NaOH焙烧Zn2SiO4反应机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第9期
论文作者:申晓毅 邵鸿媚 顾惠敏 陈兵 翟玉春 马培华
文章页码:1878 - 1886
关键词:反应机理;动力学;Zn2SiO4;NaOH焙烧;反应过程;物相转化
Key words:reaction mechanism; kinetics; Zn2SiO4; NaOH roasting; reaction process; phase transformation
摘 要:研究氢氧化钠焙烧硅酸锌的反应动力学,采用正交试验优化反应条件,优化反应条件为:NaOH和Zn2SiO4摩尔配比16:1、反应温度550 °C以及反应时间2.5 h。为了确定氧化锌和二氧化硅的物相转化和反应过程,采用XRD技术分析不同温度焙烧样品的物相。600 °C焙烧样品的最终物相为Na2ZnO2、Na4SiO4、Na2ZnSiO4和NaOH。通过未反应收缩核模型研究焙烧过程的动力学方程,选取2种反应速率控制模型考察反应机理,分别为颗粒表面化学反应控制和通过固体产物层的扩散控制模型。结果表明:NaOH焙烧Zn2SiO4的反应过程受通过固体产物层的扩散控制,反应的表观活化能为19.77 kJ/mol。
Abstract: The reaction kinetics of roasting zinc silicate using NaOH was investigated. The orthogonal test was employed to optimize the reaction conditions and the optimized reaction conditions were as follows: molar ratio of NaOH to Zn2SiO4 of 16:1, reaction temperature of 550 °C, and reaction time of 2.5 h. In order to ascertain the phases transformation and reaction processes of zinc oxide and silica, the XRD phase analysis was used to analyze the phases of these specimens roasted at different temperatures. The final phases of the specimen roasted at 600 °C were Na2ZnO2, Na4SiO4, Na2ZnSiO4 and NaOH. The reaction kinetic equation of roasting was determined by the shrinking unreacted core model. Aiming to investigate the reaction mechanism, two control models of reaction rate were applied: chemical reaction at the particle surface and diffusion through the product layer. The results indicated that the diffusion through the product layer model described the reaction process well. The apparent activation energy of the roasting was 19.77 kJ/mol.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 1878-1886
Xiao-yi SHEN1,2, Hong-mei SHAO3, Hui-min GU1, 2, Bing CHEN1,4, Yu-chun ZHAI1, Pei-hua MA1
1. School of Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
2. Liaoning Key Laboratory for Metallurgical Sensor and Technology, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
3. School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shenyang Ligong University, Shenyang 110159, China;
4. Science and Technology Laboratory, Academy of Environmental Sciences of Panjin City, Panjin 124401, China
Received 19 June 2017; accepted 31 October 2017
Abstract: The reaction kinetics of roasting zinc silicate using NaOH was investigated. The orthogonal test was employed to optimize the reaction conditions and the optimized reaction conditions were as follows: molar ratio of NaOH to Zn2SiO4 of 16:1, reaction temperature of 550 °C, and reaction time of 2.5 h. In order to ascertain the phases transformation and reaction processes of zinc oxide and silica, the XRD phase analysis was used to analyze the phases of these specimens roasted at different temperatures. The final phases of the specimen roasted at 600 °C were Na2ZnO2, Na4SiO4, Na2ZnSiO4 and NaOH. The reaction kinetic equation of roasting was determined by the shrinking unreacted core model. Aiming to investigate the reaction mechanism, two control models of reaction rate were applied: chemical reaction at the particle surface and diffusion through the product layer. The results indicated that the diffusion through the product layer model described the reaction process well. The apparent activation energy of the roasting was 19.77 kJ/mol.
Key words: reaction mechanism; kinetics; Zn2SiO4; NaOH roasting; reaction process; phase transformation
1 Introduction
Zinc is one of the important transition metals and wildly used in galvanizing and battery industry. With the gradual exhaustion of zinc sulfide ore and the rising demand for zinc, low-grade zinc oxide ore has attracted much attention in zinc metallurgy [1,2]. As the secondary ore of zinc, it is difficult to float due to high gangue, complex phases and serious pelitization [3,4]. Zinc oxide ore with utilization value mainly includes smithsonite (ZnCO3), hemimorphite [Zn4Si2O7(OH)2·H2O], zincite (ZnO), willemite (Zn2SiO4), and hydrozincite [2ZnCO3·3Zn(OH)2], etc. Zinc in these minerals usually exists as multiphase rather than a single phase, such as ZnCO3 and Zn2SiO4. Lead, iron, silica, aluminum and cadmium also exist in these minerals [5,6].
