定向凝固单相Sn-2%Sb合金的胞/枝晶转变、枝晶生长和显微硬度
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第8期
论文作者:O. L. ROCHA T. A. COSTA M. DIAS A. GARCIA
文章页码:1679 - 1686
关键词:Sn-Sb单相合金;定向凝固;热参数;显微组织;胞/枝晶可逆转变
Key words:Sn-Sb monophasic alloy; directional solidification; thermal parameters; microstructure; reverse cellular/dendritic transition
摘 要:采用单相Sn-2%Sb(质量分数)合金进行水平定向凝固实验,分析凝固热参数对显微组织形貌和长度尺度的影响。在凝固过程中,对沿铸坯长度方向的不同部位进行连续温度测量,用这些温度数据来确定凝固热参数,包括生长速率(VL)和冷却速率(TR)。高冷却速率的胞晶和枝晶可以表征铸件不同区域的显微组织,当TR>5.0 K/s时发生枝晶向胞晶的可逆转变。沿定向凝固铸造的长度方向确定胞晶尺寸(λc)和一次枝晶间距(λ1),提出关于λc和λ1与VL和TR的实验生长规律,并与垂直向上定向凝固实验结果进行对比分析,并分析显微组织形貌和长度尺度对显微硬度的影响。
Abstract: Horizontal directional solidification experiments were carried out with a monophasic Sn-2%Sb (mass fraction) alloy to analyze the influence of solidification thermal parameters on the morphology and length scale of the microstructure. Continuous temperature measurements were made during solidification at different positions along the length of the casting and these temperature data were used to determine solidification thermal parameters, including the growth rate (VL) and the cooling rate (TR). High cooling rate cells and dendrites are shown to characterize the microstructure in different regions of the casting, with a reverse dendrite-to-cell transition occurring for TR>5.0 K/s. Cellular (lc) and primary dendrite arm spacings (l1) are determined along the length of the directionally-solidified casting. Experimental growth laws relating lc and l1 to VL and TR are proposed, and a comparative analysis with results from a vertical upward directional solidification experiment is carried out. The influence of morphology and length scale of the microstructure on microhardness is also analyzed.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 1679-1686
O. L. ROCHA1,2, T. A. COSTA1, M. DIAS3, A. GARCIA3
1. Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Pará - IFPA, 66093-020, Belém-Pará, Brazil;
2. Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Pará - UFPA, 66075-110, Belém-Pará, Brazil;
3. Department of Manufacturing and Materials Engineering, University of Campinas-UNICAMP, 13083-860, Campinas-Sao Paulo, Brazil
Received 19 September 2017; accepted 18 January 2018
Abstract: Horizontal directional solidification experiments were carried out with a monophasic Sn-2%Sb (mass fraction) alloy to analyze the influence of solidification thermal parameters on the morphology and length scale of the microstructure. Continuous temperature measurements were made during solidification at different positions along the length of the casting and these temperature data were used to determine solidification thermal parameters, including the growth rate (VL) and the cooling rate (TR). High cooling rate cells and dendrites are shown to characterize the microstructure in different regions of the casting, with a reverse dendrite-to-cell transition occurring for TR>5.0 K/s. Cellular (lc) and primary dendrite arm spacings (l1) are determined along the length of the directionally-solidified casting. Experimental growth laws relating lc and l1 to VL and TR are proposed, and a comparative analysis with results from a vertical upward directional solidification experiment is carried out. The influence of morphology and length scale of the microstructure on microhardness is also analyzed.
Key words: Sn-Sb monophasic alloy; directional solidification; thermal parameters; microstructure; reverse cellular/dendritic transition
1 Introduction
The morphology and the length scale of the phases forming the microstructure of metallic alloys can have significant effect on the final properties of as-solidified products, which has stimulated the development of theoretical growth models permitting correlations between the representative length scale of the phases forming the microstructure and the thermal parameters operative during solidification to be established [1-3]. The microstructural morphologies of monophasic alloys depend on thermal and compositional features that can induce instabilities at the liquid/solid interface during growth, which makes the planar form, typical of pure metals, transform into cellular and dendritic morphologies [4-8]. Cellular and dendritic spacings are important length scale parameters, which have significant influence on the properties of castings, since they affect the microscopic segregation existing between cellular and dendritic branches [9-28]. In this sense, the prediction of the cellular/dendritic transition (CDT) in as-solidified microstructures is of great interest for the assessment and design of the corresponding final properties. The mechanisms that govern the CDT are generally based on thermal parameters of solidification, such as temperature gradient GL, growth rate VL, cooling rate TR and alloy composition [4-8].
