动态张拉载荷作用下花岗岩的层裂破坏机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第7期
论文作者:黄麟淇 汪军 Aliakbar MOMENI 王少锋
文章页码:2116 - 2127
关键词:微观检测;动态加载;层裂破坏;矿物特性;晶间断裂
Key words:microscopic observation; dynamic loading; spalling failure; mineral properties; intercrystalline fracture
摘 要:在动态载荷作用下岩石可能发生层裂破坏。在动态霍普金森压杆(SHPB)上及4种不同的冲击载荷条件下,开展动态张拉载荷作用下花岗岩的破裂发展和破坏特性研究。岩样破坏后,在破坏表面附近取样并制作薄片,用偏光显微镜观察岩石裂纹的生长模式,并利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察破坏表面的矿物颗粒形貌特征,从而评价岩石矿物特征对载荷和破坏的响应特性。研究结果表明,岩样层裂裂纹数量随着峰值冲击载荷的增加而增多,并且岩石内的石英矿物持续发生大量的晶间断裂;矿物晶体的解理面及其相对于载荷的方向对岩石强度和破裂特性有着至关重要的作用;沿垂直于载荷的矿物晶体解理面进行分离而没有云母矿物平行于载荷的运动是岩石发生层裂破坏所特有的。
Abstract: Rocks are likely to undergo spalling failure under dynamic loading. The fracture development and rock failure behaviours were investigated during dynamic tensile loading. Tests were conducted with a split-Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) in four different impact loading conditions. Thin sections near failure surfaces were also made to evaluate the growth patterns of fractures observed by polarizing microscope. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe mineral grains on failure surfaces and to evaluate their response to loading and failure. The results indicate that the number of spalling cracks increases with increase in peak impact loads and that quartz sustains abundant intergranular fracturing. Cleavage planes and their direction relative to loading play a vital role in rock strength and fracturing. Separation along cleavage planes perpendicular to loading without the movement of micaceous minerals parallel to loading appears to be unique to the rock spalling process.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 2116-2127
Lin-qi HUANG1, Jun WANG1, Aliakbar MOMENI2, Shao-feng WANG1
1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Faculty of Earth Sciences, Shahrood University of Technology, Shahrood, 3619995161, Iran
Received 10 July 2020; accepted 24 December 2020
Abstract: Rocks are likely to undergo spalling failure under dynamic loading. The fracture development and rock failure behaviours were investigated during dynamic tensile loading. Tests were conducted with a split-Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) in four different impact loading conditions. Thin sections near failure surfaces were also made to evaluate the growth patterns of fractures observed by polarizing microscope. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe mineral grains on failure surfaces and to evaluate their response to loading and failure. The results indicate that the number of spalling cracks increases with increase in peak impact loads and that quartz sustains abundant intergranular fracturing. Cleavage planes and their direction relative to loading play a vital role in rock strength and fracturing. Separation along cleavage planes perpendicular to loading without the movement of micaceous minerals parallel to loading appears to be unique to the rock spalling process.
Key words: microscopic observation; dynamic loading; spalling failure; mineral properties; intercrystalline fracture
1 Introduction
The fracture mechanisms of geological materials are dependent upon the loading speed. Dynamic loading is normally categorized as high-speed loading, and the resulting fracture dynamics are among the issues that remain poorly understood [1]. Tensile failure of rocks sometimes appears in the form of spalling, which is an important hazard that threatens human safety and the stability of civil engineering excavations and underground mines [2-6]. Therefore, it is critical to understand the tensile fracture mechanics of rocks, and several researchers have employed experimental, analytical, and numerical approaches to this subject [7-10]. The evolution of fractures in rocks is complex, in part because rocks are composed of different minerals with different characteristics and anisotropic behaviours. Among igneous rocks, granite is the most common, and because of its high strength, availability and potential to contain economic ore deposits, it has widely existed in civil and mining engineering projects. Consequently, many researchers have studied the engineering behaviour of granite in different environments and under the various loading conditions [11,12]. For example, MOMENI et al [12] investigated the engineering properties of different granitoid rocks. Their results showed that the uniaxial compressive strength of these rocks varies over a wide range (127-254 MPa) depending upon their mineral composition and texture. In fact, quartz, feldspars and micas, as the main minerals within granitic rocks, have different physico- mechanical behaviours; consequently, different compositions of these minerals lead to variation in the mechanical properties of granitic rocks [13,14].
Past studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between petrographic characteristics and the evolution of cracks and fractures in rocks. LI et al [15] presented a new analytical method for predicting the effects of historic stress paths on crack growth. AKESSON et al [16] evaluated microcrack growth patterns in the Bohus granite caused by uniaxial cyclic loading, and they observed that feldspar had a high potential trend for cracking parallel to the loading direction. ERSALAN and WILLIAMS [17,18] performed microstructural analyses of subcritical crack propagation in the Brisbane tuff. The results of these studies have shown that the petrographic characteristics of rocks, such as grain contacts and interlocking, cement volume and mineralogy, play a vital role in the fracture behaviour of rocks. Based on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results, a series of experiments on rock failure have been performed under different loading conditions, and it has been concluded that grain boundaries play an important role in rock failure performances [19-22].
