Extraction of Cd and Pb from contaminated-paddy soil with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2019年第11期
论文作者:郭朝晖 梁芳 门姝慧 肖细元 彭驰 WU Long-hua(吴龙华) Peter CHRISTIE
文章页码:2987 - 2997
Key words:contaminated paddy soil; soil washing; potentially toxic metals; speciation; soil fertility
Abstract: Potentially toxic metals, Cd and Pb in paddy soil, have important meanings for safety of rice. A comparison extraction of Cd and Pb with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid, and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility was studied. Results indicate that about 59% and 63% of soil Cd and Pb were simultaneously removed by 10 g/L EDTA at pH 5 with a soil/extractant ratio of 1:10 (W/V) for 30 min while 52% and 51% by 5 g/L DTPA. Acid extractable and reducible Cd by EDTA and DTPA contributed 58% and 53% of the removals and acid extractable and reducible Pb were about 49% and 41%, respectively. Slight changes of soil fertility, including pH, cation exchange capacity, organic matter, and soil extractable phosphorus, were observed. Extractions of citric acid and ferric chloride, however, were only efficient for Cd and the soil pH was decreased significantly. This study suggests that EDTA and DTPA can be considered as suitable agents to clean up the paddy soils contaminated with potentially toxic metals.
Cite this article as: LIANG Fang, GUO Zhao-hui, MEN Shu-hui, XIAO Xi-yuan, PENG Chi, WU Long-hua, Peter CHRISTIE. Extraction of Cd and Pb from contaminated-paddy soil with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(11): 2987-2997. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-019-4230-4.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2019) 26: 2987-2997
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4230-4
LIANG Fang(梁芳)1, GUO Zhao-hui(郭朝晖)1, MEN Shu-hui(门姝慧)1, XIAO Xi-yuan(肖细元)1,PENG Chi(彭驰)1, WU Long-hua(吴龙华)2, Peter CHRISTIE2
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Soil Environment and Pollution Remediation, Institute of Soil Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Abstract: Potentially toxic metals, Cd and Pb in paddy soil, have important meanings for safety of rice. A comparison extraction of Cd and Pb with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid, and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility was studied. Results indicate that about 59% and 63% of soil Cd and Pb were simultaneously removed by 10 g/L EDTA at pH 5 with a soil/extractant ratio of 1:10 (W/V) for 30 min while 52% and 51% by 5 g/L DTPA. Acid extractable and reducible Cd by EDTA and DTPA contributed 58% and 53% of the removals and acid extractable and reducible Pb were about 49% and 41%, respectively. Slight changes of soil fertility, including pH, cation exchange capacity, organic matter, and soil extractable phosphorus, were observed. Extractions of citric acid and ferric chloride, however, were only efficient for Cd and the soil pH was decreased significantly. This study suggests that EDTA and DTPA can be considered as suitable agents to clean up the paddy soils contaminated with potentially toxic metals.
Key words: contaminated paddy soil; soil washing; potentially toxic metals; speciation; soil fertility
Cite this article as: LIANG Fang, GUO Zhao-hui, MEN Shu-hui, XIAO Xi-yuan, PENG Chi, WU Long-hua, Peter CHRISTIE. Extraction of Cd and Pb from contaminated-paddy soil with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(11): 2987-2997. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-019-4230-4.
1 Introduction
Soil contamination with potentially toxic metals has increased greatly in recent decades with industrialization, the intensive use of fertilizers in agriculture, land application of urban wastes and atmospheric deposition [1, 2]. Potentially toxic metals such as Cd and Pb accumulate mainly in the upper layers of soils and remain for long periods due to their non-degradability and low mobility [3]. Based on a report of the Chinese soil contamination survey in 2014, Cd and Pb contents with 7.0% and 1.5% of agricultural soil samples, respectively, exceeded the Class II Standards in the recent national soil contamination survey [4]. Metals in agricultural soils can be taken up by vegetable crops and pose a human health risk through food chain. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find technically and economically feasible remediation techniques for the removal of metals from agricultural soils.