Many industrial processes encompassing solidification are associated with thermal/solutal convection effects that can affect the resulting as-solidified microstructure. The effect of the solidification growth direction with respect to the metal–mold interface has been examined by investigations with the chill placed on either the bottom, top or side of the mold [13,14]. Figure 1 illustrates schematically how the heat extraction occurs in each case. When the process is carried out vertically upwards, in conditions of positive temperature gradient in the liquid, neither thermal nor solutal significant convection occurs when the solute/solvent rejected at the solidification front provides the formation of interdendritic liquid that is denser than the global volume of the liquid metal. In the vertical downward directional solidification, the temperature distribution in the liquid induces thermal melt convection during the process. In the case of horizontal unidirectional solidification, convection as a function of the composition gradients in the liquid is always going to occur. Despite the large number of solidification studies existing in the literatures, there is a lack of experimental studies on the influence of thermo-solutal convection on the solidification thermal parameters, and consequently on their effects on the length scale of the microstructure.
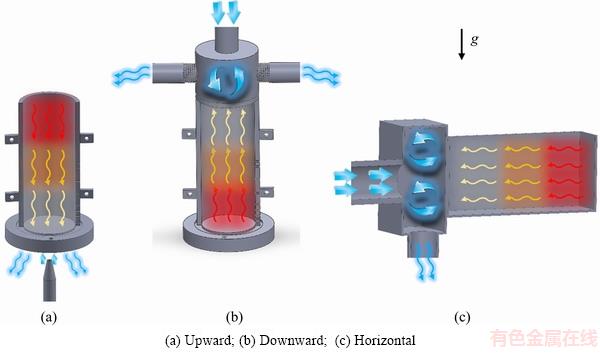
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of directional solidification techniques (g is the acceleration of gravity)
The Sn-rich side of the Sn-Sb alloy system comprises a wide range of compositions, investigated in the literature with a view as high temperature lead-free solders [15-17]. DIAS et al [18] examined the Sn-2.0%Sb and Sn-5.5%Sb (mass fraction) alloys, which were directionally solidified vertically upwards in a water-cooled mold without the presence of convection, and reported unexpected high-cooling cells in these alloys microstructures. TRIVEDI et al [7] pointed out that the reverse transition from dendrites to cells are difficult to observe for metallic alloys and that the corresponding microstructural spacings are extremely fine and associated with high growth rates. However, according to DIAS et al [18], the so-called high-velocity cells occurred for the Sn-5.5%Sb alloy for quite moderate growth rates (VL > 0.4 mm/s) and cooling rates (TR>1.2 K/s). The aim of this work is to include thermo-solutal convective effects during solidification, by using a horizontal directional solidification setup, to experimentally analyze the role of convection on the thermal parameters of solidification and on the microstructural evolution of a monophasic Sn-2%Sb (mass fraction) alloy. The analysis of the effect of morphology and length scale of the as-solidified microstructure on microhardness is also envisaged.
2 Experimental
Experiments of horizontal directional solidification were performed with a monophasic Sn-2%Sb alloy, which is indicated by a dotted vertical line in the corresponding phase diagram of Fig. 2. The chemical compositions of metals used to prepare this alloy are given in Table 1.
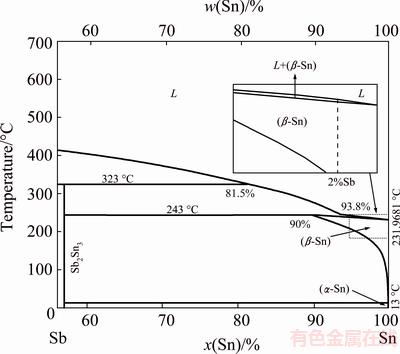
Fig. 2 Sn-Sb phase diagram with indication of examined alloy
A schematic representation of the casting assembly used in the solidification experiments is shown in Fig. 3, which has been detailed in a previous work [13]. The directional solidification device was designed to permit heat extraction only through the water-cooled system placed at the lateral mold wall, promoting horizontal directional solidification. The main design criterion was to induce unidirectional heat flow during solidification. The stainless-steel mold used has a wall thickness of 3 mm, a length of 160 mm, a height of 60 mm and a width of 60 mm. During solidification, six fine K-type thermocouples, positioned at 5, 10, 15, 30, 50 and 90 mm from the heat-extracting surface, were used to monitor temperatures along the length of the casting and these data were acquired automatically.
