青海德合龙洼铜金矿床成矿流体特征
傅晓明,戴塔根
(中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:通过流体包裹体岩相学、显微测温学和包裹体稀土元素分析,研究青海德合龙洼铜金矿床成矿流体性质和演化。研究结果表明:流体包裹体主要为气液两相包裹体,另有少量液相包裹体;包裹体气相成分主要以H2O和CO2为主。流体包裹体的均一温度为327~367 ℃,流体盐度为3.4%~6.4%,流体密度为0.55~0.88 g/cm3,为中高温、低盐度、中等密度和中等压力的成矿流体;石英和黄铁矿包裹体中,轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,具有负铕 异常。
关键词:德合龙洼;成矿流体;稀土元素;青海
中图分类号:P611.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)04-1066-06
Characteristics of ore-forming fluid of Dehelongwa
copper-gold deposit in Qinghai
FU Xiao-ming, DAI Ta-gen
(School of Geosciences and Info-physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Based on the study of the fluid inclusion, micro-thermometry and rare earth element analyses, the characteristics of ore-forming fluid, fluid evolution and the origin of the Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit were discussed and systematically studied. The results show that these inclusions consist of phases of gas and liquid, with minor inclusions of liquid, and the compositions of gas in the inclusions are H2O and CO2. The homogenization temperature, salinity and density of fluid for the major mineralization phase range from 327 ℃ to 367 ℃, 3.4% to 6.4% and 0.55 g/cm3 to 0.88 g/cm3, respectively. In fluid inclusions of quartz and pyrite, LREE (light rare earth element) is enriched, HREE (heavy rare earth element) is loss, and negative Eu is abnormal.
Key words:Dehelongwa; ore-forming fluid; rare earth element (REE); Qinghai
德合龙洼铜金矿床位于青海省黄南州同仁县东部,青藏高原北东端,大地构造位置属于松潘—甘孜褶皱系。该区又位于秦—祁—昆成矿带的交汇部位,属于西秦岭成矿区。近年来,对于秦—祁—昆结合部的研究取得了许多重要的研究成果,目前倾向于认为秦—祁—昆结合部是一个具有复杂洋陆演化历史的复合型造山带[1-7]。范立勇等[8]对该区火山岩地球化学及构造背景进行研究,认为该区火山岩具有类似洋岛玄武岩的特征,可能是含石榴子石橄榄岩低度部分熔融的产物。寇晓虎等[5]对该区的火山岩地球化学及构造环境进行研究,认为火山岩的岩石组合主要为玄武岩、安山岩、玄武安山岩等,构造环境为从拉张的过渡型洋中脊环境到闭合的岛弧环境的演化特征。张涛[9]对该矿床进行成矿规律研究,认为其成因属于破碎蚀变岩型。作者对矿床的包裹体进行研究,以便为进一步探讨成矿流体性质及来源、成矿作用和成矿模式提供依据。
1 地质概况
矿区出露地层为下二叠统大关山群上岩组碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩,岩性主要为中细粒长石石英砂岩、泥质板岩夹砂岩、中厚层状硅化大理岩、含砾中粗粒石英砂岩;下三叠统隆务河群下岩组的碎屑岩,岩性主要为粉砂岩与角岩化板岩、条带状硅质板岩夹中粗粒长石、石英砂岩和少量碳酸盐岩的类复理石建造。
