不同氧燃烧方式下污泥中重金属的形态转化特征
刘敬勇,孙水裕
(广东工业大学 环境科学与工程学院,广东 广州,510006)
摘要:采用化学热力学平衡分析方法,应用真实污泥实测数据预测污泥在氧化氛围和还原氛围焚烧过程中6种重金属(Pb,Ni,Mn,Cr,Zn和Cu)的迁移和转化特征。计算中考虑重金属和Cl化物的相互作用,也考虑重金属与S化物之间的相互作用。研究结果表明:重金属Pb,Zn,Cu和Ni在较低的焚烧温度下都是以固态金属氧化物为主;随着温度的升高,金属氧化物继续与氧结合,在较高温条件下以其气态金属单质或者低价气态金属氧化物形式挥发;Mn和Cr在整个焚烧体系中以固态存在不易挥发而残留在焚烧底渣中;在有Cl化物的焚烧体系中,Pb,Cu和Zn都有其气态金属氯化物形成,而未见到气态Ni,Mn和Cr的氯化物生成,表明污泥焚烧中Cl化物对Pb的挥发性影响最大,其次是Cu和Zn,而Ni,Mn和Cr基本不受Cl化物的影响;在有S化物的焚烧体系中,低温阶段重金属易与S化物结合形成固态金属的硫酸盐,拟制了金属的挥发特性;在高温阶段,金属的形态转化基本不受S化物的影响。焚烧体系中的Cl化物和S化物对重金属形态迁移转化影响差别较大,S化物在低温阶段有助于拟制金属的挥发特性,除Cr和Mn外,Cl化物的存在加速了金属的挥发,从而可根据污泥在不同焚烧温度下不同的产物形态对重金属的污染进行控制。
关键词:污水污泥;焚烧;重金属;形态;热力学分析
中图分类号:X705 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)01-0440-09
Speciation and partitioning of heavy metals during sewage sludge incineration with different oxygen concentrations
LIU Jingyong, SUN Shuiyu
(School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract: Thermodynamic equilibrium calculations were performed to reveal the speciation and partitioning of the heavy metals (Pb, Ni, Mn, Cr, Zn and Cu) during sewage sludge incineration under oxidative condition and reductive condition. Actual sewage sludge compositions and combustion conditions were utilized in all simulations.The interaction between heavy metals, chlorine and sulfur were all considered during calculation. The results show that heavy metals Pb, Zn, Cu and Ni are mainly in solid metal-oxide states during incineration at a lower temperature. With the increase of temperature, the metal oxide combines with oxygen continuously, and in a relatively high temperature, the heavy metals volatilization begins in the forms of their gaseous metal single-masses or gaseous metal oxides. In the whole incineration system, Mn and Cr are mainly congregated in the slags because of their solid state with non volatilization. With the presence of chloride, heavy metals Pb, Cu and Zn form their gaseous metal chlorides, while trace elements Ni, Mn and Cr do not react with chloride and don’t generate gaseous chloride. The chloride has the greatest impact on the volatilization of Cu, followed by Zn and Cu, but less impact on the metal Ni, Mn and Cr. With the presence of sulphur, trace elements are easy to react with sulphur and form solid sulphates at a lower temperature which counteracts their volatilization. With the increase of the temperature, the transformation of the trace elements is not affected by the presence of sulphur.The difference of chloride and sulphur on the impact of migration and transformation of trace elements patterns is great. At low temperature, the presence of sulfur contributes to drawing up the metal evaporation, while the chloride accelerates the evaporation of trace elements except Cr and Mn. The control of heavy metals can be realized for different kinds of metal product at different incineration temperatures.
