Simulation of PFZ on intergranular fracture based on XFEM and CPFEM
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2016年第10期
论文作者:刘文辉 邱群 陈宇强 唐昌平
文章页码:2500 - 2505
Key words:precipitation free zone (PFZ); intergranular fracture; grain boundary; extended finite element method (XFEM); crystal plasticity
Abstract: A unit cell including the matrix, precipitation free zone (PFZ) and grain boundary was prepared, and the crystal plasticity finite element method (CPFEM) and extended finite element method (XFEM) were used to simulate the propagation of cracks at grain boundary. Simulation results show that the crystallographic orientation of PFZ has significant influence on crack propagation, which includes the crack growth direction and crack growth velocity. The fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation due to the role of reducing the stress intensity at grain boundary in intergranular brittle fracture. But in intergranular ductile fracture, the fracture strain of soft orientation may be smaller than that of hard orientation due to the roles of deformation localization.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 2500-2505
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3309-4
LIU Wen-hui(刘文辉)1, 2, QIU Qun(邱群)1, 2, CHEN Yu-qiang(陈宇强)1, 2, TANG Chang-ping(唐昌平)1, 2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan 411201, China;
2. Key Lab of High Temperature Wear Resistant Materials Preparation Technology of Hunan Province, Xiangtan 411201, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: A unit cell including the matrix, precipitation free zone (PFZ) and grain boundary was prepared, and the crystal plasticity finite element method (CPFEM) and extended finite element method (XFEM) were used to simulate the propagation of cracks at grain boundary. Simulation results show that the crystallographic orientation of PFZ has significant influence on crack propagation, which includes the crack growth direction and crack growth velocity. The fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation due to the role of reducing the stress intensity at grain boundary in intergranular brittle fracture. But in intergranular ductile fracture, the fracture strain of soft orientation may be smaller than that of hard orientation due to the roles of deformation localization.
Key words: precipitation free zone (PFZ); intergranular fracture; grain boundary; extended finite element method (XFEM); crystal plasticity
1 Introduction
The high strength aluminum alloys with excellent combined mechanical properties and low densities have been widely used in aerospace industry, yet the low fracture toughness of high aluminum alloys hampers its wide application to a certain extent. Many experiments have been done to illustrate the effects of microstructures on the failure mode in aluminum alloy, such as the volume fraction of constituent particles, recrystallized microstructure [1-2], precipitates [3-4] and precipitate free zone [5-7]. The microstructure of high strength aluminum alloy is very complex. There are three scales of particles: coarse constituent particle, dispersoid particle and precipitate, and the effects of these three scales of particles on fracture behaviors are different. At the same time, the microstructures of PFZ, grain boundary and crystallographic orientation etc will also affect its fracture behavior. Because of the combined action of multiple factors of complex microstructure and the randomness of experiments, it is difficult to analyze the effect of every typical microstructure on fracture mode through experiment. Sometimes, there are some contradictory conclusions, such as the effect of PFZ. RYUM [5] thought that the existence of PFZ can reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary, and the fracture toughness of material increases with the PFZ width increasing. TAKESHI and OSAMU [6] and CHEN et al [7] showed that the PFZ was first to deform because PFZ was soft, and PFZ was preferable for crack growth, so the material toughness is reduced. A micromechanical model including main characteristic microstructure should be created to analyze the effects of microstructures on fracture mode. The node-release technique, cohesive zone technique and XFEM are mainly used in simulation of crack propagation. Because the crack path must be given before crack growth, the crack growth path cannot be predicted by node-release technique [8-9] or cohesive