矿区岩浆活动主要表现为强烈的侵入活动,侵入岩为印支期造山带“I”型系列花岗岩类,岩性由东向西为闪长岩和花岗闪长岩,它们组成岗察岩体的主体。闪长岩分布于区内东段北侧,因第四系覆盖,地表由多个小岩枝组成,出露面积为0.1~1.0 km2不等。具较明显的岩相分带,岩体中部为中粗粒闪长岩,边缘为中细粒闪长岩。花岗闪长岩分布于研究区中西段北侧,呈岩株状,面积为4~5 km2。区内脉岩发育,主要分布于下三叠统,与北西向断裂关系密切,一般分布于断裂发育地段,岩性为闪长玢岩、煌斑岩、细晶岩、辉长岩和辉绿岩等,走向长为几十米至100 m,宽为几米至十几米,脉岩破碎后,沿碎裂面有细脉状、网脉状石英和碳酸岩脉充填,石英碳酸盐脉中见有星点状、团块状的黄铜矿、黄铁矿、毒砂和辉钼矿化。德合龙洼脉岩与铜金矿体在时空上紧密相伴。
矿区位于岗察背斜南翼,断裂构造极发育,按走向分为2组:北西向断裂组与北东向断裂组。北西向断裂组以F21为代表,F21分布于工作区中部,走向长大于5 km,走向为NW—SE,倾向为SW,倾角为50°~70°。受多期次挤压和拉伸作用的影响,形成宽为300~500 m的碎裂岩和糜棱岩带,并伴随有强烈的中低温热液蚀变。北东向组是区域谢坑至阿旦断裂的一部分,主干断裂呈隐伏状,次级断裂平行于主干断裂呈不等距分布,断层两侧地层有明显位移,东盘北移,西盘南移,断距为800~900 m,属平移断层。
德合龙洼铜金矿位于岗察岩体南接触带东段,赋存于三叠系下统碎屑岩中的北西向F21断裂破碎蚀变岩带内。矿区共圈出9条铜金矿体。矿体产于F21断裂破碎蚀变带内碎裂岩和节理密集处,横向上平行产出,走向尖灭再现,出露标高为3 432~3 539 m。研究区规模较大的矿体圈出3条,由南往北分别编号为Ⅰ号、Ⅱ-1号和Ⅱ-2号。
2 样品特征与分析方法
研究样品均采自Ⅰ号矿体,将其磨制成厚度约为0.2 mm双面剖光的薄片用于岩相学与流体包裹体 观察。
包裹体成分测定对象为石英,由中南大学地质研究所流体包裹体气液相成分测定实验室完成。将纯度大于99%的包裹体样品放入烧杯中,加入HCl(体积比为1:1),在电热板80~100 ℃保温1 h,在室温下保留12 h,倒掉酸,用去离子水清洗样品数次,超声震荡5 min,再用离子水反复漂洗,在80 ℃烘箱内烘干样品。
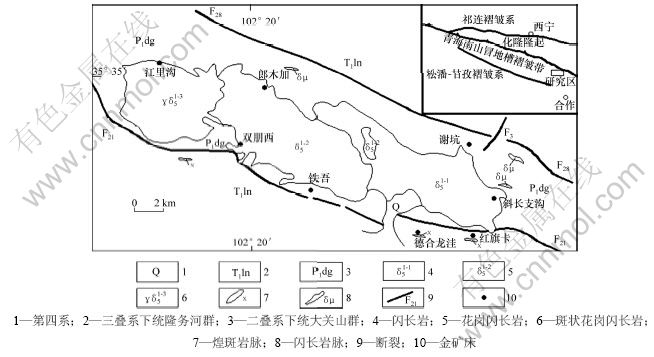
图1 德合龙洼铜金矿床地质略图[9]
Fig.1 Sketch geological map of Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit[9]
流体包裹体的气相成分分析采用加热爆裂法提取气体,其测试程序为:将清洗干净的500 mg样品放入石英管内,逐渐升温到100 ℃排气,待分析管内真空度为6×10-6 Pa以下时,将100 ℃以内的次生包裹体和样品吸附气体去除。以1 ℃/s的速度升温到500 ℃,记录压力计的读数,用液氮冷冻5 min,再用干冰冷冻5 min,记录压力计的读数(用来计算水的含量)后测定。分析仪器为Varian-3400型气相色谱仪(美国),分析误差<5%。流体包裹体的液相成分分析程序为,将清洗干净的1 g样品放入石英管中,于500 ℃爆裂 15 min,冷却后加5 mL水,超声震荡10 min。分析仪器为美国戴安公司生产的DX-120Ion Chromatograph离子色谱仪。淋洗液是浓度为2.5 mmol/L邻苯二甲酸和2.4 mmol/L三(羟)甲基氨基甲烷;阴离子流速为 1.2 mL/min,阳离子流速为1.0 mL/min。重复测定精 度<5%。
流体包裹体测温工作主要在中南大学地质研究所流体包裹体测温实验室进行。本次测试使用仪器为英国产的Linkam THMS600型冷热台,均一温度重现误差小于2 ℃,冰点温度重现误差小于0.2 ℃。冷冻测温时,利用液氮对包裹体降温,在温度下降过程中观察包裹体的变化,包裹体冷冻后,缓慢升温,至冰晶刚刚熔化,记录冰点温度。对气液两相包裹体均一温度测定时,开始的升温速度为10 ℃/min。在气液两相接近均一时,降低升温速度,将其控制在1 ℃/min,并及时记录均一温度。
流体包裹体稀土元素组分测定尝试采用等离子质谱(ICP-MS)方法测定。先将待测定的纯净单矿物样品用蒸馏水清洗,其中石英样品用1:1盐酸(体积比)低温煮30 min,清洗后用浓硝酸浸泡12 h。将处理过的单矿物样品在爆裂仪中于450~500 ℃爆裂(其中硫化物矿物爆裂温度一般低于450 ℃),用2%的稀硝酸提取包裹体中的液相组分,然后用装备有“膜去溶”装置的ICP-MS仪器进行分析测试[10]。
3 流体包裹体成分
德合龙洼铜金矿床矿石中石英的成矿溶液均是富含Na+,K+,Mg2+,Ca2+,F-,Cl-,NO3-和SO42-等的复杂成分盐水溶液。成矿流体的液相成分阳离子以Na+,K+,Mg2+和Ca2+为主,Na+和K+的总含量低于Ca2+和Mg2+的总含量,表明成矿流体以变质流体为主,部分Ca2+和Mg2+来自主矿物的溶解;阴离子主要以SO42-和Cl-为主,F-和NO3-次之。根据以上特点可得出本区成矿流体应属NaCl-KCl-CaCl2-Mg(NO3)2-H2O体系。