Key words: sewage sludge; incineration; heavy metals; speciation; thermodynamic analysis
污泥焚烧处理技术可以使污泥减容、稳定化和无害化[1-2],并可以同时以热源和气源形式回收污泥中部分能量,是一种有效的污泥处理方法。然而,这种处理方法在污泥结团、颗粒粒径不均匀及设备内温度分布不均匀、燃烧不完全的情况下也可能加大酸性气体和痕量金属元素排放等[3-4]。由于污泥焚烧是一个包含热解、挥发份燃烧和焦炭燃尽等十分复杂的过程[5],到目前为止,人们对不同来源污泥焚烧过程中重金属导致的污染物的生成、转化和防治的认识还很不足,大部分研究集中在对飞灰及底渣等重金属的最终浓度上,而对污泥焚烧中整个温度范围及在污泥不完全燃烧条件下的重金属分布研究较少。热力学方法作为研究一定宏观条件下整个体系所发生的反应方向和限度,在煤、生活垃圾、生物质焚烧体系平衡中重金属的迁移和转化使用较多[6-9]。在缺乏反应动力学参数和实验条件限制的情况下,热力学平衡方法在评价污泥燃烧过程中重金属的形态转化是一种十分重要的分析工具,它可以分析污泥在燃烧体系缺氧/富氧条件下重金属热力学上的化学组成及其形态,并且通过计算能够深入了解污泥焚烧过程中各种影响因素对重金属行为的影响。目前,应用最广的平衡方法是Gibbs最小自由能方法。通过试验发现:污泥焚烧飞灰和底渣中重金属浓度均超出了我国土地环保质量标准要求的最高范围。污泥焚烧飞灰和底渣是有较高毒性的危险废物,为了减少重金属对大气环境的危害,本文作者采用热力学平衡方法对污泥在富氧和缺氧焚烧条件下重金属元素的迁移和转化过程进行分析,以便为减少焚烧中的重金属污染提供参考。
1 焚烧体系热力学平衡分析原理与方法
污泥在焚烧装置中的热解、气化、燃烧过程属于多相多组分体系的化学反应过程。在一定的温度、压力和原始反应物(指进入燃烧装置中的空气、污泥及辅助燃料等)的条件下,将整个装置看作封闭的理想反应体系,分析在此条件下整个污泥焚烧体系达到热力学平衡状态时各物质的组成、浓度及聚集状态。
在化学热力学中处理复杂体系的化学平衡较常用的是平衡常数法和Gibbs最小自由能法。本文采用的化学热力学计算软件FACT(facility for the analysis of chemical thermodynamics)利用Flemming[10]的MINGSYS(minimization of the total Gibbs energy for a system)计算程序,即基于Gibbs最小自由能法,在等温等压条件下以体系的Gibbs自由能最小作为平衡判据,利用Lagrange待定系数法求解此时各组分的组成和浓度[11]。应用于污泥焚烧体系平衡计算程序的基本原理见图1[10]。在一定温度和压力下,空气污泥等原始反应物质加入污泥焚烧装置中进行各种复杂的化学反应,当体系达到化学平衡时,整个体系的Gibbs自由能最小,计算此平衡条件下垃圾焚烧体系内各种气态物质和固态物质的组成和浓度。

Me代表金属元素
图1 应用于污泥焚烧装置的MINGSYS平衡计算原理图
Fig.1 Scheme of equilibrium system by MINGSYS in sewage sludge incinerator
2 材料与实验
2.1 样品采集与污泥组成分析
实验中所用的污泥取自广州某大型经济开发区污水净化厂脱水污泥(下简称WN)。该污水处理厂进水中工业污水体积分数占70%。污泥在脱水污泥传送带终端上取得,污泥共采4批,每批采集时间为2 h,每隔0.5 h采集1个样品,然后混合。混匀后的污泥样品置于阴凉、通风处晾干,平铺于硬质白纸板上,用玻璃棒等压散,用玛瑙研钵研磨至样品全部通过孔径为150 μm的尼龙筛。将样品放在(100±5) ℃的干燥箱内烘干至恒质量,装瓶混匀后备用。污泥的元素分析及其工业分析结果见表1。
2.2 污泥理化性质和金属元素含量测定
采用《土壤农业化学分析方法》[12]及城市污水处理厂污泥检验方法(CJ/T 221—2005)[13]中的常规分析方法测定样品的重金属(Pb,Ni,Mn,Cr,Cu和Zn)质量分数和主量元素(Si,Al,Ca,K,Mg和Fe)的质量分数,结果见表2。