Great amount of zinc oxide ore, especially low- grade zinc oxide ore, is available in China. For example, the zinc oxide ore in Lanping, Yunnan Province is abundant. However, the recovery ratios of valuable metals are low and the cost is high when the mineral is treated directly by some traditional methods due to low grade, complex compositions and mineral intergrowth. The typical pyrometallurgy methods are gradually losing their attraction for high energy consumption and heavy pollution [7,8]. On the contrary, hydrometallurgical routes become more and more attractive. Normally, hydrometallurgical routes include acid leaching and alkaline leaching (involving NaOH leaching and ammonium leaching) [9]. All of those methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Acid leaching is a method widely studied and applied. However, silica gel is easily formed and enters into the leaching solution, causing filtration difficulty [10,11]. When NaOH leaching is applied, silica and lead dissolve in solution together with zinc. However, the decomposition of Zn2SiO4 is slow [12,13]. Ammonia is an attractive reagent. When ammonium leaching is adopted, the leaching vessels are rigorously required in order to avoid ammonium volatilization [14,15].
Many researchers have focused on comprehensive utilization of low-grade zinc oxide ore by improving the current routes or developing new method or new reaction medium in recent years, such as (NH4)2SO4 roasting [16], NaOH roasting [17] and solvent extraction [18]. NaOH roasting is a process combining the advantages of pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy routes. The stable Zn2SiO4 can be decomposed in this simple process with low energy consumption. As the key step of utilizing low-grade zinc oxide ore, it is necessary to investigate the roasting process and reaction mechanism. In this work, Zn2SiO4 was roasted by using NaOH and the reaction conditions were optimized. The phase transformation and reaction process of zinc and silica were examined. The reaction kinetic equation of roasting zinc silicate using NaOH was deduced finally.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and characterization
Analytic grade Zn2SiO4 with purity ≥99.0% was used as raw material and NaOH was used as reactant. Distilled water was homemade in laboratory.
2.2 Procedure
Appropriate masses of Zn2SiO4 with 74-104 μm in particle size and NaOH were weighted according to molar ratio (8:1, 12:1 and 16:1) and mixed uniformly in a medicine grinder. The mixture was put into a crucible, and then the crucible was placed in a roasting furnace. The roasting procedure was controlled and monitored by an intelligent temperature control instrument. When the roasting process ended, the specimens were water- leached at 80 °C for 1.5 h, filtrated and washed. Zinc oxide and silica were distributed both in leaching solution and water leaching residue. The contents of zinc oxide and silica both in solution and residue were examined by titration method to calculate the recovery ratios.
The mixed material was put into a series of crucibles. When the desired temperature was reached, the crucibles were placed into the roasting furnace. After the temperature was stabilized, the crucibles were orderly taken out at a predetermined time interval and cooled rapidly in order to reduce deviation. After leaching and filtration, the recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica were calculated.
The recovery ratio of zinc oxide or silica was calculated using
 (1)
(1)
where η is the recovery ratio of zinc oxide or silica, V is the leaching solution volume, c is the concentration of zinc oxide or silica, and C is the initial content in Zn2SiO4.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of zinc silicate
Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern of zinc silicate. The position and intensity of the diffraction peaks are consistent with those of the zinc silicate (JCPDS No. 37-1485).
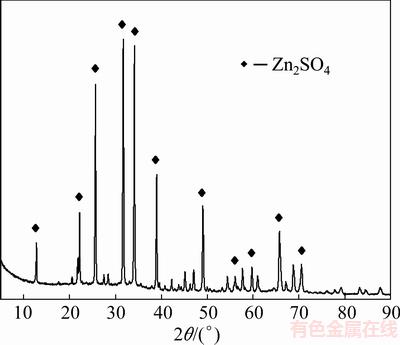
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of zinc silicate
3.2 Orthogonal test
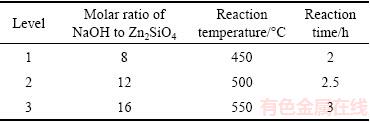
The orthogonal test was designed to optimize the reaction conditions of roasting Zn2SiO4 by using NaOH. The factors and levels are listed in Table 1, and the results are listed in Table 2. The recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica were used as evaluation indexes.