气相成分分析结果表明:气相以H2O和CO2为主,其次为H2和CH4,N2和C2H2等含量很少。成分中富含CO2,含有CH4和C2H2等挥发分,表明成矿环境为还原环境,而且生物参与了成矿作用[9]。
成矿流体的Na+/ K+和F-/Cl-可以作为判别流体来源的一个标志[11],在一般情况下,岩浆热液w(Na+)/ w(K+)小于1.00,经计算,成矿阶段石英w(Na+)/w(K+)为0.47~0.97,具岩浆热液特征。成矿阶段石英阴离子中w(SO42-)>w(Cl-)>w(F-),w(SO42-)/w(Cl-)为4.54~ 18.42,故其成矿热卤水应是富钾的硫酸盐型热卤 水[12-13]。
德合龙洼铜金矿床石英中流体包裹体群体气-液相成分及相关参数见表1。从表1可知:w(SO42-)>w(Cl-),由于SO42-含量反映的是介质中与金迁移有密切联系的HS-的含量[14],因此,可以推断:金在成矿流体中主要以硫氢络合物的形式迁移,氯络合物 次之。
表1 德合龙洼铜金矿床石英中流体包裹体群体气-液相成分及相关参数
Table 1 Composition and correlative parameters of volatiles and ions of fluid inclusions from Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit
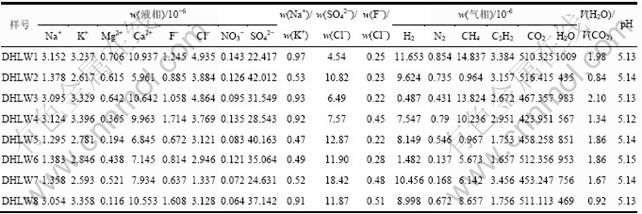
而当w(F-)/w(Cl-)比小于1时反映属大气降水(或地层流体)的特征。由表1可知:本区样品中w(F-)/w(Cl-)均小于1.00(0.22~0.51),表明有大气降水加入。因此,可以得出:成矿流体是以岩浆热液为主包含有大气降水的混合流体。
4 流体包裹体显微测温学及稀土 元素
4.1 流体包裹体显微测温学
6个样品中,流体包裹体广泛发育,各类原生包裹体多呈椭圆形、圆形和不规则状无序分布,个体较小(粒径多为5~10 μm),类型多,有液体包裹体(L,气液体积比为10%~30%)、气液包裹体(L+V,气液体积比为25%~45%)及含子矿物包裹体(L+V+H),其中以气液包裹体为主。
均一法所测的最低温度为267 ℃,最高温度为468 ℃(见表2),频数直方图表现出明显的峰值分布,且集中分布在327~367 ℃(图2),表明了热液矿化为中高温阶段。
根据6个样品冰点温度计算出成矿流体盐度为1.40%~13.40%,频数直方图中显示盐度主要为3.4%~6.4%(图2),属低盐度。
根据均一温度和冷冻法盐度,可以查压力-温度-浓度-密度表[15]获得密度。由上述不同图解或查表法所获得的数值较接近。可推算出德合龙洼铜金矿床的成矿流体的密度为0.55~0.88 g/cm3,为中等密度。
压力是控制成矿作用过程最重要却难以准确获得的参数之一,其估算方法较多,常用的有CO2包裹体的等比容法、含CO2包裹体浓度法、气体包裹体压力测定法等,分别适用于含CO2包裹体、气成或沸腾条件。鉴于德合龙洼铜金矿床6个样品中未见CO2包裹体,因而成矿压力的测定不适用含CO2包裹体的压力测定法,同时,在德合龙洼铜金矿床也未见到沸腾包裹体的特征,因而,成矿压力的测定主要根据中低盐度NaCl-H2O体系的压力估算法[15]。采用Zhang等[16]的NaCl-H2O体系的P-T等容式以及Brown等对该P-T等容式的修正式,由均一温度和盐度计算求得各样品压力(表2),代表了该区成矿压力的最低值。经计算推算出本区压力为2.25~20.61 MPa。
4.2 稀土元素
尝试采用等离子质谱方法(ICP-MS)测定包裹体中的稀土元素,取得了较好的效果。该方法灵敏度高,可以测定包裹体中的微量元素、稀土元素。国内外有关地质学家进行了一些包裹体成分研究[17-20],并对部分矿物稀土元素进行分析。
德合龙洼铜金矿床流体稀土元素组成见表3。从表3可以看出:石英和黄铁矿中稀土总含量∑w(LREE)为32.026×10-6~176.650×10-6,显示了DHLW2和DHLW4总稀土含量较高;轻稀土含量w(LREE)为22.482×10-6~161.502×10-6;重稀土含量w(HREE)为4.378×10-6~15.358×10-6;w(LREE)/w(HREE)为2.356~10.662,表明轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损。w(LaN)/w(YbN)除DHLW13(1.314)外多大于3.000,显示轻重稀土分馏较强,δw(Eu)范围为0.310~0.789,具有明显负铕异常。
表2 德合龙洼铜金矿床流体包裹体参数
Table 2 Parameters of fluid inclusion of Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit
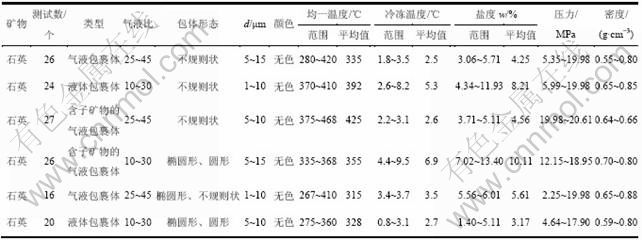
表3 德合龙洼铜金矿床稀土元素组成
Table 3 REE composition of Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit


图2 德合龙洼铜金矿床均一温度和盐度分布直方图
Fig.2 Temperature and sanility histogram plots of Dehelongwa copper-gold deposit
5 结论
(1) 德合龙洼铜金矿床中流体包裹体主要为气液包裹体,另有液相包裹体和少量含子矿物包裹体。成矿流体液相成分阳离子以Na+,K+,Mg2+和Ca2+为主,阴离子主要以SO42-和Cl-为主;气相以H2O和CO2为主。
(2) 德合龙洼铜金矿床的流体包裹体测温研究表明:均一温度主要为327~367 ℃,盐度主要为3.4%~6.4%,密度主要集中于0.55~0.88 g/cm3,压力主要为2.25~20.61 MPa。为中高温、低盐度、中等密度和中等压力的成矿流体。
(3) 德合龙洼铜金矿床石英、黄铁矿包裹体稀土元素特征为:轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,具有负铕 异常。
参考文献:
[1] 殷鸿福, 张克信.中央造山带的演化及其特点[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1998, 23(5): 437-441.
YIN Hong-fu, ZHANG Ke-xin. Evolution and characteristics of the central orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(5): 437-441.
[2] 朱云海, 张克信, PAN Yuan-ming, 等. 东昆仑造山带不同蛇绿岩带的厘定及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1999, 24(2): 134-138.
ZHU Yun-hai, ZHANG Ke-xin, PAN Yuan-ming, et al. Determination of different ophiolitic belts in Eastern Kunlun orogenic zone and their tectonic significance[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1999, 24(2): 134-138.
[3] ZHANG Ke-xing, HUANG Ji-chun, YIN Hong-fu, et al. Application of radiolarians and other fossils in non-Smithstrata: Exemplified by the Animaqing mélange belt in eastern Kunlun Mountains[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2000, 43(4): 364-374.
[4] 张克信, 朱云海, 殷鸿福, 等. 大地构造相在东昆仑造山带地质填图中的应用[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(6): 661-666.
ZHANG Ke-xin, ZHU Yun-hai, YINHong-fu, et al. Application of tectonic facies in geological mapping in East Kunlun orogenic belt [J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(6): 661-666.
[5] 寇晓虎, 朱云海, 张克信, 等. 青海省同仁地区上二叠统石关组上部火山岩的新发现及其地球化学特征和构造环境意义[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(1): 45-58.
KOU Xiao-hu, ZHU Yun-hai, ZHANG Ke-xin, et al. Discovery and geochemistry of upper Permian volcanic rocks in Tongren Area, Qinghai Province and their tectonic significance[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(1): 45-58.