污泥中重金属总量采用微波消解(CEM-MARS)-原子吸收法进行测定[14],具体步骤为:分别准确称取0.200 0 g上述制备好的干污泥样(每个样品置4个平行样)置于FR21型全聚四氟乙烯密封增压微波消解罐中,加入5 mL HNO3 和1 mL HF,旋紧消化罐盖,将溶样晃动几次,静置过夜。在120 ℃下消解5 min,在150 ℃下消解10 min ,在180 ℃下消解5min 后取出冷却约30 min,然后水浴(100 ℃)赶酸约20 min,用体积分数2%的HNO3介质洗涤溶样杯3次,合并于50 mL容量瓶中备测,并以相同条件作空白试验。分析所用试剂均为优级纯,所用的水均为超纯水,分析过程用国家标准土壤参比物质(GSS-1)进行质量控制,其结果符合质控要求。
2.3 计算工况
影响自由能的因素有:物质的化学组成和结构;物质的凝聚状态(气、液、固)、物质的质量;压力和温度。在计算过程中使用真实污泥组成数据,燃烧温度条件为400~1 800 K,选择步长为100 K,压力为1.013×105 Pa,氧燃烧方式分别为富氧(过量空气系数l=1.2)及缺氧(过量空气系数l=0.6)。每一个计算体系中包括1个重金属元素(表2)和污泥的主成分(C,H,N和O)(见表1)。为了考察S化物和Cl化物对重金属挥发的影响,计算仅有S化物或仅有Cl化物存在情况下6种重金属的迁移转化特征。模型输入数据见表3,模拟结果见图2~7。
3 计算结果与分析
3.1 污泥焚烧中重金属的迁移转化
只考虑污泥中主量元素(C,N,H和O),未考虑S化物、Cl化物及矿物质存在,在l=1.2焚烧条件下6种重金属的迁移转化特征如图2所示(其中:s表示固相产物,g表示气相产物)。从图2可见:在焚烧温度400~1 800 K下,污泥中Cr主要以CrO2(s),Cr2O3(s),CrO2(g)和CrO3(g)形态存在。
(1) 在系统温度400~500 K下,Cr主要以CrO2(s)为主;随着温度升高,CrO2(s)逐渐转化为Cr2O3(s);当温度达到1 500 K时,才有少量CrO2(g)和CrO3(g)出现。
表1 污泥样品WN成分的工业分析、元素分析结果及发热量
Table 1 Primary analysis, ultimate analysis and heating value of sludge

表2 污泥中WN重金属及金属氧化物质量分数
Table 2 Mass fractions of heavy metals and oxides in sludge

表3 模型计算工况输入条件
Table 3 Model working conditions

(2) 污泥中Pb形态变化复杂,主要以PbCO3(g),PbO(s),PbO(g)和Pb(g)形式存在;在焚烧温度为400~600 K时,Pb以PbCO3(s)为主;当温度达到500 K时,PbCO3(s)逐渐分解为PbO(s);在温度达到900 K时,PbO(s)开始转化为PbO(s);在温度为1 500 K时才有少量Pb(g)挥发。
(3) Zn在焚烧体系中主要以ZnO(g)(400~1 500 K)和Zn(g)(1 500~1 800 K)存在;当焚烧温度为400~1 400时,Ni主要以NiO(s)为主;当温度超过1 400 K时,NiO(s)逐渐转化为Ni(OH)2(s)和NiO(g)。
(4) 焚烧体系中Cu在400~1 200 K主要以CuO(s)为主;当温度超过1 200 K时,CuO(s)逐渐转化为Cu2O(s);当温度超过1 400 K时,Cu2O(s)逐渐转化为Cu(g)而挥发。
(5) Mn在焚烧体系中形成较复杂的氧化物,其中在400~700 K,Mn以Mn2O(s)存在;当温度超过700 K时,Mn2O(s)逐渐转化为Mn2O3(s);当温度超过1 400 K时,Mn2O3(s)逐渐转化为Mn3O4(s);当温度超过1 700 K时,Mn3O4(s)逐渐分解为MnO (s)。
