Microstructural evolution of (TiAl)+Nb+W+B alloy
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第10期
论文作者:黄岚 P. K. LIAW C. T. LIU 刘咏 黄劲松
文章页码:2192 - 2198
关键词:TiAl金属间化合物;W;B;拉伸延性;组织演变;大锭
Key words:TiAl intermetallics; W; B; tensile ductility; microstructural evolution; large ingot
摘 要:通过磁悬浮法制备含有W、Nb、B的重15 kg TiAl合金大锭。此合金大锭与电弧熔炼的0.05 kg的小样品相比,存在晶粒大小和相组织结构性质方面的区别。设计了一系列热处理工艺来消除大锭合金的高温残留β相,并获取理想的微观组织。铸态大锭合金在经过适当的热处理工艺后室温伸长率可达1.9%。这种大批量方式生产的TiAl合金,通过新合金设计与相应的热处理后,其力学性能可获得显著提高。
Abstract:
A newly designed TiAl alloy containing W, Nb, and B was produced through magnetic-flotation-melting method. Mass production of this TiAl-based alloy, 15 kg ingot size, which is quite different from the 0.05 kg small ingot produced by arc-melting, has a large effect on the metallurgical properties, such as the grain size and the phase structures of the alloy. Heat treatments were carefully designed in order to reduce the amount of the high-temperature remaining β phase in the alloy, and to obtain optimal microstructures for mechanical behavior studies. A room-temperature ductility of 1.9% was obtained in the cast TiAl-based alloy after the appropriate heat treatment. The mechanical behavior of the large ingot through mass production of the TiAl-based alloy was largely improved by the alloy design and subsequent heat treatments.

HUANG Lan1, P. K. LIAW 1, C. T. LIU2, LIU Yong3, HUANG Jin-song3
1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-2200, USA;
2. Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China;
3. Powder Metallurgy Research Institute, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 20 July 2011; accepted 20 September 2011
Abstract: A newly designed TiAl alloy containing W, Nb, and B was produced through magnetic-flotation-melting method. Mass production of this TiAl-based alloy, 15 kg ingot size, which is quite different from the 0.05 kg small ingot produced by arc-melting, has a large effect on the metallurgical properties, such as the grain size and the phase structures of the alloy. Heat treatments were carefully designed in order to reduce the amount of the high-temperature remaining β phase in the alloy, and to obtain optimal microstructures for mechanical behavior studies. A room-temperature ductility of 1.9% was obtained in the cast TiAl-based alloy after the appropriate heat treatment. The mechanical behavior of the large ingot through mass production of the TiAl-based alloy was largely improved by the alloy design and subsequent heat treatments.
Key words: TiAl intermetallics; W; B; tensile ductility; microstructural evolution; large ingot
1 Introduction
The mechanical property of the TiAl-based alloy is related to the microstructure of the alloy, while the microstructure of the alloy depends on the alloying compositions and heat treatments. The as-cast TiAl-based alloys usually have a coarse grain size [1-2]. A refinement in the microstructures is necessary to meet the desirable applications. Additional elements, such as W and B, added into the base alloy can help refine the grain size [3-7]. Related heat treatments can facilitate the development of the desirable microstructures. For TiAl-based alloys, the fully-lamellar (FL) structure, composed of α2/γ lamellae, has a low tensile ductility at room temperature but higher fracture toughness than the other microstructures. On the other hand, the duplex (DP) structure, composed of the lamellar colony and primary γ phase, tends to have a good room-temperature tensile ductility but low fracture strength [8]. The mechanical properties of TiAl-based alloys with lamellar structures depend on three factors: the colony size, interlamellar spacing, and alloying addition [9]. The tensile elongation at room temperature is strongly dependent on the lamellar-colony size, showing an increased ductility with decreasing the colony size. The strength at room and elevated temperatures is sensitive to the interlamellar spacing, exhibiting the increased strength with decreasing the interlamellar spacing. Thus, by refining the colony size and the lamellar spacing, the fine fully-lamellar microstructure can present both good ductility and fracture toughness [8-10].