[6] 息朝庄, 戴塔根, 王明艳. 青海双朋西金矿区原生晕特征及其指示意义[J]. 金属矿山, 2009, 393(3): 84-86.
XI Chao-zhuang, DAI Ta-gen, WANG Ming-yan. Characteristics and indication significance of the primary halo in Shuangpengxi gold deposit in Qinghai[J]. Metal Mine, 2009, 393(3): 84-86.
[7] 傅晓明, 戴塔根, 息朝庄, 等. 青海双朋西金铜矿床的成矿流体特征及流体来源[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(5): 531-537.
FU Xiao-ming, DAI Ta-gen, XI Chao-zhuang, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid and genesis of the Shuangpengxi gold-copper deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2009, 24(5): 531-537.
[8] 范立勇, 王岳军, 李晓勇. 青海西秦岭地区晚中生代基性火山岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2007, 27(3): 63-72.
FAN Li-yong, WANG Yue-jun, LI Xiao-yong. Geochemical characteristics of late Mesozoic mafic volcanic rocks from western Qinling and its tectonic implications[J]. J Mineral Petrol, 2007, 27(3): 63-72.
[9] 张涛. 青海双朋西—斜长支沟地区金矿成矿地质条件及成矿规律[J]. 西北地质, 2007, 40(3): 62-66.
ZHANG Tao. Ore-forming conditions and metallogeny of Gold deposit in Shuangpengxi—Xiechangzhigou, Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2007, 40(3): 62-66.
[10] 王莉娟, 王京彬, 王玉往, 等. 蔡家营、大井多金属矿床成矿流体和成矿作用[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2003, 33(10): 941-950.
WANG Li-juan, WANG Jing-bin, WANG Yu-wang, et al. Ore-forming fluid and mineralization of Caijiaying and Dajing polymetallic deposit[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2003, 33(10): 941-950.
[11] 卢焕章, 李秉伦, 沈昆, 等. 包裹体地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 1-246.
LU Huan-zhang, LI Bing-lun, SHEN Kun, et al. Geochemistry of fluid inclusions[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1990: 1-246.
[12] 冉崇英. 康滇地轴层控铜矿床的成矿机理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 2-47.
RAN Chong-ying. The ore-forming mechanism of Kangdian axis stratabound copper deposit[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1989: 2-47.
[13] RAN Chong-ying. On ore source and ore-forming fluid of Dongchuan-Yimen type copper deposit[J]. Sciences in China: Series B, 1989, 32(9): 1117-1124.
[14] 刘伟. 冀西石湖金矿床地球化学特征、矿床成因及成矿预测研究[D]. 中南大学地学与环境工程学院, 2007: 70-72.
LIU Wei. Research on the geochemistry feature, genesis and metallogenic prognosis in the Shihu gold deposit, Western Hebei Province[D]. Central South University. School of Geosiences and Envicromental Engineering, 2007: 70-72.
[15] 刘斌, 沈昆. 流体包裹体的氧逸度计算公式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报, 1995, 15(3): 291-302.
LIU Bin, SHEN Kun. Formulae for calculating oxygen fugacities of fluid inclusions and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogical Sinica, 1995, 15(3): 291-302.
[16] Zhang Y G, Frantz J D. Determination of the homogenization temperatures and densities of supercritical fluids in the system NaCl-KCl-CaCl2-H2O using synthetic fluid inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 1987, 64: 335-350.
[17] Ulrich T, Gunther D, Heinrich C A. Gold concentrations of magmatic brines and the metal budget of porphyry copper deposits[J]. Nature, 1999, 399(17): 676-679.
[18] Andreas A, Gunther D, Heinrich C A. Formation of a magmatic-hydrothermal ore deposit: Insights with LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions[J]. Science, 1998, 279: 2091-2094.
[19] Andreas A, Gunther D, Heinrich C A. Causes for large-scale metal zonation around mineralized plutins:Fluid inclusion LA-ICP-MS evidence from the Mole Granite, Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(8): 1563-1581.
[20] Ghazi A M, Readder E, Seeley R C. Determination of rare earth elements in fluid inclusions by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry(ICP-MS)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(18): 4513-4516.
[21] 赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 224-225.
ZHAO Zhen-hua. The principle of trace elements geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 224-225.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2010-04-20;修回日期:2010-07-03
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(41073036);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(07JJ6071)
通信作者:傅晓明(1968-),男,江西高安人,博士研究生,从事地球化学研究;电话:0755-25539837;E-mail:fuxiaoming2008@126.com