只考虑污泥中主量元素(C,N,H和O),未考虑S化物、Cl化物及矿物质存在,在l=0.6焚烧条件下6种重金属的迁移转化特征如图3所示。从图3可见:与l=1.2时的焚烧条件相比,重金属Pb,Zn,Cu和Mn的形态转化变化不大;Cr在400~1 400 K都以Cr2O3(s)存在,没有CrO2(s)出现,Ni在较高温度下只有Ni(OH)2(s)而没有NiO(g)出现。
综合图2和图3可以看出:当只考虑污泥中主量元素(C,N,H和O)条件下,污泥在l=0.6和l=1.2焚烧体系中重金属迁移转化相似,重金属在较低的温度下都是以固态金属氧化物为主;随着温度的升高,金属氧化物又与氧结合形成固态多氧金属化合物;在较高温条件下,重金属以其气态金属单质或者低价气态金属氧化物而挥发;重金属Mn和Cr在整个焚烧体系中(400~1 800 K)主要以固态存在不易挥发而残留在焚烧底渣当中,这可能与其元素化学性质有关。其结果与祝建中等[15]利用管式炉的研究结果相吻合。
3.2 Cl化物对污泥燃烧中重金属迁移转化的影响
已有研究表明固体废弃物中金属及其化合物在高温条件下会与Cl化物发生以下反应[16-17]:M+Cl2= MCl2;M+2HCl=MCl2;MO+2HCl=MCl2。这样生成的产物的熔点和沸点普遍比较低,它们会容易挥发,也容易发生冷凝并富集在飞灰表面上。本文计算了污泥中有主量元素(C,N,H和O)条件下,未考虑S化物及矿物质存在条件下,污泥在l=1.2(图4)和l=0.6(图5)焚烧体系中Cl(设定Cl质量分数为3%)对重金属迁移转化的影响。
为了便于说明问题,这里主要讨论金属氯化物迁移转化特性。从图4可以看出:
Cu在较低温度下主要以CuO(s)和CuCl2(s)存在;当温度升高到1 000 K时,CuO(s)与Cl作用开始向CuCl (g)转化,并且当温度超过1 450 K时,CuCl(g)占主导地位。
Ni在较低温度下主要以NiCl2(s)和NiO(s)存在,当温度达到1 300 K时,开始有Ni(OH)2(g)挥发,未见NiCl2(g)。
Zn在较低温度下主要以ZnCl2(s)和ZnO(s)存在,当温度超过500 K时,ZnCl2(s)逐渐转化为ZnCl2(g),当温度达到1 500 K时,ZnCl2(g)的达到最大。
Pb在较低的温度范围主要以其氯化物存在,在温度为400~700 K时,主要以PbCl2(s)存在,并且有小部分熔点较低的PbCl4(g)(其最高比例不超过10%);当温度达到700 K时,PbCl4(g)和PbCl2(s)都转化为PbCl2(g),并且PbCl2(g)在较宽温度范围存在(700~1 300 K);在温度为1 000~1 600 K时也有部分PbCl (g)存在。
重金属Cr和Mn形态转化基本不受Cl的影响。
污泥在l=0.6焚烧条件下Cl化物对6种重金属迁移转化特征的影响如图5所示。从图5可见:与l=1.2焚烧条件相比,重金属Cr,Cu和Mn的形态转化变化不大;与l=1.2的焚烧条件相比,Ni在400~600 K时有NiCl2(H2O)(s)形成,导致NiCl2(s)滞后100 K才开始形成;在温度为400~500 K时,Zn主要以ZnCl2(s)存在,在500 K时开始ZnCl2(s)由向ZnO(s)转化;在l=1.2焚烧条件下,Pb未出现PbCl4(g)和PbCl(g)。

图2 氧化性氛围焚烧条件下污泥中重金属的形态转化特征
Fig.2 Migration properties of trace elements during incineration of sludge in oxidative condition

图3 还原性氛围焚烧条件下污泥中重金属的形态转化特征
Fig.3 Migration properties of trace elements during incineration of sludge in reductive condition

图4 氧化性氛围条件下污泥中Cl元素对重金属迁移转化的影响
Fig.4 Predication for effects of chlorine on balance distribution of heavy metals speciation in oxidative condition
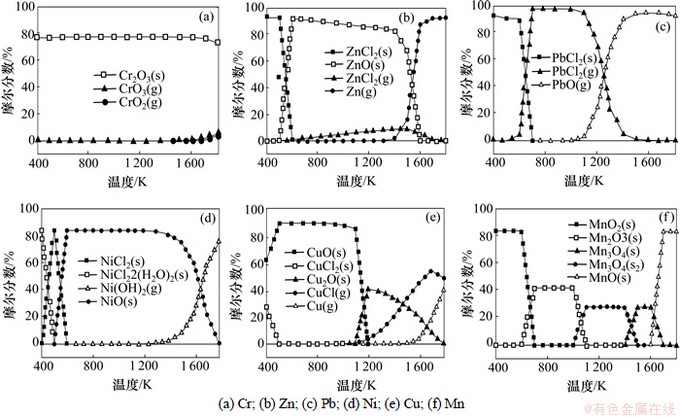