The casting technique has important effects on the microstructure of the alloy. The high-temperature remaining β phase, which can deter the room- temperature ductility of the alloy, can be observed in the mass-production alloy [11-12]. Through controlling heat treatments, the amount of the residual β phase can also be effectively reduced.
In this study, a refinement in the colony size of the TiAl-based alloy was achieved merely through alloying. Alloy design samples of the TiAl-based alloy were produced through arc-melting, and the Ti-45Al-7Nb- 0.15B-0.4W (mole fraction, %) alloy [13] was selected as an optimun composition for mass production through the magnetic-floatation-melting method. The effect of different casting techniques on the microstructures of the alloy was investigated. According to the measured α phase transus temperature, Tα, of the alloy, heat treatments were carefully designed in order to obtain desirable microstructures. The room temperature ductility of the TiAl-based alloy is usually low, as for the as-cast Ti-45Al-(8-9)Nb-(W-B-Y) (mole fraction, %) alloy is 0.49% [14]. The mechanical behavior of the Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W alloy was improved, especially the tensile ductility of the as-cast heat-treated alloy can reach 1.9% without any hot deformation process.
2 Experimental
In this research, the newly-developed TiAl intermetallic alloy, Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W, was produced through the magnetic-floatation-melting method, using the German magnetic-floatation cold crucible furnace. High-purity Nb, W, and B powders, Ti particles (99.6% purity), and Al pieces (99.99% purity), were uniformly placed in the copper crucible for the magnetic-floatation-melting process. The large-ingot sample, with a mass of 15 kg, and a large ingot size of 110 mm in diameter and 300 mm in length, was levitated and melted in the magnetic field created by the induction coils. The as-cast alloy was hot-isostatically pressed using the equipment, QIF-6, produced by the ABB Company, under the conditions: argon atmosphere, 1 250 °C, 130 MPa, 5 h, and furnace cooling. After HIPping, the porosities in the as-cast alloy were eliminated, and the alloy was more densified.
Based on the differential-thermal analyses (DTA), using the DTA & DSC machines under the conditions of a heating rate of 20 K/min in an argon atmosphere, and the reference sample of an Al2O3 powder, the phase-transformation temperatures were estimated. With the comparison of microstructures after different heat treatments, Tα was determined to be (1 290 ± 5) °C.
After HIPping, heat treatments were conducted to the large-ingot samples in order to reduce the amount of the β phase, and obtain the desirable microstructure for mechanical testing later. An optimal heat-treating method, including the heat-treating temperature and time, and cooling rate, was determined in order to obtain a fine near-fully-lamellar structure with a controlled grain size for the as-cast alloy.
Tensile tests were conducted on the large TiAl-based ingot samples with the optimal microstructure. These tensile tests were performed at room temperature, 300 °C, 600 °C, and 800 °C in air using the MTS testing machine, at a strain rate of 1×10-4 s-1. The geometry of the specimens was of a bar shape, with a gauge length of 12.7 mm, and a cross section of 2.49 mm.
The scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used for microstructure analyses of the specimens. Samples were prepared by conventional grinding and polishing, using a 0.5-μm-diamond paste, followed by etching with the Kroll solution, 1% HNO3 + 1% HF + 98% H2O (volume fraction, %). For the backscattering detection, specimens did not need any etching. JSM-5600LV was employed for the SEM analyses, with an acceleration voltage of 20 kV. The electron beam used was 2 μm in size, the electric current was 100 μA, and the working voltage was 20 kV.