zone model [10]. At the same time, to obtain accurate solutions of crack tip driving force, the simulation of crack propagation typically requires fine meshing and re-meshing near the crack tip as the crack propagates. The special re-meshing along the crack front makes the simulation of crack propagation very troublesome. BELYTSCHKO et al [11] and MOES and DOLBOW [12] presented the XFEM in which the crack can propagate through elements in an arbitrary manner, and crack propagation modeling without constant re-meshing were made possible. LIU et al [13] studied the effects of PFZ width, particle shape, particle size and yield stress on the intergranular fracture of high strength aluminum alloy by XFEM, and they analyzed the mechanical properties of PFZ on the intergranular fracture strain by changing the constitutive parameters of PFZ. But the effects of crystallographic orientation and fracture mode on the failure strain were not discussed. Crystal plasticity theory is a hot topic in the damage mechanics area, and most of the microstructures, such as the inclusion, grain boundary and crystallographic orientation can be taken into account. KIYAK et al [14] studied the crack growth under low cycle fatigue by CPFEM through node-release technique. LI et al [15] created a 3D model to simulate crack growth in pre-cracked BCC single crystals. BISWAS et al [16] studied the influence of crack tip constraint on void growth in ductile FCC single crystals by CPFEM, and found that negative T-stress retarded the mechanisms of ductile fracture, and the extent of retardation was depended on the crystal orientation. Though some research has been done to study the crack propagation by CPFEM or XFEM, little work has been done to study crack propagation by using CPFEM and XFEM. In the work, the effects of crystallographic orientation of PFZ on the growth behaviors of cracks at the grain boundary are to be considered based on CPFEM and XFEM.
2 Simulation model
2.1 Geometry model
A simplified multi-layer model is created to simulate the crack growth in high strength aluminum alloys. Because the simulation calculation must call the user material subroutine, and the microstructure is complex, one half of the model is created due to symmetry, as shown in Fig. 1. The unit cell is made up of three layers: the grain boundary, PFZ and matrix. The side length (l) of unit cell is 100 mm, and the PFZ width h is 1 mm. The crack is at the center of the unit cell, and the initial radius of crack is 5 mm. The axis X is parallel to the sample rolling direction, and the axis Z is parallel to the plate normal direction. The displacement d along axis X is prescribed.
To analyze the effects of crystallographic orientation of PFZ on the growth behavior of cracks at grain boundary, three common orientations, Cube (0°, 0°, 0°), Brass (35°, 45°, 90°), Cu (90°, 35°, 45°), are selected. To discuss the effects of soft orientation and hard orientation on crack growth, the misorientation between the two grains is very small. For example, the Grain 1 with orientation (0°, 0°, 0°), and Grain 2 with orientation (0°, 0°, 0.1°) are selected to calculate. In fact, we can even think that the orientation difference of the two grains is (0°, 0°, 0°), although there is no grain boundary in single crystal. The aim of the selection is to discuss the effects of orientation on crack propagation. In this work, to simplify the description, we will use Cube, Bs, Cu orientation to describe the corresponding orientation assembly of the two grains, and we know that the stress increases according to the order of orientation Cube, Bs, Cu under the uniaxial tension along rolling direction. The reaction force T of the right area of the unit cell along axis X is output during deformation, and we think that the unit cell fails when the reaction force T drops.
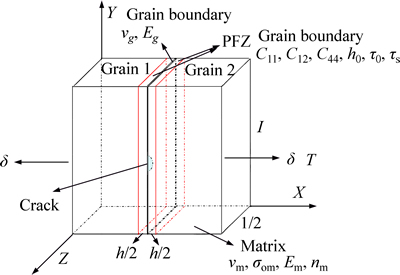
Fig. 1 Unit cell for crack growth
2.2 Mechanical properties
In our previous research [13], a simplified multi- layer model was created to simulate the crack growth in aluminum alloys, and the effect of PFZ on intergranular fracture was analyzed by changing the work hardening rate and yield stress of PFZ. In fact, the work hardening rate and yield stress of PFZ are related to the crystallographic orientation of PFZ. In this work, the effects of crystallographic orientation of PFZ on the propagation of cracks at grain boundary will be discussed based on CPFEM and XFEM.