Table 1 Chemical composition of metals used to prepare alloys (mass fraction, %)
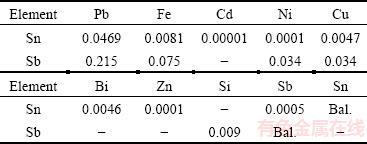
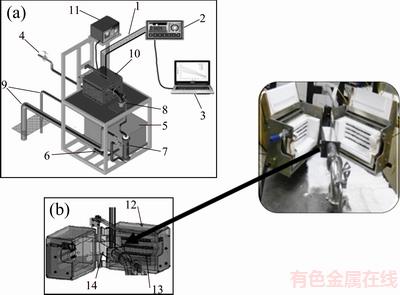
Fig. 3 Schematic representation of horizontal experimental solidification setup (a) (1—Thermocouples; 2—Fieldlogger; 3—Computer and data acquisition software; 4—Cooling water; 5—Water container; 6—Water pump; 7—Rotameter; 8—Water inlet; 9—Water outlet; 10—Directional solidification device; 11—Temperature controller) and view inside of solidification device (b) (12—Insulating ceramic shielding; 13—Electric heaters; 14—Rectangular mold (stainless steel mold-inner wall))
The horizontally directionally solidified (HDS) casting was sectioned along its longitudinal direction, which was parallel to both the sample axis and the direction of solidification. Then, the metallographic samples were mechanically polished with abrasive papers and subsequently etched in a sequence of solutions to reveal the macrostructure: (1) 100 mL H2O, 10 mL HNO3, 4 g (NH4)2MoO4, 5 min; (2) 1:1 proportion of glacial acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), 3 min; (3) 10 mL HCl, 140 mL H2O, 10 g CuCl2, 5 min; (4) Kroll etching (20 mL HF, 10 mL HNO3, 70 mL H2O), 5 min. Selected transverse sections (perpendicular to the horizontal growth direction) of the directionally solidified specimens at 4.5, 9, 13.5, 18, 27.5, 37.2, 46.7, 54.4, 63.4, 72.5, 82 and 91.9 mm from the metal-mold interface were then subjected to ultrasonic cleaning before etching with a solution of 2 mL hydrochloric acid (HCl), 3 mL nitric acid (HNO3), ethyl alcohol to achieve 100 mL, to reveal the microstructure. Measurements of cellular (λC) and primary dendritic arm (λ1) spacings on transverse sections were carried out using the triangle method [19,20]. The triangle is formed by joining the centers of three neighboring cells or primary dendrite trunks, with the sides of the triangle corresponding to λC and λ1, as shown in Fig. 4.
Vickers microhardness tests were also carried out on transverse sections of the samples using a test load of 300 g and a dwell time of 10 s, with the average hardness (HV) determined from about 20 measurements on each sample.
3 Results and discussion
Experimental cooling curves for the six thermocouples inserted into the HDS casting can be seen in Fig. 5(a). The thermocouples readings collected during solidification were used to generate a plot of position (P) from the metal/mold interface as a function of time corresponding to the liquid front passing by each thermocouple. A curve fitting technique on experimental points permitted a power function of P vs time (t) [P=f (t)] to be derived, as shown in Fig. 5(b). The derivative of this function with respect to time permitted an expression relating the growth rate (VL) to time to be determined. Additionally, the data acquisition system for temperature measurement allows the slopes of experimental cooling curves to be accurately described, which permitted the solidification cooling rate (TR) to be determined from the temperature data recorded just after the passage of the liquid isotherm by each thermocouple. The method used for measuring the solidification cooling rate has been detailed by ROCHA et al [4]. In Fig. 6, the experimental growth and cooling rates data are plotted as a function of position in the HDS casting, i.e., (VL, TR)=f(P).