3 Results and discussion
In the design of the TiAl-based alloy, a small ingot was produced through an arc-melting method with different kinds of compositions. After the determination of the optimal composition of the alloy, which is Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W, mass production (15 kg) was made through the magnetic-flotation-melting method. There is a difference in the microstructures of the TiAl-based alloy produced through different kinds of casting techniques. The small ingot produced through arc-melting has an average grain size of approximately 50 μm, after the HIPping and homogenization treatment at 1 250 °C for 16 h. A duplex structure of the alloy can be obtained. No β phase is found under this condition, as shown in Fig. 1(a). The large ingot produced through the magnetic-flotation-melting method has an equiaxed structure with an average grain size of 60 μm in the as-cast condition. After the HIPping and homogenization treatment, the average grain size of the alloy increases to 110 μm. The microstructure is composed of a near-fully-lamellar structure, with a significant amount of the β phase dispersed along the grain boundaries, presented in Fig. 1(b).
The difference in the microstructural features of the alloys is mainly due to the size of the ingot, which greatly affects the cooling rate of the TiAl-based alloy. For the small ingot, which is cooled down rapidly, the as-cast microstructure of the sample is composed of a non-equilibrium structure, and there is no strong microsegregation in the alloy. After the HIPping and homogenization treatment at a temperature of 1 250 °C in the α+γ phase range, the microstructure of the alloy reaches an equilibrium condition, and there is no β phase observed in the alloy. For the large ingot, it is cooled down at a slower rate, compared to the small arc-melted alloy. The high-temperature remaining β phase in the large ingot sample can be observed in the as-cast condition. When the requirements of the structural, energy, and composition fluctuations of the alloy have been met, borides with a very high melting point act as a nucleation core for the β-phase to form and grow. The β-phase casting structure is finer than the α-phase casting structure. For the α crystal, the solidification direction is only in the C-axis, which is easy to form columnar structures in the heat-conducting direction, and the grains in the alloy tend to combine and grow large. For the β crystal, the solidification direction is along the á110? direction, which has three equivalent directions, such as [100], [010], and [001]. Thus, different from the C-axis solidification, the β crystal is easier to form equiaxed crystals. During cooling, the β phase transforms into the α phase in the relationships as: ![]() β//(0001)αá111?βá
β//(0001)αá111?βá![]() ?α. The transformation starts in the grains toward the grain boundaries, since the transformation cannot be completed, the remaining β phase exists at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, since Nb and W are β phase stabilizers, the segregation of Nb and W in the residual β phase tends to grow, which makes it more difficult for the transformation to proceed under the as-cast condition of the large ingot. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of the β phase in the large ingot shows that the amount of Nb is 12.95% (mole fraction) and the amount of W is 3.46% (mole fraction), which are much higher than the original alloy composition, proving that both Nb and W are enriched in the β phase. Hence, the remaining bulky β phase can be easily observed at the grain boundaries of the alloy. After the HIPping and homogenization treatment at 1 250 °C, the kinetic energy for the atomic diffusion is not sufficient to reach an equilibrium condition.
?α. The transformation starts in the grains toward the grain boundaries, since the transformation cannot be completed, the remaining β phase exists at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, since Nb and W are β phase stabilizers, the segregation of Nb and W in the residual β phase tends to grow, which makes it more difficult for the transformation to proceed under the as-cast condition of the large ingot. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of the β phase in the large ingot shows that the amount of Nb is 12.95% (mole fraction) and the amount of W is 3.46% (mole fraction), which are much higher than the original alloy composition, proving that both Nb and W are enriched in the β phase. Hence, the remaining bulky β phase can be easily observed at the grain boundaries of the alloy. After the HIPping and homogenization treatment at 1 250 °C, the kinetic energy for the atomic diffusion is not sufficient to reach an equilibrium condition.
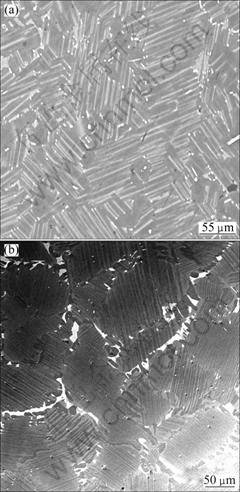
Fig. 1 Microstructures of small ingot (a) and large ingot (b)
The large amount of the high-temperature residual β phase, which is observed in the large-ingot alloy, can deter the room-temperature ductility, since it is quite brittle at the ambient temperature. In order to reduce the amount of the bulky β phase, heat treatments were conducted to the TiAl-based alloy after HIPping. As indicated in the Ti-Al-Nb phase diagram (Fig. 2) [14], annealing the alloy at a higher temperature for a sufficient time, when the driving force for the atomic diffusion can be increased, allows the alloy to reach an equilibrium state, then the residual β phase in the alloy can be reduced.