PFZ is a solid solution with relatively low solute content compared with the matrix. The solute content of PFZ may be different, so the material constitution of PFZ will be different, but the order of magnitude of the yield stress of PFZ is in the range 50–100 MPa. Here, the rate dependent crystal plasticity constitutive theory and parameter definition are the same with those in Refs. [17-19], and we treat the crystal plasticity properties of PFZ as being the same with the pure aluminum. The crystal model is considered as having anisotropic elasticity with elasticity tensor C11=106.75 GPa, C12=60.41 GPa and C44=28.34 GPa, reference slip rate γ0=0.001, strain rate sensitivity m=0.02, and the hardening parameters h0=60 MPa, t0=12.5, ts=75 and a=2.25 [17]. A user material subroutine in Fortran is used to implement the constitutive relationship of crystal plasticity theory.
The aim of this work is to discuss the effects of crystallographic orientation of PFZ on the intergranular fracture in high strength aluminum alloy, and the mechanical properties of matrix and grain boundary are given according to our previous research [13]. The parameters were kept constant for high strength aluminum alloys, shown as follows (the subscript “m” and “g” stand for matrix and grain boundary, respectively): Em=0.5Eg= 70 GPa, vm=vg=0.3, s0m= 350 MPa and nm=0.15.
3 Results and discussion
The fracture energy of grain boundary in high strength aluminum alloy is about 100–500 J/m2 according to the research done by DUMONT et al [20]. To discuss the effects of PFZ and fracture mode on the intergranular fracture in high strength aluminum alloy, the grain boundaries with different fracture energies are discussed. Here, the grain boundary fracture energies of 100 J/m2 and 200 J/m2 are used to represent the cases of low fracture energy and high fracture energy, respectively, corresponding to intergranular brittle fracture and intergranular ductile fracture.
3.1 Intergranular brittle fracture
Figures 2-4 show the status of the XFEM element that exhibits the crack shape during deformation. Figrues 2(a) and (b) show the crack shape on YZ plane at ex=0.031 and 0.039, and the orientation of PFZ is Cu orientation. In our previous research [13], we studied the growth behavior of crack at grain boundary using the general elastic-plastic constitutive equation, and found that the crack at grain boundary extends in plane expansion under uniaxial tensile load condition, and the crack with initial round shape remains round during deformation. From Fig. 2, it can be found that the round crack becomes irregular during deformation.
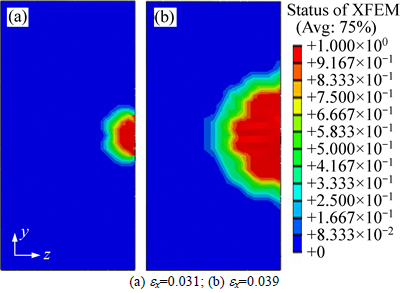
Fig. 2 Evolution of crack shape in Cu orientation at different strains:
Figures 3(a) and (b) corresponding to the crack evolution at ex=0.03 and 0.04, reveal the crack shape and size during deformation, and the orientation of PFZ is Bs orientation. Similar to Fig. 2, the crack shape becomes irregular during deformation, but the crack shape and size are different. Comparing Fig. 3 with Fig. 2, we can find that the size of crack at ex=0.04 in Bs orientation is smaller than the size of crack at ex=0.039 in Cu orientation, which indicates that the crack growth velocity in Bs orientation is smaller than that in Cu orientation.