Chemical approaches for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation generally include solidification/stabilization and soil washing [5, 6]. Metals still remain in the soil after solidification/ stabilization and may possibly leak to surface waters or groundwater. Soil washing, however, may rapidly and permanently remove metals from soils, allow the recycling of metals in certain cases and maintain soil biological properties [7-10]. Water, FeCl3 [11], citric acid [12, 13], oxalic acid [14], ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) [15, 16], nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) [17] and diethylenetriaminepentacetate acid (DTPA) [18] have been used as soil washing agents. EDTA has shown a high Cd removal efficiency of 89.6% [14]. DTPA has a Cd removal efficiency of about 57.8% [19] and is widely used to assess the phytoavailability of metals [20]. Citric acid, a weak organic acid, is biodegradable, forms strong metal-ligand complexes [12] and can extract 58.7% of Cd and 69.9% of Pb from contaminated soils [21]. FeCl3 is an inorganic salt with a low pKa value and anionic chloride ligands can form various metal-chloride complexes and thus combine with about 66% of soil Cd [22]. The removal of trace metals in soils can be significantly affected by the application rate of the reagents and the processing conditions such as solution pH, mixing time and liquid/solid ratio [23]. Previously, a number of studies were conducted, which addressed the influencing factors of heavy metal removal efficiency for soil washing with various washing agents [24, 14]. However, interactions among different factors in removal of metal in contaminated soils and the main effects among these factors were seldom studied. In addition, changes in soil fertility are also important index to reflect the efficiency of remediation of contaminated soils [25]. The study reported that 0.43 mol/L EDTA and 0.47 mol/L citric acid were excessive for soil remediation, leading to large changes in soil properties [26]. However, changes in soil properties after washing with DTPA were not studied [27, 28]. Moreover, the influences on soil organic matter, available nitrogen and available potassium due to washing with FeCl3 were not evaluated [22]. Changes in soil fertility due to washing have received little attention and require more detailed study. It is essential to find an effective washing reagent in Cd and Pb removal while maintain the soil fertility.
In this study, the removal of Cd and Pb from a contaminated paddy soil using the four reagents, including EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3, was studied. The objectives of the study were: 1) to optimize the washing conditions through an orthogonal experiment, including reagent concentration, extractant/soil (L/S) ratio, mixing time and solution pH, 2) to determine the changes in Cd and Pb speciation distribution in the contaminated soil, and 3) to evaluate the changes in soil fertility after washing.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Test soil and washing reagents
Samples of surface paddy soil (0-20 cm) were collected from the vicinity of a Pb-Zn smelting plant (27°52′17.44″ N, 113°03′48.84″ E) in Hunan Province, China. The samples were air-dried at room temperature, passed through a 2-mm nylon sieve, homogenized and stored until analysis and subsequent experiments. Selected soil physico- chemical properties are shown in Table 1. The soil Cd and Pb concentrations were 10.8 and 210 mg/kg, respectively.
Table 1 Selected physico-chemical properties of test soil

2.2 Experimental
The removal of soil Cd and Pb was studied using analytical grade EDTA, DTPA, citric acid, and FeCl3. An orthogonal experiment with L16 (44) was carried out with four factors, namely reagent concentration (A), extractant/soil (L/S) ratio (B), mixing time (C), and solution pH (D) (Table 2). The protocol was as follows. Air-dried soil samples were placed in individual 100 mL centrifuge tubes; reagent solution was added and the tubes were shaken at 200 r/min in a water bath at 25 °C according to the design of the orthogonal experiment. The tubes were then centrifuged for 10 min at 4000 r/min and the supernatant was filtered for analysis.
Table 2 Orthogonal design of experiment

An optimized experiment based on the orthogonal experiment was conducted with deionized water (control), EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 to assess the removal efficiency of both Cd and Pb from the contaminated soil. The experiment was conducted in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks and the soil samples were shaken in a mechanical shaker at 200 r/min in a water bath at 25 °C. All suspensions were then centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 10 min and the supernatants were filtered for analysis. The retained residues were also collected for analysis of both metal fractions and soil fertility.
2.3 Analytical methods
Soil properties were determined using air-dried samples as described by PANSU et al [29]. Soil pH was measured with a pH meter (Mettler Toledo 420), with a soil to water ratio of 1:2.5 (W/V), and cation exchange capacity was determined by extraction using 1.0 mol/L ammonium acetate solution (pH 7.0). Soil organic matter content was determined using a volumetric K2Cr2O7-heating method. The content of available nitrogen in soil was measured using the alkaline hydrolysis method, and that of available P was extracted with 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 and determined using the molybdenum blue method. The content of available potassium was extracted with 1 mol/L ammonium acetate solution and determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS, Model TAS-990, Beijing Persee General Instrument Co., Ltd.).
The soil samples were digested with HF- HNO3-HClO4 and the speciation of Cd and Pb in soil was determined using the sequential extraction procedure of BCR method [30]. The concentrations of Cd and Pb in the extractant and digest solutions were measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA).