All of the aforementioned studies have been conducted under static or low strain rates, and the evolution of microscopic cracks and its dependence upon petrographic characteristics have rarely been studied under dynamic loading. Meanwhile, dynamic and either medium or high strain-rate loading occurs in many situations, such as engineering blasts and earthquakes. It is true that experimental testing provides the most direct and reliable results on the fracture mechanics of rocks. However, using common direct (direct tension test) and indirect indices (e.g., via the Brazilian test, point load test, beam test, etc.) offers some disadvantages and shortcomings for evaluating dynamic tensile behaviour. The split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar (SHPB) is one of the best dynamic testing machines, and has been used by many researchers to evaluate the dynamic strength of rocks [23,24]. For example, TAO et al [25-27] investigated the dynamic responses of pre-stressed granite with a circular hole during transient loading and found that the combined action of static and dynamic stress concentrations played an important role in dynamic strength. Meanwhile, LI et al [28] observed that the spalling strength of pre-confined granitic rocks decreased with increase in confining pressures, and ZHOU et al [29] comprehensively analyzed the dynamic tensile behaviour of granitic rocks subjected to coupled loads using a modified SHPB test. They founded that the dynamic tensile strength of the studied granite under coupled loads decreased with increasing axial static pre-stresses. More recently, ZHU et al [30] investigated the indirect tensile strength of rock using SHPB with intermediate strain rates, and LI et al [31] performed SHPB tests on sandstone with different strain rates. They reported that dynamic indirect tensile strength increased with increasing strain rates and that visible cracks developed after peak stress loading. FAKHIMI et al [32] evaluated the dynamic strength of sandstone using SHPB tests and numerical simulations and achieved a relatively good agreement between their experimental results and numerical simulations.
Most recent studies on the dynamic behaviour of granite have been performed under compressive conditions to predict the behaviour of rocks in deep mines. However, the dynamic strength of granite under dynamic tensile loading without pre-stress has mostly been neglected. Additionally, the failure characteristics of these rocks were measured macroscopically by high-speed cameras and not microscopically surveyed. The primary aim of this study is to fill this gap. Therefore, the spalling process of granite under dynamic tensile loading was investigated via SHPB tests. Petrographic and morphological analyses were conducted to reveal the development of cracks and the relationship between the distribution of mineral grains and rock fractures. This work is performed as an interdisciplinary collaboration between geological and rock engineers to contribute new knowledge on the spalling failure of hard rocks due to dynamic tensile loading.
2 Experimental
2.1 Material and sampling preparation
Rock samples were chosen from the relatively homogeneous granite of a quarry mine in the town of Dingzi, Changsha, Hunan Province, China. One large rock block was collected, which was capable of providing a sufficient number of core samples to perform laboratory tests. After thin sections preparation, the petrographic characteristics of this rock were studied via optical microscopy to determine the mineralogical composition and texture, as well as the size and shape of constituent minerals. Basic physico-mechanical properties (e.g., density ρ, porosity n, ultrasonic wave velocity Vp, Brazilian tensile strength σt, uniaxial compressive strength σc and elastic modulus Et) were measured prior to performing SHPB tests. It should be noted that the International Society for Rock Mechanics (ISRM) standard methods were employed in these tests [33]. For SHPB tests, four cylindrical specimens with 50 mm in diameter and 400 mm in length were also prepared. The ends of the samples were polished to ensure sufficient contact with the end of the incident bar during testing.
2.2 Split-Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) tests
Modified SHPB tests were used to obtain the rock failure characteristics under tensile stress produced by dynamic impact loading. The device was modified at Central South University in China. The actual and schematic views of the modified SHPB device are shown in Fig. 1. The SHPB device used an improved spindle-shaped striker with a length of 380 mm. Based on elastic wave theory, it is known that the wavelength of an incident wave is approximately 76 mm. Furthermore, the elastic bar was cylindrical, with a diameter of 50 mm and length of 2000 mm. After setting up the test system, specimens were contacted with the input bar. In this device, dynamic loads were controlled by a gas tank with high-pressure nitrogen gas [25,27]. Based on our previous experiences, four impact loads with peak values between the rock tensile strength and uniaxial compressive strength were applied.
Split-Hopkinson pressure bars always generate compressive waves, which can be reflected as tensile waves on the boundary surfaces of two materials with specific differences in impedance. In fact, during the propagation of compressive waves from two materials, if the wave impedance of the second material is lower than that of the first, part of the compressive wave will propagate into the second material without changing and the rest will be reflected as a tensile wave propagating in the first material. Therefore, rock samples and air boundary surfaces exhibit this relationship, and rock samples will be subjected to tensile stress waves when the incident wave is reflected on the free surface of the specimens. When the tensile wave stress is higher than the dynamic tensile strength of a rock specimen, dynamic tensile fracturing, which is known as ‘spalling’, will occur. If the stress wave increases slowly, subsequent spalling may occur after the first spallation.
2.3 Fracture and failure monitoring
Fracture and failure processes were monitored at both micro- and macro-scales. Failure of the tested rock specimens occurred suddenly because of the high strain rate during dynamic loading. A high-speed camera (FASTCAM SA 1.1, Photron, Japan) was employed to macroscopically monitor the fracture and failure processes. For micro-scale analyses of crack characteristics, both petrographic studies of thin sections and SEM analysis were employed. It should be noted that these two types of fracture analyses were used to perform the fracture characterization on the fractured surfaces after rock failure. Thin sections were prepared perpendicular to the loading direction, which contained the fracture as a line. The SEM analysis was applied to the fracture surface, which was performed using the SEM system (Zeiss EVO MA10, Germany) set up at Central South University. Due to the electrical insulation of the rock sample, the test samples needed to be sprayed with gold before vacuum SEM. Three fracture surfaces of each broken sample were tested to evaluate the responses of mineral grains to spalling failure.