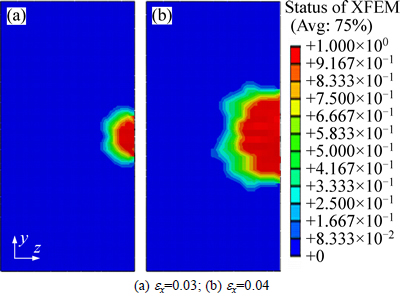
Fig. 3 Evolution of crack shape in Bs orientation at different strains:
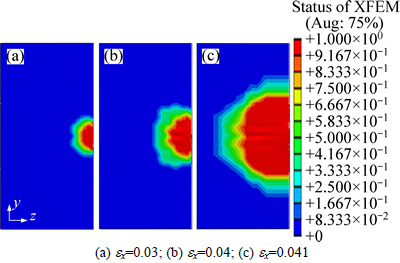
Fig. 4 Evolution of crack shape in cube orientation at different strains:
Figures 4(a)-(c) show the status of the XFEM element in Cube orientation at ex=0.03, 0.04 and 0.041. By comparing Fig. 4(b) with Fig. 3(b), it can be found that the crack size in Cube orientation is smaller than the crack size in Bs orientation at ex=0.04, which indicates that the crack growth velocity in Cube orientation is smaller than that in Bs orientation. From Fig. 4, it can be found that the size of crack at ex=0.04 is small, but at ex=0.041, the crack size becomes large rapidly, and the high strength aluminum alloy fails. That is to say, the crack starts to propagate at low velocity before the failure of the strain. Once it gets near the failure strain, the crack size increases suddenly, and the material will fail at the same time.
Figures 2-4 show the status of the XFEM element during deformation. If we think the regions in which the value of status of XFEM equals 1 are real crack, the crack size along Y axis can be plotted as positive direction during deformation. Figure 5 demonstrates the evolution of crack size along Y axis positive direction. From Fig. 5, it can be found that the crack size at small strain increases slowly at first. Once it reaches the failure strain, the crack size increases rapidly, and the material fails. We can divide the crack size evolution curves into two stages. In the first stage, the crack size increases slowly, and the slope is small. In the second stage, the crack size increases fast, and the slope is large. It can be found that the stress intensity reducing effect of Cube orientation is larger than that of the others, so the slope of Cube orientation at the first stage is smaller than that of the others, and the fracture strain of Cube orientation is larger than that of the others.
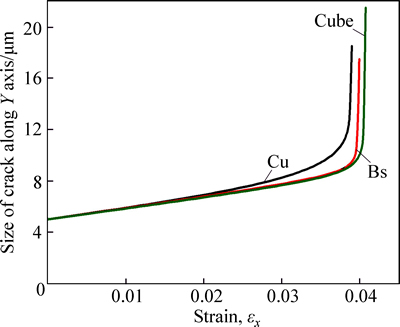
Fig. 5 Evolution of crack size in intergranular brittle fracture
Figure 6 shows the change of reaction force T for different orientations during deformation. Because the PFZ width is very narrow, the reaction forces T for different orientations are very small. From Fig. 6, we can find that the failure strain increases according to the order of Cu, Bs and Cube orientation in intergranular brittle fracture. From Fig. 6, we can conclude that the fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation, which may be due to the fact that the PFZ can reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary, and because the stress intensity reducing effect of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation, the fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation.
3.2 Intergranular ductile fracture
Figures 7-9 demonstrate the crack propagation for different orientations with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy, and the material undergoes relatively larger deformation compared with Figs. 2-4.