2.4 Data analysis
Removal efficiencies of Cd and Pb in soil were calculated using the following equation:
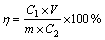 (1)
(1)
where η is the removal efficiency; C1 is the concentration of Cd or Pb in reagent solution, mg/L; V is the volume of reagent solution, mL; m is the mass of soil, g; C2 is the concentration of Cd or Pb in soil, mg/kg.
Fraction distribution of Cd and Pb in soil was calculated as follows [31]:
 (2)
(2)
where CFi is the concentration of each fraction of Cd or Pb in soil, and D is the extraction percentage of each fraction in the sum of all fractions.
Means and standard deviations were calculated using Excel 2013. Range analysis, variance analysis (ANOVA) and one-way analysis of variance were conducted using the SPSS 19.0. Significant differences between means were detected with Duncan’s multiple range test at the 5% level.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Optimization conditions of soil washing
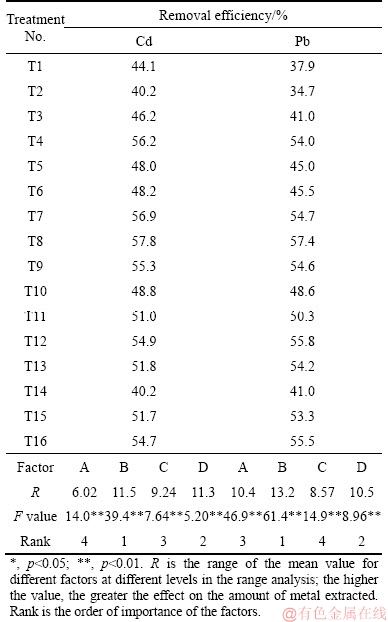
The orthogonal soil washing experiment with EDTA indicates that the reagent concentration, L/S ratio, mixing time and pH all had significant influences on the soil Cd and Pb removal (p<0.05) (Table 3). Mixing time was the most significant factor according to the range analysis, possibly associated with the dissolution and desorption of metals [24]. The optimum conditions for EDTA washing were 30 min, pH 5, L/S ratio 20 and 10 g/L EDTA (Figure 1). Cd removal increased with L/S ratio; the higher the liquid-solid ratio, the more the waste water was produced. Thus, an L/S ratio of 10 was selected. The final optimum conditions for EDTA washing were 10 g/L EDTA solution at pH 5 and L/S ratio of 10 for 30 min.
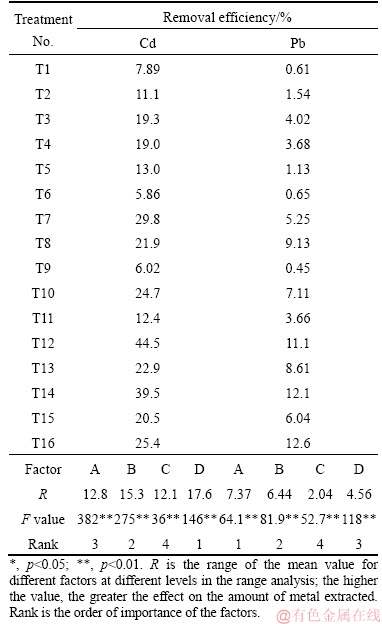
Similarly, all factors examined had a significant influence (p<0.05) on the removal of soil Cd and Pb washed with DTPA (Table 4). L/S ratio played the dominant role in washing according to the range analysis. The optimum conditions of DTPA washing were 10 g/L DTPA, L/S ratio 20, pH 5, and 30 min (Figure 1). However, the removal of DTPA showed only a slight difference between concentration of 5 and 10 g/L and a suitable L/S ratio can save costs and processing time at the site. The lower concentration of 5 g/L, and L/S ratio of 10 were finally considered.
The soil Cd and Pb removal using critic acid and FeCl3 was significantly different from that of EDTA or DTPA. Solution pH played the dominant role in Cd removal for citric acid washing, while for Pb removal, the most significant factor was reagent concentration (Table 5). The optimum conditions for soil Cd and Pb extraction were 30 g/L citric acid at pH 3 with an L/S ratio of 20 for 30 min and 60 min, respectively (Figure 1). However, the optimum pH 3 is very acidic and may have seriously adverse effects on soil functions. A solution pH 4 was therefore selected based on the Cd removal results in soil washing. The optimum conditions for citric acid washing were 30 g/L citric acid at pH 4 and an L/S ratio of 20 for 30 min. Soil Cd removal efficiency with FeCl3 solution was significantly related to the reagent concentration and L/S ratio (Table 6) but Pb removal was significantly affected by the L/S ratio. The influence of mixing time can be ignored according to the range analysis. The removal of Cd and Pb from contaminated soil increased with increasing FeCl3 concentration. According to the orthogonal experiment (Figure 1), the optimum conditions for Cd washing from soil were FeCl3 concentration of 8 g/L, L/S ratio of 20, and 120 min, and those for Pb were FeCl3 concentration of 8 g/L, L/S ratio of 20, and 30 min. Similarly to citric acid, a high- concentration FeCl3 solution was too acidic for soil washing and hence a FeCl3 concentration of 2 g/L was selected. Different mixing times gave no clear differences in Cd or Pb extraction and 30 min was therefore selected (Figure 1). Thus, the optimum washing conditions for soil Cd and Pb were L/S ratio of 10, 30 min, 10 g/L EDTA at pH 5, 5 g/L DTPA at pH 5, 30 g/L citric acid at pH 4, or 2 g/L FeCl3 at initial pH.
