生物医用多孔钛的力学性能及孔结构变形行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第5期
论文作者:王晓花 李金山 胡 锐 寇宏超
文章页码:1543 - 1550
关键词:生物材料;多孔钛;力学性能;孔结构;变形行为
Key words:biomaterials; porous titanium; mechanical properties; pore structure; deformation behaviour
摘 要:多孔钛材料因其优良的综合性能被视为最有潜力的生物医用材料之一。考虑到生物材料在使用过程中必然受到力的作用,重点研究了多孔钛的力学性能及其孔结构变形行为。采用添加造孔剂的粉末烧结方法制备孔隙率为36%~66%、平均孔径为230 μm的多孔钛。采用扫描电镜观察孔结构形貌,通过室温压缩测试检测力学性能。多孔钛的弹性模量和抗压强度分别为1.86~14.7 GPa和85.16~461.94 MPa,具力学性能与人骨的力学性能相近。建立了多孔钛的相对屈服强度和相对密度间关系,结果表明相对密度是影响多孔钛力学性能和变形的主要因素。对于低相对密度的多孔钛而言,其变形方式为孔壁的屈服、弯曲和屈曲;而对于高相对密度的多孔钛,其变形方式主要为孔壁的屈服和弯曲。
Abstract: Porous titanium has been shown to exhibit desirable properties as biomedical materials. In view of the load-bearing situation, the mechanical properties and pore structure deformation behaviour of porous titanium were studied. Porous titanium with porosities varying from 36%-66% and average pore size of 230 μm was fabricated by powder sintering. Microstructural features were characterized using scanning electron microscopy. Uniaxial compression tests were used to probe the mechanical response in terms of elastic modulus and compressive strength. The mechanical properties of porous titanium were found to be close to the those of human bone, with stiffness values ranging from 1.86 to 14.7 GPa and compressive strength values of 85.16-461.94 MPa. The relationships between mechanical properties and relative densities were established, and the increase in relative density showed significant effects on mechanical properties and deformations of porous titanium. In a lower relative density, the microscopic deformation mechanism of porous titanium was yielding, bending and buckling of cell walls, while the deformation of yielding and bending of cell walls was observed in the porous titanium with higher relative density.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1543-1550
Xiao-hua WANG, Jin-shan LI, Rui HU, Hong-chao KOU
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 29 April 2014; accepted 13 July 2014
Abstract: Porous titanium has been shown to exhibit desirable properties as biomedical materials. In view of the load-bearing situation, the mechanical properties and pore structure deformation behaviour of porous titanium were studied. Porous titanium with porosities varying from 36%-66% and average pore size of 230 μm was fabricated by powder sintering. Microstructural features were characterized using scanning electron microscopy. Uniaxial compression tests were used to probe the mechanical response in terms of elastic modulus and compressive strength. The mechanical properties of porous titanium were found to be close to the those of human bone, with stiffness values ranging from 1.86 to 14.7 GPa and compressive strength values of 85.16-461.94 MPa. The relationships between mechanical properties and relative densities were established, and the increase in relative density showed significant effects on mechanical properties and deformations of porous titanium. In a lower relative density, the microscopic deformation mechanism of porous titanium was yielding, bending and buckling of cell walls, while the deformation of yielding and bending of cell walls was observed in the porous titanium with higher relative density.
Key words: biomaterials; porous titanium; mechanical properties; pore structure; deformation behaviour
1 Introduction
Titanium (Ti) and Ti alloys have been used extensively as bone-implant materials due to their high specific strength, good biocompatibility and excellent corrosion resistance [1-3]. However, the mismatch of the elastic modulus between bone (10-30 GPa) and these metallic implant materials (110 GPa for Ti) has been identified as a major reason for implant loosening following stress-shielding of bone. Many investigators have shown that the stress-shielding retards bone remodeling and healing, which result in increased porosity in the surrounding bone [4,5]. Hence, there is an increasing interest in adjusting the elastic modulus of metallic materials to overcome stress-shielding. An alternative is the use of porous materials [6-8].