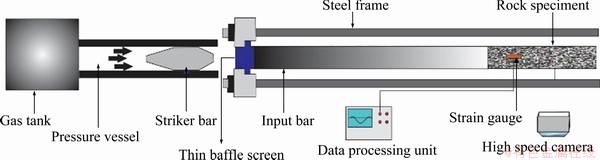
Fig. 1 Schematic views of modified split-Hopkinson pressure bar
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Petrographic characteristics and basic physico-mechanical properties
The results of petrographic studies on thin sections showed that the studied granite was fine to medium-grained and exhibited an anhedral granular texture. Evaluation of mineral shapes revealed that plagioclase and micaceous minerals were subhedral to anhedral, while quartz and K-feldspar (orthoclase) were anhedral (Fig. 2). The modal composition of the tested samples included ~20% feldspars (plagioclase and K-feldspar), 55% quartz, 20% micas (biotite and muscovite) and 5% minor constituents (sericite and apatite). Due to the lower melting point of quartz in granitic rocks, crystallisation occurs more slowly and with a lower degree of crystallite formation, which indirectly leads to quartz having a higher strength and no cleavage. Additionally, quartz fills the empty spaces between minerals. Both feldspar and micas develop cleavage: feldspar with two sets of nearly complete cleavage (with an angle of ~90°) and micas with one set of complete cleavage. Micas, with their low strength and hardness, are mostly found in the form of flakes and are more likely to break along their plane of cleavage. It should be noted that biotite was well-dispersed in the rock samples, whereas muscovite occurred in clusters, which were clear in specimens.
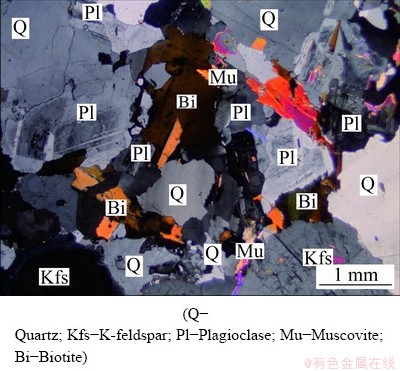
Fig. 2 Typical photomicrograph of studied granite
Based on physical tests, the mean porosity and density were measured to be ~0.62% and 2654 kg/m3, respectively. Wave velocity was measured to be approximately 4755 m/s. The results of mechanical tests indicated that uniaxial compressive strength (UCS or σc), Brazilian tensile strength (σt), elastic modulus (Et) were ~123 MPa, ~8.95 MPa and 32 GPa, respectively. The physic- mechanical parameters of rock material are listed in Table 1.
3.2 SHPB test results and fracture process
The dynamic stress–time curves induced within the incident bar at different loading strengths are shown in Fig. 3. As is clear from this figure, by setting the nitrogen gas to different pressures, four different impact loads with peak values of approximately 28 MPa (T1), 35 MPa (T2), 41 MPa (T3) and 45 MPa (T4) were applied. These stress–time curves were plotted based on the strain gauge data and elastic modulus obtained for this rock type. The resolution of the high-speed camera was 960×144 at 40000 fps, which recorded images at an interval of 25 μs. The camera was triggered by a logic level signal generated on an oscilloscope coordinated with the incident signal [25]. The time when the incident wave triggered the strain gauge at the input bar was treated as the starting time. After testing, more than 1000 images were recorded but many were not analytically useful. Therefore, a relative time which had experienced 100 μs before the occurrence of the first visible crack, namely for the high-speed camera image when the first visible crack appeared in the fourth image after it was defined as 0 μs. The spalling fracture process of Sample T4 is shown in Fig. 4.
The diagram of the Hopkinson bar spalling process under a half-sine stress wave is shown in Fig. 5.
The peak stress of the incident wave was less than the uniaxial compression strength of the rock sample and higher than the tensile strength. The peak stress of the incident compressive wave was always greater than that of the reflected tensile wave before the wave reached the free surface of a given sample. After the reflected half-period, the reflected tensile stress wave gradually exceeded that of the incident compressive wave and a net tensile stress zone appeared. When the tensile stress was greater than the dynamic tensile strength of the rock specimens, spalling occurred. The several potential fracture locations are also shown in Fig. 5.