Table 1 Factors and levels of orthogonal test
The optimized reaction conditions were as follows: molar ratio of NaOH to Zn2SiO4 of 16:1, reaction temperature of 550 °C and reaction time of 2.5 h. The sequence influencing the recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2 in molten NaOH system is molar ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time. The verification experiments were carried out and the recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2 were stable at approximate 96% and 92%, respectively. This is because Na2ZnSiO4 is generated in roasting, which is the main component in leaching residue. From the residual Na2ZnSiO4 formula, Zn is involved in the reaction; however, Si has no change. Thereby, the recovery ratio of ZnO is higher than that of SiO2.
Table 2 Results of orthogonal test
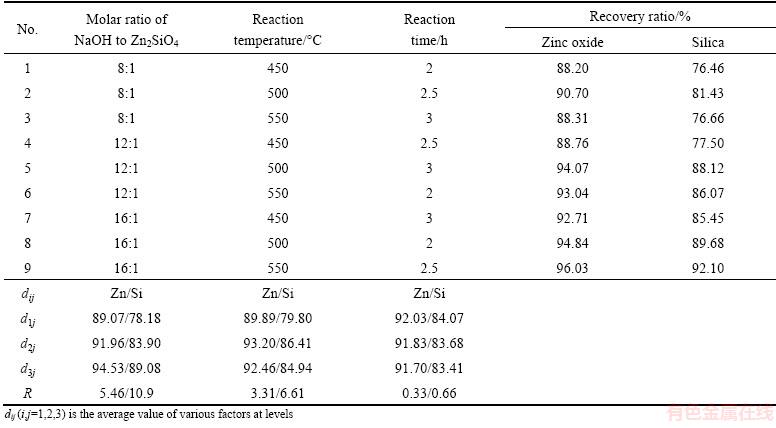
The recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2 increased with molar ratio rising due to the improvement of interface area between Zn2SiO4 and NaOH. Raising reaction temperature was contributed to the mass transfer between the liquid and solid phases.
3.3 Reaction process analysis
Zn2SiO4 was roasted for 2 h by using NaOH at molar ratio of 16:1 at different temperatures. The mineral phases of the specimens are displayed in Fig. 2.
The existence of Na2ZnO2, Na2ZnSiO4 and Na2Zn(OH)4 in Fig. 2(a) indicated that the reaction between Zn2SiO4 and NaOH had started at 250 °C. When the reaction temperature was 300 °C, the diffraction peaks of Zn2SiO4 disappeared in the XRD pattern, indicating that Zn2SiO4 had been completely reacted. The phases were Na2ZnO2, Na2ZnSiO4, Na2Zn(OH)4 and ZnO. Na2Zn(OH)4 was an intermediate product, which could be seen as Na2ZnO2.
The main compositions in Fig. 2(c) were Na2ZnSiO4, Na2Zn(OH)4 and NaOH, which were similar with those in Fig. 2(d). Na2Zn(OH)4 disappeared when the temperature was 400 °C. At 450 °C, Na2SiO3 and Na4SiO4 were synthesized. Na2SiO3 disappeared when the temperature reached 500 °C because of the transformation from Na2SiO3 to Na4SiO4. The XRD patterns in Figs. 2(g) and (h) were almost the same. The final phases in the specimen roasted at 600 °C were Na2ZnO2, Na4SiO4 and Na2ZnSiO4. Residual NaOH still existed. However, the reaction between Zn2SiO4 and NaOH was not complete, which could be confirmed from Na2ZnSiO4 phase in the XRD pattern. The existence of Na2ZnSiO4 explained why the recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2 were only about 96% and 92%. NaOH·H2O was attributed to the moisture adsorption capacity of NaOH in air. Na2ZnO2 and Na4SiO4 are easily soluble in water and enter into the liquid phase; however, Na2ZnSiO4 dissolves slowly in alkaline solution, so Na2ZnSiO4 enters into the leaching residue after filtration.