Table 3 Removal of Cd and Pb washed with EDTA in orthogonally designed experiment with L16(44)
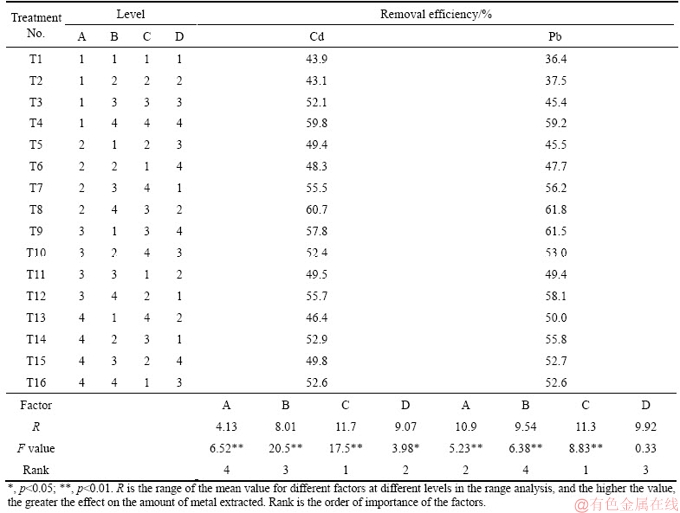

Figure 1 Effects of reagent concentration (c), extractant/soil ratio (L/S), mixing time (t) and solution pH on the removal of soil Cd and Pb using EDTA (a), DTPA (b), citric acid (c) and FeCl3(d)
Table 4 Removal of Cd and Pb washed with DTPA in orthogonally designed experiment with L16(44)
3.2 Removal efficiency of Cd and Pb from contaminated paddy soil
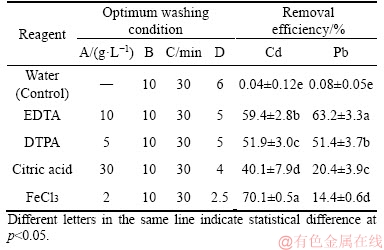
The removal efficiencies of Cd and Pb under optimized conditions are shown in Table 7. The removal efficiencies of soil Cd using EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 were 59.4%, 51.9%, 40.1% and 70.1%, respectively, and the corresponding values for Pb were 63.2%, 51.4%, 20.4% and 14.4%, respectively. These results indicated that both EDTA and DTPA can remove Cd and Pb simultaneously from contaminated soils, and are suitable washing reagents for soil Cd and Pb extraction. The results may be contributed to EDTA and DTPA can form strong metal-ligand complexes, which enhance the extraction of Cd and Pb in soil [12, 32].
Table 5 Removal of Cd and Pb washed with citric acid in orthogonally designed experiment with L16(44)
By comparison, FeCl3 and citric acid were efficient in the removal of Cd but slight for Pb, a similar result to that reported by LI et al [33]. Although FeCl3 can be considered a suitable choice for Cd extraction from contaminated soil, it may be unsuitable for Pb removal. This may be attributed to the low pH of the FeCl3 solution, resulting from proton release coupled with the generation of hydroxides, and the formation of Cd–Cl complexes can enhance Cd extraction by hindering the reabsorption of the extracted Cd onto adsorption sites on soil particles [22, 34]. Furthermore, Fe(III) in the soil-washing solutions may increase the exchange capacity of Cd(II) on the soil colloids and occupy the original soil binding sites of Cd(II) [35]. Similarly, citric acid is a carboxylic acid with three —COOH groups and behaves as a tetradentate ligand that may be combined with other cations and lead to give a lower removal efficiency of metals [36, 37].
