
Thermal decomposition and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite ceramic
YANG Chun(杨 春)1, 2, GUO Ying-kui(郭英奎)1, ZHANG Mi-lin(张密林)2
1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150080, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
Received 10 February 2009; accepted 4 May 2009
Abstract: Pure hydroxyapatite (HAP) ceramic and HAP composite ceramic with B2O3 were prepared by isostatic press forming and pressureless sintering. The relationships between thermal decomposition ratio and mechanical properties for pure HAP ceramic and the composite ceramic were investigated by means of FTIR, X-ray diffraction and three-point bending method. The results indicate that the decomposition ratio of pure HAP ceramic increases with ascending the sintering temperature and nearly reaches 80% at 1 350 ℃. For the HAP composite ceramic, the thermal decomposition is inhibited obviously due to the addition of B2O3. The added B atoms incorporate into the crystal lattice of HAP to form solid solution, resulting in an enlargement in the crystal spacing and an improvement in the binding strength of HAP crystal cell. Thermal decomposition ratio of HAP decreases but bending strength and fracture toughness are enhanced for HAP composite ceramics. However, when the added B2O3 is more than 5% (mass fraction), HAP decomposition is promoted and a steady β-TCP is formed due to the fact that when B atoms with higher negative electricity are combined with O, sp2 and a full-air p are formed, and those voids have a strong trend to intake of the outer electrons. So, it is very possible to occupy the place where HAP loses OH- or PO43-.
Key words: B2O3; hydroxyapatite ceramic; thermal decomposition; bending strength; fracture toughness
1 Introduction
Hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, HAP) is the principal inorganic component of bones and teeth, which gets 72% and 97%, respectively. HAP possesses more excellent biocompatibility and interactive bioactivity than biomedical Ti alloys, silastic and carbon materials. It is the most typical bioactive material[1-3] that the traditional metallic materials can not match. At present, HAP is mainly applied in repair and replacements of hard tissues, such as oral implants, alveolar ridge strengthening, ear ossicle and vertebra repairs, and it also has great potential in biomimetic area[4-6]. However, HAP can easily be composed at a certain temperature, which results in poor sintering characteristics and mechanical properties for HAP ceramic[7-8], that is why prepared HAP ceramics usually possess low bending strength and fracture toughness, far away from the clinical demand. Therefore, how to inhibit the decomposition of HAP ceramics is a hotspot that needs to be solved. Normally, ZrO2 is added into HAP ceramics to inhibit HAP thermal decomposition and improve the bending strength and fracture toughness[9-10]. But, the improvement was very limited. At the same time, the preparation cost of hot-pressed sintered materials is too high to apply in clinic.
B2O3 is an evaporable oxide at high temperature because of its low melting point (450 ℃), so it can be used as a applicable steam dopant[11]. Besides, it is also used as combustion improver to decrease sintering temperature[12]. So far, there is less report on the effect of B2O3 addition on mechanical properties of HAP ceramics.
In the present study, HAP ceramic with B2O3 as additive was prepared by cold iso-press molding and pressureless sintering on the basis of previous work[13], aiming at the presence manner of B2O3 in the HAP and its effects on thermal decomposition and mechanical properties.
2 Experimental
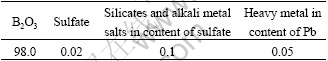
HAP powders were synthesized according to sol-gel method[14]. B2O3 was from Shunyi Weixin Chemical Plant of Beijing, China and its main chemical constitutions are given in Table 1.
Table 1 Main chemical constitutions of B2O3 powder (mass fraction, %)
HAP with B2O3 addition up to 20% (mass fraction) was ball ground for 50 h with Al2O3 beads as the grinding media. The ground powders were screened with a 275 mesh screener, and then preformed at 15 MPa. The preformed cake-like bodies were further isostatic pressed with a pressure of (250±2) MPa at ambient temperature, followed by pressless sintering at ambient atmosphere and covered with pure HAP powder. The sintering curve is shown in Fig.1. The sintering temperature of HAP composite ceramics was determined according to pure HAP ceramic.