Porous materials in orthopaedic implants are increasingly attracting the widespread interest of researchers as a method of reducing modulus mismatches and achieving stable long-term fixation by means of full bone in growth and there have been a number of previous reviews on many different porous coatings and fully porous matrices that have been developed [9-11]. However, the implanted material must be strong enough and durable to withstand the physiological loads placed upon it over the years. A suitable balance between strength and stiffness has to be found to best match the behaviour of bone [12,13]. The relationship between strength and stiffness of implant and the microstructural features has been established in the aspect of theory and experiments and confirms that changes in mechanical properties of porous solids are an effect of relative density [14,15]. Moreover, morphological property concern on pore size and porosity is very important for osteogenesis on the surface of the porous implants [16]. GIBSON [17] gave the dependence of the properties on the relative density and the solid properties by dimensional analysis to model the mechanisms of deformation and failure observed in the cellular material. But a major problem of the model is that it is just suitable for porous solids with relative density lower than 0.2. A second approach is to use finite element analysis of either regular or random cellular structures [18-20]. Finite element analysis allows local effects, such as imperfections, to be studied [21]. And it can also be used in conjunction with imaging techniques such as micro-computed tomography to model the exact architecture of a particular structure [22]. But the technique is too computationally intensive to get the final results.
Porous titanium is increasingly used as biomaterials to replace or regenerate tissue in the body, especially for load-bearing biomaterials. Although a number of research results on mechanical properties of porous titanium have been achieved, it is not enough for getting the optimal match of properties of biomedical porous titanium. In the present work, we fabricated a porous titanium by powder sintering, and compared its property results of micromechanical models above-mentioned, and studied the deformation behaviour of the porous titanium by describing the microstructural features in uniaxial compression tests at a given compressive strain.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Specimen preparation
Porous titanium was prepared by a space-holder method. Commercially pure titanium (purity: 99.9%, powder size: 45 μm) was used as raw material and soluble sodium chloride particles with different volume fractions were used as spacer-holder materials. To attain the exact distribution of pore size of porous titanium, the sodium chloride powder was sieved to select similar particle sizes in the range of 200-300 μm. Ti powders and spacer-holder particles were thoroughly mixed in an agate mortar box. After the ingredients were homogeneously blended, the mixture of metallic powders and space-holder powders can be pressed uniaxially at a pressure of 180 MPa into green compacts, thus imparting enough green strength to the metal powder to prevent collapsing upon removal of the space-holder and subsequent sintering. Subsequent desalting in the distilled water resulted in original foams. Finally, sintering at 1473 K in a vacuum furnace of 10-3 Pa for 8 h achieved porous titanium with pore size and porosity designed in advance.
2.2 Tests and characterization
Scanning electron microscopy was used to characterize the sintered open-cellular titanium foam samples. Porosity was evaluated according to the apparent densities method, and the pore size distributions were measured by quantitative image analyses.
The compression tests were performed on three samples at room temperature, and the test specimens had a size of d13 mm × 13 mm (GB 6526—86). The initial strain rate for compression tests was 10-3 s-1. Compressive strength refers to the local maximum stress after the linear elastic region of the curve. Elastic modulus was calculated as the slope of the linear elastic region.
The elastic modulus and yield strength of porous titanium in this work were compared with the predictions of the Gibson-Ashby (G&A) model [23] and the finite element method (FEM) model proposed by ROBERTS and GARBOCZI [19,20,24].
As predicted by the Gibson-Ashby model, the relationships between the relative properties and the relative density (ρ/ρs) for open-cell foam are
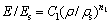 (1)
(1)
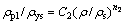 (2)
(2)
where E is the elastic modulus of the foam, Es is the elastic modulus of the cell surface solid material, σpl is the plateau stress of the porous material, σys is the yield strength of the cell surface solid material and C1, C2, n1 and n2 are constants, depending on the cell structure. To date, the complex dependence of C and n on the structure has not been well understood. Experimental evidences suggest that n1=2, n2=1.5 for open-cell foams, C1=1, C2=0.3 for cellular metals and polymers.