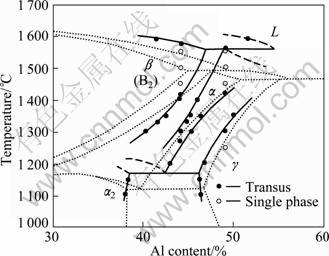
Fig. 2 Ti-Al-8Nb phase diagram [14]
When the alloy is heat-treated at a lower temperature, above the eutectoid temperature, Te, at 1 240 °C, 16 h, furnace cool (FC), in the α+γ phase region, as shown in Fig. 3(a), a large amount of the β phases still remain in the alloy, indicating that at lower heat-treating temperature, even heat treating for a longer time, the β phase cannot be eliminated. When the annealing temperature rises to 1 280 °C, the amount of the β phase can be reduced (see Fig. 3(b)), showing that the dissolution of the high-temperature residual β phase has taken place. But since the annealing time is limited to only 30 min, the amount of the β phase can only be reduced but not eliminated, due to the insufficient time for the alloy to reach an equilibrium condition. As the heat-treating temperature increases above the Tα point, at 1 310 °C, and the heat-treating time extends to 8 h, as shown in Fig. 3(c), the residual β phase can almost be eliminated.
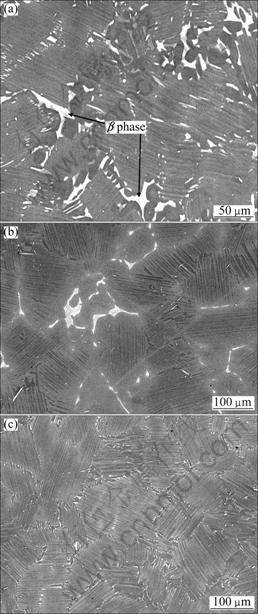
Fig. 3 Microstructures of Ti-Al-Nb-W-B alloy: (a) Heat treated at 1 240 °C, 16 h, furnace cooled (FC); (b) Heat treated at 1 280 °C, 30 min, FC; (c) Heat treated at 1 310 °C, 8 h, FC
Therefore, when heat treating at a higher temperature and annealing for a long enough time, the kinetic energy is sufficient for the atom diffusion to take place. Thus, the residual β phase can be mostly eliminated. When the alloy reaches an equilibrium, the residual β phase can be transformed into the α and γ phases. When the cooling rate is slow, a lamellar structure composed of α2+γ can be obtained.
The transformation of the β phase in the TiAl-based alloy is related to the heat-treating temperature and time. As shown in the Ti-Al-Nb phase diagram (Fig. 2), when the heat-treating temperature is above the single-phase region (1 295 °C), and kept for a sufficient amount of time, the dissolution of the β phase can take place. When the heat-treating temperature is lower, for instance at 1 240 °C, the annealing time should be held longer, in order to reduce the amount of the β phase. The bulky β phase, which is precipitated along the grain boundary of the lamellar grain, reduces as the alloy is heat treated at 1 310 °C for 8 h. While heat treating the TiAl-based alloy, the residual β phase dissolves mainly in the α phase. Since the solubility of Nb and W is high in the α phase, the concentration gradient between the α phase and the β phase is small, and, thus, the required driving force for the β phase to dissolve is also small. The β phase is usually dispersed at the ends of the α lamellae. When the heat-treatment condition for the atomic diffusion is sufficient, almost no β phase can be observed in the alloy.