Table 6 Removal of Cd and Pb washed with FeCl3 in orthogonally designed experiment with L16(44)
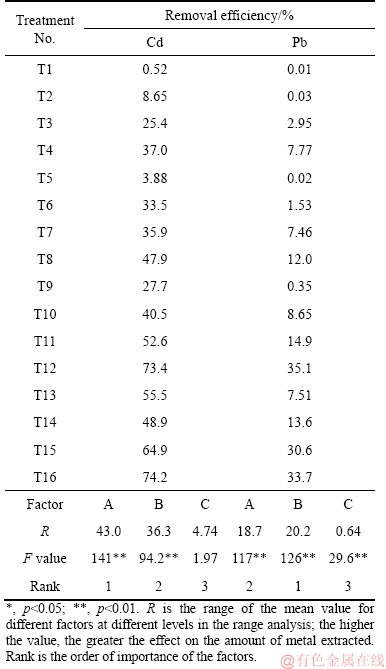
Table 7 Removal efficiencies of Cd and Pb in contaminated paddy soil using reagents or water (control) under optimized conditions
3.3 Speciation of metals in soil
The speciation analysis of heavy metals in soil before and after washing will help to further explore the effectiveness of the repair technology to degrade the bioavailability of heavy metals. According to BCR procedure, the oxidizable fraction and residual fraction are steady state and only possess a small effect on the environment. However, the acid extractable fraction and reducible fraction can lead to large environmental risks due to their high activity and bioavailability [38]. The initial fractions of Cd in the soil were mainly acid extractable and reducible but the main fraction of Pb was the reducible (Figure 2). After washing, the content of acid extractable Cd and reducible Pb was decreased significantly. Most of acid extractable and reducible Cd in contaminated soil can be extracted with EDTA, DTPA and FeCl3;however, the amount of reducible Cd in soil changed slightly after washing with citric acid. Most of acid extractable Pb in soil can be extracted by EDTA and DTPA. Soil reducible Pb can be removed with the four reagents. About 63.6% and 53.5% of reducible Pb can be extracted with EDTA and DTPA. After washing with FeCl3, however, the proportion of acid exchangeable Pb in soil was increased compared with the original soil, indicating that FeCl3 can change the mobility and redistribution of Pb in soil. The residual and oxidizable fractions of Cd and Pb in soil changed slightly after washing with the four reagents, and similar to the previous results [13]. The results suggested that soil washing effectively extracted the amount of acid extractable and reducible Cd and Pb in soil and can effectively reduce the bioavailability and environmental risk of Cd and Pb in contaminated paddy soil.

Figure 2 Fraction of Cd (a) and Pb (b) in a contaminated paddy soil before and after washing
3.4 Changes in soil fertility
Soil pH changed slightly after washing with EDTA and DTPA, while decreased significantly after washing with citric acid and FeCl3 (p<0.05)(Table 8), which may be attributed to the lower pH of the citric acid and FeCl3 solutions. Soil pH values in the presence of FeCl3 were especially low (pH 2.5), which may cause the solubility of potentially toxic elements from insoluble hydroxides after washing and enhance toxicity to plants [39, 40]. Soil available N content increased with the four washing reagents; especially the content of available N in soil washed by EDTA was significantly increased by about 34.8% (p<0.05). Soil available P content changed slightly with EDTA and DTPA washing but increased significantly (p<0.05) by about 30.1% and 60.5% after citric acid and FeCl3 washing. The results may be contributed to the low pH of the citric acid and FeCl3 solutions and enhance the transformation of unavailable P into available forms [21, 41]. However, the soil available K content declined significantly (p<0.05) by about 22.7%, 29.8%, 21.8% and 56.4% with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 washing, respectively. The results suggested that the potassium ions (K+) may be desorbed from the soil colloids and available K in soil can be easily lost during the washing process [35], and need to be amended by fertilizer application after washing for future crop growth. Furthermore, soil cation exchange capacity and soil organic matter content changed slightly after washing with the four reagents. Generally, soil washing with EDTA and DTPA had only slightly adverse effects on soil cation exchange capacity, soil organic matter content, available N and available P and maintained soil fertility (except for soil available potassium). But, the cost of EDTA and DTPA is high [42, 43]. If EDTA and DTPA are not too expensive, they may be considered to be suitable reagents for the removal of heavy metals from contaminated paddy soils.