Elastic modulus of both open-cell and closed-cell foams based on the FEM have been proposed by ROBERTS and GARBOCZI [19,20]. The FEM model is assumed to be a highly irregular structure with curved struts of variable thickness. Equation to fit the results of their simulations is
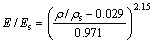 , ρ/ρs>0.2 (3)
, ρ/ρs>0.2 (3)
2.3 Structural observation
Owing to pore morphologies controlling the onset of yielding [25], microstructure observation was used to indicate the deformation mode of cell walls. For microstructure observation, the specimens with the relative densities of 0.36 and 0.66 were fabricated via the spacer-holder sintered method. The specimens had plane outer surfaces. Both specimens were observed before deformation and at a nominal compressive strain of 10% to investigate their compressive deformation behaviour.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 shows the typical SEM morphology of the porous titanium with porosities ranging from 36% to 66%. The pore structures are uniform throughout the specimen owing to proper sieving of the spacer-holder particles. The morphology of pores located on the surface and within the porous scaffolds exhibits good pore interconnectivity. Statistical analysis of pore sizes reveals that the porous titanium sintered using space- holder particles of 200-300 μm gives an average pore size of 230 μm, as shown in Fig. 2. The pore sizes are a little smaller than those of spacer particles, owing to specimen shrinkage during sintering. This kind of porous titanium is expected to be used as biocompatible implant materials because its open-cellular structure permits ingrowths of the new-bone tissues and the transport of the body fluids.
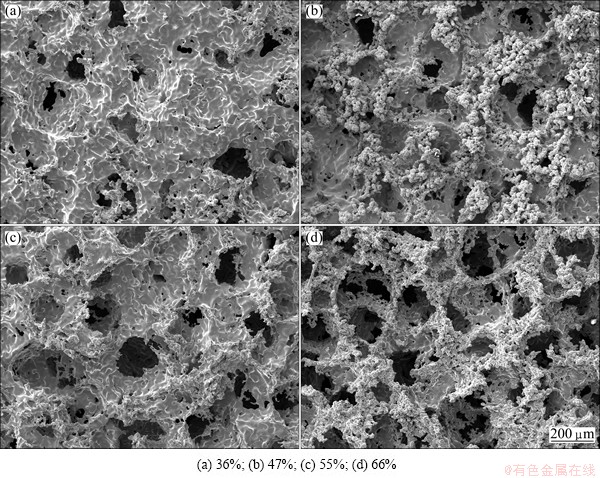
Fig. 1 Pore structure of porous titanium samples with different porosities
3.2 Stress-strain curves
Figure 3 shows the compressive stress-strain curves of porous Ti with porosities ranging from 36% to 66% (relative density: 0.34-0.64). The curves show the typical features of metallic foams [26], i.e., an elastic deformation stage at the beginning of deformation, a long plateau stage with a nearly constant flow stress to large strain, about 85% for the porous titanium with high porosity up to 66%, and a densification stage where the flow stress rapidly increases. It is found that the plateau regions are different for porous titanium with different porosities. Plateau region becomes more evident with the increase of porosity. Moreover, plateau stresses increase with the decrease of the porosity of the porous titanium.
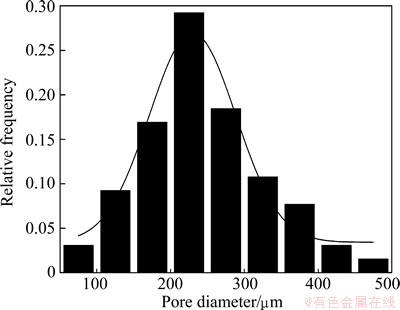
Fig. 2 Pore size distribution of porous titanium adding 70% pore maker
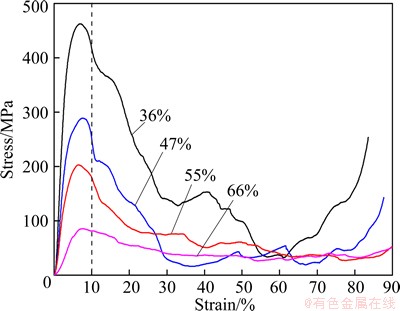
Fig. 3 Compressive stress-strain curves of porous titanium with porosities ranging from 36% to 66%
Figure 4 shows the elastic modulus and the compressive strength of the porous titanium with different porosities. In this work, the slope of the linear elastic region of curves was taken as a measure of the elastic modulus of porous Ti. The measured elastic modulus is found to be 1.86-14.7 GPa for the porous Ti samples. The elastic modulus increased with decreasing porosity. The specimens with a low porosity of 36% showed a high elastic modulus of 14.7 GPa. When the porosity increased from 36% to 66%, the elastic modulus was only1.86 GPa.