The duplex structure of the TiAl-based alloy usually has a better room-temperature tensile ductility than the fully-lamellar structure. This is mainly due to the reason that the primary α phase in the duplex structure usually offers better ductility. The fully-lamellar structure has a higher creep resistance under the high-temperature application. In order to obtain a good room-temperature tensile ductility, it is important to obtain a fine-grain sized, fully-lamellar structure after heat treatments. The high-temperature residual β phase, which is observed in the large ingot alloy, can be reduced and eliminated after different kinds of heat treatments. After being heat treated at a temperature of 1 310 °C for 8 h, the amount of the β phase can significantly be reduced, and almost no residual β phase can be observed. Since the heat-treating temperature has exceeded the Tα point, the average grain size of this fully-lamellar structure is large. Hence, in order to obtain the fine-grain-sized lamellar structure, the heat-treating temperature cannot be higher than Tα. At a heat-treating temperature of 1 280 °C, which is very close to the Tα point, a near-fully-lamellar structure can be obtained with a smaller average grain size. Because at 1 280 °C, the microstructure tends to transform into the single α-phase region, which can later develop into a large fully-lamellar structure after cooling, the heat-treating time needs to be carefully monitored, in order to control the growth of the grains.
Based on the above concerns, the heat-treating temperature needs to be controlled at a temperature under the Tα point, and the heat-treating time should be carefully scheduled. Thus, four kinds of heat treatments were designed for tensile tests, in order to understand the relationship between the microstructures of the alloy and the mechanical properties. The heat-treating temperature was scheduled under the Tα point, and the heat-treating time was carefully controlled in order to compromise a fine microstructure with a less amount of the β phase in the alloy. Heat treatments were conducted at (1 130 °C, 24 h, FC), (1 130 °C, 24 h) + (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC), (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC), and (1 280 °C, 40 min, FC), respectively. The previous two heat treatments were scheduled to compare the amount of the residual β phase in the alloy relating to the heat-treating temperature. As shown in Fig. 4(a), after heat treating the alloy at (1 130 °C, 24 h, FC), a duplex structure, with an average grain size of 80 μm, can be obtained. It is noteworthy that the amount of the β phase is significant in the alloy, with an area percentage of 6.0%. This trend results from the fact that the heat-treating temperature is not high enough so as to supply enough kinetic energy for the elimination of the β phase. Therefore, a (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) heat treatment was scheduled following the (1 130 °C, 24 h) heat treatment. As shown in Fig. 4(b), the microstructure of the alloy after this heat treatment is composed of a near-fully-lamellar structure, with an average grain size of 88 μm. Compared to Fig. 4(a), the amount of the residual β phase in the alloy is largely reduced, with an area percentage of 3.5%. This trend is mainly due to the increase in the annealing temperature. Thus, if the annealing temperature of the alloy is increased, the amount of the residual β phase can be effectively reduced. The heat-treating time has a large effect on the grain size of the alloy, especially approaching the Tα point, which greatly affects the ductility of the alloy. When the TiAl-based alloy is heat treated at (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) alone, the microstructure of the alloy is composed of a near-fully-lamellar structure, with an average grain size of 85 μm, as shown in Fig. 4(c). Compared to the heat treatment at (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC), the microstructures are similar, except that for the alloy with pre-heat treatment at (1 130 °C, 24 h), the grain size tends to be slightly larger. When heat treating the alloy at (1 280 °C, 40 min, FC), the microstructure of the alloy is almost the same as that of the (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) sample, except that the grain size extends somewhat to an average grain size of 90 μm.
