potentially ecological risk assessment based on PERI
The results of potential ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in CM, SG and IRM are shown in Table 4. As for the single-factor pollution, the potential ecological risk level of Cd in all the samples was classified as serious risk, which posed a serious risk to the environment. Especially for CM, the potentially ecological risk index (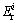 ) of Cd was 1.54×105. The potential risk level of Zn was low in all the samples based on the
) of Cd was 1.54×105. The potential risk level of Zn was low in all the samples based on the 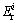 values.
values.
Table 4 Potential ecological risk indices of single elements and PERIs for samples
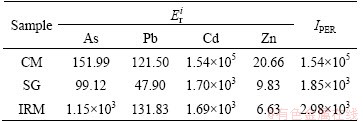
The comprehensive potential ecological risk indices (IPER) of all the samples were greater than 600, indicating that the ecological risk level was serious. The main donation of IPER came from Cd for all the samples. CM had the maximum IPER value of 1.54×105. This value was two orders of magnitude higher than those for SG and IRM, suggesting that the ecological risk level for CM was much more serious than that for SG and IRM.
4 Conclusions
1) The leachable concentrations of the four metals (Cd, Zn, Pb and As) in SG and IRM by TCLP test and H2SO4-HNO3 leaching test were much lower than those in CM, except for the leachable As concentration by TCLP test. This indicated that the leaching toxicity of the lead-bearing wastes and iron-rich wastes decreased after the reducing-matting smelting treatment.
2) According to the BCR results, the heavy metals of Zn and Cd were transformed into the more stable fractions after the reducing-matting smelting, however, As in the by-products from the reducing-matting smelting process, especially for IRM, presented a significant environmental risk due to their direct and potential eco-toxicity and bioavailability.
3) The overall risk indexes calculated for the four metals were 1.54×105, 1.85×103 and 2.98×103 in CM, SG and IRM, respectively, while Cd is the main donation. The ecological risk levels for SG and IRM were significantly reduced after the reducing-matting smelting process compared with CM. In general, the environmental risk of heavy metals in SG and IRM was relatively low. The reducing-matting smelting process is a potentially effective technology for both recovering metal and protecting the environment.
4) The data in this work would be helpful to the management of the by-products from reducing-matting smelting process with lead-bearing solid wastes and iron-rich wastes. It is also concluded that some efforts should be made to improve the reducing-matting smelting process at environmental protection.
References
[1] LIU Zhao-cheng, ZHENG Ya-jie. Effect of Fe(II) on the formation of iron oxide synthesized from pyrite cinders by hydrothermal process [J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 209: 119-123.
[2] Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. The 2012 State of Environment Report [EB/OL] [2013-12-25]. http://www.mep.gov.cn/zwgk/hjtj/.
[3] ZHU Han-na, YUAN Xing-zhong, ZENG Guang-ming, JIANG Min, LIANG Jie, ZHANG Chang, YIN Juan, HUANG Hua-jun, LIU Zhi-feng, JIANG Hong-wei. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(7): 1470-1477.
[4] RASHCHI F, DASHTI A, ARABPOUR-YAZDI M, ABDIZADEH H. Anglesite flotation: A study for lead recovery from zinc leach residue [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(2): 205-212.
[5] RAGHAVAN R, MOHANAN P K, SWAMKAR S R. Hydrometallurgical processing of lead-bearing materials for the recovery of lead and silver as lead concentrate and lead metal [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 58(2): 103-116.
[6] LIU Qing, YANG Sheng-hai, CHEN Yong-ming, HE Jing, XUE Hao-tian. Selective recovery of lead from zinc oxide dust with alkaline Na2EDTA solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(4): 1179-1186.
[7] GENAIDY A M, SEQUEIRA R, TOLAYMAT T, KOHLERC J, RINDERD M. Evidence-based integrated environmental solutions for secondary lead smelters: Pollution prevention and waste minimization technologies and practices [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(10): 3239-3268.
[8] OKADA T, YONEZAWA S. Reduction–melting combined with a Na2CO3 flux recycling process for lead recovery from cathode ray tube funnel glass [J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(8): 1470-1479.
[9] HUANG Chao, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming, TANG Mo-tang, ZHANG Duo-mo. Thermodynamics analysis on reducing-matting smelting of suifide ore of lead, antimony and bismuth which using ferric oxide as sulfur fixed agent [J]. Sohn International Symposium on Advanced Processing of Metals and Materials, 2006, 34(8): 387-398.