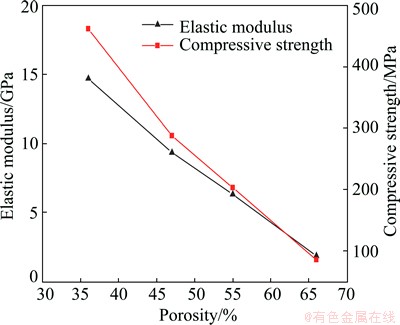
Fig. 4 Elastic modulus and compressive strength of sintered porous titanium as function of porosity
The compression strength is in the range from 85.16 to 461.94 MPa for the porous Ti with different porosities and decreases with the increase of porosity. The current bulk implant materials have higher stiffness than that of human bone, which prevents from the needed stress being transferring to adjacent bone, resulting in bone desorption around the implant and consequently implant loosening. Thus, a material with an excellent combination of high strength and low modulus close to the bone has to be used for implantation to avoid loosening of implants and higher service period to avoid revision surgery [27]. Human compact bone possesses a elastic modulus of elasticity ranging between 12 and 17 GPa, while the stiffness of human cancellous bone is less than 3 GPa [1]. And compression strength of human bone is in the range of 2 to 180 MPa [23]. In this work, porous titanium with a wide range of elastic modulus and compressive strength shows a good match to human bone, therefore, this porous titanium can be considered as promising biomedical materials.
3.3 Elastic modulus
Figure 5 shows the predicted elastic modulus (E) of the porous titanium normalized to the elastic modulus of the solid titanium (Es) as a function of the relative density (ρ/ρs). The elastic modulus of the solid titanium (Es) is 105 GPa. For comparison, the Gibson-Ashby model and FEM model are also included. It can be seen that the experimental data are better predicted by the FEM model than the Gibson-Ashby model in the whole range of relative densities. It should be noted that the FEM model deals with a highly irregular structure with curved struts of variable thickness. Meanwhile, the Gibson-Ashby model assumes a regular periodic structure with the same thickness walls surrounding the pore cell. Since the elastic modulus of a porous structure is determined by the thinnest struts [28], the mass in the thickest regions of the struts contributes little to the overall elastic modulus. This has the effect of reducing the elastic modulus of a porous structure for a given density, compared with models having struts with a uniform cross-sectional area [20]. It is clear that the experimental data in the present work are slightly lower than the values predicted by the FEM model in the higher porosity range (Fig. 6). It can deduce that there are highly non-uniform struts in the porous titanium with high porosity and this leads to a decrease in the elastic modulus of the porous titanium. The elastic modulus of the porous alloys with higher porosities is very sensitive to the homogeneity of strut thickness of the porous structure.
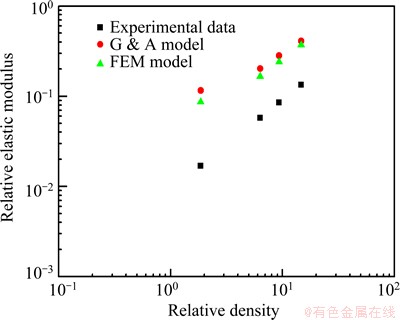
Fig. 5 Relative elastic modulus of porous Ti (E/Es) as function of relative density (ρ/ρs) and predictions of Gibson-Ashby model and finite element method (FEM) model
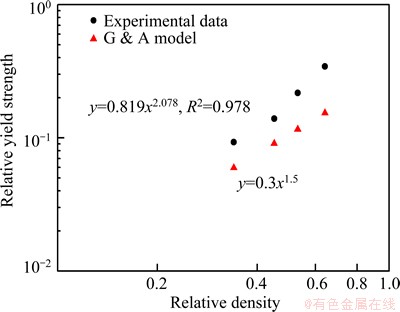
Fig. 6 Relative yield strength of porous Ti (σpl/σys) as function of relative density (ρ/ρs) and prediction of Gibson-Ashby model for porous Ti
3.4 Compressive yield stress