Table 1 Physic-mechanical parameters of rock material

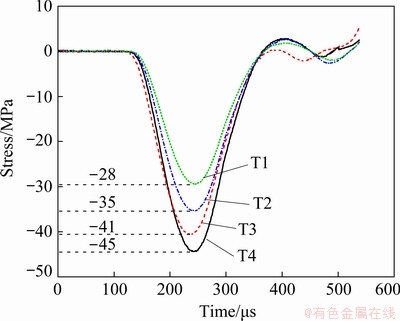
Fig. 3 Experimental stress–time relationship for tested samples
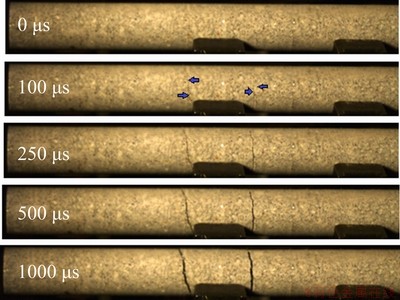
Fig. 4 High-speed camera images of rock fracture process for Sample T4
To evaluate the effect of peak impact loads on spalling failure, images of the four tests after 1000 μs were analyzed, as shown in Fig. 6. As is clear in this figure, for Samples T1 and T2, just one crack developed, whereas for Samples T3 and T4, two cracks can be observed. This difference may have occurred because of wave propagation. In fact, the generation of rock damage as a crack leads to the consumption of a considerable amount of loaded wave energy and consequently decreases the remaining wave stress level. Therefore, for Samples T1 and T2, the dynamic loading stress after such decrease was less than the dynamic spalling strength of rock and could not induce additional new cracks. Meanwhile, in the case of Samples T3 and T4, the remaining dynamic stress was greater than the dynamic spalling strength and could generate a new (second) crack. After the second crack formed, the intensity of the wave was further reduced, and after this time, it was less than the dynamic spalling strength of the rocks.
The dynamic spalling strength of the samples was measured based on high-speed camera images. The dynamic spalling strengths of the samples were 10.38 MPa (T1), 14.9 MPa (T2), 16.1 MPa (T3) and 17.2 MPa (T4). Compared to the static Brazilian splitting test, the dynamic spalling strengths were 1.16, 1.66, 1.80 and 1.92 times as high as the Brazilian tensile strength of 8.95 MPa for Samples T1, T2, T3 and T4, respectively.
3.3 Fracture behavior
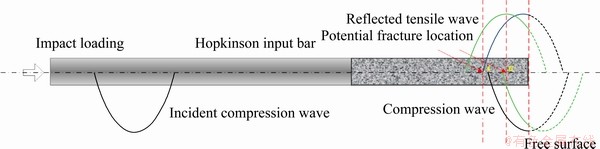
Fig. 5 Schematic of wave propagation in tested specimens
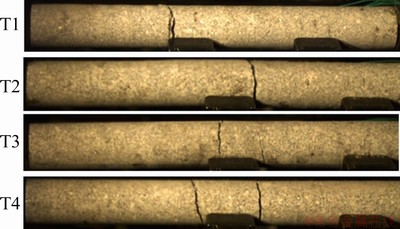
Fig. 6 High-speed images of rock failure subjected to different dynamic stress loads after 1000 μs
Knowledge of the properties and processes of rock failure plays a vital role in the safe design of structures in or on rocks, including dams, tunnels and caverns. Additionally, the field of rock mechanics is applicable to the development of natural resource extraction methods, such as hydraulic fracturing for the increased recovery of oil and gas. In the past, microanalyses of spalling fracture surfaces have been conducted based upon visual inspection. When the fracture surface relative to the light was turned, a shiny surface was visible (Fig. 7). Close inspection of these surfaces has indicated that these surfaces are cleavage planes and can be seen for the micaceous and feldspar minerals based upon their distribution. As is clear from Figs. 6 and Fig.7, the growth paths of cracks sometimes deviate from the direction of the maximum tensile stress, and fracture surfaces exhibit different degrees of roughness. To quantify the roughness of fracture surfaces, a fracture roughness index was introduced as the ratio between the maximum deviator height (maximum amplitude) to the sample diameter. This index is dependent on the abundant of cleavage-bearing minerals and their distribution pattern with respect to tensile load direction. By increasing this index, the spalling tensile strength will decrease. Despite increasing the fracture surface area, the low strength of cleavage-bearing minerals in the direction of the cleavage plane compared to other directions leads to fracture development along these planes. The effect of cleavage planes on fracturing is schematically shown in two dimensions in Fig. 7. Micaceous minerals have one perfect cleavage plane, and when this plane is at a low angle to the direction of maximum tensile stress, fracture surfaces follow the plane. By increasing this angle, the dependence of the fracture surface on the cleavage plane will be decreased but still develop approximately parallel to the plane. When this angle increases to nearly 90°, the fracture surface will not be affected by the cleavage of micaceous minerals, and fractures will develop perpendicular to the cleavage and follows the direction of maximum tensile strength. Feldspar minerals, with two cleavage planes, play a more important role in the roughness of granitic rock fracture surfaces. Our analyses indicted that interactions between feldspar cleavage planes and the direction of stress lead to the step-like appearance of fracture surfaces. Moreover, the perfect and well-developed cleavage planes were mainly located in berms and at the height of the step-like surfaces, respectively. This description applies to two dimensions. However, in three dimensions, the interactions of stress and cleavage planes are more complex.