From above, the reaction process could be summarized as follows: Na2ZnO2 [Na2Zn(OH)4] and Na2ZnSiO4 were obtained when zinc silicate reacted with NaOH. The reaction between Zn2SiO4 and NaOH proceeded with reaction temperature rising. When the reaction temperature was above 450 °C, Na2SiO3 and Na4SiO4 were synthesized. In addition, Na2SiO3 was transformed into Na4SiO4 finally. The final phases in the specimen were Na2ZnO2, Na4SiO4, Na2ZnSiO4 and NaOH. Na2ZnSiO4 was more stable than Zn2SiO4 in the chemical property. The chemical equations in roasting could be summarized as follows:
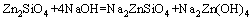 (2)
(2)
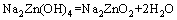 (3)
(3)
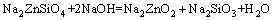 (4)
(4)
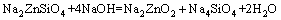 (5)
(5)
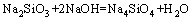 (6)
(6)
3.4 Dynamics computation
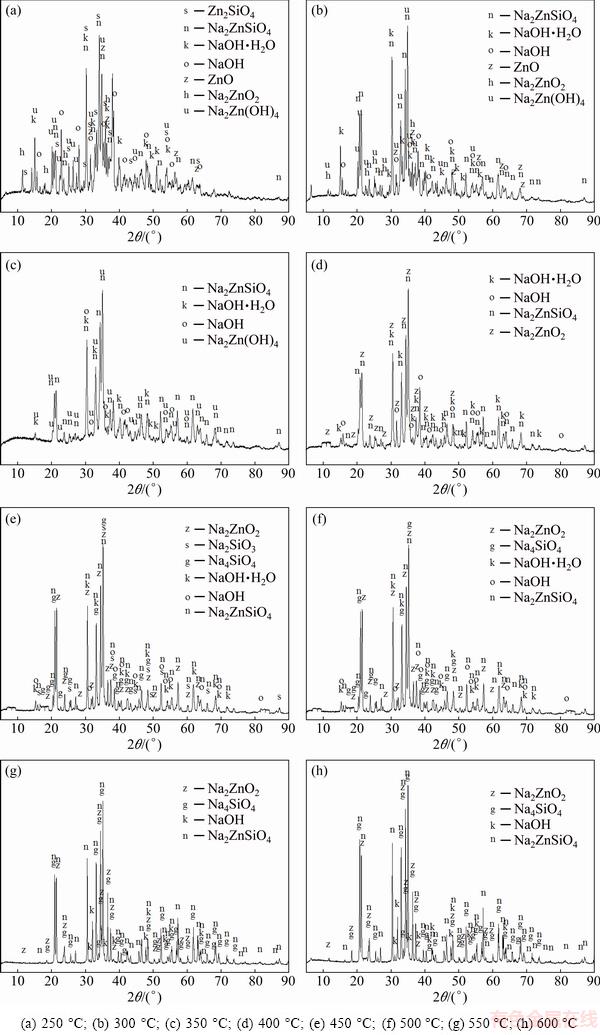
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of specimens obtained at different temperatures
The reaction between NaOH and Zn2SiO4 can be regarded as liquid-solid reaction in experiments because the melting point of NaOH is 318 °C. Therefore, the roasting process can be examined by the shrinking unreacted core model if Zn2SiO4 particles are sphere- shaped [19]. The reaction rate of molten NaOH roasting Zn2SiO4 may be controlled by two different models: the chemical reaction at the particle surface or diffusion through the product layer [19,20]. Equation (7) can describe the reaction rate controlled by chemical reaction at the particle surface. The reaction rate controlled by the diffusion through the product layer can be expressed as Eq. (8):
 (7)
(7)
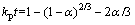 (8)
(8)
where t is the reaction time (min), α is the recovery fraction of zinc oxide or silica, and kc and kp are the reaction rate constants.
3.4.1 Effect of molar ratio of NaOH to zinc silicate on recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2
The effect of molar ratio of NaOH to zinc silicate on the recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica was investigated. The roasting temperature was kept at 500 °C, and the results are plotted in Fig. 3.
The recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica increased with rising molar ratio of NaOH to Zn2SiO4.
Increasing the NaOH dosage was contributed to the improvement of the real contact area. The recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica kept increasing within 100 min, and the maximum values were 81% and 73%, respectively.