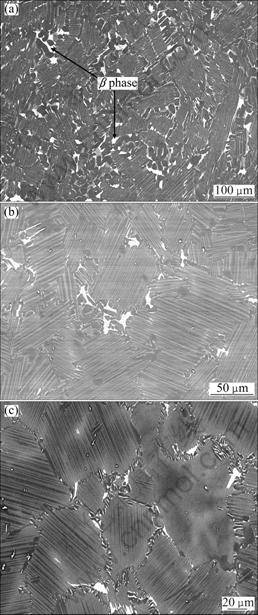
Fig. 4 Microstructures of Ti-Al-Nb-W-B alloy heat treated at: (a) 1 130 °C, 24 h, FC; (b) (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC); (c) 1 280 °C, 20 min, FC
Tensile tests were conducted on the (1 130 °C, 24 h, FC) and (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) samples at room temperature, 300 °C, 600 °C, and 800 °C, respectively. For the (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) and (1 280 °C, 40 min, FC) samples, tensile tests were performed at room temperature. The overall results are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Mechanical behavior of Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W alloy
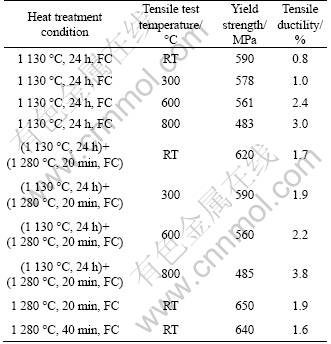
The tensile property, especially the room- temperature ductility of the TiAl-based alloy, is sensitively related to the grain size of the alloy, and the amount of the β phase. Comparing the (1 130 °C, 24 h, FC) heat-treated sample with the (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) sample, the previous one has a larger amount of the β phase. Thus, the tensile property of the alloy is poorer than the later one. For the (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) and (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC) heat-treated samples with the same near-fully- lamellar structure, the later one, with a smaller grain size, exhibits better room-temperature tensile ductility. As compared to other TiAl-based alloys reported previously [14], the Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W alloy shows a superior tensile ductility of 1.9%. For the as-cast alloys, the room-temperature ductility is usually less than 0.5%, and in general, a ductility greater than 1.0 % is required for industrial applications. Thus, the Ti-45Al-7Nb- 0.15B-0.4W, with a tensile ductility of 1.9%, is a considerable design of TiAl-based alloys for structural uses in the cast conditions. The yield strength of the alloy does not change too much with the increase of tensile-testing temperature, while the ductility of the alloy increases with the increase of tensile-testing temperature.
Thus, in order to obtain better tensile property, the optimum heat treatment is designed at (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC), a temperature slightly below the Tα point, so as to prevent the growth of the grain size, and to effectively reduce the amount of the β phase. This newly-developed TiAl-based alloy, composed of a fine near-fully-lamellar structure after the optimum heat treatment, with a yield strength of 650 MPa, and a room-temperature ductility of 1.9%, is a good candidate for industrial applications.
When tensile tested at temperatures of RT, 300 °C, 600 °C, and 800 °C, a delamenation and interlamellar fracture can be observed in the alloy with numerous cleavage planes. Cracks in the alloy are mainly initiated at the residual bulky β phases, as exhibited in Fig. 5.

Fig. 5 Microcracks at interface of β phase and matrix of Ti-Al-Nb-W-B alloy heat-treated at (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC)
Microcracks can be initiated between the interfaces of the β phase and the grain boundaries. This trend is caused by the deformation incompatibility of the β phase and the lamellar colony of the alloy. The cracks in the alloy propagate along the grain boundaries and in a direction parallel to the lamellae, as shown in Fig. 6. The alloy exhibits both transgranular fracture mode and intergranular fracture mode.
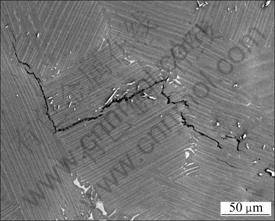
Fig. 6 Fracture surface of Ti-Al-Nb-W-B alloy heat-treated at (1 130 °C, 24 h)+(1 280 °C, 20 min, FC)
4 Conclusions
1) Large ingot with a slow cooling rate results in the formation of the high-temperature residual β phase, which should be eliminated due to its low-temperature brittleness.
2) A fine near-fully-lamellar structure can be obtained in the Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.15B-0.4W alloy through optimal heat-treatment, such as (1 280 °C, 20 min, FC), which shows a good ductility of 1.9% with high fracture strength.