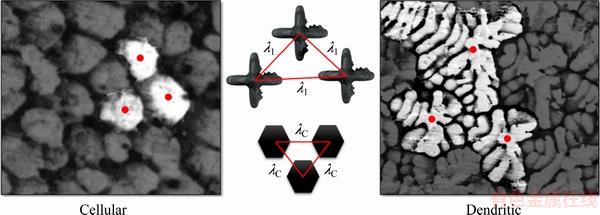
Fig. 4 Schematics of triangle method used to measure λ1 and λC and typical solidification microstructures of alloy investigated in this work
The microstructure of the monophasic Sn-2%Sb alloy is characterized by a Sn-rich matrix of either cellular or dendritic morphologies, as shown in Fig. 7, where typical longitudinal (top) and transverse (bottom) microstructures are related to the corresponding position along the length of the casting, local solidification thermal parameters (TR and VL) and length scale of the matrix (λC/λ1). It is worth noting that during the horizontal solidification the microstructure exhibits a cellular/dendritic reverse transition, i.e., the micro- structure has a cellular morphology for a region close to the cooled mold, changing to a dendritic morphology with the decrease in cooling rate and growth rate along a transition zone, as shown in Fig. 8, where λC and λ1 are depicted as a function of position in the HDS casting. These cells are called high-velocity cells in the literature [7]; however, under transient solidification conditions, high-cooling rate cells seem to be a more appropriate designation since both the growth rate and the thermal gradient (GL) vary continuously, are interdependent and can be combined by the cooling rate (TR=GL·VL).
With a view of establishing correlations between processing parameters and microstructural features, the experimental values of λC and λ1 are plotted in Figs. 9 and 10 as a function of growth rate and cooling rate, respectively. The use of a water-cooled solidification setup imposed higher VL and TR values near the casting surface and decreasing profiles along the length of the HDS casting due to the progressive increase in the thermal resistance of the solidified shell with distance from the cooled surface. This affects correspondingly the observed experimental scatter of spacing values, with the spacings decreasing with the increase in VL and TR.
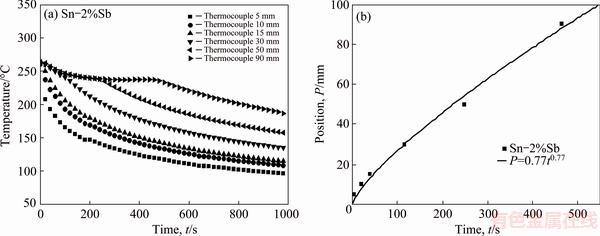
Fig. 5 Typical cooling curves along length of HDS casting (a) and experimental time corresponding to passage of liquid isotherm by each thermocouple position (P) (b)
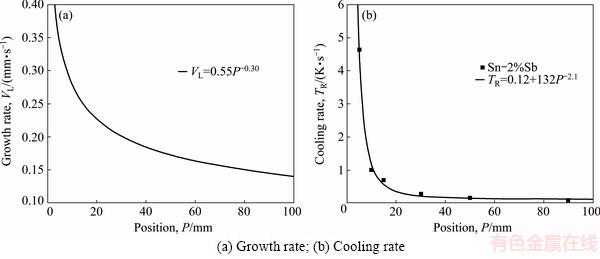
Fig. 6 Experimental thermal parameters as function of position along length of HDS casting
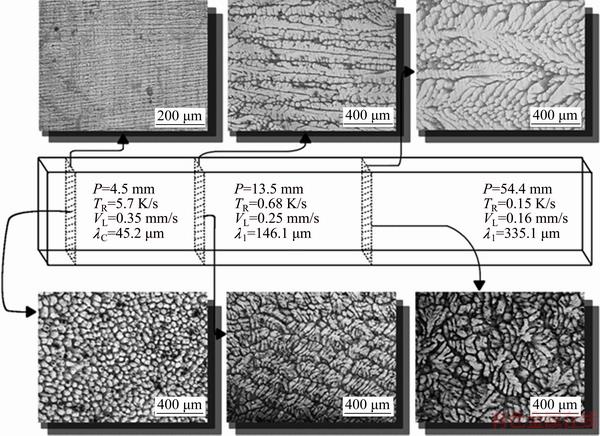
Fig. 7 Micrographs of horizontally solidified Sn-2%Sb alloy
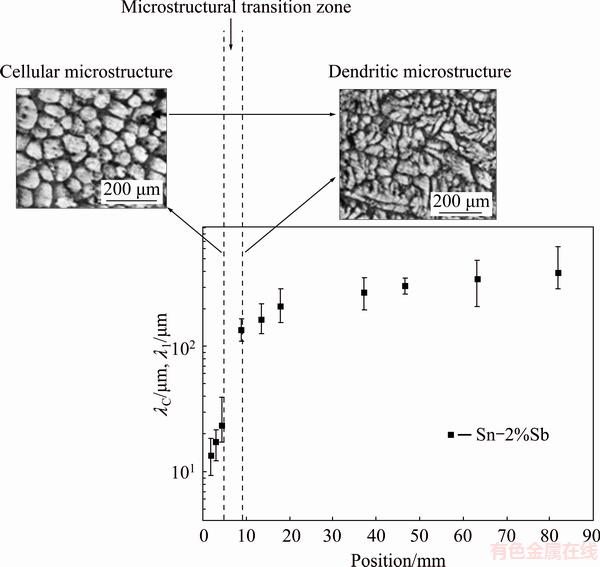
Fig. 8 Evolutions of cellular/primary dendritic arm spacings with position of liquid isotherm along length of casting, showing occurrence of cellular/dendritic transition