图5 还原性氛围条件下污泥中Cl元素对重金属迁移转化的影响
Fig.5 Predication for effects of chlorine on balance distribution of heavy metals speciation in reductive condition
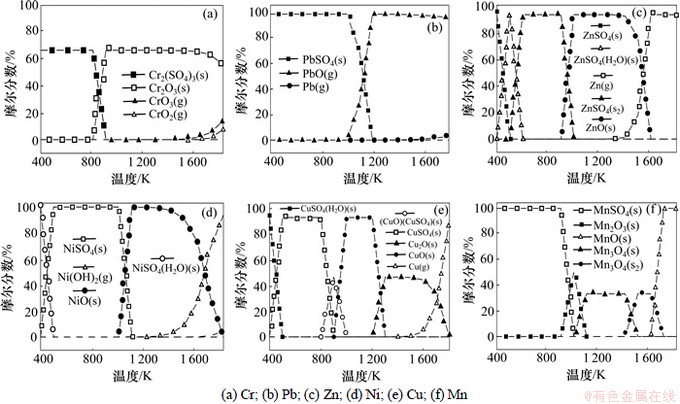
图6 氧化性氛围条件下污泥中S元素对重金属迁移转化的影响
Fig.6 Predication for effects of sulfur on balance distribution of heavy metals speciation in oxidative condition

图7 还原性氛围条件下污泥中S元素对微量元素迁移转化的影响
Fig.7 Predication for effects of sulfur on balance distribution of heavy metals speciation in reductive condition
综合图4和图5可以看出:当只考虑污泥中主量元素C,N,H和O而未考虑S化物条件下,污泥在l=0.6和l=1.2焚烧体系中Cl化物对重金属迁移转化有一定的差别:过量空气系数对Cr,Cu和Mn的形态转化影响不大,在低温还原性气氛条件下,有助于拟制Pb的挥发,可以使Ni和Zn低沸点物质滞后产生。
对照图2~5可以看出:在有Cl化物的焚烧体系中,Pb在650~1 200 K都以PbCl2(g)存在,Cu在1 000 K开始有大量的CuCl(g)生成,Zn在较宽温度范围有一小部分ZnCl2(g)生成,而未见到气态Ni,Mn和Cr的氯化物生成:因此,结合污泥焚烧实际温度(1 000~1 300 K),说明Cl元素对Pb的挥发性影响最大,其次是Cu和Zn,而Ni,Mn和Cr基本不受Cl化物的影响,这也与文献[18]报道的结果一致。
3.3 S化物对污泥燃烧中重金属的迁移转化的影响
已有研究表明焚烧中S化物对重金属的挥发有一定的抑制作用[19-21]。为了探索污泥焚烧中S对重金属迁移转化特性的影响,本文计算了污泥中存在C,N,H和O条件下,未考虑Cl化物及矿物质存在,污泥在l=1.2和l=0.6焚烧体系中S化物(设定w(S)=3%)对重金属迁移转化的影响,结果分别见图6和图7。
从图6可以看出:Cu在较低的温度(400~800 K)下主要以CuSO4(H2O)(s)和CuSO4(s)存在;当温度达到900 K时,CuSO4(s)和CuO(s)反应生成了CuO(CuSO4)(s);当温度较高时(大于1 000 K),主要以CuO(s),Cu2O(s)和Cu(g)存在;Ni在低温(400~1 000 K)下主要以NiSO4(H2O)(s)和NiSO4存在,当温度高于1 000 K时,主要以NiO(s)和Ni(OH)2(g)存在;Mn在温度低于1 000 K时,主要以MnSO4(s)存在,当温度高于1 000 K时,主要以Mn的氧化物如Mn2O3(s),Mn3O4(s)和MnO(s)存在;Zn在低温(400~950 K)主要以ZnSO4(H2O)(s)和ZnSO4(s)存在,当温度高于950 K时以ZnO(s)和Zn(g)存在;Pb在400~1 100 K都是以PbSO4(s)存在,当高于1 100 K时,PbSO4(s)逐渐分解为PbO(g)和Pb(g)而挥发;Cr在400~800 K时主要以Cr2(SO4)3(s)存在,当温度较高时以Cr的氧化物存在,不受S的影响。
从图7可以看出:Pb,Zn,Ni和Cu形态转化特征与图6的类似,而Cr和Mn有一定的差别,主要表现为高温条件下Cr没有CrO3(g)和CrO2(g)生成,Mn没有Mn2O3(s)生成。图6和图7表明:在有S化物存在时,污泥的氧化性焚烧与还原性焚烧对重金属形态转化影响较小。
对照图2、图3、图6和图7可以看出:焚烧体系中的S化物对重金属形态迁移转化影响较大。在有S化物存在条件下,低温阶段由原来金属的氧化物转化为金属的硫酸盐生成。由于硫酸盐比较稳定,拟制了金属的挥发特性;在高温阶段,金属的形态转化基本不受S化物的影响。