Fig. 7 Fracture surface in spalling test with cleavage (left side) and schematic view of fracture growth pattern and cleavage effects on crack development
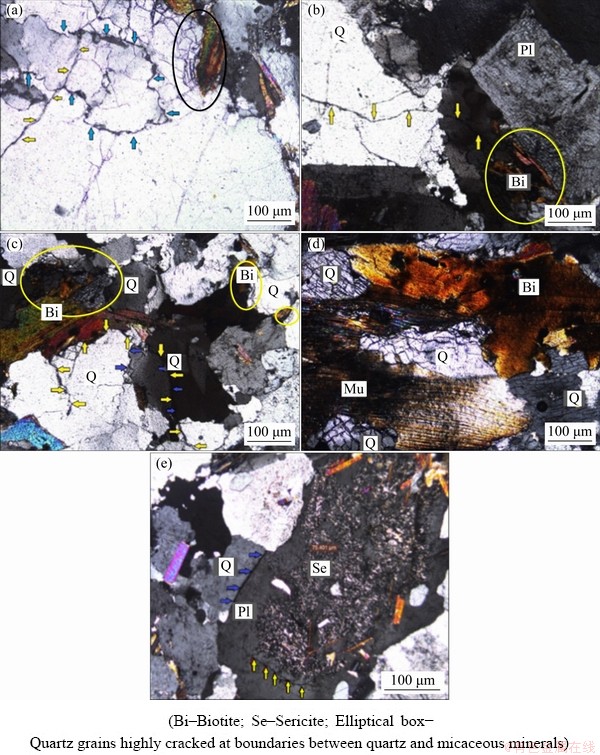
Fig. 8 Different types of cracks developed in granite near failure surfaces
It is already known that rock failure is a process of macro- and micro-fracture initiation and propagation. Therefore, in this study, microcrack development and the responses of different minerals to high strain-rate dynamic loading were investigated using petrographic and SEM analyses. Thin sections for each sample were prepared beside the developed crack and near the damage zone. Based on our results, three different types of cracks were found in the studied granite (Fig. 8). The first and most common type was intergranular cracks. This type was limited to the interiors of single minerals and was most common in quartz polycrystals and along cleavage planes in feldspars, whereas nearly no cracks of this type were observed in biotite or muscovite (Fig. 8(d)). The crushing severity of minerals also increased closer to the failure surface. The second type of crack was grain boundary cracks, which followed the grain boundaries around most of the minerals, especially quartz. In Figs. 8(a) and (c), grain boundary cracks are highlighted by blue arrows. The third type of crack was transgranular cracks, which intercepted more than one mineral grain. More transgranular cracks were observed in the tested samples to occur exclusively through quartz and sometimes feldspars. In fact, this type of crack was mainly formed by the joining and growth of intragranular cracks within quartz grains (yellow arrows in Figs. 8(a–c)).
As seen from Fig. 8(e), some of the plagioclase minerals had been weathered into sericite. Feldspars behave in a brittle manner, while sericite is ductile, like clay minerals and micas. Consequently, the sericitisation stops crack development in the weathered parts of feldspars. A close inspection on the thin sections revealed that there was a considerable contrast between the quartz and micaceous minerals boundaries. As is clear in the elliptical boxes in Figs. 8(a-c), and especially highlighted in Fig. 8(d), at these boundaries, quartz grains were highly cracked, while the micaceous minerals were resistant to brittle deformation, and crack was rarely developed within micaceous minerals due to their ductile and more flexible behaviour.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is very useful for surveying the microstructural morphology of geological materials. In this study, SEM was employed to detect the morphology of fracture surfaces and to evaluate the responses of each mineral during fracture development. Micaceous minerals, with complete cleavage, broke along one dominant plane of cleavage. Cleavage refers to the tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weakness in the chemical bonds, or along planes where bond strength is the least. Based on the direction of a cleavage plane with respect to that of tensile stress, different types of fractures were observed for these minerals (Fig. 9). When the cleavage plane of biotite or muscovite is perpendicular to the direction of tensile stress, these minerals separate along their cleavage plane, and the resulting fracture surface is smooth and flat. This condition leads to the lower resistance of micaceous minerals to fracture development, and there is a typical sparkling cleavage that can be observed through the minerals (Figs. 9(a) and (b)). Observations made via SEM showed that the cleavage plane inclined between 20-70° with respect to the direction of tensile stress, micaceous minerals separated along their cleavage plane, with a smooth surface but a stepped shape. This type of fracture caused micas to present flaky shape. In this situation, the strength of these minerals was moderate. As beyond separation along their cleavage plane, the edges of micas were damaged and some fracture surfaces splintered, which is clear in Figs. 9(c) and (d). For micaceous minerals, when tensile stress is parallel to the cleavage plane, the failure surfaces develop differently and may not parallel the cleavage plane. When the stress rate is not very high, a fracture surface is developed perpendicular to the cleavage plane, exhibiting a book-like shape with rough and irregular edges (Fig. 9(e)). When these minerals break at a higher strain rate, some parts of the mica are pulled out during tensile failure, leading to a relatively deep notch (Fig. 9(f)). This phenomenon is a reliable sign of rock spalling.