Power law functions characterize the experimental variation of λC and λ1 with VL and TR, i.e., with both λC and λ1 being directly proportional to VL–1.1 and to TR–0.55. These exponents are in agreement with the study by DIAS et al [11], in which power function relationships λC,1=C1·VL-1.1 and λC,1=C2·TR-0.55 have been reported to best represent the experimental variation of λC and λ1 with these solidification thermal parameters along the unsteady-state upward directional solidification of Sn-2%Sb and Sn-5%Sb alloys.
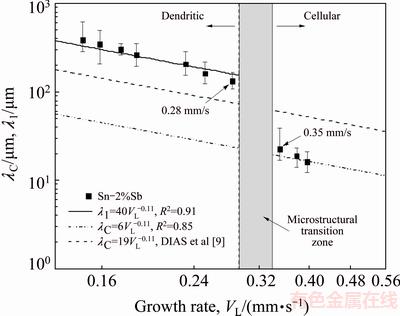
Fig. 9 Evolutions of cellular/primary dendritic arm spacings as function of growth rate
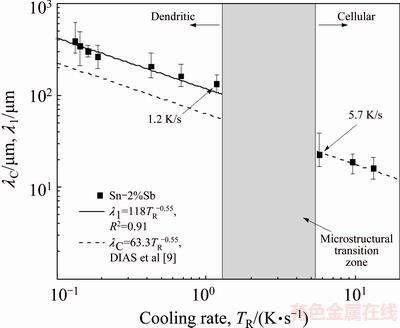
Fig. 10 Evolutions of cellular/primary dendritic arm spacings as function of cooling rate
In the present work, cells prevailed for VL>0.34 mm/s and TR>5.0 K/s, as shown in Figs. 9 and 10, respectively, with the dendritic morphology occurring for VL<0.29 mm/s and TR<1.5 K/s. A transition region over which one structure changes into another can be seen located along intermediate ranges of such limiting values. DIAS et al [11] reported the occurrence of cellular growth along the entire length of a Sn-2%Sb alloy casting, which was directionally solidified vertically upwards (Fig. 1(a)), in which the cooling rate varied between 1 and 40 K/s. For the case of the horizontal solidification of the present study (Fig. 1(c)), the TR values associated with the cellular morphology ranged from 5 to 15 K/s, i.e. the morphological transition from cells to dendrites begins for TR<5 K/s, and to well-defined dendrites for TR<1.5 K/s. That is to say, in the vertical directional solidification configuration cells are stable in a wider range of cooling rates, whereas in the horizontal directional solidification the minimum cooling rate for which cells are stable is about 5 K/s. This seems to be caused by the occurrence of both thermal and solutal convection in the horizontal solidification, which induces instabilities in the solidification front that contribute to the cellular/ dendritic transition, and in such case the morphological transition depends simultaneously on thermal parameters and convective effects. In contrast, for the vertical upward directional solidification, the melt is solutally and thermally stable since the rejection of Sb at the solidification front (that grows upwards toward the open liquid) leads to a local Sb-enriched liquid that is denser than the open liquid. Additionally, the temperature profile in the liquid increases from the solidification front to the top of the casting, and thus convection cannot be induced by temperature differences. It is also reported that the microstructural evolution of an Al-1.5%Fe (mass fraction) alloy sample has a cellular microstructure after a laser remelting treatment, in which significant thermal and solutal convection are induced [21]. Even so, no evidence of cellular/dendritic transition has been found and the cellular spacing, λC, varied from 13 μm in the non-treated zone to about 1.4 μm in the laser-treated resolidified zone.