For porous materials, the plateau region in their stress-strain curves is the typical characteristics. And in Gibson-Ashby model [23], the typical mechanical characteristic of metallic foam is the plateau stress rather than the peak stress. Because the curves of specimens with higher relative densities do not have clear plateau regions [29], and the plateau stress is ambiguous, the plateau stress is substituted for the yield stress in Eq. (2). The density and yield stress of pure bulk Ti is 4.5 g/cm3 and 692 MPa. Figure 6 shows the yield strength of the porous titanium (σ) normalized to the yield strength of the solid metal (σs) as a function of relative density (ρ/ρs) and that predicted by the Gibson-Ashby model. The slope of the plots in Fig. 6 is the density exponent n in Eq. (2). From Fig. 6, the constant C and density exponent n of the porous titanium are 0.819 and 2.078, respectively. It is noted that the constant C and density exponent n of experimental data are better predicted by the Gibson-Ashby model in lower relative density. According to Eq. (2), C is a constant for the geometric effect and the variation of the value of C is probably due to heterogeneity in pore shape and size [28]. It is reported that the value of n in Eq. (2) is governed by the deformation mode of the individual cell struts, i.e., yielding, bending, and buckling, and the value of n is in a wide range of 1.0 to 6.3 [29]. YAMADA et al [30] suggested that the value of n for cell walls or struts bending is 2 and that for struts buckling is 3, while the value of n is 1 for struts yielding. It was noted that the deformation mode can be divided into three regions by the critical value of n, for the values of 1, 2, and 3. In the present work, the experimental value of n is 2.078, which suggests that the deformation mode of the porous Ti with relative densities ranging from 0.34 to 0.64 is mainly strut bending and buckling of the cell struts. But in the research of HAKAMADA et al [29], the deformation can be divided into three regions: Region I in the lower relative density range (0.20-0.55), Region II in the higher relative density range (0.55-0.90) and Region III in the highest relative density range close to 1, and every region have an unique value of n. The value of 2.078 does not indicate the deformation completely because the relative density in this work is from 0.34 to 0.66, both contains the two regions. Therefore, in order to investigate the compressive deformation behaviour, we observe the surface of the specimens at a nominal compressive strain of 0.1, and the results will discuss in the next section.
The mechanical properties of the porous titanium are well represented by the Gibson-Ashby relations as shown above (Figs. 4 and 5). The major deviation from the model is that the linear regression lines do not pass through zero. This is not astonishing as the titanium foam has an irregular pore structure and therefore contains pore walls which do not fully contribute to load bearing. The irregular pore structure (anisotropy) of porous titanium is due to the nonspherical shape of the space holder particles. The space holder particles are preferentially arranged along their elongated sides during the compaction of the powder mixture [31].
3.5 Macroscopic deformation band
Figure 7 shows the surface of the deformed porous titanium specimen with the relative density of 0.34, and Fig. 8 shows that with the relative density of 0.64, where both specimens were compressed at a nominal strain of 0.1. Four pictures in Figs. 7 and 8 merged of 8 individual metallographic pictures. From the figures, it is found that all the pores in porous titanium after compression deform slightly on edges than those before compression. And clear deformation bands form inside the specimens with a lower relative density of 0.34, while the deformation bands are not evident in the porous titanium with a high relative density of 0.64, but local deformation is observed partially around the pores.