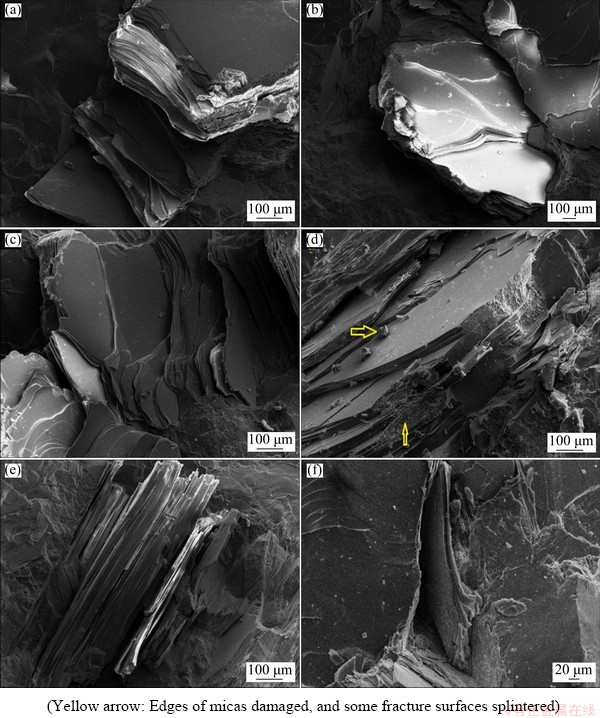

Fig. 9 Typical SEM images of micaceous minerals on spalling fracture surface
The fracture surfaces of feldspar minerals in the granite are shown in Fig. 10. Feldspars have two sets of nearly vertical cleavage planes. One of cleavage planes is perfect and other is well-developed. Because of this difference in cleavage development, ladder-shaped fracture surfaces appeared during the fracturing of these minerals (Figs. 10(a) and (b)). If the perfectly developed cleavage plane was perpendicular to the fracture surface, a scarp shape was generated, making the fracture surface quite rough (Fig. 10(b)).
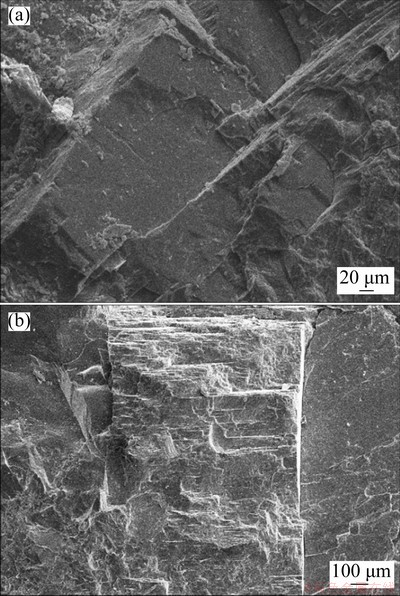
Fig. 10 Typical SEM images of feldspar minerals on spalling fracture surface
Observation of the quartz crystals by SEM indicated that during failure, a series of conchoidal fractures were developed. Conchoidal fractures can be seen macroscopically in some rocks, which behave in a more elastic manner. Due to the structure of the quartz crystalline lattice, this mineral dose not exhibit predictable weaknesses along specified bonds. Sometimes, quartz is broken in terrace-like steps with conchoidal surfaces (Fig. 11(a)). Based on the analysis of fracture surfaces, we concluded that quartz did not play a considerable role in the roughness of fracture surfaces because of its smoothly curving surface (Fig. 11(b)). Additionally, the results show that with increasing dynamic impact loads, the amount of deformation and fracturing considerably increased.
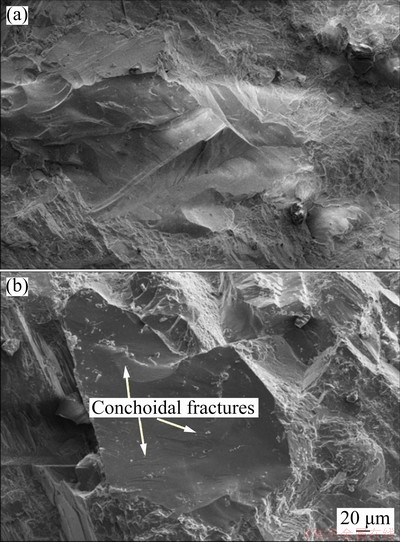

Fig. 11 Typical SEM images of quartz on spalling fracture surface
Fractographic analyses of granite fracture surfaces via SEM indicated that there was typically sparkling cleavage cracking through micaceous minerals, with low occurrence along cleavage planes, ruptured edges, and kinks of the cleavage plane. In fact, during cracking, biotite and muscovite were cleaved in the usual way along the plane (Fig. 12(a); white arrows in Fig. 12(b)). This type of crack, without shear sliding, represented failure that occurred by spalling under tensile stress. When spalling stress was high enough and loaded with a high rate parallel to the cleavage plane, micas were broken along another plane and were pulled out (blue arrows in Fig. 12(c)).
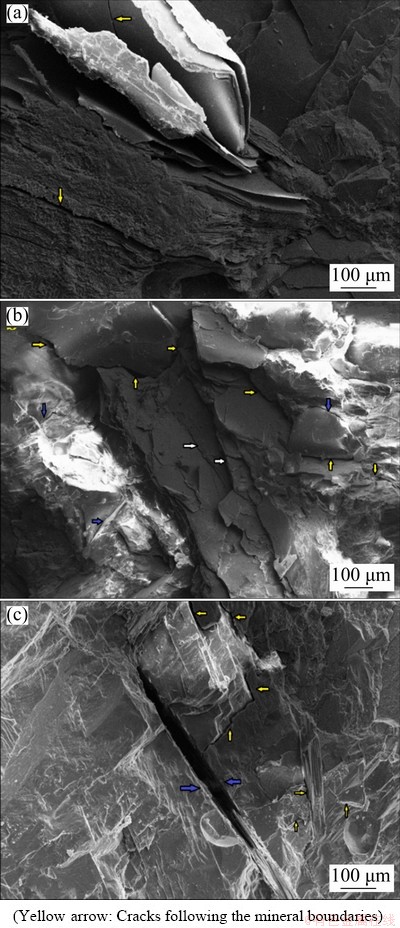
Fig. 12 Typical SEM images of cracks developed in different minerals during dynamic loading
As can be seen from Fig. 12, grain boundary fractures and cleavage fractures were the main types of cracks developed on fracture surfaces. The results show that the generated cracks sometimes followed the mineral boundaries (yellow arrows in Figs. 12(b) and (c)). Typical grain boundary cracking is shown in Fig. 12(c) and occurred between a feldspar and quartz. Furthermore, some of the quartz grains showed nucleated intergranular cracks, causing grain decohesion (Fig. 12(b)). Finally, during crack propagation, the developed cracks joined together to generate a dendritic pattern.