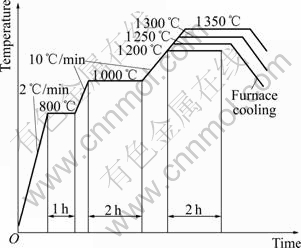
Fig.1 Sketch map of sintering curve for HAP ceramic
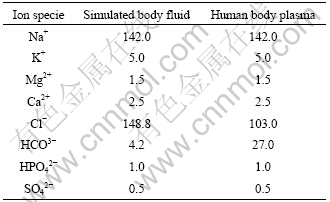
We soaked four pieces of HAP composite ceramics of 20 mm×7 mm×3 mm in 100 mL simulated body fluid (SBF), which is referenced to No.9 SBF synthesized by KOKUBO[13], taking human body programming as base. The contents of different ions are listed in Table 2. And then these HAP ceramics were cultivated continually for 14 d in water bath at (37±1) ℃, and in SBF for another day. The contents of Ca2+ and HPO42- were tested at the 1st, 3rd, 7th, 10th, and 14th day, respectively. The biological activities of HAP ceramics were preliminarily evaluated by analyzing the change of the contents of Ca2+ and HPO42- and deducing the possible action in the solution.
Table 2 Comparison of ion species and concentration between simulated body fluid and human body plasma (mmol/L)
The bending strength and fracture toughness were measured by three-point bending method and single edge-notched beam (SENB) on DCS-500 Universal Testing Machine from Chinese Academy of Science. The samples were made into 3 mm×4 mm×36 mm in size and 1.0 mm in notch depth. The speed of pressure head was 0.1 mm/min. Phase identification was investigated by Y500-type X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα as radiation source, at a accelerating voltage of 40 kV, a current of 50 mA and a scan speed of 0.06 (?)/s. The scanning range was from 20? to 45?. The resultant HAP volume fraction was determined by the relationship between the phase content and the corresponding peak area. HAP thermal decomposition ratio was detained by the difference of HAP volume fractions for biscuit and for sintered HAP ceramic. The FTIR analysis was performed by AVATAR 370 Fourier infrared spectrometer from Nicolet Company, United States.
3 Results and discussion
Fig.2 shows the XRD patterns of pure HAP ceramics sintered at 1 200, 1 250, 1 300 and 1 350 ℃, respectively. HAP ceramics sintered at different temperatures were all decomposed into β-TCP. The decomposition ratio increased with ascent of sintering temperature, as shown in Fig.3. It needs to be pointed out that when the sintering temperature was 1 350 ℃, this ceramic was decomposed badly with a decomposition ratio near 80%.
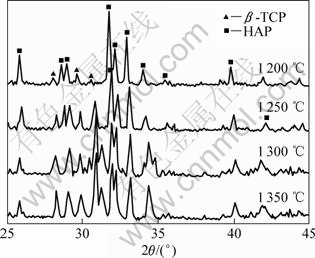
Fig.2 XRD patterns of HAP ceramics sintered at different temperatures for 2 h
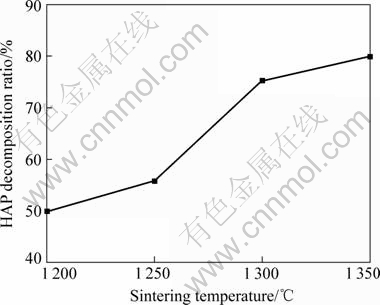
Fig.3 HAP decomposition ratio as function of sintering temperature
Fig.4 shows the XRD patterns of HAP composite ceramic with B2O3 addition sintered at 1 250 ℃. It suggests that HAP was decomposed into β-TCP. Fig.5 gives the decomposition ratio of HAP calculated according to Fig.4. Fig.5 indicates that the decomposition ratio of HAP ceramic increases with ascending the content of B2O3, and B2O3 inhibits thermal decomposition of HAP at higher temperature obviously compared with pure HAP ceramic. When the content of B2O3 is over 5%, the thermal decomposition ratio of HAP is the lowest.