对照图4~7可以看出:焚烧体系中的Cl化物和S化物对重金属形态迁移转化影响有较大差别;在有S化物存在时,低温阶段有金属的硫酸盐生成,拟制了金属的挥发特性;而有Cl化物存在条件下,除Cr和Mn外都有金属的气态氯化物生成,加速了金属的挥发特性。在焚烧过程中,重金属与Cl化物结合生成易挥发的重金属氯化物,这会导致大量的重金属无法残留在焚烧的底渣中,而是进入烟气并随烟气一同排入大气环境中,从而对环境、人畜健康造成巨大危害:因此,研究焚烧过程中Cl化物对重金属污染物排放的影响,对于危险废弃物的焚烧处理、重金属污染物排放的有效控制有重要意义。
4 结论
(1) 重金属Pb,Zn,Cu和Ni在较低的焚烧温度下都是以固态金属氧化物为主。随着温度的升高,金属氧化物继续与氧结合,在较高温条件下,以其气态金属单质或者低价气态金属氧化物形式挥发;重金属Mn和Cr在整个焚烧体系中以固态存在不易挥发而残留在焚烧底渣中。
(2) 在有Cl化物的焚烧体系中,Pb,Cu和Zn都有其气态金属氯化物生成,而未见到气态Ni,Mn和Cr的氯化物生成,表明污泥焚烧中Cl化物对Pb的挥发性影响最大,其次是Cu和Zn,而Ni,Mn和Cr基本不受Cl化物的影响。
(3) 在有S化物的焚烧体系中,低温阶段重金属易与S化物结合形成固态金属的硫酸盐,拟制了金属的挥发特性;在高温阶段,金属的形态转化基本不受S化物的影响。
(4) 在焚烧体系中,Cl化物和S化物对重金属形态迁移转化影响差别较大。S化物在低温阶段有助于拟制金属的挥发特性,除Cr和Mn外,Cl化物的存在加速了重金属的挥发。
参考文献:
[1] 王裕明, 胡建红, 冉景煜, 等. 混合工业污泥燃烧及动力学特性实验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(17): 44-50.
WANG Yuming, HU Jianhong, RAN Jingyu, et al. Experimental study oil combustion and kinetic characteristics of mixed industrial sludge[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2007, 27(17): 44-50.
[2] 姚洪, 罗光前, 徐明厚, 等. 煤和污泥燃烧和气化过程中汞析出行为的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(2): 64-69.
YAO Hong, LUO Guangqian, XU Minghou, et al. Study on behaviors of mercury emission during combustion/gasification processes of coal and sludges[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2007, 27(2): 64-69.
[3] 吴成军, 段钰锋, 赵长遂. 污泥与煤混烧中飞灰对汞的吸附特性[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(4): 54-59.
WU Chengjun, QUAN Yufeng, ZHAO Changsui. Adsorption characterization of mercury by fly ashes during co-combustion of sludge and coal[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2008, 28(4): 54-59.
[4] Tang P, Zhao Y C, Xia F Y. Thermal behaviors and heavy metal vaporization of phosphatized tannery sludge in incineration process[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(9): 1146-1152.