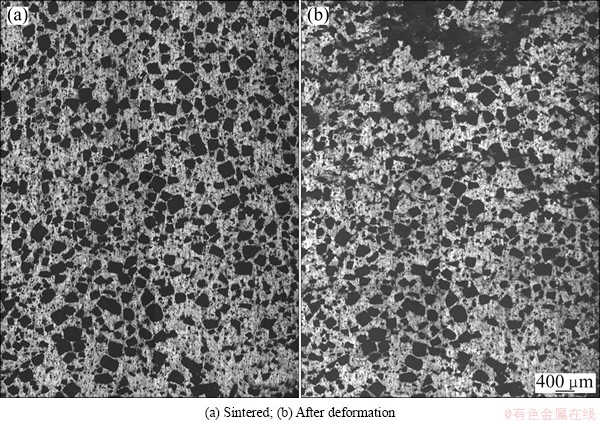
Fig. 7 Surface of compressed porous titanium (ε=10%) with relative density 0.34
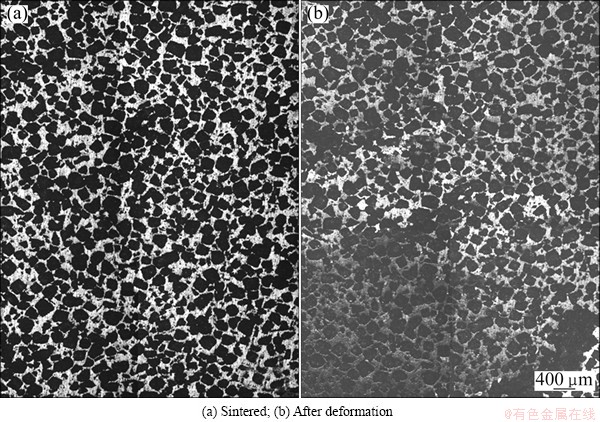
Fig. 8 Surface of compressed porous titanium (ε=10%) with relative density 0.64

Fig. 9 Cell wall yielding (a), buckling (b) and bending (c) in porous titanium with relative density 0.34 (ε=10%)
We know that the emergence of the plateau region in the compressive stress-strain curve for a porous material is closely related to the formation of deformation bands [32]. And the occurrence of the plateau region in the stress-strain curves for the low-relative-density specimens, as shown in Fig. 2, is probably because the specimens tend to deform layer by layer, and the microstructure observation revealed that clear deformation bands form inside the specimens. This is in agreement with the results in previous works [25]. In the specimen with a relative density of 0.64, however, clear deformation bands were not found, and local deformation was observed partially around the pores. This result is in agreement with the result that the plateau region is not evident in the stress-strain curves, as shown in Fig. 3. Therefore, deformations in porous titanium mostly depend on the varying relative density.
3.6 Microscopic deformation mode of cell wall
It is reported that the deformation modes of cell wall contain three kinds: i.e., yielding, bending and buckling [30]. Figure 9 shows the observed three kinds of cell wall deformation in the specimen with a relative density of 0.34, and Fig. 10 shows the observed two kinds of cell wall deformation in the specimen with the relative density of 0.64. The specimens both have the same portions compressed at a nominal strain of 0.1, and the loading direction is vertical in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8. In specimen with a relative density of 0.34, as shown in Fig. 9, bending, buckling and yielding of cell walls were observed. BASTAWROS et al [32] demonstrated that buckling and bending occur in each cell, resulting in localized deformation. The deformation in Fig. 8 is in agreement with their results. However, as shown in Fig. 10, a few bending and no buckling are found, and most of the cell walls yield. Cracks of cell walls after yielding are present, and the cracks and the axial of the cell walls lay at an angle of about 45°, as shown in Fig. 9(a) and Fig. 10(a). In Fig. 9(b) and Fig. 10(b), the bending of cell walls are present and cause plastic hinges at the nodes.
Therefore, it is conclusively demonstrated from the results in Fig. 6 and the observations in Figs. 9 and 10 that porous titanium with a relative density of 0.34 deforms by the yielding, bending and buckling of their cell walls and that porous titanium with a relative density of 0.64 deforms by the yielding and bending of their cell walls.
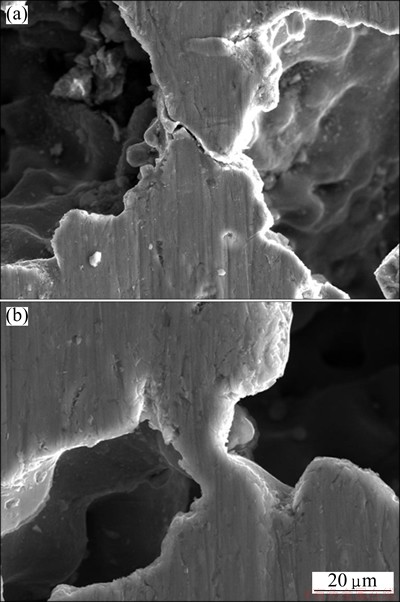
Fig. 10 Cell wall yielding (a) and bending (b) in porous titanium with relative density 0.64 (ε=10%)
The microscopic and macroscopic deformation behaviours have strong relationships [29]. It is reported that the deformation of a porous metal was divided into three processes: localized straining at cell nodes, discrete bands of concentrated strain and complete plastic collapse. The bending and buckling of cell walls caused intense local deformation, compared with the yielding of cell walls, resulting in the enhancement of the formation of deformation bands.