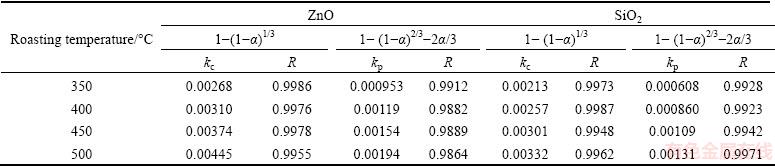
In order to identify the rate-controlling step, the kinetics of molten NaOH roasting Zn2SiO4 was analyzed with the two different models. Based on experimental data in Fig. 3, the relationships of the right-hand sides of Eq. (7) and Eq. (8) against reaction time are shown in Fig. 4 and Fig, 5, respectively. The apparent reaction rate constants kc and kp could be obtained from the slopes of those straight fitting lines. These constants with corresponding correlation coefficients R are recorded in Table 3. The straight lines in Fig. 5 are closer to zero point than those in Fig. 4, indicating that the reaction rate might be controlled by the diffusion through the product layer.
3.4.2 Effect of roasting temperature on recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2
The effect of roasting temperature on the recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica was investigated in a temperature range of 350-500 °C. The molar ratio of NaOH to zinc silicate was 16:1. The experimental results are plotted in Fig. 6.
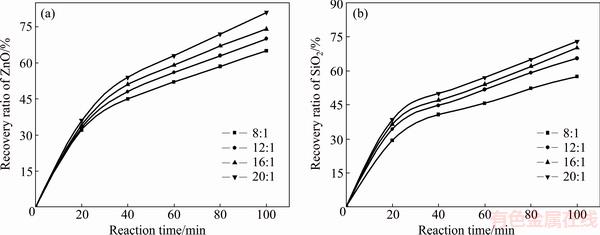
Fig. 3 Influence of NaOH to Zn2SiO4 molar ratio on recovery ratios of zinc oxide (a) and silica (b)
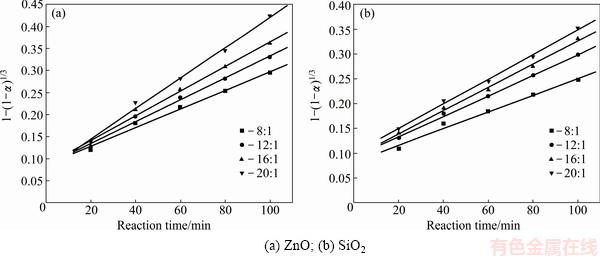
Fig. 4 Plots of 1-(1-α)1/3 against reaction time at different NaOH to Zn2SiO4 molar ratios
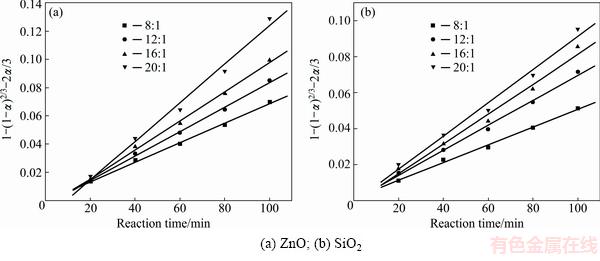
Fig. 5 Plots of 1-(1-α)2/3-2α/3 against reaction time at different NaOH to Zn2SiO4 molar ratios
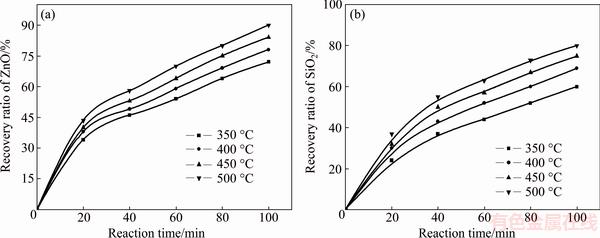
Fig. 6 Effect of reaction temperature on recovery ratios of zinc oxide (a) and silica (b)
Table 3 Apparent rate constants and correlation coefficients at different molar ratios
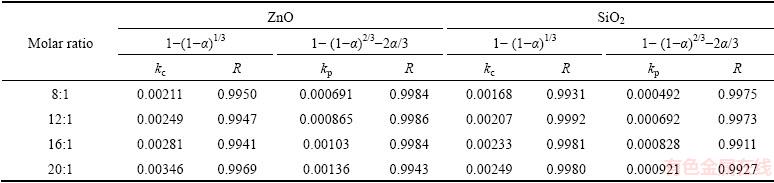
It was obvious that the roasting temperature played a significant role in roasting. The recovery ratios of zinc oxide and silica increased with the roasting temperature rising. About 90% zinc oxide and 80% silica were recovered at 500 °C for 100 min. The two models were used to investigate the kinetics of roasting process. The plots of the right-hand sides of Eq. (7) and Eq. (8) against reaction time are shown in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8, respectively. The apparent rate constants kc and kp were calculated from the slops of those fitting straight lines in Figs. 7 and 8, as listed in Table 4 together with the corresponding correlation coefficients R. All the fitting straight lines in Fig. 8 were closer to zero point than those in Fig. 7. In other words, the results were better fitted by Eq. (8) than by Eq. (7).