4 Conclusions
The removal of Cd and Pb in contaminated paddy soil washed with EDTA, DTPA, critic acid and FeCl3 is significantly affected by the reagent concentration, the pH of reagent solution, the L/S ratio and the mixing time. Mixing time is the most significant factor in EDTA washing, while L/S ratio plays a dominant role in washing with DTPA. For citric acid, pH and reagent concentration are most significant for Cd and Pb removal, respectively. FeCl3 concentration is most important in Cd removal, while L/S ratio is most significant in Pb removal. The optimum washing conditions for Cd and Pb in a contaminated soil are L/S ratio of 10, mixing time of 30 min, reagent of 10 g/L EDTA at pH 5 or 5 g/L DTPA at pH 5, 30 g/L citric acid at pH 4, and 2 g/L FeCl3 at initial pH.
Table 8 Variation in soil fertility before and after washing (25 °C, L/S ratio 10: 1 and 30 min)

EDTA and DTPA can simultaneously remove Cd and Pb from the contaminated paddy soils. Citric acid and ferric chloride, however, were only efficient for Cd. The available soil fractions of Cd and Pb, especially acid extractable Cd and reducible Pb in soil, decreased significantly after washing with EDTA, DTPA and FeCl3, and only a slight influence on the residual and oxidizable forms. Washing with EDTA and DTPA can maintain soil fertility and may be suitable (but expensive) for the remediation of metal contaminated paddy soils.
References
[1] CALISI A, ZACCARELLI N, LIONETTO M G, SCHETTINO T. Integrated biomarker analysis in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris: Application to the monitoring of soil heavy metal pollution [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(11): 2637-2644. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere. 2012.11.040.
[2] YANG Sheng-xiang, LIAO Bin, YANG Zhi-hui, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Jin-tian. Revegetation of extremely acid mine soils based on aided phytostabilization: A case study from southern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 562: 427-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.208.
[3] LIU Ya-nan, GUO Zhao-hui, XIAO Xi-yuan, WANG Shuo, JIANG Zhi-chao, ZENG Peng. Phytostabilisation potential of giant reed for metals contaminated soil modified with complex organic fertiliser and fly ash: A field experiment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 576: 292-302. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.065.
[4] ZHAO Fang-jie, MA Yi-bing, ZHU Yong-guan, TANG Zhong, MCGRATH S P. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies [J]. Environment Science and Technology, 2015, 49(2): 750-759. DOI: 10.1021/es5047099.
[5] SHEORAN V, SHEORAN A S, POONIA P. Role of hyperaccumulators in phytoextraction of metals from contaminated mining sites: A review [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 2(41): 168-214. DOI: 10.1080/10643380902718418.
[6] HAZRAT A, EZZAT K, MUHAMMAD A S. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Concepts and applications [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(7): 869-881. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075.
[7] ABUMAIZAR R J, SMITH E H. Heavy metal contaminants removal by soil washing [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, B70: 71-86. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00149-1.
[8] PETERS R W. Chelant extraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, 66: 151-210. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00010-2.
[9] LE TAN D, LUO Chun-ling, LI Xiang-dong. The use of chelating agents in the remediation of metal-contaminated soils: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 153: 3-13. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.015.
TAN D, LUO Chun-ling, LI Xiang-dong. The use of chelating agents in the remediation of metal-contaminated soils: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 153: 3-13. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.015.
[10] GUO Xiao-fang, WEI Ze-bin, WU Qi-tang, LI Chun-ping, QIAN Tian-wei, ZHENG Wei. Effect of soil washing with only chelators or combining with ferric chloride on soil heavy metal removal and phytoavailability: Field experiments [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 147: 412-419. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.087.
[11] PAKZADEH B, BATISTA J R. Surface complexation modeling of the removal of arsenic from ion-exchange waste brines with ferric chloride [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 188: 399-407. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011. 01.117.
[12] WEN Jia, STACEY S P, MCLAUGHLIN M J, KIRBY J K. Biodegradation of rhamnolipid, EDTA and citric acid in cadmium and zinc contaminated soils [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 41(10): 2214-2221. DOI: 10.1016/ j.soilbio.2009.08.006.
[13] JIANG Jian-guo, YANG Meng, GAO Yu-chen, WANG Jia-ming, LI De-an, LI Tian-ran. Removal of toxic metals from vanadium-contaminated soils using a washing method: Reagent selection and parameter optimization [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 180: 295-301. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2017.03.116.
[14] WEI Meng, CHEN Jia-jun, WANG Xing-wei. Removal of arsenic and cadmium with sequential soil washing techniques using Na2EDTA, oxalic and phosphoric acid: Optimization conditions, removal effectiveness and ecological risks [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 156: 252-261. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.106.
[15] UDOVIC M, LESTAN D. EDTA and HCl leaching of calcareous and acidic soils polluted with potentially toxic metals: Remediation efficiency and soil impact [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(6): 718-724. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2012.04.040.