A comparison between the cellular growth laws that have been experimentally derived for both the horizontal and vertical solidification of the Sn-2%Sb alloy, can also be seen in Figs. 9 and 10 as a function of growth and cooling rates, respectively. A single experimental cellular growth law can represent both the vertical and the horizontal directional solidification as a function of TR (Fig. 10). However, in Fig. 9, it can be seen that different experimental growth laws as a function of VL are indicated representing the cellular growth for vertical and horizontal configurations. This is because VL and GL are interdependent and vary according to different experimental profiles in both configurations, i.e., a given value of VL will be associated with different values of G in the horizontal and vertical solidification systems. To the best of the present authors’ knowledge, previous studies on the effect of convection on the length scale of high cooling rate cells cannot be found in the literature. However, the effect of convection on the size of primary dendritic arms (λ1) has been investigated for many binary alloys. Experimental studies on upward and downward directional solidification of Sn-5%Pb and Sn-15%Pb (mass fraction) alloys [22], hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys [23] and Al-Cu alloys in the range of 3%-8% Cu (mass fraction) [24], have reported reduction of about 2-3 times in λ1 for conditions of downward vertical solidification (in presence of thermal and solutal convection) as compared with λ1 values of upward vertical solidification (no significant convection) when a same cooling rate is considered. A similar trend has also been reported with results from low-gravity experiments in Al-Cu samples grown in a convection free environment [25], in which λ1 was reported to be 2-4 times larger than that observed in similar samples grown on earth in the presence of natural convection. Recent studies also report the effect of solidification thermal parameters on the resulting microstructural features [26-28].
The Vickers microhardness dependence on the evolution of the scale of the microstructure (λC/λ1) along the length of the HDS casting is shown in Fig. 11, where the effect of the cellular and dendritic morphologies on hardness can be observed. Microhardness remains constant in the cellular region (HV 11), followed by a gradual decrease in hardness along the dendritic region, that is, with the increase in the dendritic spacing. Such behavior in the dendritic region is represented in Fig. 11 by an experimental Hall-Petch type equation: H=65+ 52.9l1-0.5.
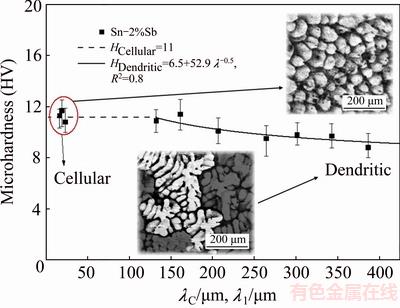
Fig. 11 Evolution of microhardness as function of cellular/ primary dendrite arm spacings
4 Conclusions
1) A cellular/dendritic reverse transition was observed to occur for the Sn-2%Sb (mass fraction) alloy and the region of completely cellular microstructure was shown to occur for VL>0.34 mm/s and TR>5.0 K/s, and the dendritic region occurred for VL<0.29 mm/s and TR<1.5 K/s. Thermal and solutal induced convection seems to induce instabilities at the growth front making the cellular morphology occur for higher cooling rates when being compared with the vertical directional solidification (cells for TR>1 K/s).
2) It was shown that the experimental microstructural spacings, λC and λ1, decrease as VL and TR increase, and experimental growth laws relating these spacings to the growth rate and cooling rate have been proposed: λC=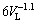 , λC=
, λC=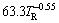 ; λ1=
; λ1= , λ1=144
, λ1=144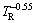 . The cooling rate was shown to be the more appropriate thermal parameter representing transient solidification conditions since it encompasses both GL and VL, thus permitting a single experimental growth law to represent the cellular growth in both horizontal and vertical solidification setups.