From above, the reaction rate of roasting Zn2SiO4 in molten NaOH might be controlled by the diffusion through the product layer. However, as we know, there must be deviation when the experiments were carried out. And the reaction started before the roasting temperature was stable.
3.4.3 Calculation of apparent activation energy
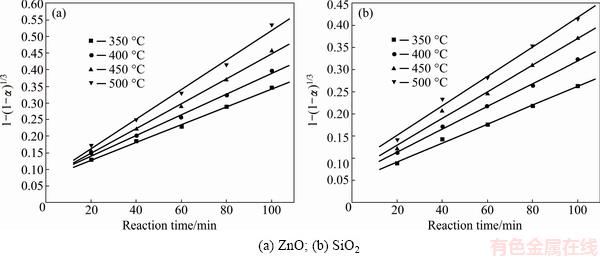
Fig. 7 Plots of 1-(1-α)1/3 against reaction time at different roasting temperatures
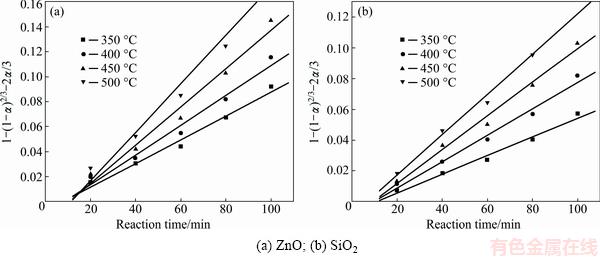
Fig. 8 Plots of 1-(1-α)2/3-2α/3 against reaction time at different roasting temperatures
Table 4 Apparent rate constants and correlation coefficients at different roasting temperatures
The reaction rate constant k is a function of temperature. The relationship between them is expressed by the Arrhenius equation [21]:
k=Aexp[-E/(RT)] (9)
where A is the frequency factor, E is the apparent activation energy, and R is the gas constant.
The activation energy E determined by the plots of ln k against 1/T in Figs. 9(a) and (b) (calculated by using Eq. (7)) was 13.61 and 11.99 kJ/mol, respectively. And the frequency factor A was 0.0363 and 0.0218, respectively. The average values of E and A were 12.80 kJ/mol and 0.0291, respectively.
The activation energy E determined from the plots of ln k against 1/T in Figs. 10(a) and (b) (calculated by using Eq. (8)) was 19.07 and 20.46 kJ/mol, respectively. And the frequency factor A was 0.0371 and 0.0323, respectively. The average values of E and A were 19.77 kJ/mol and 0.0347, respectively.
The values of the activation energy E calculated using Eq. (7) and Eq. (8) were both less than 20 kJ/mol. According to the literatures [21,22], the roasting process was controlled by diffusion through the product layer when the activation energy was less than 20 kJ/mol. So, the kinetic equation could be expressed as
1-(1-α)2/3-2α/3=0.0347exp[-19.77/(RT)]t (10)
3.5 Characterization of leaching residue
Figure 11 shows the XRD pattern and SEM image of leaching residue. The position and intensity of the diffraction peaks were consistent with those of the sodium zinc silicate (JCPDS No. 76-0714). No other phases were detected. Na2ZnSiO4 particles were regular and in a narrow size distribution.