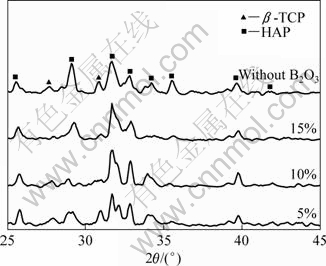
Fig.4 XRD patterns of HAP ceramics with different addition contents of B2O3
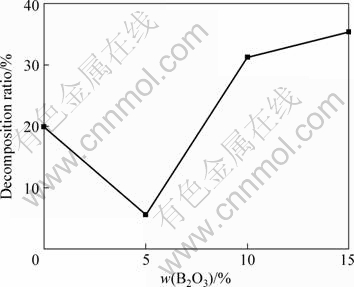
Fig.5 Effect of B2O3 content on HAP decomposition ratio
Fig.6 illustrates the effect of B2O3 addition on bending strength and fracture toughness for HAP composite ceramics. Pure HAP ceramic sintered at 1 250 ℃ possesses an average bending strength of 30 MPa and a fracture toughness of 0.4 MPa·m1/2. They were improved obviously by B2O3 addition. For HAP composite ceramic with 5% B2O3, the bending strength and fracture toughness reached their maximum of 125 MPa and 1.35 MPa·m1/2, respectively. Further adding B2O3 caused the decrease of bending strength and fracture toughness. When B2O3 addition was up to 15%, the bending strength and fracture toughness were decreased to 86.3 MPa and 1.07 MPa·m1/2, respectively.
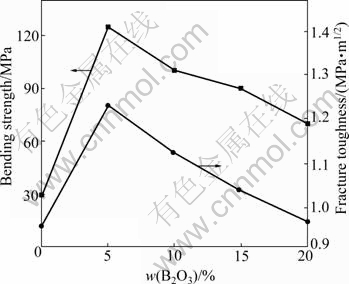
Fig.6 Relationships between fracture toughness and fracture toughness with B2O3 content for HAP composite ceramics
By comparing Fig.2 with Fig.4, it is found that B2O3 addition makes the main peaks of HAP shift left. The interplanar spacing (d211) for the main peak of the samples was calculated according to Bragg equation, as shown in Table 3. It is indicated that the d211 for HAP ceramics with B2O3 is larger than that for pure HAP ceramic, and gets the maximum value when 5% B2O3 is added due to the fact that HAP belongs to P63/m space group and hexagonal system structure. There are octahedral void and tetrahedral void in the main hexagon frame O2-. B2O3 has a melting point of 450 ℃ and has become vapor when being sintered at 1 250 ℃, which may go into grain boundary of HAP. A part of positive ion B3+ in B2O3 molecule may insert into the octahedron void of HAP and grow into another framework as shown in Fig.7, which contributes to B3+ with small semidiameter. Therefore, the incorporation of B3+ into HAP crystal cell will further enlarge the crystal spacing, and make the diffraction peaks of HAP shift left, which benefits for improving the bending strength and fracture toughness of HAP.
Table 3 Effect of B2O3 content on interplanar spacing of (211) crystal plane for HAP
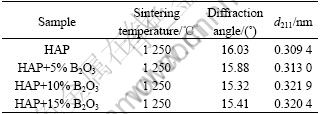
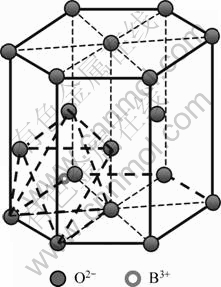
Fig.7 Possible location of B3+ in HAP crystal
The interspace of HAP octahedron bears a strong interaction with the atoms around. Once B3+ goes into the interspace of the octahedron, the neighboring octahedron is difficult to take in B3+ any more. This is consistent with research in Refs.[14-16], showing the limited adulterant in HAP composites. Therefore, in the present study, 5% B2O3 addition is the best to inhibit the catabolism of HAP. When B2O3 content is more than 5%, HAP decomposition is promoted and a steady β-TCP is formed due to the fact that there is a strong trend to intake of outside electrons because B atoms have strong negativity. B—O bonds are most covalent bonds as heterozygous orbit and B still has a empty p orbit with lost electron. As a result, it is very likely to take the position of OH- or PO43- tetrahedron lost by HAP.