. The cooling rate was shown to be the more appropriate thermal parameter representing transient solidification conditions since it encompasses both GL and VL, thus permitting a single experimental growth law to represent the cellular growth in both horizontal and vertical solidification setups.
3) It was observed that the microhardness remained constant (HV 11) in the cellular microstructural zone, decreasing slightly in the dendritic microstructural zone, in which the microhardness dependence on l1 has been represented by a Hall-Petch type equation: H=65+ 52.9l1-0.5.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by IFPA, Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Pará, FAPESP-Sao Paulo Research Foundation, Brazil (grants 2016/18186-1 and 2017/15158-0), and CNPq, The Brazilian Research Council (grants 301600/2015-5; 472745/2013-1 and 308784/2014-6).
References
[1] BOUCHARD D, KIRKALDY J S. Prediction of dendrite arm spacings in unsteady- and steady-state heat flow of unidirectionally solidified binary alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1997, 28(4): 651-663.
[2] HUNT J D, LU S Z. Numerical modelling of cellular and dendritic array growth: Spacing and structure predictions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1993, 173(1): 79-83.
[3] RAPPAZ M, BOETTINGER W J. On dendritic solidification of multicomponent alloys with unequal liquid diffusion coefficients [J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(11): 3205-3219.
[4] ROCHA O L, SIQUEIRA C A, GARCIA A. Cellular/dendritic transition during unsteady-state unidirectional solidification of Sn-Pb alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 347(1-2): 59-69.
[5] ROCHA O L, SIQUEIRA C A, GARCIA A. Cellular spacings in unsteady-state directionally solidified Sn-Pb alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 361(1-2): 111-118.
[6] WANG K, LI B, MI G, GUO J, FU H. Modeling of cell/dendrite transition during directional solidification of Ti-Al alloy using cellular automaton method [J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel International, 2008, 15: 82-866.
[7] TRIVEDI R, SHEN Y X, LIU S. Cellular-to-dendritic transition during the directional solidification of binary alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34A: 395-401.
[8] XU W, FENG Y P, LI Y, LI Z Y. Cellular growth of Zn-rich Zn-Ag alloys processed by rapid solidification [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 373(1-2): 139-145.
[9]  W R, SPINELLI J E, AFONSO C R M, GARCIA A. Microstructure, corrosion behavior and microhardness of a directionally solidified Sn-Cu solder alloy [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 8891-8899.
W R, SPINELLI J E, AFONSO C R M, GARCIA A. Microstructure, corrosion behavior and microhardness of a directionally solidified Sn-Cu solder alloy [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 8891-8899.
[10]  U, ENGIN S, KAYA H. Effect of silicon content on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of the directionally solidified Al-based quaternary alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 694: 471-479.
U, ENGIN S, KAYA H. Effect of silicon content on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of the directionally solidified Al-based quaternary alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 694: 471-479.
[11] DIAS M, BRITO C, BERTELLI F, ROCHA O L, GARCIA A. Interconnection of thermal parameters, microstructure, macrosegregation and microhardness of unidirectionally solidified Zn-rich Zn-Ag peritectic alloys [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 63: 848-855.
[12] BRITO C, SIQUEIRA C A, SPINELLI J E, GARCIA A. Effects of cell morphology and macrosegregation of directionally solidified Zn-rich Zn-Cu alloys on the resulting microhardness [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 80: 106-109.
[13] COSTA T A, MOREIRA A L, MOUTINHO D J, DIAS M, FERREIRA I L, SPINELLI J E, ROCHA O L, GARCIA A. Growth direction and Si alloying affecting directionally solidified structures of Al-Cu-Si alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2015, 31(9): 1103-1112.
[14] COSTA T A, DIAS M, GOMES L G, ROCHA O L. Effect of solution time in T6 heat treatment on microstructure and hardness of a directionally solidified Al-Si-Cu alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 683: 485-494.
[15] EL-DALY A A, FAWZY A, MOHAMAD A Z, EL-TAHER A M. Microstructural evolution and tensile properties of Sn-5Sb solder alloy containing small amount of Ag and Cu [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(13): 4574-4582.