Comparing the fracture surfaces of different tests revealed that with increase in the dynamic impact loads, some dust and small mineral fragments attached to the fracture surface of the rock samples. The appearance of these fragments increased number and decreased dimension with increase in the dynamic impact load. In fact, during high strain-rate loading, there was not enough time for crack growth, and the accumulation of high energy in minerals led to crushing and the development of small grain fragments. This phenomenon is similar to the rock bursting that occurs in deep mines.
4 Conclusions
(1) The time-to-development of the first spalling crack at different loading rates was similar, while the number of cracks that ultimately formed differed. After the first spalling, dynamic stress decreased, and when the remaining stress was greater than the dynamic spalling strength, new spalling cracks developed. Therefore, it was concluded that the dynamic spalling strength of the rocks increased with increasing loading stress.
(2) Petrographic analyses revealed that three types of cracks developed: intergranular, grain boundary and transgranular. Quartz, which has a brittle behaviour, was highly cracked, whereas the more ductile micaceous minerals showed resistance to brittle deformation and greatly affected the crack paths by changing their direction. Furthermore, morphological surveys of fracture surfaces via SEM indicted that micaceous minerals were separated along cleavage plane as expected. Cracks that developed along cleavage planes without shear sliding and were pulled out with the generation of narrow grooves can be considered as unique results of spalling fracture.
(3) The remarked results in this study can provide some information for clearly understanding the macro/micro fracture mechanism of rock material and stability analysis of underground rock engineering under dynamic loading such as rock blasting, earthquake and excavation disturbance.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51904335, 51904333, 11772357, 51927808)
References
[1] YOSHIDA S, FURUYA S, NISHIDA M. High speed impact test on rock specimens with a compressive stress pulse [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2019, 210: 132-146.
[2] LI Xi-bing, CHEN Zheng-hong, WENG Lei, LI Chong-jin. Unloading responses of pre-flawed rock specimens under different unloading rates [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(7): 1516-1526.
[3] WANG Shao-feng, SUN Li-cheng, HUANG Lin-qi, LI Xi-bing, SHI Ying, YAO Jin-rui, DU Shao-lun. Non-explosive mining and waste utilization for achieving green mining in underground hard rock mine in China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(9): 1914-1928.
[4] WANG Shao-feng, LI Xi-bing, YAO Jin-rui, GONG Feng-qiang, LI Xiang, DU Kun, TAO Ming, HUANG Lin- qi, DU Shao-lun. Experimental investigation of rock breakage by a conical pick and its application to non- explosive mechanized mining in deep hard rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 122: 104063.
[5] HUANG Lin-qi, LI Jin, HAO Hong, LI Xi-bing. Micro-seismic event detection and location in underground mines by using convolutional neural networks (CNN) and deep learning [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 81: 265-276.
[6] LONG Yi, LIU Jian-po, LEI Gang, SI Ying-tao, ZHANG Chang-yin, WEI Deng-cheng, SHI Hong-xu. Progressive fracture processes around tunnel triggered by blast disturbances under biaxial compression with different lateral pressure coefficients [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(9): 2518-2535.
[7] ZHANG Cun, BAI Qing-sheng, CHEN Yan-hong. Using stress path-dependent permeability law to evaluate permeability enhancement and coalbed methane flow in protected coal seam: A case study [J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2020, 6(3): 53.
[8] MAHABADI O K, COTTRELL B E, GRASSELLI G. An example of realistic modelling of rock dynamics problems: FEM/DEM simulation of dynamic Brazilian test on Barre granite [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2010, 43(6): 707-716.
[9] YI Wei, RAO Qiu-hua, LI Zhou, SHEN Qing-qing. A new measurement method of crack propagation rate for brittle rock under THMC coupling condition [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(8): 1728-1736.
[10] CAO Wen-zhuo, SHI Ji-quan, DURUCAN S, SI Guang-yao, KORRE A. Gas-driven rapid fracture propagation under unloading conditions in coal and gas outbursts [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 130: 104325.
[11] WANG Shao-feng, HUANG Lin-qi, LI Xi-bing. Analysis of rockburst triggered by hard rock fragmentation using a conical pick under high uniaxial stress [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 96: 103195.
[12] MOMENI A A, KHANLARI G R, HEIDRAI M, SEPAHI A A, BAZVAND E. New engineering geological weathering classifications for granitoid rocks [J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 185: 43-51.
[13] FEREIDOONI D. Assessing the effects of mineral content and porosity on ultrasonic wave velocity [J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2018, 14(4): 399-406.
[14] KAHRAMAN S, FENER M, KASLING H, THURO K. Investigating the effect of strength on the LCPC abrasivity of igneous rocks [J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2018, 15(2): 805-810.