[10] YANG Sheng-hai, TANG Guo-liang, AI Qing-ping, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming, AI Guo-sheng, HU Guo-quan, HE Jing, KUANG Jian-xiong, YANG Jian-guang. A clean method and equipment for utilization of lead-bearing wastes by blast furnace reducing- matting smelting: China, 201110048459.5 [P]. 2011-08-17. (in Chinese)
[11] Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China. Advanced and Applicable Technologies Catalog for Industrial Solid Waste Utilization [EB/OL] [2013-04-12]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/ n11293472/ n11293832/n12845605/n13916898/15337300.html.
[12] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.
[13] SUNDARAY S K, NAYAK B B, LIN S, BHATTA D. Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2-3): 1837-1846.
[14] YAO Wei-yi, TANG Chao-bo, TANG Mo-tang, LI Zeng-rong, LIU Feng-cheng. One-stage smelting lead from lead sulfide concentrates in reverberatory furnace without sulfur dioxide [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001, 11(6): 1127-1130.
[15] USEPA Method 3052. Microwave assisted acid digestion and organically based matrices [S].
[16] GB/T 15555.12—1995. Solid waste-glass electrode test—Method of corrosivity [S]. (in Chinese)
[17] USEPA Method 1311. Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) [S].
[18] HJ/T 299—2007. Solid waste-extraction procedure for leaching toxicity-sulphuric acid & nitric acid method [S]. (in Chinese)
[19] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851.
[20] GUSIATIN Z M, KULIKOWSKA D. The usability of the IR, RAC and MRI indices of heavy metal distribute on to assess the environmental quality of sewage sludge composts [J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34: 1227-1236.
[21] ANJU M, BANJEE D K. Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for heavy metal partitioning in mine tailings [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(11): 1393-1402.
[22] XIE Xian-de, MIN Xiao-bo, CHAI Li-yuan, TANG Cong-jian, LIANG Yan-jie, LI Mi, KE Yong. CHEN Jie, WANG Yan. Quantitative evaluation of environmental risks of flotation tailings from hydrothermal sulfidation–flotation process [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 20: 6050-6058.
[23] LU Li-li, LI Dong-wei, ZHU Fang-zhi. Study on the morphological analysis of heavy metals of the smelting slag for lead and zinc [J]. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 2011, 15: 164-168.
[24] DAVIDSON C M, DUNCAN A L, LITTLEJOHN D, URE A M, GARDEN L M. A critical evaluation of the three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure to assess the potential mobility and toxicity of heavy metals in industrially-contaminated land [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1998, 363(1): 45-55.
[25] HUANG Hua-jun, YUAN Xing-zhong, ZENG Guang-ming, ZHU Han-na, LI Hui, LIU Zhi-feng, JIANG Hong-wei, LENG Li-jian, BI Wen-kai. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(22): 10346-10351.
[26] GB15618—1995. Environmental quality standard for soils [S]. (in Chinese)
[27] ZHOU Yun, NING Xun-an, LIAO Xi-kai, LIN Mei-qing, LIU Jing-yong, WANG Jiang-hui. Characterization and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals found in fly ashes from waste filter bags obtained from a Chinese steel plant [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 95: 130-136.
[28] LARIOS R, FEMANDEZ-MARTINEZ R, SILVA V, RUCANDIO I. Chemical availability of arsenic and heavy metals in sediments from abandoned cinnabar mine tailings [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68: 535-546.
[29] VOLPE M, OLIVERI D, FERRARA M, SALVAGGIO M, PIAZZA S, ITALIANO S, SUNSERI C. Metallic lead recovery from lead-acid battery paste by urea acetate dissolution and cementation on iron [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 96(1-2): 123-131.
[30] ZHANG Shu-hui,  Qing, HU Xiao. Thermodynamics of arsenic removal from arsenic-bearing iron ores [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(7): 1705-1708. (in Chinese).
Qing, HU Xiao. Thermodynamics of arsenic removal from arsenic-bearing iron ores [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(7): 1705-1708. (in Chinese).
柴立元1,2,吴见珣1,吴延婧1,唐朝波1,2,杨卫春1,2
1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,长沙 410083
摘 要:还原造锍熔炼技术是可综合回收利用高铁、含铅固体废物的一种新技术。其主要副产物是炉渣和铁锍。采用浸出毒性实验、BCR三步连续浸提以及Hakanson潜在生态风险评价等方法系统地对还原造锍主要副产物和进炉炉料中重金属(Cd、Zn、Pb和As)的环境风险进行评价。结果表明,经过还原造锍熔炼后,水淬渣和铁锍中重金属潜在的环境生态风险明显比进炉炉料的低。
关键词:还原造锍熔炼;含铅固体废物;重金属;环境风险
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (2012BAC12B02) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China; Project (2014FJ1011) supported by the Key Projects of Science and Technology of Hunan Province, China; Project (2011AA061001) supported by the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China
Corresponding author: Wei-chun YANG; Tel: +86-731-88830875; Fax: +86-731-88710171; E-mail: yang220@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63978-4