Fig.8 shows FIRT spectra of samples with different B2O3 contents, in which diffusion peaks at 1 650 cm-1 and 3 500 cm-1 belong to absorption peaks of absorbed water. Absorption peaks at 3 571 cm-1 and 632 cm-1 correspond to flex vibrational peak (νρ) and swing vibrational peak (νδ) for hydroxyl, 962 cm-1 corresponds to symmetry flex vibrational peak (ν1) for PO43-, and 608 cm-1 and 561 cm-1 correspond to bend vibrational peak (ν4) for PO43-. Absorption peaks at 1 014 cm-1 and 1 102 cm-1 correspond to unsymmetry flex vibrational peak (ν3) for PO43-. From Fig.8, it is found that absorption peaks for HAP with B2O3 are stronger than those for the pure HAP. With increasing B2O3 content, absorption peaks for OH- become weak and wide, leading to the three vibrational peaks for PO43- (962 cm-1, 1 014 cm-1 and 1 102 cm-1) combining together and confusing. These changes suggest that addition of 5% B2O3 can effectively restrain HAP decomposition, and further increasing B2O3 leads to a decline in stability of HAP conformed by XRD analysis.
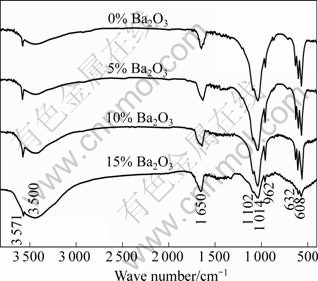
Fig.8 FTIR patterns for samples with different contents of B2O3
The contents of Ca2+ and HPO42- were measured by chemical titration at 1st, 2nd, 7th, 10th, and 14th day respectively (Table 4), when HAP composite ceramics were soaked in SBF. From Table 4, we can see, with increasing the time, the content of Ca2+ tends to increase, while that of HPO42- tends to decrease. It is attributed to the fact that Ca2+ migrates from HAP to solution until being saturated. Ca and P happened to sediment on the surface, resulting in appearing an amorphous apatite layer structure, as well as the content of HPO42- declining because HPO42- in the SBF was consumed. This suggests that the prepared HAP ceramic materials behave a better biological activity.
Table 4 Concentration of Ca2+ and HPO42- at different time

The HAP composite ceramics that were soaked in SBF for 14 d were detected by FIRT(Fig.9). There are five peaks in Fig.9. Two at 1 040 cm–1 and 957 cm–1 belong to amorphous calcium phosphate(ACP); and the other two peaks at 870 cm-1 and 742 cm-1 correspond to NO3-; and the rest peak at 962 cm-1 may be a overlapping peak corresponding to NO3- and phosphate [17]. These results lead to the conclusion that after the HAP composite ceramics are soaked in SBF for 14 d, a new ACP structure is generated, which plays an important role in normal metabolism and repair of bone tissue.
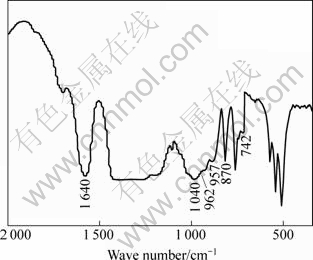
Fig.9 FTIR spectrum for sample after being soaked in SBF for 14 d
4 Conclusions
1) The decomposition ratio for pure HAP ceramic increases with ascending sintering temperature. It reaches nearly 56% when being sintered at 1 250 ℃. The average bending strength and fracture toughness are 30 MPa and 0.4 MPa·m1/2, respectively.
2) When 5% B2O3 is added into HAP ceramic and the mixture is sintered at 1 250 ℃, the thermal decomposition of HAP composite ceramics is inhibited effectively. The average bending strength and fracture toughness are improved to 125 MPa and 1.35 MPa·m1/2, respectively.