[15] LI Xiao-zhao, QI Cheng-zhi, SHAO Zhu-shan, QU Xiao-lei. Static shear fracture influenced by historic stresses path and crack geometries in brittle solids [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 96: 64-71.
[16] AKESSON U, HANSSON J, STIGH J. Characterisation of microcracks in the Bohus granite, western Sweden, caused by uniaxial cyclic loading [J]. Engineering Geology, 2004, 72(1): 131-142.
[17] ERARSLAN N, WILLIAMS D J. The damage mechanism of rock fatigue and its relationship to the fracture toughness of rocks [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2012, 56(56): 15-26.
[18] ERARSLAN N. Microstructural investigation of subcritical crack propagation and fracture process zone (FPZ) by the reduction of rock fracture toughness under cyclic loading [J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 208: 181-190.
[19] YANG Hai-qing, LIU Jun-feng, ZHOU Xiao-ping. Effects of the loading and unloading conditions on the stress relaxation behavior of pre-cracked granite [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(5): 1-13.
[20] ZABIHI M, AYATOLLAHI M R, REZAIE H R. Mixed-mode fracture of synthesized nanocrystalline forsterite for biomedical applications [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 94: 173–180.
[21] HE Zhen-guo, LI Gen-sheng, TIAN Shou-cheng, WANG Hai-zhu, SHEN Zhong-hou, LI Jing-bin. SEM analysis on rock failure mechanism by supercritical CO2 jet impingement [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 146: 111–120.
[22] HAMIDI S, MARANDI S M. Effect of clay mineral types on the strength and microstructure properties of soft clay soils stabilized by epoxy resin [J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2018, 15(2): 729–738.
[23] LI Xi-bing, ZOU Yang, ZHOU Zi-long. Numerical simulation of the rock SHPB test with a special shape striker based on the discrete element method [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2014, 47(5): 1693–1709.
[24] LI Xi-bing, GONG Feng-qiang, TAO Ming, DONG Long-jun, DU Ku, MA C D, ZHOU Zi-long, YIN Tu-bing. Failure mechanism and coupled static-dynamic loading theory in deep hard rock mining: A review [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 9(4): 767–782.
[25] TAO Ming, LI Zhan-wen, CAO Wen-zhuo, LI Xi-bing, WU Cheng-qing. Stress redistribution of dynamic loading incident with arbitrary waveform through a circular cavity [J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2019, 43: 1279-1299.
[26] TAO Ming, MA A, CAO Wen-zhuo, LI Xi-bing, GONG Feng-qiang. Dynamic response of pre-stressed rock with a circular cavity subject to transient loading [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 99: 1–8.
[27] TAO Ming, ZHAO Hua-tao, LI Xi-bing, LI Xiang, DU Kun. Failure characteristics and stress distribution of pre-stressed rock specimen with circular cavity subjected to dynamic loading [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 81: 1–15.
[28] LI Xi-bing, TAO Ming, WU Cheng-qing, DU Kun, WU Qiu-hong. Spalling strength of rock under different static pre-confining pressures [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 99: 69–74.
[29] ZHOU Zi-long, LI Xi-bing, ZOU Yang, JIANG Yi-hui, LI Guo-nan. Dynamic Brazilian tests of granite under coupled static and dynamic loads [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2014, 47(2): 495–505.
[30] ZHU W C, NIU L L, LI S H, XU Z H. Dynamic Brazilian test of rock under intermediate strain rate: pendulum hammer-driven SHPB test and numerical simulation [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2015, 48: 1867–1881.
[31] LI Shi-hao, ZHU Wan-cheng, NIU Lei-lei, DAI Feng. Constant strain rate uniaxial compression of green sandstone during SHPB tests driven by pendulum hammer [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2017, 2017: 1–12.
[32] FAKHIMI A, AZHDARI P, KIMBERLEY J. Physical and numerical evaluation of rock strength in split Hopkinson pressure bar testing [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 102: 1–11.
[33] BROWN E T. Rock characterization testing and monitoring—ISRM suggested methods [M]. Oxford: Pergamon, 1981.
黄麟淇1,汪 军1,Aliakbar MOMENI2,王少锋1
1. 中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. Faculty of Earth Sciences, Shahrood University of Technology, Shahrood, 3619995161, Iran
摘 要:在动态载荷作用下岩石可能发生层裂破坏。在动态霍普金森压杆(SHPB)上及4种不同的冲击载荷条件下,开展动态张拉载荷作用下花岗岩的破裂发展和破坏特性研究。岩样破坏后,在破坏表面附近取样并制作薄片,用偏光显微镜观察岩石裂纹的生长模式,并利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察破坏表面的矿物颗粒形貌特征,从而评价岩石矿物特征对载荷和破坏的响应特性。研究结果表明,岩样层裂裂纹数量随着峰值冲击载荷的增加而增多,并且岩石内的石英矿物持续发生大量的晶间断裂;矿物晶体的解理面及其相对于载荷的方向对岩石强度和破裂特性有着至关重要的作用;沿垂直于载荷的矿物晶体解理面进行分离而没有云母矿物平行于载荷的运动是岩石发生层裂破坏所特有的。
关键词:微观检测;动态加载;层裂破坏;矿物特性;晶间断裂
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Shao-feng WANG, Tel: +86-18073369486, E-mail: sf.wang@csu.edu.cn, wsfcumt@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65642-X
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