[5] 刘敬勇, 孙水裕, 龙来寿, 等. 金属化合物对工业污水污泥燃烧的催化作用及机制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2009, 29(23): 51-60.
LIU Jingyong, SUN Shuiyu, LONG Laishou, et al. Catalytic actions and reaction mechanism of compounds with metal elements on the combustion of mixed industrial sludge[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2009, 29(23): 51-60.
[6] Thompson D, Argent B B. Thermodynamic equilibrium study of trace element mobilization under pulverized fuel combustion conditions[J]. Fule, 2002, 81(3): 345-361.
[7] 李季, 杨学民, 林伟刚. 城市生活垃圾焚烧体系化学热力学平衡分析[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2003, 31(6): 584-588.
LI Ji, YANG Xueming, LIN Weigang. Thermodynamics equilibrium analysis of municipal solid wastes in incineration system[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2003, 31(6): 584-588.
[8] 陈安合, 杨学民, 林伟刚. 生物质燃烧过程中Cl及碱金属逸出的化学热力学平衡分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2007, 7(5): 989-998.
CHEN Anhe, YANG Xueming, LIN Weigang.Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis on release characteristics of chlorine and alkali metals during combustion of biomass residues[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2007, 7(5): 989-998.
[9] 刘敬勇, 孙水裕. 城市污泥焚烧过程中重金属形态与分布的热力学平衡分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(8): 1645-1655.
LIU Jingyong, SUN Shuiyu. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis of heavy metals speciation transformation and distribution during sewage sludge incineration[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(8): 1645-1655.
[10] Flemming F. Trace elements from coal combustion[D]. Copenhagen: Technical University of Denmark, 1995: 6-52.
[11] 许志宏, 王乐珊. 无机热化学数据库[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 50-74.
XU Zhihong, WANG Leshan. Database of inorganic thermochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 50-74.
[12] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 130-357.
LU Rukun. The methods for agricultural chemical study[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000: 130-357.
[13] CJ/T 221—2005, 城市污水处理厂污泥检验方法[S].
CJ/T 221—2005, Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant[S].
[14] 刘敬勇, 孙水裕, 许燕滨, 等. 广州城市污泥中重金属的存在特征及其农用生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(12): 2545-2556.
LIU Jingyong, SUN Shuiyu, XU Yanbin, et al. Heavy metal characteristics in sewage sludge and its potential ecological risk assessment for agriculture use in Guangzhou[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(12): 2545-2556.
[15] 祝建中, 胡志华. 垃圾焚烧过程中影响重金属分布因素的研究[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2004, 5(12): 48-51.
ZHU Jianzhong, HU Zhihua. A study on factors influencing distribution of heavy metals in waste incineration[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2004, 5(12): 48-51.
[16] Vassileva S V, Braekman D C. Behavior, capture and inertization of some trace elements during combustion of refuse- derived char from municipal solid waste[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1131-1145.
[17] Sucan K, Durlak A, Pratim B. Equilibrium analysis of the affect of temperature, moisture and sodium content on heavy metal emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1997, 56(1/2): 1-20.
[18] Fraissler G, Joller M, Mattenberger H, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium calculations concerning the removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge ash by chlorination[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2009, 48(1): 152-164.
[19] Zhang Y G, Chen Y, Meng A H, et al. Experimental and thermodynamic investigation on transfer of cadmium influenced by sulfur and chlorine during municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(1/2): 309-319.
[20] Zhang Y G, Li Q H, Meng A H, et al. Effects of sulfur compounds on Cd partitioning in a simulated municipal solid waste incineration[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2007, 15(6): 889-894.
[21] Verhulst D, Buekens A, Spencer P J, et al. Thermodynamic behavior of metal chlorides and sulfates under the conditions of incineration furnaces[J]. Environment Science and Technology, 1996, 30(1): 50-56.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2011-11-18;修回日期:2012-02-25
基金项目:广东省高校优秀青年创新人才培养项目(LYM11059);广东省科技计划项目(2012B050300023);广东省部产学研结合项目(2011B090400161, 2011B090400144, 2012B090700005)
通信作者:刘敬勇(1979-),男,河南南阳人,博士,副教授,从事环境污染控制化学研究;电话020-39322290;E-mail: www053991@126.com