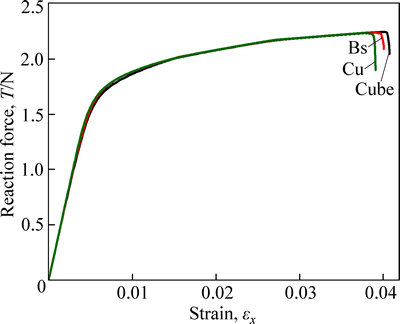
Fig. 6 Evolution of reaction force T for different orientations in intergranular brittle fracture
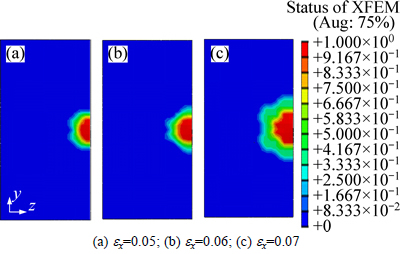
Fig. 7 Evolution of crack shape in Cu orientation at different strains with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy:
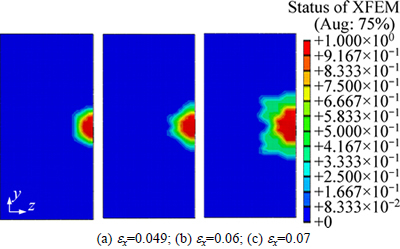
Fig. 8 Evolution of crack shape in Bs orientation at different strains with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy:
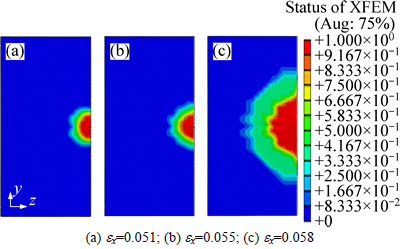
Fig. 9 Evolution of crack shape in cube orientation at different strains with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy:
Figures 7(a)-(c) show the crack shape in Cu orientation at ex=0.05, 0.06 and 0.07. Similar to Fig. 2, the crack shape becomes irregular, but the crack size is relatively small at the same strain ex.
Figures 8(a)-(c) show the crack shape in Bs orientation at ex=0.049, 0.06 and 0.07. By comparing Fig. 8 with Fig. 7, it can be found that the crack size in Bs orientation is larger than that in Cu orientation, which indicates that the crack growth velocity in Bs orientation is larger than that in Cu orientation. Bs orientation is soft orientation compared with Cu orientation, so the Bs orientation is more effective to reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary than that of Cu orientation. On the other hand, the soft PFZ with Bs orientation is easy to cause deformation localization near grain boundary with deformation increasing, and accelerates the crack growth conversely.
Figures 9(a)-(c) show the crack shape in Cube orientation at ex=0.051, 0.055 and 0.058. At ex=0.051 and 0.055, the crack size is still small. At ex=0.058, the crack size increases suddenly. Comparing the crack size in Fig. 9 with Fig. 8, we can find that the crack growth velocity in Cube orientation is larger than that in Bs orientation. From Figs. 7-9, it can be found that the fracture strain of hard orientation is larger than that of soft orientation, which is opposite to the case in intergranular brittle fracture.
Figures 7-9 show the status of the XFEM element during deformation for intergranular ductile fracture. Compared to intergranular brittle fracture, the area fraction of the status of XFEM less than 1 is larger when the material fails. In intergranular ductile fracture, the grain boundary fracture energy is large, and it will induce large plastic deformation and damage ahead of crack tip as the crack extends. But in intergranular brittle fracture, the material fails suddenly, and the material may fail without inducing much plastic deformation and damage ahead of crack.
Figure 10 demonstrates the evolution of crack size along Y axis positive direction. From Fig. 10, it can be found that the crack size increases slowly at the first stage, and the crack growth velocity of Cube orientation is smaller than that of the others. Then it increases sharply, and the material fails ahead of orientations Bs and Cu. Because the effect of reducing stress intensity at grain boundary of soft orientation is better than that of hard orientation, the crack size of Cube orientation at the first stage is smaller than that of Bs and Cu orientations. But with deformation increasing, the existence of soft PFZ will induce deformation localization, such as necking and new damage, which will accelerate crack propagation. Because the deformation localization of PFZ with soft orientation is more serious than that of hard orientation, the crack size of Cube orientation increases sharply.