References
[1] SANKARAN A, BOUZY E, FUNDENBERGER J J, HAZOTTE A. Texture and microstructure evolution during tempering of gamma-massive phase in a TiAl-based alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2009, 17(12): 1007-1016
[2] GUAN D L, BROOKS C R, LIAW P K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast and aged Nb-15 at.% Al-10 at.% Ti, -25 at.% Ti and -40 at.% Ti alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(5): 441-458.
[3] MAZIASZ P J, RAMANUJAN R V, LIU C T, WRIGHT J L. Effects of B and W alloying additions on the formation and stability of lamellar structures in two-phase γ-TiAl [J]. Intermetallics, 1997, 5(2): 83-95.
[4] LARSON D J, LIU C T, MILLER M K. Tungsten segregation in α2+γ titanium aluminides [J]. Intermetallics, 1997, 5(7): 497-500.
[5] HU D. Effect of boron addition on tensile ductility in lamellar TiAl alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(9): 851-858.
[6] SHIDA Y, ANADA H. Role of W, Mo, Nb and Si on oxidation of TiAl in air at high temperature [J]. Mater Trans, JIM, 1994, 35(9): 623-631.
[7] LIU Z C, LIN J P, LI S J, CHEN G L. Effects of Nb and Al on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high Nb containing TiAl base alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(7): 653-659.
[8] LIU C T, SCHNEIBEL J H, MAZIASZ P J, WRIGHT J L, EASTON D S. Tensile properties and fracture toughness of TiAl alloys with controlled microstructures [J]. Intermetallics, 1996, 4(6): 429-440.
[9] LIU C T, MAZIASZ P J, LARSON D J. Effect of B and W addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of dual phase lamellar TiAl alloys [C]// BAKER I, NOEBE P D, GEORGE E P. Interstitial and Substitutional Solute Effects in Intermetallics. Warrendale, PA: TMS Publication, 1998: 179-188.
[10] RECINA V, KARLSSON B. Tensile properties and microstructure of Ti-48Al-2W-0.5Si γ-titanium aluminide at temperature between room temperature and 800 °C [J]. Mater Sci Techno, 1999, 15(1): 57-66.
[11] YU R, HE L L, CHENG Z Y, ZHU J, YE H Q. B2 precipitates and distribution of W in a Ti-47Al-2W-0.5Si alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(7): 661-665.
[12] CHEN G L, XU X J, TENG Z K, WANG Y L, LIN J P. Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloy ingots beyond laboratory scale [J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15(5-6): 625-631.
[13] HUANG L, LIAW P K, LIU C T. Microstructural control of Ti-Al-Nb-W-B alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38: 2290-2297.
[14] XU X J, LIN J P, WANG Y L, GAO J F, LIN Z, CHEN G L. Microstructure and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-45Al-(8–9)Nb- (W, B, Y) alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 414: 131-136.
黄 岚1, P. K. LIAW1, C. T. LIU2, 刘 咏3, 黄劲松3
1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-2200, USA;
2. 香港城市大学 机械与生物医学工程系,香港九龙特区;
3. 中南大学 粉末冶金研究院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过磁悬浮法制备含有W、Nb、B的重15 kg TiAl合金大锭。此合金大锭与电弧熔炼的0.05 kg的小样品相比,存在晶粒大小和相组织结构性质方面的区别。设计了一系列热处理工艺来消除大锭合金的高温残留β相,并获取理想的微观组织。铸态大锭合金在经过适当的热处理工艺后室温伸长率可达1.9%。这种大批量方式生产的TiAl合金,通过新合金设计与相应的热处理后,其力学性能可获得显著提高。
关键词:TiAl金属间化合物;W;B;拉伸延性;组织演变;大锭
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (11X-SP173V) supported by the U.S. Fossil Energy Materials Program; Project supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation Combined Research-Curriculum Development (CRCD) Program; Project (DE-AC05-00OR-22725 UT-Battelle, LLC) supported by Division of Materials Science and Engineering, Office of Basic Energy Science, U. S. Department of Energy
Corresponding author: HUANG Lan; Tel: +86-15873128295; E-mail: hazefog31@yahoo.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60994-1