3) B3+ could incorporate into HAP crystal structure and form a solid solution, enlarging the crystal spacing and enhancing the binding force of HAP crystals, resulting in a great decrease in HAP decomposition ratio and excellent improvement in both bending strength and fracture toughness. When B2O3 addition is over 5%, HAP decomposition is promoted and a stable HAP β-TCP is formed because electron defective structure of B—O occupies the tetrahedron position where HAP loses OH- or PO43-.
4) After the HAP composite ceramics are soaked in SBF for 14 d, a new ACP structure is formed, which performs a better biology activity and plays an important role in normal metabolism and repair of bone tissue.
References
[1] SONG Yun-jiang, WEN Shu-lin. Preparation and physicochemical process of nanosized hydroxyapatite powders with high purity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(5): 985-991.
[2] GUO Lian-feng, ZHANG Wen-guang, WANG Cheng-tao. Synthesis of nanoparticle hydroxyapatite and crystallization control [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2004, 20(3): 291-295. (in Chinese)
[3] HAN Ying-chao, WANG Xin-yu, LI Shi-pu, YAN Yu-hua. Nanosized HAP powders prepared by auto-combustion methods [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2002, 30(3): 38-44. (in Chinese)
[4] LIU Lei, LI Sheng-wei, TIAN Wei-dong. A clinical study on immediate implantation of particulate hydroxyapatite artificial bone after teeth extraction [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2002, 20(1): 42-44. (in Chinese)
[5] FENG Lin-yun, LI Shi-pu, YAN Yu-hua. Inhibition of HAP nano-particles on W-256 sarcoma of rats in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2001, 10(7): 302-306. (in Chinese)
[6] KEYKHOSRAVANI M., HARVEY A. Comprehensive identification of post-translational modifications of rat bone osteopontin by mass spectrometry [J]. Biochemistry, 2005, 44: 6990-7003.
[7] MILEV A., KANNANGARA G. S. K, NISSAN B. B. Morphological stability of hydroxyapatite precursor [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 1960-1965.
[8] KIM H W, KONG Y M, KOH Y H. Pressureless sintering and mechanical and biological properties of fluor-hydroxyapatite composite with zirconia [J]. Journal of American Ceramic Society, 2003, 86(12): 2019-2026.
[9] YE Bin, CUI Kai, FENG Qing-ling. Synthesis and high temperature resistance properties of silver loaded fluorapatite antibacterial [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(2): 485-489. (in Chinese)
[10] LIAO C J, LIN F H, CHEN K S. New observations on middle term hydroxyapatite-coated titanium-alloy HIP prostheses [J]. Biomaterials, 1999, 20: 1807-1813.
[11] QI Jian-quan, LI Long-shi, ZHU Qing. Abnormal behavior of B2O3 vapor dopants in BaTiO3 based PTCR ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(4): 739-741. (in Chinese)
[12] QI Jian Quan, LI Long-shi, FAN Yi-wei. Media-low temperature sintered Y-BaTiO3 ceramics modified by B2O3 vapor and its PTCR effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(4): 818-822. (in Chinese)
[13] GUO Hai-feng. The preparation of hydroxyapatite bioceramic material [D]. Harbin: University of Science and Technology, 2006. (in Chinese)
[14] GUO Hai-feng, GUO Ying-kui, ZHAO Xiao-xu, LIANG Yan-yuan. Study on preparation and technology of HAP with an advanced sol-gel method [J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2005, 10(6): 38-43. (in Chinese)
[15] LI Ming-ou, XIAO Xiu-feng, LIU Rong-fang. Hydrothermal preparation and structure characterization of zinc-substituted hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 36(3): 378-382. (in Chinese)
[16] LI Dong-xu, GENG Yan-li, LI Yan-bao. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals using hydrolysis of dicalcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 24(1): 83-87. (in Chinese)
[17] HUANG Zhi-liang, WANG Da-wei, LIU Yu. FTIR Investigation on crystal chemistry of various CO32-substituted hydroxyapatite solid solutions [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2002, 18(5): 496-473. (in Chinese)
Corresponding author: GUO Ying-kui; Tel: +86-451-84026381; E-mail: gyk100@hrbust.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60131-X
(Edited by YANG Hua)