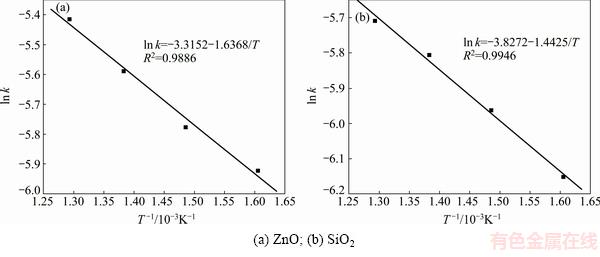
Fig. 9 Plots of ln k against 1/T at different roasting temperatures using Eq. (7)
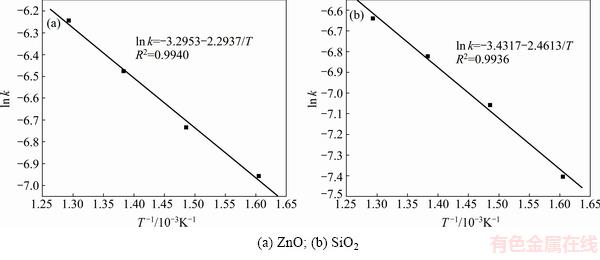
Fig. 10 Plots of ln k against 1/T at different roasting temperatures using Eq. (8)

Fig. 11 XRD pattern (a) and SEM image (b) of leaching residue
4 Conclusions
1) The optimized reaction conditions of roasting zinc silicate by using NaOH were as follows: molar ratio of NaOH to zinc silicate of 16:1, reaction temperature of 550 °C and reaction time of 2.5 h. The influencing sequence was molar ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time. Under optimized reaction conditions, the recovery ratios of ZnO and SiO2 were approximately 96% and 92%, respectively. The apparent activation energy of the roasting was 19.77 kJ/mol. The reaction rate of roasting zinc silicate was controlled by the diffusion through the product layer.
2) Na2ZnO2 [Na2Zn(OH)4] and Na2ZnSiO4 were obtained when Zn2SiO4 reacted with NaOH. The reaction between Zn2SiO4 and NaOH proceeded with rising reaction temperature. When the reaction temperature was above 450 °C, Na2SiO3 and Na4SiO4 were obtained, and Na2SiO3 was transformed into Na4SiO4 finally. The final phases in the specimen obtained at 600 °C were Na2ZnO2, Na4SiO4, Na2ZnSiO4 and NaOH. Na2ZnSiO4 was more stable than Zn2SiO4 in the chemical property.
References
[1] LI Yong, WANG Ji-kun, WEI Chang, LIU Chun-xia, JIANG Ji-bo, WANG. Fan. Sulfidation roasting of low grade lead-zinc oxide ore with elemental sulfur [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2010, 23(7): 563-566.
[2] YANG Sheng-hai, LI Hao, SUN Yan-wei, CHEN Yong-ming, TANG Chao-bo, HE Jing. Leaching kinetics of zinc silicate in ammonium chloride solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(6): 1688-1695.
[3] SUN Yi, SHEN Xiao-yi, ZHAI Yu-chun. Thermodynamics and kinetics of extracting zinc from zinc oxide ore by ammonium sulfate roasting method [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015, 22(5): 467-475.
[4] FRENAY J. Leaching of oxidized zinc ores in various media [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1985, 15(2): 243-253.
[5] HE Shan-ming, WANG Ji-kun, Yan Jiang-feng. Pressure leaching of synthetic zinc silicate in sulfuric acid medium [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108(3-4): 171-176.
[6] ABKHOSHK E, JORJANI E, AL-HARAHSHEH M S, RASHCHI F, NAAZERI M. Review of the hydrometallurgical processing of non-sulfide zinc ores [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 149(10): 153-167.
[7] MORADI S, MONHEMIUS A J. Mixed sulphide oxide lead and zinc ores problems and solutions [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(10): 1062-1076.
[8] YANG Tian-zu, DOU Ai-chun, LEI Cun-mao, REN Jin, LIU Zhen-zhen. Ligand selection for complex-leaching valuable metals in hydrometallurgy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(6): 1148-1153.
[9] JHA M K, KUMAR V, SINGH R J. Review of hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial wastes [J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2001, 33(1): 1-22.