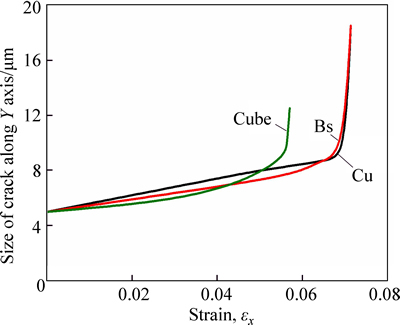
Fig. 10 Evolution of crack size in intergranular ductile fracture with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy
Figure 11 shows the evolution of reaction force T for high grain boundary fracture energy. The fracture strain of material is larger than that in Fig. 6 with low grain boundary fracture energy, and the failure strain increases according to the order of Cube, Bs and Cu orientation in intergranular ductile fracture. From Fig. 11, we can find that the fracture strain of hard orientation is larger than that of soft orientation, which is opposite to the case in intergranular brittle fracture. From the above discussion, we can conclude that the effects of soft PFZ on intergranular fracture have two aspects: reducing the stress intensity at grain boundary and causing deformation localization near grain boundary, and there are controversial conclusions about the effects of PFZ on intergranular fracture [5-7]. From our simulation results, we can find that the effect of PFZ on intergranular fracture is to reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary, and then, the existence of PFZ will cause deformation localization around grain boundary. For low grain boundary fracture energy condition, the material fails by intergranular brittle fracture at small strain, and the effect of reducing the stress intensity at grain boundary works, but the deformation localization does not operate. The stress intensity reducing effect of soft orientation is more effective than that of hard orientation, so the fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation. For high grain boundary fracture energy condition, the material fails by intergranular ductile fracture at large strain, and the two aspects of the effects of soft PFZ on intergranular fracture, reducing the stress intensity at grain boundary and causing deformation localization near grain boundary, will act during deformation. Although the soft orientation is effective to reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary compared to hard orientation, it is also easy to cause deformation localization. Once the deformation localization near grain boundary occurs, it will accelerate the growth velocity of crack at grain boundary, so the fracture strain of soft orientation may be smaller than that of hard orientation in intergranular ductile fracture.
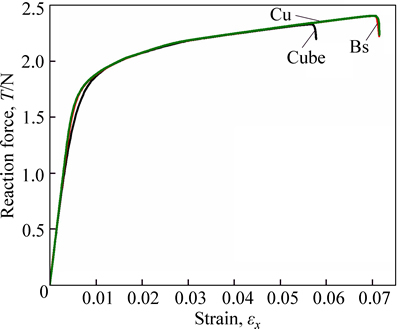
Fig. 11 Evolution of reaction force T for different orientations in intergranular ductile fracture with relatively higher grain boundary fracture energy
4 Conclusions
1) The crystallographic orientation of PFZ not only plays a role in the crack growth direction and crack shape, but also affects the crack growth velocity, and the effects may be different in different fracture modes.
2) The roles of PFZ in the intergranular fracture in high strength aluminum alloy include two aspects. Firstly, the existence of PFZ can reduce the stress intensity around grain boundary, and then, it will induce deformation localization around grain boundary.
3) For low grain boundary fracture energy condition, the material may fail by intergranular brittle fracture at small strain, and the effect of PFZ on intergranular fracture is to reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary. Because the stress intensity reducing effect of soft orientation is more effective than that of hard orientation, the fracture strain of soft orientation is larger than that of hard orientation.
4) For high grain boundary fracture energy condition, the material may fail by intergranular ductile fracture at large strain. Although the soft orientation is effective to reduce the stress intensity at grain boundary compared to hard orientation, it is also easy to cause deformation localization. Once the deformation localization near grain boundary occurs, it will accelerate the growth velocity of crack at grain boundary, so the fracture strain of soft orientation may be smaller than that of hard orientation.
References
[1] DESHPANDE N U, GOKHALE A M, DENZER D K, LIU J. Relationship between fracture toughness, fracture path, and microstructure of 7050 aluminum alloy: Part I: Quantitative characterization [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29: 1191-1201.
[2] GOKHALE A M, DESHPANDE N U, DENZER D K, LIU J. Relationship between fracture toughness, fracture path, and microstructure of 7050 aluminum alloy: Part II: multiple micromechanisms-based fracture toughness model [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29: 1203-1210.