From the macroscopic observations in Figs. 7 and 8 and the microscopic observations in Figs. 9 and 10, it is demonstrated that the yielding, bending and buckling of cell walls in porous titanium with a relative density of 0.34 cause the intense deformation bands and that the yielding and a few bending of cell walls in porous titanium with a relative density of 0.64 cause the uniform deformation, result in no clear deformation bands.
4 Conclusions
1) Porous titanium with porosities of 36%-66% and an average pore size of 245 μm was fabricated by powder sintering. Increase in relative density showed significant effects on mechanical properties and deformations of porous titanium.
2) The mechanical properties of porous titanium were found to be close to those of human bone, with stiffness values ranging from 1.86 to 14.7 GPa and compressive strength values of 85.16-461.94 MPa. Thus, this porous titanium can be considered as promising biomedical materials.
3) In a lower relative density, the microscopic deformation mechanism of porous titanium was yielding, bending and buckling of cell walls causing the intense deformation bands, while the deformation of yielding and bending of cell walls was observed in the porous titanium with higher relative density.
References
[1] LONG M, RACK H J. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—A materials science perspective [J]. Biomaterials, 1998, 19(18): 1621-1639.
[2] EISENBARTH E, VELTEN D,  M, THULL R, BREME J. Biocompatibility of [beta]-stabilizing elements of titanium alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(26): 5705-5713.
M, THULL R, BREME J. Biocompatibility of [beta]-stabilizing elements of titanium alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(26): 5705-5713.
[3] BEDI R S, BEVING D E, ZANELLO L P, YAN Y. Biocompatibility of corrosion-resistant zeolite coatings for titanium alloy biomedical implants [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(8): 3265-3271.
[4] RACK H J, QAZI J I. Titanium alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2006, 26(8): 1269-1277.
[5] BAHRAMINASAB M, SAHARI B B, EDWARDS K L, FARAHMAND F, ARUMUGAM M. Aseptic loosening of femoral components—Materials engineering and design considerations [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 44: 155-163.
[6] XIE F, HE X, LU X, CAO S, QU X. Preparation and properties of porous Ti–10Mo alloy by selective laser sintering [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2013, 33(3): 1085-1090.
[7] SU Xu-bin, YANG Yong-qiang, YU Peng, SUN Jian-feng. Development of porous medical implant scaffolds via laser additive manufacturing [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(S1): s181-s187.
[8] TORRES Y, LASCANO S, BRIS J, PAV N J, RODRIGUEZ J A. Development of porous titanium for biomedical applications: A comparison between loose sintering and space-holder techniques [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2014, 37: 148-155.
[9] de AZA P N, LUKLINSKA Z B, SANTOS C, GUITIAN F, de AZA S. Mechanism of bone-like formation on a bioactive implant in vivo [J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(8): 1437-1445.
[10] KARAGEORGIOU V, KAPLAN D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis [J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(27): 5474-5491.
[11] CAMPOLI G, BORLEFFS M S, AMIN YAVARI S, WAUTHLE R, WEINANS H, ZADPOOR A A. Mechanical properties of open-cell metallic biomaterials manufactured using additive manufacturing [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 49: 957-965.
[12] WIEDING J, WOLF A, BADER R. Numerical optimization of open-porous bone scaffold structures to match the elastic properties of human cortical bone [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2014, 37: 56-68.
[13] SALLICA-LEVA E, JARDINI A L, FOGAGNOLO J B. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of porous Ti-6Al-4V parts obtained by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2013, 26: 98-108.
[14] OH I H, NOMURA N, MASAHASHI N, HANADA S. Mechanical properties of porous titanium compacts prepared by powder sintering [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 49(12): 1197-1202.
[15] ZOU Chun-ming, LIU Yan, YANG Xin, WANG Hong-wei, WEI Zun-jie. Effect of sintering neck on compressive mechanical properties of porous titanium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(S2): s485-s490.