[10] DING Zhi-ying, YIN Zhou-lan, HU Hui-ping, CHEN Qi-yuan. Dissolution kinetics of zinc silicate (hemimorphite) in ammoniacal solution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(2): 201-206.
[11]  E, KOCAKERIM M M. Optimization study of the leaching of roasted zinc sulphide concentrate with sulphuric acid solutions [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 2004, 43(8): 1007-1014.
E, KOCAKERIM M M. Optimization study of the leaching of roasted zinc sulphide concentrate with sulphuric acid solutions [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 2004, 43(8): 1007-1014.
[12] CHEN Ai-liang, ZHAO Zhong-wei, JIA Xi-jun, LONG Shuang, HUO Guang-sheng, CHEN Xing-yu. Alkaline leaching Zn and its concomitant metals from refractory hemimorphite zinc oxide ore [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 97(3-4): 228-232.
[13] FENG Lin-yong, YANG Xian-wan, SHEN Qing-feng, XU Ming-li, JIN Bing-jie. Pelletizing and alkaline leaching of powdery low grade zinc oxide ores [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 89(3-4): 305-310.
[14] CHEN Qi-yuan, LI Liang, BAI Lan, HU Hui-ping, LI Jian, LIANG Qi-wen, LING Jiang-hua. Synergistic extraction of zinc from ammoniacal ammonia sulfate solution by a mixture of a sterically hindered beta-diketone and tri-n-octylphosphine oxide (TOPO) [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105(34): 201-206.
[15] DING Zhi-ying, CHEN Qi-yuan, YIN Zhou-lan, LIU Kui. Predominance diagrams for Zn(II)-NH3-Cl--H2O system [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 832-840.
[16] SHAO Hong-mei, SHEN Xiao-yi, SUN Yi, LIU Yan, ZHAI Yu-chun. Reaction condition optimization and kinetic investigation of roasting zinc oxide ore using (NH4)2SO4 [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2016, 23(10): 1133-1140.
[17] CHEN Bing, SHEN Xiao-yi, GU Hui-min, SUN Yi, LI De-guan, ZHAI Yu-chun, MA Pei-hua. Extraction of ZnO from zinc oxide ore by alkali roasting method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(2): 658-661. (in Chinese)
[18] DOU Ai-chun, YANG Tian-zu, YANG Ji-xing, WU Jiang-hua, WANG An. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in Ida2--H2O system [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(11): 2548-2553.
[19] LI Hong-gui. Metallurgical principles [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
[20] HUA Yi-xin. Introduction of metallurgical process kinetics [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[21] SHON H Y, WADSWORTH M E. Rate process of extractive metallurgy [M]. New York: Springer, 1979.
[22] CHEN Jia-yong. Handbook of hydrometallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
申晓毅1,2,邵鸿媚3,顾惠敏1,2,陈 兵1,4,翟玉春1,马培华1
1. 东北大学 冶金学院,沈阳 110819;
2. 东北大学 辽宁省冶金传感器及技术重点实验室,沈阳 110819;
3. 沈阳理工大学 环境与化工学院,沈阳 110159;
4. 盘锦市环境科学研究院 科技研究室,盘锦 124401
摘 要:研究氢氧化钠焙烧硅酸锌的反应动力学,采用正交试验优化反应条件,优化反应条件为:NaOH和Zn2SiO4摩尔配比16:1、反应温度550 °C以及反应时间2.5 h。为了确定氧化锌和二氧化硅的物相转化和反应过程,采用XRD技术分析不同温度焙烧样品的物相。600 °C焙烧样品的最终物相为Na2ZnO2、Na4SiO4、Na2ZnSiO4和NaOH。通过未反应收缩核模型研究焙烧过程的动力学方程,选取2种反应速率控制模型考察反应机理,分别为颗粒表面化学反应控制和通过固体产物层的扩散控制模型。结果表明:NaOH焙烧Zn2SiO4的反应过程受通过固体产物层的扩散控制,反应的表观活化能为19.77 kJ/mol。
关键词:反应机理;动力学;Zn2SiO4;NaOH焙烧;反应过程;物相转化
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (51774070, 51204054) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (150204009) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China; Project (2014CB643405) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Xiao-yi SHEN; Tel: +86-24-83687731; E-mail: shenxy@smm.neu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64833-2