[16] ZHANG Shu-juan, YANG Zhi-hui, WU Bao-lin, WANG Yang-yang, WU Rui-ping, LIAO Ying-ping. Removal of Cd and Pb in calcareous soils by using Na2EDTA recycling washing [J]. Clean-Soil, Air, Water, 2014, 42 (5): 641-647. DOI: 10.1002/clen.201200634.
[17] DENG Tian-lin, ZHANG Bing-ru, LI Feng-ting, JIN Lu-yao. Sediment washing by EDTA and its reclamation by sodium polyamidoamine-multi dithiocarbamate [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 450-456. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016. 09.152.
[18] MODIBA P, MATOETOE M, CROUCH A M. Kinetics study of transition metal complexes (Ce–DTPA, Cr–DTPA and V–DTPA) for redox flow battery applications [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 94: 336-343. DOI: 10.1016/ j.electacta.2013.01.081.
[19] REN Jie, WANG Feng-hua, ZHAI Yun-bo, ZHU Yun, PENG Chuan, WANG Teng-fei, LI Cai-ting, ZENG Guang-ming. Effect of sewage sludge hydrochar on soil properties and Cd immobilization in a contaminated soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 189: 627-633. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2017.09.102.
[20] UDOVIC M, LESTAN D. Zn and Cd mobility, availability and fractionation in aged soil remediated by EDTA leaching Pb [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 74(10): 1367-1373. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.013.
[21] REN Xiang-hao, YAN Rui, WANG Hong-cheng, KOU Ying-ying, CHAE K J, KIM I S, PARK Y J, WANG A J. Citric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as effective washing agents to treat sewage sludge for agricultural reuse [J]. Waste Management, 2015, 46: 440-448. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.021.
[22] MAKINO T, TAKANO H, KAMIYA T, ITOU T, SEKIYA N, INAHARA M, SAKURAI Y. Restoration of cadmium- contaminated paddy soils by washing with ferric chloride: Cd extraction mechanism and bench-scale verification [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(6): 1035-1043. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2007.07.080.
[23] DERMONT G, BERGERON M, MERCIE R G, RICHER- LAFL CHE M. Soil washing for metal removal: A review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(1): 1-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.043.
CHE M. Soil washing for metal removal: A review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(1): 1-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.043.
[24] KIM E J, LEE J, BAEK K. Abiotic reductive extraction of arsenic from contaminated soils enhanced by complexation: Arsenic extraction by reducing agents and combination of reducing and chelating agents [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 283: 454-461. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2014.09.055.
[25] IM J, YANG K, JHO E H, NAM K. Effect of different soil washing solutions on bioavailability of residual arsenic in soils and soil properties [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 253-258. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.004.
[26] LIU Cheng-chung, LIN Ying-chen. Reclamation of copper-contaminated soil using EDTA or citric acid coupled with dissolved organic matter solution extracted from distillery sludge [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 178: 97-101. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.034.
[27] RODR GUEZ-JORD
GUEZ-JORD M P, GARRIDO F, GARC
M P, GARRIDO F, GARC A- GONZ
A- GONZ LEZ M T. Potential use of gypsum and lime rich industrial by-products for induced reduction of Pb, Zn and Ni leachability in an acid soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1-3): 762-769. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jhazmat.2009.10.074.
LEZ M T. Potential use of gypsum and lime rich industrial by-products for induced reduction of Pb, Zn and Ni leachability in an acid soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1-3): 762-769. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jhazmat.2009.10.074.
[28] UNVER I, MADENO LU S, DILSIZ A, NAMLI A. Influence of rainfall and temperature on DTPA extractable nickel content of serpentine soils in Turkey [J]. Geoderma, 2013, 202-203: 203-211. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013. 03.025.
LU S, DILSIZ A, NAMLI A. Influence of rainfall and temperature on DTPA extractable nickel content of serpentine soils in Turkey [J]. Geoderma, 2013, 202-203: 203-211. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013. 03.025.
[29] PANSU M, GAUTHEYROU J. Handbook of soil analysis: Mineralogical, organic and inorganic methods [M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2006. DOI: 10.1007/978-3- 540-31211-6.
[30] RAURET G, LO'PEZ-SA'NCHEZ J F, SAHUQILLO A, RUBIO R, DAVIDSON C, URE A, QUEVAUVILLER P H. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1999, 1(1): 57-61. DOI: 10.1039/a807854h.
[31] LEI Ming, LIAO Bo-han, ZENG Qing-ru, QIN Pu-feng, KHAN S. Fraction distributions of lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc in metal-contaminated soil before and after extraction with disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2008, 39: 1963-1978. DOI: 10.1080/00103620802134776.