[16] WANG Xiao-hua, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, KOU Hong-chao, ZHOU Lian. Mechanical properties of porous titanium with different distributions of pore size [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(8): 2317-2322.
[17] GIBSON L J. Biomechanics of cellular solids [J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2005, 38(3): 377-399.
[18] GETLMACHER A, KOSS D A. Computer simulation of specimen shape and ductility in porous materials [J]. Int J Powder Metallurgy, 1990, 26(3): 205-216
[19] ROBERTS A P, GARBOCZI E J. Elastic moduli of model random three-dimensional closed-cell cellular solids [J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(2): 189-197.
[20] ROBERTS A P, GARBOCZI E J. Elastic properties of model random three-dimensional open-cell solids [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2002, 50(1): 33-55.
[21] TSUKROV I, NOVAK J. Effective elastic properties of solids with defects of irregular shapes [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2002, 39(6): 1539-1555.
[22] SINGH R, LEE P D, LINDLEY T C, KOHLHAUSER C, HELLMICH C, BRAM M, IMWINKELRIED T, DASHWOOD R J. Characterization of the deformation behavior of intermediate porosity interconnected Ti foams using micro-computed tomography and direct finite element modeling [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(6): 2342-2351.
[23] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids: Structure and properties [M]. Cambidge: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
[24] ROBERTS A P, GARBOCZI E J. Elastic properties of model porous ceramics [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(12): 3041-3048.
[25] BART-SMITH H, BASTAWROS A F, MUMM D R, EVANS A G, SYPECK D J, WADLEY H N G. Compressive deformation and yielding mechanisms in cellular Al alloys determined using X-ray tomography and surface strain mapping [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(10): 3583-3592.
[26] WEN C E, MABUCHI M, YAMADA Y, SHIMOJIMA K, CHINO Y, ASAHINA T. Processing of biocompatible porous Ti and Mg [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 45(10): 1147-1153.
[27] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397-425.
[28] WANG X, LI Y, XIONG J, HODGSON P D, WEN C E. Porous TiNbZr alloy scaffolds for biomedical applications [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(9): 3616-3624.
[29] HAKAMADA M, ASAO Y, KUROMURA T, CHEN Y, KUSUDA H, MABUCHI M. Density dependence of the compressive properties of porous copper over a wide density range [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(7): 2291-2299.
[30] YAMADA Y, WEN C, SHIMOJIMA K, HOSOKAWA H, CHINO Y, MABUCHI M. Compressive deformation characteristics of open-cell Mg alloys with controlled cell structure [J]. Materials Transactions, 2002, 43(6): 1298-1305.
[31] IMWINKELRIED T. Mechanical properties of open-pore titanium foam [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2007, 81(4): 964-970.
[32] BASTAWROS A F, BART-SMITH H, EVANS A G. Experimental analysis of deformation mechanisms in a closed-cell aluminum alloy foam [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2000, 48(2): 301-322.
王晓花,李金山,胡 锐,寇宏超
西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安710072
摘 要:多孔钛材料因其优良的综合性能被视为最有潜力的生物医用材料之一。考虑到生物材料在使用过程中必然受到力的作用,重点研究了多孔钛的力学性能及其孔结构变形行为。采用添加造孔剂的粉末烧结方法制备孔隙率为36%~66%、平均孔径为230 μm的多孔钛。采用扫描电镜观察孔结构形貌,通过室温压缩测试检测力学性能。多孔钛的弹性模量和抗压强度分别为1.86~14.7 GPa和85.16~461.94 MPa,具力学性能与人骨的力学性能相近。建立了多孔钛的相对屈服强度和相对密度间关系,结果表明相对密度是影响多孔钛力学性能和变形的主要因素。对于低相对密度的多孔钛而言,其变形方式为孔壁的屈服、弯曲和屈曲;而对于高相对密度的多孔钛,其变形方式主要为孔壁的屈服和弯曲。
关键词:生物材料;多孔钛;力学性能;孔结构;变形行为
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (2012CB619101) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Rui HU; Tel: +86-29-88491764; Fax: +86-29-88460294; E-mail: rhu@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63756-6