[16] El-DALY A A, SWILEM Y, HAMMAD A E. Creep properties of Sn-Sb based lead-free solder alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 471(1-2): 98-104.
[17] GERANMAYEH A R, NAYYERI G, MAHMUDI R. Microstructure and impression creep behavior of lead-free Sn-5Sb solder alloy containing Bi and Ag [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 547: 110-119.
[18] DIAS M, COSTA T, ROCHA O, SPINELLI J E, CHEUNG N, GARCIA A. Interconnection of thermal parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties in directionally solidified Sn-Sb lead-free solder alloys [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 106: 52-61.
[19]  E. Directional solidification of aluminium–copper alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 327(2): 167-185.
E. Directional solidification of aluminium–copper alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 327(2): 167-185.
[20] KAYA H,  U, MARASLI N. Variation of microindentation hardness with solidification and microstructure parameters in the Al-based alloys [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 255: 3071-3078.
U, MARASLI N. Variation of microindentation hardness with solidification and microstructure parameters in the Al-based alloys [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 255: 3071-3078.
[21] BERTELLI F, MEZA E S, GOULART P R, CHEUNG N, RIVA R, GARCIA A. Laser remelting of Al-1.5wt%Fe alloy surfaces: Numerical and experimental analyses [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2011, 49: 490-497.
[22] SPINELLI J E, FERREIRA I L, GARCIA A. Influence of melt convection on the columnar to equiaxed transition and microstructure of downward unsteady-state directionally solidified Sn-Pb alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 384: 217-226.
[23] SPINELLI J E, PERES M D, GARCIA A. Thermosolutal convective effects on dendritic arm spacings in downward transient directional solidification of Al-Si alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 403: 228-238.
[24] SPINELLI J E, ROSA D M, FERREIRA I L, GARCIA A. Influence of melt convection on dendritic spacings of downward unsteady-state directionally solidified Al-Cu alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 383: 271-282.
[25] DUPOUY M D, CAMEL D, FAVIER J J. Natural convective effects in directional dendritic solidification of binary metallic allows: Dendritic array morphology [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1993, 126: 480-492.
[26] CHEN R, SHI Y F, XU Q Y, LIU B C. Effect of cooling rate on solidification parameters and microstructure of Al-7Si-0.3Mg- 0.15Fe alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 1645-1652.
[27] XU Y, ELLENDT N, LI X G , UHLENWINKEL V , FRITSCHING U. Characterization of cooling rate and microstructure of CuSn melt droplet in drop on demand process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1636-1644.
[28] ZHAO G J, WEN G H, SHENG, G M. Influence of rapid solidification on Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy characteristics and microstructural evolution of solder/Cu joints during elevated temperature aging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 234-240.
O. L. ROCHA1,2, T. A. COSTA1, M. DIAS3, A. GARCIA3
1. Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Pará - IFPA, 66093-020, Belém-Pará, Brazil;
2. Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Pará - UFPA, 66075-110, Belém-Pará, Brazil;
3. Department of Manufacturing and Materials Engineering, University of Campinas-UNICAMP, 13083-860, Campinas-Sao Paulo, Brazil
摘 要:采用单相Sn-2%Sb(质量分数)合金进行水平定向凝固实验,分析凝固热参数对显微组织形貌和长度尺度的影响。在凝固过程中,对沿铸坯长度方向的不同部位进行连续温度测量,用这些温度数据来确定凝固热参数,包括生长速率(VL)和冷却速率(TR)。高冷却速率的胞晶和枝晶可以表征铸件不同区域的显微组织,当TR>5.0 K/s时发生枝晶向胞晶的可逆转变。沿定向凝固铸造的长度方向确定胞晶尺寸(λc)和一次枝晶间距(λ1),提出关于λc和λ1与VL和TR的实验生长规律,并与垂直向上定向凝固实验结果进行对比分析,并分析显微组织形貌和长度尺度对显微硬度的影响。
关键词:Sn-Sb单相合金;定向凝固;热参数;显微组织;胞/枝晶可逆转变
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: T. A. COSTA; E-mail: thiago.costa@ifpa.edu.br
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64811-3