[32] NORTH A E, SARPONG-KUMANKOMAH S, BELLAVIE A R, WHITE W M, GAILER J. Environmentally relevant concentrations of aminopolycarboxylate chelating agents mobilize Cd from humic acid [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 57: 249-257. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2017. 02.004.
[33] LI Yu-jiao, HU Peng-jie, ZHAO Jie, DONG Chang-xun. Remediation of cadmium- and lead-contaminated agricultural soil by composite washing with chlorides and citric acid [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(7): 5563-5571. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-014-3720-z.
[34] YOO J C, SHIN Y J, KIM E J, YANG J S, BAEK K. Extraction mechanism of lead from shooting range soil by ferric salts [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2016, 103: 174-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2016.07.002.
[35] WANG Gui-yin, ZHANG Shi-rong, XU Xiao-xun, LI Ting, LI Yun, DENG Ou-ping, GONG Guo-shu. Efficiency of nanoscale zero-valent iron on the enhanced low molecular weight organic acid removal Pb from contaminated soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 117: 617-624. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2014.09.081.
[36] QUARTACCI M F, BAKER A J M, NAVARI-IZZO F. Nitrilotriacetate- and citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of cadmium by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj, Brassicaceae) [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59(9): 1249-1255. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.053.
[37] EVANGELOU M W H, EBEL M, HOMMES G, SCHAEFFER A. Biodegradation: The reason for the inefficiency of small organic acids in chelant-assisted phytoextraction [J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2008, 195: 177-188. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-008-9738-4.
[38] ZHANG Hong-jiao, GAO Yun-tao, XIONG Hua-bin. Removal of heavy metals from polluted soil using the citric acid fermentation broth: A promising washing agent [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(10): 9506-9514. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-017-8660-y.
[39] CONTIN M, MALEV O, IZOSIMOVA A, NOBILI M D. Flocculation of sewage sludge with FeCl3 modifies the bioavailability of potentially toxic elements when added to different soils [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 81: 278-288. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.033.
[40] TANG Qiang, ZHOU Ting, GU Fan, WANG Yan, CHU Jia-ming. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from soil through desorption using citric acid: Kinetic and equilibrium studies [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(9): 1941-1952. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3602-x.
[41] WANG Gui-yin, ZHANG Shi-rong, XU Xiao-xun, ZHONG Qin-mei, ZHANG Chu-er, JIA Yong-xia, LI Ting, DENG Ou-ping, LI Yun. Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: Optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 569-570: 557-568. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.155.
[42] QIU Rong-liang, ZOU Ze-li, ZHAO Zhi-hao, ZHANG Wei-hua, ZHANG Tao, DONG Han-ying, WEI Xian-ge. Removal of trace and major metals by soil washing with Na2EDTA and oxalate [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2010, 10(1): 45-53. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-009-0083-z.
[43] WANG Sen, WANG Zhao-hui, GAO Ya-jie, LIU Lu, YU Rong, JIN Jing-jing, LUO Lai-chao, HUI Xiao-li, LI Fu-cui, LI Meng-hua. EDTA alone enhanced soil zinc availability and winter wheat grain Zn concentration on calcareous soil [J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 141: 19-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.06.008.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
EDTA、DTPA、柠檬酸和FeCl3对污染稻田土壤镉铅的去除及土壤肥力的影响
摘要:潜在有害金属镉和铅对水稻的安全生产有着重要意义。本文对比研究了EDTA、DTPA、柠檬酸和FeCl3对镉和铅的去除能力以及对土壤肥力的影响。结果表明,选取固液比1:10振荡30 min用10 g/L EDTA(pH 5)可去除59% Cd 和 63% Pb,而在同等条件下,5 g/L DTPA可去除52% Cd和 51%Pb。EDTA的土壤淋出液含58%酸可提取态和可还原态Cd,49%酸可提取态和可还原态Pb,DTPA淋出液中含53%和41%。土壤pH值、阳离子交换量、有机质、土壤有效磷变化较小。而柠檬酸和氯化铁仅对Cd淋洗有效,且淋洗后土壤pH值下降显著。研究表明EDTA和DTPA可以作为潜在有害金属污染稻田土壤净化的合适淋洗剂。
关键词:污染稻田土壤;土壤淋洗;潜在有害金属;形态分析;土壤肥力
Foundation item: Project(2015BAD05B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Support Program, China
Received date: 2018-02-04; Accepted date: 2019-06-17
Corresponding author: GUO Zhao-hui, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-731-88879325; E-mail: zhguo@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0002-0916- 455X