[3] DORWARD R C, BEERNTSEN D J. Grain structure and quench-rate effects on strength and toughness of AA 7050 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy plate [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26: 2481-2484
[4] DUMONT D, DESCHAMPS A, BRECHET Y. On the relationship between microstructure, strength and toughness in AA7050 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 356: 326-336.
[5] RYUM N. The influence of a precipitation-free zone on the mechanical properties of an Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Acta Metall, 1968, 16: 327-332.
[6] TAKESHI K, OSAMU I. The relationship between fracture toughness and transgranular fracture in an Al-6.0%Zn-2.5%Mg alloy [J]. Acta metall, 1977, 25: 505-512.
[7] CHEN Y, PEDERSEN K O, CLAUSEN A H, HOPPERSTAD O S. An experimental study on the dynamic fracture of extruded AA6xxx and AA7xxx aluminium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 523: 253-262.
[8] POTIRNICHE G P, DANIEWICZ S R. Finite element modeling of microstructurally small cracks using crystal plasticity theory [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2003, 25: 877-884.
[9] POTIRNICHE G P, DANIEWICZ S R, NEWMAN J C. Simulating small crack growth behavior using crystal plasticity theory and finite element analysis [J]. Fatigue Fract Engng Mater Struct, 2004, 27: 59-71.
[10] YAMAKOV V, SAETHER E, PHILLIPS D R, GLAESSGEN E H. Molecular- dynamics simulation-based cohesive zone representation of intergranular fracture processes in aluminum [J]. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2006, 54: 1899-1928.
[11] BELYTSCHKO T, FISH J, ENGELMANN B. A finite element with embedded localization zones [J]. Comput Meth Appl Mech Engng, 1988, 70: 59-89.
[12]  N, DOLBOW J, BELYTSCHKO T. A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing [J]. Int J Numer Meth in Engng, 1999, 46: 131-150.
N, DOLBOW J, BELYTSCHKO T. A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing [J]. Int J Numer Meth in Engng, 1999, 46: 131-150.
[13] LIU Wen-hui, HE Zhen-tao, YAO Wei, LI Mao-hua, TANG Jian-guo. XFEM simulation of the effects of microstructure on the intergranular fracture in high strength aluminum alloy [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 84: 310-317.
[14] KIYAK Y, FEDELICH B, MAY T, PFENNIG A. Simulation of crack growth under low cycle fatigue at high temperature in a single crystal superalloy [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75: 2418-2443.
[15] LI J, PROUDHON H, ROOS A, CHIARUTTINI V, FOREST S. Crystal plasticity finite element simulation of crack growth in single crystals [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 94: 191-197.
[16] BISWAS P, NARASIMHAN R, TEWARI A. Influence of crack tip constraint on void growth in ductile FCC single crystals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 823-831.
[17] PI Hua-chun, HAN Jing-tao, ZHANG Chuan-guo, TIEU A K, JIANG Zheng-yi. Modeling uniaxial tensile deformation of polycrystalline Al using CPFEM [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008, 15(1): 43-47.
[18] TANG Jian-guo, ZHANG Xin-ming, CHEN Zhi-Yong, DENG Yun-lai. Finite element simulation of influences of grain interaction on rolling textures of fcc metals [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(2): 117-121.
[19] LIU Wen-hui, ZHANG Xin-ming, TANG Jian-guo, DU Yu-xuan. Simulation of void growth and coalescence behavior with 3D crystal plasticity theory [J]. Comput Mater SCi, 2007, 40: 130-139.
[20] DUMONT D, DESCHAMPS A, BRECHET Y. A model for predicting fracture mode and toughness in 7000 series aluminium alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2004, 52: 2529-2540.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Projects(51475162, 51405153) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(14JJ5015) supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China
Received date: 2015-07-30; Accepted date: 2016-01-30
Corresponding author: LIU Wen-hui, Associate Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-18873216868; E-mail: lwh@hnust.edu.cn

